RocketMQ消息消费源码分析(一消费者的启动、消息拉取)
消息消费方式
Consumer分为两种,PullConsumer和PushConsumer。从名字就可以看出一种是拉取的方式,一种是主动Push的方式。具体实现如下:
PullConsumer,由用户主动调用pull方法来获取消息,没有则返回
PushConsumer,在启动后,Consumer客户端会主动循环发送Pull请求到broker,如果没有消息,broker会把请求放入等待队列,新消息到达后返回response。
所以本质上,两种方式都是通过客户端Pull来实现的。
大部分的业务场合下业界用的比较多的是push模式,一句话你没有特殊需求就用push,push模式可以达到准实时的消息推送
那什么时候可以用pull模式呢?比如在高并发的场景下,消费端的性能可能会达到瓶颈的情况下,消费端可以采用pull模式,消费端根据自身消费情况去拉取,虽然push模式在消息拉取的过程中也会有流控(当前ProcessQueue队列有1000条消息还没有消费或者当前ProcessQueue中最大偏移量和最小偏移量超过2000将会触发流控,流控的策略就是延迟50ms再拉取消息),但是这个值在实际情况下,可能每台机器的性能都不太一样,会不好控制。
消费模式
Consumer有两种消费模式,broadcast和Cluster,由初始化consumer时设置。对于消费同一个topic的多个consumer,可以通过设置同一个consumerGroup来标识属于同一个消费集群。
在Broadcast模式下,消息会发送给group内所有consumer。
在Cluster模式下,每条消息只会发送给group内的一个consumer,但是集群模式的支持消费失败重发,从而保证消息一定被消费。
消息消费Demo:
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer("test_quick_consumer_name");
consumer.setNamesrvAddr(Const.NAMESRV_ADDR);
consumer.setConsumeFromWhere(ConsumeFromWhere.CONSUME_FROM_LAST_OFFSET);
consumer.subscribe("test_quick_topic","*");
consumer.registerMessageListener(new MessageListenerConcurrently() {
@Override
public ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus consumeMessage(List msgs, ConsumeConcurrentlyContext consumeConcurrentlyContext) {
MessageExt me = msgs.get(0);
try {
String topic = me.getTopic();
String tags = me.getTags();
String keys = me.getKeys();
String msgBody = new String(me.getBody(), RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET);
System.out.println("topic: "+topic+" ,tags: "+tags+",keys: "+keys+",body: "+ msgBody);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
//记录重试次数
int recousumeTimes = me.getReconsumeTimes();
if(recousumeTimes == 3){
// 记录日志......
// 做补偿处理
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS;
}
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.RECONSUME_LATER;
}
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS;
}
});
consumer.start();
System.out.println("consumer start ................");
}
}
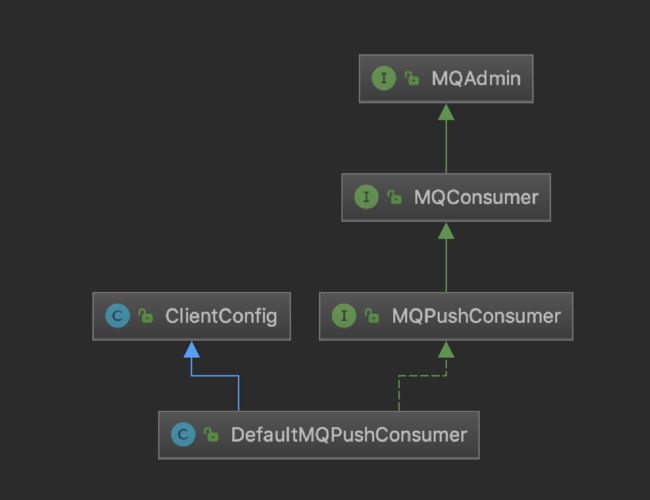
消息消费者具体实现类:org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl。
先看下DefaultMQPushConsumer的重要参数
//消费组
private String consumerGroup;
//消费端模式,默认为集群模式,还有一种广播模式
private MessageModel messageModel = MessageModel.CLUSTERING;
//根据消费进度从broker拉取不到消息时采取的策略
//1.CONSUME_FROM_LAST_OFFSET 最大偏移量开始
//2.CONSUME_FROM_FIRST_OFFSET 最小偏移量开始
//3.CONSUME_FROM_TIMESTAMP 从消费者启动时间戳开始
private ConsumeFromWhere consumeFromWhere = ConsumeFromWhere.CONSUME_FROM_LAST_OFFSET;
//集群模式下消息队列负载策略
private AllocateMessageQueueStrategy allocateMessageQueueStrategy;
//消息过滤关系
private Map();
//消息消费监听器
private MessageListener messageListener;
//消息消费进度存储器
private OffsetStore offsetStore;
//消费线程最小线程数
private int consumeThreadMin = 20;
//消费线程最大线程数,因为消费线程池用的是无界队列,所以这个参数用不上,原因请参考线程池原理
private int consumeThreadMax = 64;
//动态调整线程数量的阀值
private long adjustThreadPoolNumsThreshold = 100000;
//并发消费时拉取消息前会有流控,会判断处理队列中最大偏移量和最小偏移量的跨度,不能大于2000
private int consumeConcurrentlyMaxSpan = 2000;
//push模式下任务拉取的时间间隔
private long pullInterval = 0;
//每次消费者实际消费的数量,不是从broker端拉取的数量
private int consumeMessageBatchMaxSize = 1;
//从broker端拉取的数量
private int pullBatchSize = 32;
//是否每次拉取之后都跟新订阅关系
private boolean postSubscriptionWhenPull = false;
//消息最大消费重试次数
private int maxReconsumeTimes = -1;
//延迟将该消息提交到消费者的线程池等待时间,默认1s
private long suspendCurrentQueueTimeMillis = 1000;
//消费超时时间,15分钟
private long consumeTimeout = 15; 消费者的启动代码入口DefaultPushConsumerImpl.start()方法
