研究dlmalloc和dlfree算法
文章目录
- 一.背景知识
-
- 内存模型
- state
- chunk和tree_chunk
- smallBins
- treeBins
- 二.dlmalloc
-
- 流程图
- 代码分析
-
- dlmalloc
- allocateFromSmallBin
- splitFromSmallBin
- insertSmallChunk
- splitSmallFromTree
- splitFromTree
- splitFromDesignatedVictim
- splitFromTop
- 三.dlfree
-
- 流程图
- 代码分析
-
- dlfree
一.背景知识
内存模型
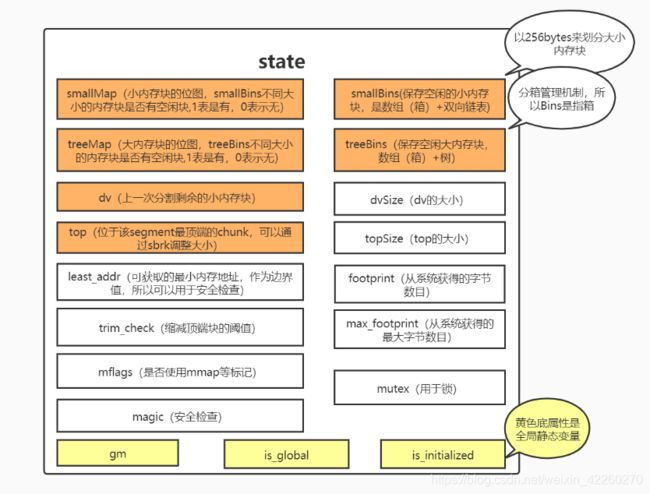
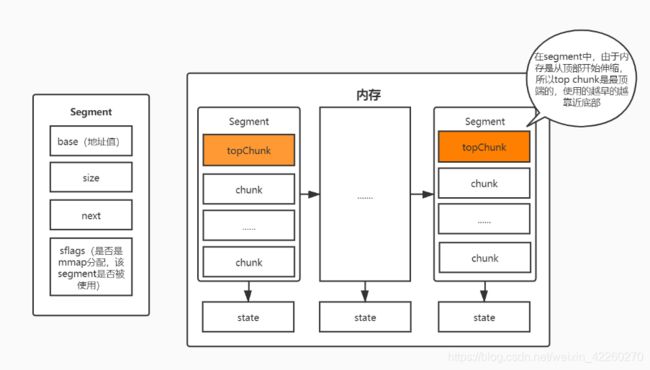
我理解的是,与ehcache中EhcacheConcurrentOffHeapClockCache的segment对应,在内存里面会划分很多个segment,每个segment有存储bins,dv,top等重要全局信息(便于后续分配内存块chunk/treeChunk),base,size,next,sflags属性,且包含了top chunk,chunk,tree chunk内存块。
state
chunk和tree_chunk
tree_chunk仅比chunk多child和parent属性。

smallBins
数组加双向链表的结构。
数组的index即是内存大小除以8。

treeBins
二.dlmalloc
流程图
代码分析
dlmalloc
private int dlmalloc(int bytes) {
//加上额外数据大小,最后nb=bytes/8+8(head+prev_foot)
int nb = bytes < 7 ? 16 : padRequest(bytes);
int index;
if (bytes <= 240) {
//属于小内存块,找到在小内存中的箱号(除以8)
index = smallBinIndex(nb);
//将smallMap的index的位移到最右边【smallMap是32个箱子是否有空闲内存的位图,0表示该箱没有空闲内存,1表示有空闲内存】
int smallBits = this.smallMap >>> index;
//符合以下条件的是:低2位为01,10,11三种情况。01表示当前箱子有空闲内存,隔壁箱子没有空闲内存;10表示当前箱子没有空闲 内存,隔壁箱子有空闲内存;11表示当前箱子和隔壁箱子都有空闲内存。
if ((smallBits & 3) != 0) {
index += ~smallBits & 1;
//分配小内存中的空闲内存
return this.allocateFromSmallBin(index, nb);
}
//需要的内存大于 最近分割的内存大小
if (nb > this.designatedVictimSize) {
//不等于0,说明一定有空闲内存,所以要寻找到和当前大小最接近的内存index;smallBits << index表示index至0位都是0,所以找到右边第一个为1的,一定是能装下当前容量的内存
if (smallBits != 0) {
return this.splitFromSmallBin(Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(smallBits << index), nb);
}
if (this.treeMap != 0) {
//因为此时nb一定小于256bytes,所以一定是能在tree的范围内,所以直接从最低位开始找内存块,不用像上面小内存块一样进行移位操作
return this.splitSmallFromTree(nb);
}
}
} else {
if (bytes > 2147483584) {
return -1;
}
if (this.treeMap != 0) {
//从treeBins分配空闲内存
index = this.splitFromTree(nb);
if (okAddress(index)) {
return index;
}
}
}
if (nb <= this.designatedVictimSize) {
//需要的内存小于 最近分割的内存大小
return this.splitFromDesignatedVictim(nb);
} else {
//从top chunk分配
return nb < this.topSize ? this.splitFromTop(nb) : -1;
}
}
allocateFromSmallBin
private int allocateFromSmallBin(int index, int nb) {
int h = this.smallBins[index];
// 校验下内存大小是否一致
Validation.validate(!VALIDATING || this.chunkSize(h) == smallBinIndexToSize(index));
int f = this.forward(h);
int b = this.backward(h);
if (f == h) {
//说明只有一个空闲内存,取出使用后要清除该位置的空闲标识
Validation.validate(!VALIDATING || b == h);
this.clearSmallMap(index);
this.smallBins[index] = -1;
} else {
//移除h,改变f,b的关系
this.smallBins[index] = f;
this.backward(f, b);
this.forward(b, f);
}
//在该chunk附近的内存块,标记该内存在使用,设置其大小
this.setInUseAndPreviousInUse(h, smallBinIndexToSize(index));
int mem = chunkToMem(h);
this.checkMallocedChunk(mem, nb);
return mem;
}
splitFromSmallBin
private int splitFromSmallBin(int index, int nb) {
int h = this.smallBins[index];
Validation.validate(!VALIDATING || this.chunkSize(h) == smallBinIndexToSize(index));
int f = this.forward(h);
int b = this.backward(h);
if (f == h) {
Validation.validate(!VALIDATING || b == h);
this.clearSmallMap(index);
this.smallBins[index] = -1;
} else {
this.smallBins[index] = f;
this.backward(f, b);
this.forward(b, f);
}
//计算出剩余的内存大小
