源码学习《4》Launcher 启动 app 和 apk 资源的加载流程 (App 换肤原理 2)
Android开发中我们的apk资源是如何被加载到的,我们知道当我们点击桌面launcher 的图标拉起我们的app显示我们的页面资源。这个是如何被加载的呢?今天就引出两个看源码的问题 基于 8.0 源码:
不同版本源码实现略有差异。
- Launcher启动app的流程?
- Apk资源是如何被加载到页面上的?
1. Launcher 启动app的流程
做过 launcher app 的同学都知道,我们 launcher 是如何在点击app的时候启动我们的app的,之前做过 launcher 的app,所以对着一点个人还是比较熟悉的,接下来就引出app的启动。
其实launcher启动app很简单,我们知道我们每个 app 在manifast.xml中都会配置一个主activity/根activity。
/**
* Activity Action: Start as a main entry point, does not expect to
* receive data.
*/
可以知道我们配置了 action 和 category ,这两个标签其实就标志我们app启动的地一个 activity 页面。所以在launcher中我们要想启动我们的activity 就是要根据这两个参数 去start activity。
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN);
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER);
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(pkg,cls));
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED);
startActivity(mContext, intent, null);根据actiion 和 category 启动我们具体的 那个 package 下的主activity。(包括launcher的查询app显示到页面,也是根据查询action 和 category 属性来确定有那些 app list列表的)
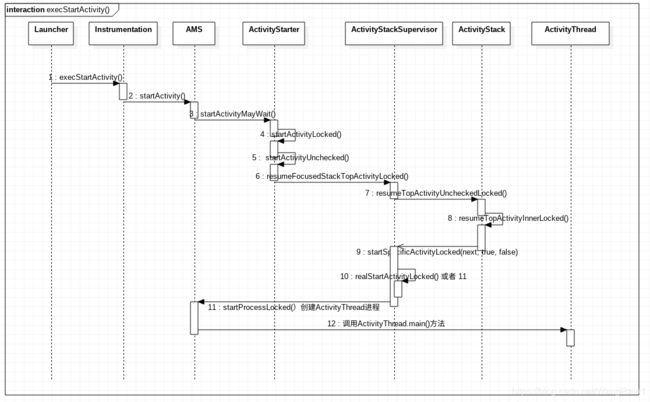
接下来就要根据 startActivity(mContext, intent, null); 入手整个 app 启动流程。
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent, Bundle options) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
// Calling start activity from outside an activity without FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK is
// generally not allowed, except if the caller specifies the task id the activity should
// be launched in.
mMainThread.getInstrumentation().execStartActivity(
getOuterContext(), mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), null,
(Activity) null, intent, -1, options);
}跟着流程走,其中涉及到的其他类,不要太关心,防止迷失~,然后就触发了 Instrumentation 这个类,
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
..........
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess(who);
切换进程
int result = ActivityManager.getService()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}在这里通过 ActivityManager.getService() 拿到 AMS 的服务,调用了AMS 的startActivity() 方法。追到 AMS 中
@Override
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle bOptions, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = mUserController.handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(),
userId, false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mActivityStarter.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, bOptions, false, userId, null, "startActivityAsUser");
}中间的调用过程就用UML 图代替了,防止代码太多,到ApplicationThread就是我们比较熟悉的流程了。
在第8步有两个方法需要注意
//先从task里面去取,如果有之前启动过就走当前task里面的APPlicationThread
//的relauncheractivity,反之走下面
next.app.thread.scheduleResumeActivity(next.appToken, next.app.repProcState,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), resumeAnimOptions);
//如果task里面没有,上面方法抛出异常走 ,重新创建新的activity
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, false);源码是这样的:
走到 10 的时候回去判断当前进程是否存活,存活就走realstartactivity方法,否则就start process 进程。
1. 走realStartActivityLocked方法回去调用ApplicationThread的scheduleLauncherActivity方法,后面就是我们熟悉的启动activity流程了。
2. 走startProcessLocked方法,创建进程(后面文章单独分析 // TODO :)
其实如果我们首次从launcher点开我们app 应该先走 start process 创建进程,然后调用ActivityThread的main()方法。
到这里整个应用进程就被创建了,接下来就是进程解析 apk 加载资源。
2. 加载 apk 资源
通过 问题一我们知道了,初始化新的进程后会 触发 ActivityThread 的 main 方法:
public final class ActivityThread {
......
public static void main(String[] args) {
.....
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
.....
}
private void attach(boolean system) {
.......
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
....
}
}通过main方法调用了 attach 方法,然后获取 AMS 调用 attachApplication(IApplicationThread var1) 方法:
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
//获取applicationThread的进程id(也就是淘宝应用进程)
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
// Find the application record that is being attached... either via
// the pid if we are running in multiple processes, or just pull the
// next app record if we are emulating process with anonymous threads.
ProcessRecord app;
if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) {
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
}
} else {
app = null;
}
//因为进程由AMS启动,所以在AMS中一定会有ProcessRecord(进程记录)
//如果没有ProcessRecord,则需要杀死该进程并退出
if (app == null) {
``````
return false;
}
// If this application record is still attached to a previous
// process, clean it up now.