public synchronized void start() throws MQClientException {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
//1、基本的参数检查,group name不能是DEFAULT_CONSUMER
this.checkConfig();
//2、将DefaultMQPushConsumer的订阅信息copy到RebalanceService中
//如果是cluster模式,如果订阅了topic,则自动订阅%RETRY%topic
this.copySubscription();
//3、修改InstanceName参数值为PID
if (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel() == MessageModel.CLUSTERING) {
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.changeInstanceNameToPID();
}
//4、新建一个MQClientInstance,客户端管理类,所有的i/o类操作由它管理
//缓存客户端和topic信息,各种service
//一个进程只有一个实例
this.mQClientFactory = MQClientManager.getInstance().getAndCreateMQClientInstance(this.defaultMQPushConsumer, this.rpcHook);
this.rebalanceImpl.setConsumerGroup(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.rebalanceImpl.setMessageModel(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel());
//5、Queue分配策略,默认AVG
this.rebalanceImpl.setAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getAllocateMessageQueueStrategy());
this.rebalanceImpl.setmQClientFactory(this.mQClientFactory);
//6、PullRequest封装实现类,封装了和broker的通信接口
this.pullAPIWrapper = new PullAPIWrapper(
mQClientFactory,
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), isUnitMode());
//7、消息被客户端过滤时会回调hook
this.pullAPIWrapper.registerFilterMessageHook(filterMessageHookList);
//8、consumer客户端消费offset持久化接口
if (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getOffsetStore() != null) {
this.offsetStore = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getOffsetStore();
} else {
switch (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
case BROADCASTING://广播消息本地持久化offset
this.offsetStore = new LocalFileOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
case CLUSTERING://集群模式持久化到broker
this.offsetStore = new RemoteBrokerOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
default:
break;
}
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.setOffsetStore(this.offsetStore);
}
//9、如果是本地持久化会从文件中load
this.offsetStore.load();
//10、消费服务,顺序和并发消息逻辑不同,接收消息并调用listener消费,处理消费结果
if (this.getMessageListenerInner() instanceof MessageListenerOrderly) {
this.consumeOrderly = true;
this.consumeMessageService =
new ConsumeMessageOrderlyService(this, (MessageListenerOrderly) this.getMessageListenerInner());
} else if (this.getMessageListenerInner() instanceof MessageListenerConcurrently) {
this.consumeOrderly = false;
this.consumeMessageService =
new ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService(this, (MessageListenerConcurrently) this.getMessageListenerInner());
}
//11、只启动了清理等待处理消息服务
this.consumeMessageService.start();
//12、注册(缓存)consumer,保证CID单例
boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerConsumer(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), this);
if (!registerOK) {
this.serviceState = ServiceState.CREATE_JUST;
this.consumeMessageService.shutdown();
throw new MQClientException("The consumer group[" + this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup()
+ "] has been created before, specify another name please." + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.GROUP_NAME_DUPLICATE_URL),
null);
}
//13、启动MQClientInstance,会启动PullMessageService和RebalanceService
mQClientFactory.start();
log.info("the consumer [{}] start OK.", this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case RUNNING:
case START_FAILED:
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
...
