Java this关键字——this,当前对象所在的地址
目录
- 0 小结在先
- 1 this:引用当前类的实例变量——解决形参和实参的重名尴尬
- 2. this:调用当前类方法——对象调用方法时其实调用的this.[方法],但在实际中时隐去的
- 3. this():调用当前类的构造函数
- 4 this:作为参数传递给方法
- 5 this:在构造函数调用中作为参数传递
- 6. this关键字用来返回当前类的实例
- 验证 this 关键字
0 小结在先
-【this——即当前对象的所在的地址】 在所有的普通方法(即非static静态方法,因为static是类的构造方法,无对象参与)里,系统默认隐形在方法的形参中夹带this,super参数.
-
- 比如 study()方法,其实为 study(this,super),其中,this存着对象的地址。super存着该对象父类的地址,从而可以通过this调用方法的实参。
更深刻的说
- 比如 study()方法,其实为 study(this,super),其中,this存着对象的地址。super存着该对象父类的地址,从而可以通过this调用方法的实参。
void Study(){
num = 13; //等价于this.name = 13;
name=‘lixin’; //等价于this name=‘lixin’
}
在java中,this关键字有很多种用法。 在java中,这是一个引用当前对象的引用变量。
java this关键字的用法如下:
- this关键字可用来引用当前类的实例变量。
- this关键字可用于调用当前类方法(隐式)。
- this()可以用来调用当前类的构造函数。
- this关键字可作为调用方法中的参数传递。
- this关键字可作为参数在构造函数调用中传递。
- this关键字可用于从方法返回当前类的实例
建议:如果你是java初学者,只学习 this 关键字的前三个用法就可以了。
1 this:引用当前类的实例变量——解决形参和实参的重名尴尬
this关键字可以用来引用当前类的实例变量。如果实例变量和参数之间存在歧义,则 this 关键字可用于明确地指定类变量以解决歧义问题。
了解没有 this 关键字的问题
下面先来理解一个不使用 this 关键字的示例:
class Student {
int rollno;
String name;
float fee;
Student(int rollno, String name, float fee) {
rollno = rollno;
name = name;
fee = fee;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + fee);
}
}
class TestThis1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student s1 = new Student(111, "ankit", 5000f);
Student s2 = new Student(112, "sumit", 6000f);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下 -
0 null 0.0
0 null 0.0
在上面的例子中,参数(形式参数)和实例变量(rollno和name)是相同的。 所以要使用this关键字来区分局部变量和实例变量。
使用 this 关键字解决了上面的问题
class Student {
int rollno;
String name;
float fee;
Student(int rollno, String name, float fee) {
this.rollno = rollno;
this.name = name;
this.fee = fee;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + fee);
}
}
class TestThis2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student s1 = new Student(111, "ankit", 5000f);
Student s2 = new Student(112, "sumit", 6000f);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下 -
111 ankit 5000
112 sumit 6000
如果局部变量(形式参数)和实例变量不同,则不需要像下面的程序一样使用this关键字:
不需要 this 关键字的程序示例
class Student {
int rollno;
String name;
float fee;
Student(int r, String n, float f) {
rollno = r;
name = n;
fee = f;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + fee);
}
}
class TestThis3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student s1 = new Student(111, "ankit", 5000f);
Student s2 = new Student(112, "sumit", 6000f);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下 -
111 ankit 5000
112 sumit 6000
对变量使用有意义的名称是一种好的编程习惯。所以使用相同名称的实例变量和参数,并且总是使用this关键字。
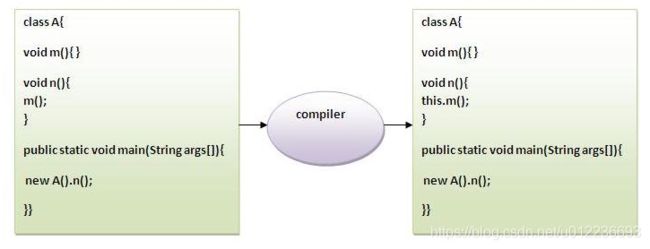
2. this:调用当前类方法——对象调用方法时其实调用的this.[方法],但在实际中时隐去的
可以使用this关键字调用当前类的方法。如果不使用this关键字,编译器会在调用方法时自动添加此 this 关键字。我们来看看这个例子。
3. this():调用当前类的构造函数
this()构造函数调用可以用来调用当前类的构造函数。 它用于重用构造函数。 换句话说,它用于构造函数链接。
也就是说调用一次 this(); 也就调用了一次类(其构造方法也就调用了一次类)
从参数化构造函数调用默认构造函数
class A {
A() {
System.out.println("hello a");
}
A(int x) {
this();
System.out.println(x);
}
}
class TestThis5 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
A a = new A(10);
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下 -
hello a
10
从默认构造函数调用参数化构造函数【即不同的构造方法通过this();相互调用】:
class A {
A() {
this(5);
System.out.println("hello a");
}
