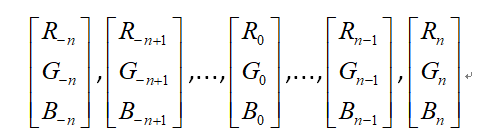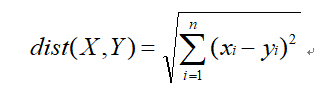图像处理——边缘轮廓拟合算法
前言:
在标注工具上标注时,时常有锯齿形的轮廓需要耗费大量脑细胞来标,因为懒所以思考。。。
需求:简单的点条直线,并调整相应的参数,算法将自动拟合出轮廓曲线,完成此边的标注任务。

算法流程:
-
读取XML文件的房屋标注框信息,每条边的两个起始点连成一条直线方程。
-
在此直线方程上取m个等距离的“基点”(m值可调节)。
-
以每个“基点”为中心,作一条法线,左右各长为n个像素的距离(n值可调节)。
-
欧式距离最大值点即为所求得的“边界位置点”。
-
将“基点”向“边界位置点”偏移,连接所有新的点,拟合成曲线。
python代码:
from xml.dom.minidom import parse
import re
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
import time
# 获取直线上‘基点’的坐标
def straightline(p1, p2, m):
x_spacing = (p2[0] - p1[0]) / (m + 1)
y_spacing = (p2[1] - p1[1]) / (m + 1)
return [[p1[0] + i * x_spacing, p1[1] + i * y_spacing] for i in range(1, m + 1)]
# 图像坐标系与数学坐标系变换
def transforme(List,H):
for i in range(len(List)):
List[i][1] = H - List[i][1]
return List
# 过每一个基点,作垂线,
# 设直线方程为Ax+By+C=0,则垂线的斜率k=B/A=(a[0]-a[1])/(b[1]-b[0]);Ci=(a[1]-a[0])P[i][0]+(b[1]-b[0])P[i][1]
# 垂线上距离基点长度为L的点的坐标为(Px+L/(sqrt((1+k)^2)),k*Px+kL/(sqrt((1+k)^2)+Ci)
def verticalline(P, i, L, N, H, d1, d2):
Pv = []
d1[1] = H - d1[1]
d2[1] = H - d2[1]
if L < N:
for n in range(1, N + 1):
k = (d1[0] - d2[0]) / (d2[1] - d1[1])
Ci = P[i][1] - k * P[i][0]
Pv.append([round(P[i][0] + L / (math.sqrt((1 + k) ** 2))),
round(k * (P[i][0]) + (k * L) / (math.sqrt((1 + k) ** 2)) + Ci)])
L = n + 1
return Pv
def detect(K,M,N):
dom = parse(xmlpath)
rootdata=dom.documentElement
image_list=rootdata.getElementsByTagName('image')
for image in image_list:
name=image.getAttribute("name")
H=int(image.getAttribute("height"))
W=int(image.getAttribute("width"))
polygon_list = rootdata.getElementsByTagName('polygon')
img = cv2.imread(name)
for polygon in polygon_list:
points_arry = []
label=polygon.getAttribute("label")
points_list=polygon.getAttribute("points")
points_list=re.split(r'[,;]', points_list)
points_list=list(float(points_list[i]) for i in range(len(points_list)))
if (len(points_list) % 2 == 0):
for idx in range(0, len(points_list), 2):
points_arry.append([points_list[idx], points_list[idx + 1]])
points_arry.append(points_arry[0])
print('points_arry:', points_arry)
#获取第一组端点
for i in range(0,len(points_arry)-1):
d1=points_arry[i]
d2=points_arry[i+1]
P = straightline(d1, d2, m=M)
P = transforme(P,H)
line = [d1]
for i in range(len(P)):
Pv = verticalline(P, i, L=1, N=N,H=H,d1=d1,d2=d2)
Pv = transforme(Pv,H)
# 获取像素值
R = []
G = []
B = []
for n in range(len(Pv)):
B.append(img[Pv[n][1], Pv[n][0], 0])
G.append(img[Pv[n][1], Pv[n][0], 1])
R.append(img[Pv[n][1], Pv[n][0], 2])
# 计算相邻点的相似度
J = []
S = []
for j in range(len(R)):
J.append(j + 1)
S.append(math.sqrt(R[j] ^ 2 + G[j] ^ 2 + B[j] ^ 2))
# 返回边界点的索引值
Index = J[S.index(max(S))]
# 返回坐标点并可视化
X0, Y0 = Pv[Index - 1][0], Pv[Index - 1][1]
line.append([X0, Y0])
line.append(d2)
# 将边界点连成一条可视化线
line = np.array(line, np.int32)
line = line.reshape((-1, 1, 2))
cv2.polylines(img, [line], False, (0, 0, 255), 1)
cv2.imshow("image", img)
cv2.imwrite("./output/" + str(K) + ".bmp", img)