...
default:
break;
}
//14、从NameServer更新topic路由和订阅信息
this.updateTopicSubscribeInfoWhenSubscriptionChanged();
this.mQClientFactory.checkClientInBroker();//如果是SQL过滤,检查broker是否支持SQL过滤
//15、发送心跳,同步consumer配置到broker,同步FilterClass到FilterServer(PushConsumer)
this.mQClientFactory.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
//16、做一次re-balance
this.mQClientFactory.rebalanceImmediately();
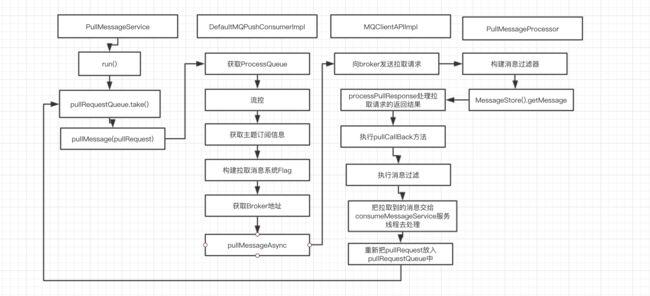
}checkConfig(),检查配置信息,主要检查消费者组(consumeGroup)、消息消费方式(messageModel)、消息消费开始偏移量(consumeFromWhere)、消息队列分配算法(AllocateMessageQueueStrategy)、订阅消息主题(Map copySubscription().加工订阅信息,将Map 第4步,初始化一个 第5步,对于同一个group内的consumer, 比如现在有4个消息队列(q1,q2,q3,q4),3个消费者(m1,m2,m3),那么消费者与消息队列的对应关系是什么呢?我们按照一个轮询算法来表示, m1(q1,q4) m2(q2) m3(q3),如果此时q2消息队列失效(所在的broker挂了),那么消息队列的消费就需要重新分配,RebalanceImpl 就是干这事的,该类的调用轨迹如下:(MQClientInstance start --> (this.rebalanceService.start()) ---> RebalanceService.run(this.mqClientFactory.doRebalance()) ---> MQConsumerInner.doRebalance(DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl) --->RebalanceImpl.doRebalance。 在这里着重说明一点:消息队列数量与消费者关系:1个消费者可以消费多个队列,但1个消息队列只会被一个消费者消费;如果消费者数量大于消息队列数量,则有的消费者会消费不到消息(集群模式)。 MQClientInstance 下面看一下this.mQClientFactory =MQClientManager.getInstance().getAndCreateMQClientInstance(this.defaultMQPushConsumer, this.rpcHook); 从这段代码可以看成,一个客户端 IP@InstanceName 只会持有一个 MQClientInstance 对象,MQClientInstance 无论是消费者还是生产者,都在应用程序这一端。 有了这一层认识,我们就重点关注一下该类的属性: ClientConfig clientConfig 然后回到 1.this.startScheduledTask();启动了定时任务,看下启动了哪里定时任务 2.this.pullMessageService.start(); 启动了pullMessageService服务线程,这个服务线程的作用就是拉取消息,我们去看下他的run方法: 从pullRequestQueue中获取pullRequest,如果pullRequestQueue为空,那么线程将阻塞直到有pullRequest放入,那么pullRequest是什么时候放入的呢,有2个地方: executePullRequestImmediately 和 executePullRequestLater,一个是立即放入pullRequest,一个是延迟放入pullRequest,什么时候需要延迟放入pullRequest呢,都是出现异常的情况下,什么时候立即放入呢,我们看下这个方法的调用链: 有3个地方调用,去掉延迟调用的那一处,还有两处 我们看下PullRequest类 consumerGroup 消费组 这里的consumer直接强制转换成了DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl,为什么呢,看来这个拉取服务只为push模式服务,那么pull模式呢,TODO一下,回头看看,进入DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.pullMessage方法,这个方法就是整个消息拉取的关键方法 消费进度,消费等等功能的底层核心数据保存都是有ProcessQueue提供,类似于消息快照的意思,主要是因为在消息拉取到的时候,会把消息存放在其中。 这里想说一下很多地方都用到了状态,是否停止,暂停这样的属性,一般都是用volatile去修饰,在不同线程中起到通信的作用。 上面的6,7,8步都在进行流控判断,防止消费端压力太大,未消费消息太多 这里通过pullRequest的messageQueue获取topic,再从rebalanceImpl中通过topic获取SubscriptionData,作用是去broker端拉取消息的时候,broker端要知道拉取哪个topic下的信息,过滤tag是什么 这一步的回调方法后文再分析,先过 从内存中获取MessageQueue的commitLog偏移量,为什么是从内存中获取呢,集群模式消费进度不是存储在broker端的吗?这个问题我们留着,等我们分析消费进度机制的时候再来看 进入PullAPIWrapper#pullKernelImpl,看下具体的拉取实现 根据brokerName,brokerId从mQClientFactory中查找Broker信息,最后调用MQClientAPIImpl#pullMessage去broker端拉取消息,MQClientAPIImpl封装了网络通信的一些API,我们找到broker端处理拉取请求的入口,根据RequestCode.PULL_MESSAGE搜索,找到PullMessageProcessor#processRequest方法: 这个方法调用了MessageStore.getMessage()获取消息,方法的参数的含义: 这里minOffset和maxOffset都是broker端的consumeQueue中的最大最小值,现在已经从commitLog中拿到了需要消费的消息,回到PullMessageProcessor#processRequest中 如果从节点数据包含下一次拉取偏移量,设置下一次拉取任务的brokerId,如果commitLog标记可用并且当前节点为主节点,那么更新消息的消费进度,关于消费进度后文会单独分析 根据服务端返回的结果code码来处理拉取结果,组装PullResultExt 现在调用pullCallback.onSuccess(pullResult);我们进入pullCallback中: pullAPIWrapper.processPullResult是处理拉取到的消息进行解码成一条条消息,并且执行tag模式的消息过滤,并且执行hook操作并填充到MsgFoundList中,接下来按照正常流程分析,就是拉取到消息的情况 先跟新下一次拉取的偏移量,如果MsgFoundList为空,那么立即触发下一次拉取,为什么可能为空呢,因为有tag过滤,服务端只验证了tag的hashcode,为什么要采用这样的方式呢,还有个疑问就是,这个时候被过滤掉的消息怎么才能被其他消费者消费,因为broker端已经提交了消费进度。 