socket编程入门实践——基于TCP的echo服务器/客户端
最近在学习Linux网络编程,参考《TCP/IP网络编程》写下这个socket编程示例——基于TCP的echo服务器/客户端。echo服务器,顾名思义就是将收到的客户端数据原封不动地传回客户端。
无论多么复杂的TCP服务器,其函数调用顺序几乎都是socket -> bind -> listen -> accept -> read/write -> close,因此掌握这些基本函数的使用方法是很重要的。以下是基于TCP的echo服务器的完整代码(附带详细注释):
#include \n" , argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
// get a server socket
serv_sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); // domain, service types (should be SOCK_STREAM because of TCP), detailed protocol(usually 0)
// if failed
if (serv_sock == -1) {
errorHandling("socket() error");
}
// initialize the server socket address
memset(&serv_adr, 0, sizeof(serv_adr));
// set the address family
serv_adr.sin_family = AF_INET;
// set the port, convert host to network byte order
serv_adr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2]));
// set the IPv4 address
serv_adr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]);
// bind the server socket with server address
if (bind(serv_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&serv_adr, sizeof(serv_adr)) == -1) {
errorHandling("bind() error");
}
// listen for connections on the socket
if (listen(serv_sock, 5) == -1) {
// 5 means that the maximum length to which the queue of pending connections for sockfd
errorHandling("listen() error");
}
// get the size of the client address
clnt_adr_sz = sizeof(clnt_adr);
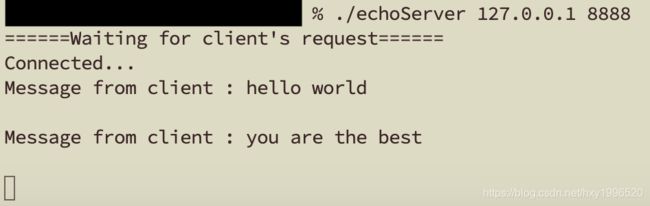
printf("======Waiting for client's request======\n");
while (1) {
// accept a connection on the socket
clnt_sock = accept(serv_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&clnt_adr, &clnt_adr_sz);
if (clnt_sock == -1) {
errorHandling("accept() error");
} else {
printf("Connected... \n");
}
// echo
while ((str_len = read(clnt_sock, message, BUF_SIZE)) != 0) {
write(clnt_sock, message, str_len);
message[str_len] = '\0';
printf("Message from client : %s\n", message);
}
// close the socket of the client
close(clnt_sock);
}
// close the socket of the server
close(serv_sock);
return 0;
}
TCP客户端的函数调用顺序几乎都是socket -> connect -> read/write -> close,以下是基于TCP的echo客户端的完整代码(附带详细注释):
#include \n" , argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
// get a server socket
sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
// if failed
if (sock == -1) {
errorHandling("socket() error");
}
// initialize the server socket address
memset(&serv_adr, 0, sizeof(serv_adr));
// set the address family
serv_adr.sin_family = AF_INET;
// set the IPv4 address
serv_adr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]);
// set the port, convert host to network byte order
serv_adr.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2]));
// connect to the server socket
if (connect(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&serv_adr, sizeof(serv_adr)) == -1) {
// if failed
errorHandling("connect() error");
} else {
puts("Connected......");
}
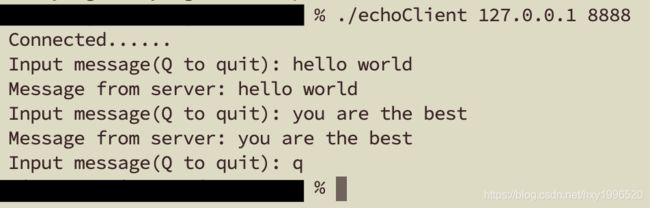
while (1) {
fputs("Input message(Q to quit): ", stdout);
fgets(message, BUF_SIZE, stdin);
// check if it is time to quit
if (!strcmp(message, "q\n") || !strcmp(message, "Q\n"))
break;
// send message to server
str_len = write(sock, message, strlen(message));
recv_len = 0;
while (recv_len < str_len) {
// read the message received
recv_cnt = read(sock, &message[recv_len], BUF_SIZE - 1);
if (recv_cnt == -1) {
errorHandling("read() error");
}
recv_len += recv_cnt;
}
message[recv_len] = 0;
printf("Message from server: %s", message);
}
close(sock);
return 0;
}