java并发源码:AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
java并发源码:AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
一、简介
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-pEGdDFSw-1575887227561)
AQS(队列同步器)是用来构建锁或者其它同步组件的基础框架,它使用了一个int成员变量来标识同步状态,通过内置的FIFO队列来完成资源获取线程的排队工作。
AQS面向的是锁的实现者,它简化了锁的实现方式,屏蔽了同步状态管理,线程的排队,等待与唤醒等底层操作。
二、数据结构
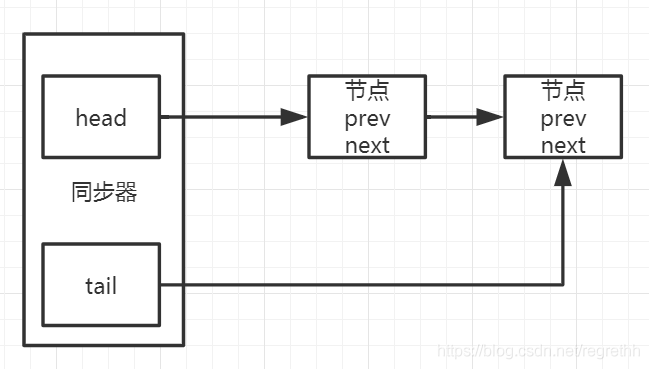
1、Node
| 属性类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int waitStatus | ①CANCELLED:1 由于在同步队列中等待的线程等待超时或者被中断,需要从同步队列中取消等待,节点进入该状态不会变化 ②SIGNAL:-1 后继节点处于等待状态,而当前节点的线程如果释放了同步状态或者被取消,将会通知后继节点,使后继节点的线程得以运行。 ③CONDITION:-2 节点在等待队列中,节点线程等待在Condition上,当其它线程对Condition调用了signal()方法后,该节点将会从等待队列中转移到同步队列中,加入到同步状态的获取中。 ④PROPAGATE:-3 表示下一次共享式同步状态获取将会无条件的被传播下去。 ⑤INITIAL:0 初始状态 |
| Node prev | 前驱节点 |
| Node next | 后继节点 |
| Node nextWaiter | 等待队列中的后继节点,如果当前的节点是共享的,那么这个字段将是一个SHARED常量,也就是说节点类型(独占和共享)和等待队列中的后继节点共用同一个节点。 |
| Thread thread | 获取同步状态的线程 |
2、ConditionObject
| 属性类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int REINTERRUPT | 中断中退出。 |
| int THROW_IE | 值为-1,在等待过程中,抛出中断。 |
| Node firstWaiter | 等待队列的头结点 |
| Node lastWaiter | 等待队列的尾结点 |
同步队列的基本结构
三、方法解读
独占式同步状态获取和释放
1、acquire()
public final void acquire(int arg) {
//执行自定义同步器的tryAcquire方法。该方法保证线程安全的获取同步状态,如果同步状态获取失败,则构造同步结点,并将该节点,添加到同步队列尾部。最后调用acquireQueued()方法,使得该节点以"死循环"的方式获取同步状态。
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
//根据线程构造node结点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
//将尾结点赋值给pred
Node pred = tail;
//判断队列是不是为空
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
//通过unsafe.compareAndSwapObject()方法,确保节点能够被线程安全添加。
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
private Node enq(final Node node) {
//在死循环中,只有通过CAS将节点设置为尾结点,或者头结点时,当前线程才能从该方法返回。
//通过enq方法,将并发的添加节点请求通过CAS变得“串行化”。
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
// Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
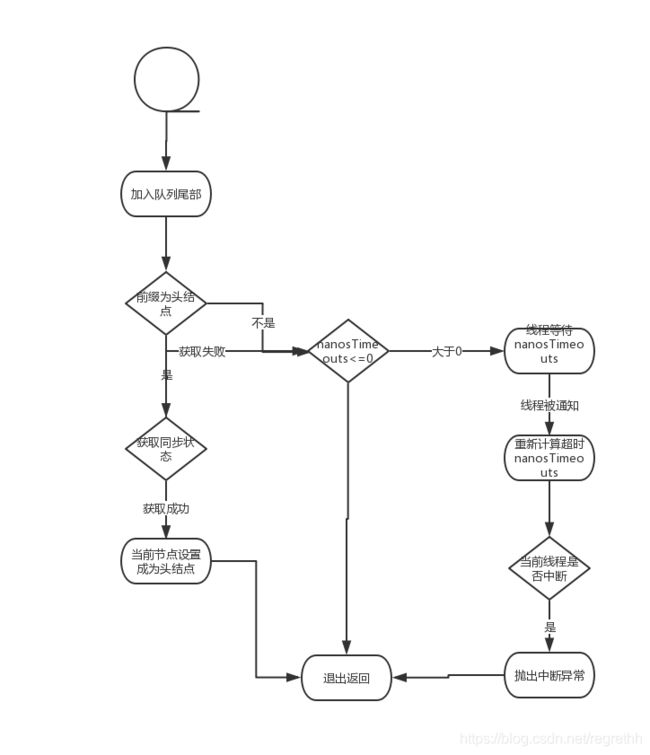
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//只有前驱节点是头结点才能尝试获取同步状态。
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
流程图:
2、release()
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//该方法会唤醒头结点的后继结点,unparkSuccessor()使用LockSupport来唤醒处于等待中的线程。
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
总结:
在获取同步状态时,同步器维护一个同步队列,获取状态失败的线程都会被加入到队列中进行自旋,移出队列的条件是:前驱节点为头结点,并且成功获取了同步状态。
在释放同步状态时,同步器调用tryRelease()方法释放同步状态,然后唤醒头结点的后继节点。
是一个典型的模板模式。
共享式同步状态获取和释放
1、acquireShared()
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
//调用自定义同步器的tryAcquireShared()方法,尝试获取同步状态。
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
同步器调用tryAcquireShared()方法,尝试获取同步状态,当返回值>=0时,表示能够获取同步状态。
2、release()
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void doReleaseShared() {
/*
* Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other
* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual
* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs
* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to
* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.
* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added
* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of
* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status
* fails, if so rechecking.
*/
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, x.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
释放同步状态之后,会唤醒后续处于等待状态中的节点,确保同步状态(资源数)线程的安全释放。
独占式超时获取同步状态
同传统的synchronized相比,具备了在指定时间段内获取同步状态。如果获取到同步状态,返回true,否则返回false。
1、tryAcquireNanos()
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquire(arg) ||
doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
//计算出来休眠时间。如果还有需要休眠,则继续休眠一段时间。
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}