将msgFoundList提交保存到processQueue中,承载的对象是msgTreeMap,processQueue中用到了读写锁,后面分析一下,然后将拉取到的消息提交到consumeMessageService线程中,这里将是消费消息的入口处,到这里消息的拉取就完成了,这次消息拉取完成后,pullRequest将会被重新放入pullrequestQueue中,再次进行消息的拉取。下面一张流程图就是消息拉取的整个过程 MQClientInstance,这个实例在一个JVM中消费者和生产者共用,MQClientManager中维护了一个factoryTable,类型为ConcurrentMap,保存了clintId和MQClientInstance。RebalanceImpl负责分配具体每个consumer应该消费哪些queue上的消息,以达到负载均衡的目的。Rebalance支持多种分配策略,比如平均分配、一致性Hash等(具体参考AllocateMessageQueueStrategy实现类)。默认采用平均分配策略(AVG)。public MQClientInstance getAndCreateMQClientInstance(final ClientConfig clientConfig, RPCHook rpcHook) {
String clientId = clientConfig.buildMQClientId();
MQClientInstance instance = this.factoryTable.get(clientId);
if (null == instance) {
instance =
new MQClientInstance(clientConfig.cloneClientConfig(),
this.factoryIndexGenerator.getAndIncrement(), clientId, rpcHook);
MQClientInstance prev = this.factoryTable.putIfAbsent(clientId, instance);
if (prev != null) {
instance = prev;
log.warn("Returned Previous MQClientInstance for clientId:[{}]", clientId);
} else {
log.info("Created new MQClientInstance for clientId:[{}]", clientId);
}
}
return instance;
}
public String buildMQClientId() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(this.getClientIP());
sb.append("@");
sb.append(this.getInstanceName());
if (!UtilAll.isBlank(this.unitName)) {
sb.append("@");
sb.append(this.unitName);
}
return sb.toString();
}
private String clientIP = RemotingUtil.getLocalAddress();
配置信息。
int instanceIndex
MQClientInstance在同一台机器上的创建序号。
String clientId
客户端id。
ConcurrentMap
生产组--》消息生产者,也就是在应用程序一端,每个生产者组在同一台应用服务器只需要初始化一个生产者实例。
ConcurrentMap
消费组--》消费者,也就是在应用程序一 端 ,每个消费组,在同一台应用服务器只需要初始化一个消费者即可。
ConcurrentMap
主要是处理运维命令的。
NettyClientConfig nettyClientConfig
网络配置。
MQClientAPIImpl mQClientAPIImpl
MQ 客户端实现类。
MQAdminImpl mQAdminImpl
MQ 管理命令实现类。
ConcurrentMap
topic 路由信息。
ConcurrentMap
broker信息,这些信息存在于NameServer,但缓存在本地客户端,供生产者、消费者共同使用。
ClientRemotingProcessor clientRemotingProcessor
客户端命令处理器。
PullMessageService pullMessageService
消息拉取线程,一个MQClientInstance 只会启动一个消息拉取线程。
RebalanceService rebalanceService
队列动态负载线程。
DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer
默认的消息生产者。
ConsumerStatsManager consumerStatsManager
消费端统计。
AtomicLong sendHeartbeatTimesTotal = new AtomicLong(0)
心跳包发送次数。
ServiceState serviceState = ServiceState.CREATE_JUST
状态。
MQClientInstance mq客户端实例,每台应用服务器将持有一个MQClientInstance对象,供该应用服务器的消费者,生产者使用。该类是消费者,生产者网络处理的核心类。DefaultPushConsumerImpl.start()方法中的this.mQClientFactory.start();启动MQClientInstance public void start() throws MQClientException {
synchronized(this) {
switch(this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
if (null == this.clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) {
this.mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr();
}
this.mQClientAPIImpl.start();
// 1、Start various schedule tasks
this.startScheduledTask();
// 2、Start pull service,开始处理PullRequest
this.pullMessageService.start();
// 3、Start rebalance service
this.rebalanceService.start();
// 4、Start push service,consumer预留的producer,发送要求重新的消息
this.defaultMQProducer.getDefaultMQProducerImpl().start(false);
