大批量数据修改解决方案
我先建立一个测试表
create table plsql_test(
dept_id char(1), 部门id
p_id char(5), 员工id
p_age number(2),员工的年龄
p_sal number(5) 员工的月薪
);
alter table plsql_test add primary key(p_id)
create index in_index on plsql_test(dept_id)
假设一个简单的需求,30岁以上(包含30)的员工在原有工资基础上上涨600元,小于30岁的员工在原有工资基础上上涨300元。
再写一个插入试验数据的java类,方便起见,就用jdbc直接连接。
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:zhanglei","scott","tiger");
PreparedStatement st = conn.prepareStatement("insert into plsql_test(dept_id,p_id,p_age,p_sal) values(?,trim(to_char(?,'00000')),?,?)");
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
//循环分三个部门
// for (int i = 50000; i < 100000; i++)
// for (int i = 100000; i < 150000; i++)
System.out.println(i);
st.setString(1,"3");
st.setInt(2,i);
st.setInt(3,r.nextInt(55));
st.setInt(4,r.nextInt(3000));
st.execute();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
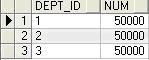
部门1,2,3每个部门插入50000名员工,共计150000条数据,查询sql如下
select distinct dept_id,count(*)over(partition by dept_id) num from plsql_test where dept_id='1'
union all
select distinct dept_id,count(*)over(partition by dept_id) num from plsql_test where dept_id='2'
union all
select distinct dept_id,count(*)over(partition by dept_id) num from plsql_test where dept_id='3'
编写一个存储过程t_cursor,大致思路是通过显式游标读取每行进行修改,也就是“快速返回”,因为它是逐条操作的而不是全部读取数据后才执行,过程如下
create or replace procedure t_cursor(v_dept_id in varchar2)
is
Cursor tmp is
select p_id,p_age,p_sal from plsql_test where dept_id = v_dept_id;
tmp_row tmp%rowtype;
begin
open tmp;
loop fetch tmp into tmp_row;
exit when tmp%notfound;
if tmp_row.p_age>=30 then
update plsql_test set p_sal = tmp_row.p_sal+600 where p_id = tmp_row.p_id;
else
update plsql_test set p_sal = tmp_row.p_sal+300 where p_id = tmp_row.p_id;
end if;
end loop;
end t_cursor;
执行这个存储过程
call t_cursor('1');
得到执行时间为9.125s
这个时间在实际应用中的确不尽如人意
为了尝试效率的提高我用集合类和forall子句重新编写一个过程t_collect
create or replace procedure t_collect(v_dept_id in varchar2)
is
type p_age_list is table of plsql_test.p_age%type index by pls_integer;
type p_sal_list is table of plsql_test.p_sal%type index by pls_integer;
type p_id_list is table of plsql_test.p_id%type index by pls_integer;
v_age p_age_list;
v_id p_id_list;
v_sal p_sal_list;
v_new_sal p_sal_list;
procedure insert_list
is
begin
select p_age,p_id,p_sal bulk collect into v_age,v_id,v_sal
from plsql_test where dept_id = v_dept_id;
end;
procedure data_op
is
begin
for i in v_id.first..v_id.last
loop
if v_age(i) >= 30 then
v_new_sal(i) := v_sal(i)+600;
else
v_new_sal(i) := v_sal(i)+300;
end if;
end loop;
end;
procedure update_new
is
begin
forall j in v_id.first..v_id.last
update plsql_test set p_sal = v_new_sal(j) where p_id = v_id(j);
end;
begin
insert_list;
data_op;
update_new;
end t_collect;
考虑到执行上一个存储过程后update语句被保存在内存中,如果直接比较与上一条的执行时间存在不公平,所以我将机器重新启动再执行t_collect
Call t_collect(‘2’)
得到执行时间为5.844s