if (app.thread != null) {
//如果从ProcessRecord中获取的IApplicationThread不为空,则需要处理该IApplicationThread
//因为有可能此Pid为复用,旧应用进程刚释放,内部IApplicationThread尚未清空,
//同时新进程又刚好使用了此Pid
handleAppDiedLocked(app, true, true);
}
//创建死亡代理(进程kill后通知AMS)
AppDeathRecipient adr = new AppDeathRecipient(app, pid, thread);
//进程注册成功,移除超时通知
mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);
``````
try {
//******绑定Application******
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, app.instrumentationClass,
profilerInfo, app.instrumentationArguments, app.instrumentationWatcher,
app.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(mConfiguration), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked());
updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
} catch (Exception e) {
``````
//bindApplication失败后,重启进程
startProcessLocked(app, "bind fail", processName);
return false;
}
try {
//******启动Activity(启动应用MainActivity)******
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;//didSomething表示是否有启动四大组件
}
} catch (Exception e) {
badApp = true;
}
``````
//绑定service和Broadcast的Application
if (badApp) {
//如果以上组件启动出错,则需要杀死进程并移除记录
app.kill("error during init", true);
handleAppDiedLocked(app, false, true);
return false;
}
//如果以上没有启动任何组件,那么didSomething为false
if (!didSomething) {
//调整进程的oom_adj值, oom_adj相当于一种优先级
//如果应用进程没有运行任何组件,那么当内存出现不足时,该进程是最先被系统“杀死”
updateOomAdjLocked();
}
return true;
}两个重要的方法:
thread.bindApplication(…) : 绑定Application到ActivityThread
mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app) : 启动Activity(7.0前为mMainStack.realStartActivityLocked())通过AIDL接口IApplicationThread远程通知到ApplicationThreadNative的onTransact方法指定执行BIND_APPLICATION_TRANSACTION方法,而ActivityThread的内部类ApplicationThread实现ApplicationThreadNative抽象类bindApplication(),由于bindApplication()是运行在服务端Binder的线程池中,所以bindApplication会通过Handler发送BIND_APPLICATION的Message消息,ActivityThread中handler接受到之后调用handleBindApplication。
public final class ActivityThread {
private class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
.....
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableOpenGlTrace, boolean trackAllocation, boolean isRestrictedBackupMode,
boolean persistent, Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
Map services, Bundle coreSettings) {
.........
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();
......
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
}
.....
}
private class H extends Handler {
.....
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
....
case BIND_APPLICATION:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication");
AppBindData data = (AppBindData)msg.obj;
handleBindApplication(data);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
.....
}
....
}
} 初始化ContextImpl加载Apk资源
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
//..........
// Context初始化(ContextImpl)
final ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this/*ActivityThread*/, data.info/*LoadedApk*/);
//........
在这里创建ContextImpl对象:
static ContextImpl createAppContext(ActivityThread mainThread, LoadedApk packageInfo) {
if (packageInfo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("packageInfo");
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo, null, null, null, 0,
null);
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
return context;
}可以看出在这里 new 了一个 ContextImp 并且把resources对象传入 : context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
LoadApk中获得 Resources对象
public Resources getResources() {
if (mResources == null) {
final String[] splitPaths;
try {
splitPaths = getSplitPaths(null);
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
// This should never fail.
throw new AssertionError("null split not found");
}
mResources = ResourcesManager.getInstance().getResources(null, mResDir,
splitPaths, mOverlayDirs, mApplicationInfo.sharedLibraryFiles,
Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY, null, getCompatibilityInfo(),
getClassLoader());
}
return mResources;
}ResourcesManager中:
public @Nullable Resources getResources(@Nullable IBinder activityToken,
@Nullable String resDir,
@Nullable String[] splitResDirs,
@Nullable String[] overlayDirs,
@Nullable String[] libDirs,
int displayId,
@Nullable Configuration overrideConfig,
@NonNull CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES, "ResourcesManager#getResources");
final ResourcesKey key = new ResourcesKey(
resDir,
splitResDirs,
overlayDirs,
libDirs,
displayId,
overrideConfig != null ? new Configuration(overrideConfig) : null, // Copy
compatInfo);
classLoader = classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
return getOrCreateResources(activityToken, key, classLoader);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_RESOURCES);
}
}通过封装 key 来创建 对象:
private @Nullable Resources getOrCreateResources(@Nullable IBinder activityToken,
@NonNull ResourcesKey key, @NonNull ClassLoader classLoader) {
synchronized (this) {
// If we're here, we didn't find a suitable ResourcesImpl to use, so create one now.
ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = createResourcesImpl(key);
if (resourcesImpl == null) {
return null;
}
................
resources = getOrCreateResourcesLocked(classLoader, resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
return resources;
}
}最终要的一个方法 createResourcesImpl();创建 AssetManager:
private @Nullable ResourcesImpl createResourcesImpl(@NonNull ResourcesKey key) {
final AssetManager assets = createAssetManager(key);
if (assets == null) {
return null;
}
final ResourcesImpl impl = new ResourcesImpl(assets, dm, config, daj);
return impl;
}在创建 ResourcesImpl对象之前先创建了 AssetManager 对象,这里是非常重要的信息,在这里会把 apk 路径传给 AssetManager对象:
protected @Nullable AssetManager createAssetManager(@NonNull final ResourcesKey key) {
AssetManager assets = new AssetManager();
// resDir can be null if the 'android' package is creating a new Resources object.
// This is fine, since each AssetManager automatically loads the 'android' package
// already.
if (key.mResDir != null) {
if (assets.addAssetPath(key.mResDir) == 0) {
Log.e(TAG, "failed to add asset path " + key.mResDir);
return null;
}
}
......................
return assets;
}在这里把 resDir 传给了 addAssetPath(key.mResDir) 这个方法对我们换肤起到至关重要作用,用这个方法可以替换我们的 apk 资源。再往下就是一些 native 源码jni 方面的,篇幅 太长,这块可以去参考 :
https://blog.csdn.net/s13383754499/article/details/79041291 (注意源码版本不同,有些实现差异)
到这里我们学完了整个app启动 和 apk 的加载流程。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/s13383754499/article/details/79041291
注意源码版本 ,本篇是基于 8.0.