this.log.info("the client factory [{}] start OK", this.clientId);
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
case RUNNING:
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
default:
return;
case START_FAILED:
throw new MQClientException("The Factory object[" + this.getClientId() + "] has been created before, and failed.", (Throwable)null);
}
}
}private void startScheduledTask() {
//每隔2分钟尝试获取一次NameServer地址
if (null == this.clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr();
} catch (Exception var2) {
MQClientInstance.this.log.error("ScheduledTask fetchNameServerAddr exception", var2);
}
}
}, 10000L, 120000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
每隔30S尝试更新主题路由信息
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer();
} catch (Exception var2) {
MQClientInstance.this.log.error("ScheduledTask updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer exception", var2);
}
}
}, 10L, (long)this.clientConfig.getPollNameServerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//每隔30S 进行Broker心跳检测
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.cleanOfflineBroker();
MQClientInstance.this.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
} catch (Exception var2) {
MQClientInstance.this.log.error("ScheduledTask sendHeartbeatToAllBroker exception", var2);
}
}
}, 1000L, (long)this.clientConfig.getHeartbeatBrokerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//默认每隔5秒持久化ConsumeOffset
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.persistAllConsumerOffset();
} catch (Exception var2) {
MQClientInstance.this.log.error("ScheduledTask persistAllConsumerOffset exception", var2);
}
}
}, 10000L, (long)this.clientConfig.getPersistConsumerOffsetInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//默认每隔1S检查线程池适配
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.adjustThreadPool();
} catch (Exception var2) {
MQClientInstance.this.log.error("ScheduledTask adjustThreadPool exception", var2);
}
}
}, 1L, 1L, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}@Override
public void run() {
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
//从LinkedBlockingQueue中拉取pullRequest
PullRequest pullRequest = this.pullRequestQueue.take();
this.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Pull Message Service Run Method exception", e);
}
}public void executePullRequestLater(final PullRequest pullRequest, final long timeDelay) {
if (!isStopped()) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
PullMessageService.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}
}, timeDelay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
log.warn("PullMessageServiceScheduledThread has shutdown");
}
}
public void executePullRequestImmediately(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
try {
this.pullRequestQueue.put(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("executePullRequestImmediately pullRequestQueue.put", e);
}
}
public class PullRequest {
private String consumerGroup;
private MessageQueue messageQueue;
private ProcessQueue processQueue;
private long nextOffset;
private boolean lockedFirst = false;
...
}
messageQueue 消费队列
ProcessQueue 承载拉取到的消息的对象
nextOffset 下次拉取消息的点位
如果从pullRequestQueue中take到pullRequest,那么执行this.pullMessage(pullRequest);private void pullMessage(PullRequest pullRequest) {