A(int x) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
class TestThis6 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
A a = new A();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下
5
hello a
使用this()构造函数调用
this()构造函数调用用于从构造函数重用构造函数。 它维护构造函数之间的链,即它用于构造函数链接。看看下面给出的示例,显示this关键字的实际使用。
class Student {
int rollno;
String name, course;
float fee;
Student(int rollno, String name, String course) {
this.rollno = rollno;
this.name = name;
this.course = course;
}
Student(int rollno, String name, String course, float fee) {
this(rollno, name, course);// reusing constructor
this.fee = fee;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + course + " " + fee);
}
}
class TestThis7 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student s1 = new Student(111, "ankit", "java");
Student s2 = new Student(112, "sumit", "java", 6000f);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下 -
111 ankit java null
112 sumit java 6000
注意:调用this()必须是构造函数中的第一个语句。
下面示例为不把 this() 语句放在第一行,因此编译不通过。
class Student {
int rollno;
String name, course;
float fee;
Student(int rollno, String name, String course) {
this.rollno = rollno;
this.name = name;
this.course = course;
}
Student(int rollno, String name, String course, float fee) {
this.fee = fee;
this(rollno, name, course);// C.T.Error
}
void display() {
System.out.println(rollno + " " + name + " " + course + " " + fee);
}
}
class TestThis8 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Student s1 = new Student(111, "ankit", "java");
Student s2 = new Student(112, "sumit", "java", 6000f);
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下 -
Compile Time Error: Call to this must be first statement in constructor
4 this:作为参数传递给方法
this关键字也可以作为方法中的参数传递。 它主要用于事件处理。 看看下面的一个例子:
class S2 {
void m(S2 obj) {
System.out.println("method is invoked");
}
void p() {
m(this);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
S2 s1 = new S2();
s1.p();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下
method is invoked
这个应用程序可以作为参数传递:
在事件处理(或)的情况下,必须提供一个类的引用到另一个。 它用于在多个方法中重用一个对象。
5 this:在构造函数调用中作为参数传递
也可以在构造函数中传递this关键字。 如果必须在多个类中使用一个对象,可以使用这种方式。 看看下面的一个例子:
class B {
A4 obj;
B(A4 obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
void display() {
System.out.println(obj.data);// using data member of A4 class
}
}
class A4 {
int data = 10;
A4() {
B b = new B(this);
b.display();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
A4 a = new A4();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下
10
6. this关键字用来返回当前类的实例
可以从方法中 this 关键字作为语句返回。 在这种情况下,方法的返回类型必须是类类型(非原始)。 看看下面的一个例子:
作为语句返回的语法
return_type method_name(){
return this;
}
从方法中返回为语句的 this 关键字的示例
class A {
A getA() {
return this;
}
void msg() {
System.out.println("Hello java");
}
}
class Test1 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
new A().getA().msg();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下 -
Hello java
验证 this 关键字
现在来验证 this 关键字引用当前类的实例变量。 在这个程序中将打印参考变量,这两个变量的输出是相同的。
class A5 {
void m() {
System.out.println(this);// prints same reference ID
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
A5 obj = new A5();
System.out.println(obj);// prints the reference ID
obj.m();
}
}
执行上面代码输出结果如下 -
A5@22b3ea59
A5@22b3ea59