MQConsumerInner consumer = this.mQClientFactory.selectConsumer(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup());
if (consumer != null) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl impl = (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl)consumer;
impl.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} else {
this.log.warn("No matched consumer for the PullRequest {}, drop it", pullRequest);
}
}public void pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
//1.获取处理队列ProcessQueue
final ProcessQueue processQueue = pullRequest.getProcessQueue();
//2.如果dropped=true,那么return
if (processQueue.isDropped()) {
log.info("the pull request[{}] is dropped.", pullRequest.toString());
return;
}
//3.然后更新该消息队列最后一次拉取的时间
pullRequest.getProcessQueue().setLastPullTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
//4.如果消费者 服务状态不为ServiceState.RUNNING,默认延迟3秒再执行
this.makeSureStateOK();
} catch (MQClientException e) {
log.warn("pullMessage exception, consumer state not ok", e);
//4.1 这个方法在上文分析过,延迟执行放入pullRequest操作
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_EXCEPTION);
return;
}
//5.是否暂停,如果有那么延迟3s执行,目前我没有发现哪里有调用暂停,可能是为以后预留
if (this.isPause()) {
log.warn("consumer was paused, execute pull request later. instanceName={}, group={}", this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getInstanceName(), this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_SUSPEND);
return;
}//6.消息的拉取会有流量控制,当processQueue没有消费的消息的数量达到(默认1000个)会触发流量控制
long cachedMessageCount = processQueue.getMsgCount().get();
long cachedMessageSizeInMiB = processQueue.getMsgSize().get() / (1024 * 1024);
if (cachedMessageCount > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdForQueue()) {
//PullRequest延迟50ms后,放入LinkedBlockQueue中,每触发1000次打印一次警告
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
if ((queueFlowControlTimes++ % 1000) == 0) {
log.warn(
"the cached message count exceeds the threshold {}, so do flow control, minOffset={}, maxOffset={}, count={}, size={} MiB, pullRequest={}, flowControlTimes={}",
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdForQueue(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().firstKey(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().lastKey(), cachedMessageCount, cachedMessageSizeInMiB, pullRequest, queueFlowControlTimes);
}
return;
}
//7.当processQueue中没有消费的消息体总大小 大于(默认100m)时,触发流控,
if (cachedMessageSizeInMiB > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdSizeForQueue()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
if ((queueFlowControlTimes++ % 1000) == 0) {
log.warn(
"the cached message size exceeds the threshold {} MiB, so do flow control, minOffset={}, maxOffset={}, count={}, size={} MiB, pullRequest={}, flowControlTimes={}",
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdSizeForQueue(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().firstKey(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().lastKey(), cachedMessageCount, cachedMessageSizeInMiB, pullRequest, queueFlowControlTimes);
}
return;
}
//8.如果不是顺序消息,判断processQueue中消息的最大间距,就是消息的最大位置和最小位置的差值如果大于默认值2000,那么触发流控
if (!this.consumeOrderly) {
if (processQueue.getMaxSpan() > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeConcurrentlyMaxSpan()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
if ((queueMaxSpanFlowControlTimes++ % 1000) == 0) {
log.warn(
"the queue's messages, span too long, so do flow control, minOffset={}, maxOffset={}, maxSpan={}, pullRequest={}, flowControlTimes={}",
processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().firstKey(), processQueue.getMsgTreeMap().lastKey(), processQueue.getMaxSpan(),
pullRequest, queueMaxSpanFlowControlTimes);
}
return;
}//9.获取主题订阅信息
final SubscriptionData subscriptionData = this.rebalanceImpl.getSubscriptionInner().get(pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic());//10.new一个回调方法,这个回调方法在broker端拉取完消息将调用
PullCallback pullCallback = new PullCallback() {//11.如果是集群消费模式,从内存中获取MessageQueue的commitlog偏移量
boolean commitOffsetEnable = false;
long commitOffsetValue = 0L;
if (MessageModel.CLUSTERING == this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
commitOffsetValue = this.offsetStore.readOffset(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), ReadOffsetType.READ_FROM_MEMORY);
if (commitOffsetValue > 0) {
commitOffsetEnable = true;
String subExpression = null;
boolean classFilter = false;
//12.这里又去获取了一遍SubscriptionData,上面不是获取了吗,没有必要的感觉
SubscriptionData sd = this.rebalanceImpl.getSubscriptionInner().get(pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic());
if (sd != null) {
if (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.isPostSubscriptionWhenPull() && !sd.isClassFilterMode()) {
//过滤信息
subExpression = sd.getSubString();
}
//是否是类过滤模式,现在已经不建议用类过滤模式了,5.0版本之后将弃用
classFilter = sd.isClassFilterMode();
}
//13.构建拉取消息系统Flag: 是否支持comitOffset,suspend,subExpression,classFilter
int sysFlag = PullSysFlag.buildSysFlag(
commitOffsetEnable, // commitOffset
true, // suspend
subExpression != null, // subscription
classFilter // class filter
);//14.调用pullAPI方法来拉取消息
this.pullAPIWrapper.pullKernelImpl(
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), // 消息消费队列
subExpression,//消息订阅子模式subscribe( topicName, "模式")
subscriptionData.getExpressionType(),
subscriptionData.getSubVersion(),// 版本
pullRequest.getNextOffset(),//拉取位置
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullBatchSize(),//从broker端拉取多少消息
sysFlag,// 系统标记,FLAG_COMMIT_OFFSET FLAG_SUSPEND FLAG_SUBSCRIPTION FLAG_CLASS_FILTER
commitOffsetValue,// 当前消息队列 commitlog日志中当前的最新偏移量(内存中)
BROKER_SUSPEND_MAX_TIME_MILLIS, // 允许的broker 暂停的时间,毫秒为单位,默认为15s
CONSUMER_TIMEOUT_MILLIS_WHEN_SUSPEND, // 超时时间,默认为30s
CommunicationMode.ASYNC, // 超时时间,默认为30s
pullCallback // pull 回调
);//15.查找Broker信息
FindBrokerResult findBrokerResult =
this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInSubscribe(mq.getBrokerName(),
this.recalculatePullFromWhichNode(mq), false);
//16.如果没有找到对应的broker,那么重新从nameServer拉取信息
if (null == findBrokerResult) {
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(mq.getTopic());
findBrokerResult =
this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInSubscribe(mq.getBrokerName(),
this.recalculatePullFromWhichNode(mq), false);
}final GetMessageResult getMessageResult =
this.brokerController.getMessageStore().getMessage(requestHeader.getConsumerGroup(), requestHeader.getTopic(),
requestHeader.getQueueId(), requestHeader.getQueueOffset(), requestHeader.getMaxMsgNums(), messageFilter);
String group, 消息组名称
String topic, topic名称
int queueId, 队列ID,就是ConsumerQueue的ID
long offset, 待拉取偏移量
int maxMsgNums, 最大拉取数量
MessageFilter messageFilter 消息过滤器GetMessageStatus status = GetMessageStatus.NO_MESSAGE_IN_QUEUE;
//待查找的队列的偏移量
long nextBeginOffset = offset;
//当前队列最小偏移量
long minOffset = 0;
//当前队列最大偏移量
long maxOffset = 0;
GetMessageResult getResult = new GetMessageResult();
//当前commitLog最大偏移量
final long maxOffsetPy = this.commitLog.getMaxOffset();
//根据topicId和queueId获取consumeQueue
ConsumeQueue consumeQueue = findConsumeQueue(topic, queueId);
minOffset = consumeQueue.getMinOffsetInQueue();
maxOffset = consumeQueue.getMaxOffsetInQueue();
//当前队列没有消息
if (maxOffset == 0) {
status = GetMessageStatus.NO_MESSAGE_IN_QUEUE;
nextBeginOffset = nextOffsetCorrection(offset, 0);
} else if (offset < minOffset) {
status = GetMessageStatus.OFFSET_TOO_SMALL;
nextBeginOffset = nextOffsetCorrection(offset, minOffset);
} else if (offset == maxOffset) {
status = GetMessageStatus.OFFSET_OVERFLOW_ONE;
nextBeginOffset = nextOffsetCorrection(offset, offset);
} else if (offset > maxOffset) {
status = GetMessageStatus.OFFSET_OVERFLOW_BADLY;
if (0 == minOffset) {
nextBeginOffset = nextOffsetCorrection(offset, minOffset);
} else {
nextBeginOffset = nextOffsetCorrection(offset, maxOffset);
}
}
这四种情况下都是异常情况,只有minOffset <= offset <= maxOffset情况下才是正常,从commitLog获取到数据之后,返回getResult.setStatus(status);
getResult.setNextBeginOffset(nextBeginOffset);
getResult.setMaxOffset(maxOffset);
getResult.setMinOffset(minOffset);if (getMessageResult.isSuggestPullingFromSlave()) {
responseHeader.setSuggestWhichBrokerId(subscriptionGroupConfig.getWhichBrokerWhenConsumeSlowly());
} else {
responseHeader.setSuggestWhichBrokerId(MixAll.MASTER_ID);
}
服务端消息拉取处理完毕之后,我们回到consumer端,我们进入MQClientAPIImpl#processPullResponsePullStatus pullStatus = PullStatus.NO_NEW_MSG;
switch (response.getCode()) {
case ResponseCode.SUCCESS:
pullStatus = PullStatus.FOUND;
break;
case ResponseCode.PULL_NOT_FOUND:
pullStatus = PullStatus.NO_NEW_MSG;
break;
case ResponseCode.PULL_RETRY_IMMEDIATELY:
pullStatus = PullStatus.NO_MATCHED_MSG;
break;
case ResponseCode.PULL_OFFSET_MOVED:
pullStatus = PullStatus.OFFSET_ILLEGAL;
break;
default:
throw new MQBrokerException(response.getCode(), response.getRemark());
}return new PullResultExt(pullStatus, responseHeader.getNextBeginOffset(), responseHeader.getMinOffset(),
responseHeader.getMaxOffset(), null, responseHeader.getSuggestWhichBrokerId(), response.getBody()); pullResult = DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.pullAPIWrapper.processPullResult(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), pullResult,
subscriptionData);long prevRequestOffset = pullRequest.getNextOffset();
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
...
if (pullResult.getMsgFoundList() == null || pullResult.getMsgFoundList().isEmpty()) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}boolean dispatchToConsume = processQueue.putMessage(pullResult.getMsgFoundList());
//消费消息服务提交
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.consumeMessageService.submitConsumeRequest(
pullResult.getMsgFoundList(),
processQueue,
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
dispatchToConsume);