int rsize = smallBinIndexToSize(index) - nb;
int mem;
//剩余的小于16就直接分别给用户
if (rsize < 16) {
this.setInUseAndPreviousInUse(h, smallBinIndexToSize(index));
} else {
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfInUseChunk(h, nb);
mem = h + nb;
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfFreeChunk(mem, rsize);
this.replaceDesignatedVictim(mem, rsize);
}
mem = chunkToMem(h);
this.checkMallocedChunk(mem, nb);
return mem;
}
insertSmallChunk
这里只展示插入到小内存块的过程,主要是为了验证,链表的第一个是最近可以被使用、也是最近插入的内存块
private void insertSmallChunk(int p, int s) {
//找到一样大小的内存index
int index = smallBinIndex(s);
int h = this.smallBins[index];
if (!this.smallMapIsMarked(index)) {
//该index的箱子没有被使用
this.markSmallMap(index);
//插入该空闲内存,待下次使用
this.smallBins[index] = p;
this.forward(p, p);
this.backward(p, p);
} else {
if (!okAddress(h)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
//插入该空闲内存,待下次使用
int b = this.backward(h);
this.forward(b, p);
this.forward(p, h);
this.backward(h, p);
this.backward(p, b);
}
this.checkFreeChunk(p);
}
splitSmallFromTree
private int splitSmallFromTree(int nb) {
//找到最符合nb大小的树
int index = Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(this.treeMap);
int t;
//记录最符合的内存地址
int v = t = this.treeBins[index];
//记录最符合的内存剩余大小
int rsize = this.chunkSize(t) - nb;
int r;
//顺着父节点找到其下最符合大小的左节点
while((t = this.leftmostChild(t)) != -1) {
r = this.chunkSize(t) - nb;
if (r >= 0 && r < rsize) {
rsize = r;
v = t;
}
}
if (!okAddress(v)) {
throw new AssertionError();
} else {
r = v + nb;
Validation.validate(!VALIDATING || this.chunkSize(v) == rsize + nb);
if (okNext(v, r)) {
//移除内存块
this.unlinkLargeChunk(v);
//分配内存给用户,标记内存已被使用,还有可能要替换dv(最近剩余的分割内存)
if (rsize < 16) {
this.setInUseAndPreviousInUse(v, rsize + nb);
} else {
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfInUseChunk(v, nb);
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfFreeChunk(r, rsize);
this.replaceDesignatedVictim(r, rsize);
}
int mem = chunkToMem(v);
this.checkMallocedChunk(mem, nb);
return mem;
} else {
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
}
splitFromTree
private int splitFromTree(int nb) {
int v = -1;
int rsize = 2147483647 & -nb;
//内存相近的树的位置(箱号)
int index = treeBinIndex(nb);
int t;
int trem;
int r;
if ((t = this.treeBins[index]) != -1) {
//将nb中的关键码移到最左边(决定了内存大小,左右节点方向)
//leftShiftForTreeIndex内部是 i == 31 ? 0 : 31 - ((i >>> 1) + 8 - 2) ;其中((i >>> 1) + 8 - 2)代表了内存大小;比如index为0,即0号箱,规定了他的内存大小是128,所以是满足前方表达式的。
trem = nb << leftShiftForTreeIndex(index);
r = -1;
while(true) {
//计算剩余的大小
int trem = this.chunkSize(t) - nb;
//如果比之前的rsize还小,说明该chunk大小更适合nb
if (trem >= 0 && trem < rsize) {
//记录当前的树
v = t;
//记录当前的剩余大小
rsize = trem;
//等于则直接返回该内存块
if (trem == 0) {
break;
}
}
//以上是找到最符合的节点不是叶子节点
//右子树
int rt = this.child(t, 1);
//关键位(可能是0/1),所以可能是左子树、右子树
t = this.child(t, trem >>> 31);
//右子树,且关键位是左子树
if (rt != -1 && rt != t) {
r = rt;
}
//左子树不存在,就直接返回右子树
if (t == -1) {
t = r;
break;
}
trem <<= 1;
}
}
//没有找到合适树
if (t == -1 && v == -1) {
//看比index大的箱子有没有空闲的内存
trem = leftBits(1 << index) & this.treeMap;
if (trem != 0) {
//找到与index最相近的有空闲的树
t = this.treeBins[Integer.numberOfTrailingZeros(trem)];
}
}
//优先使用左节点内存
for(; t != -1; t = this.leftmostChild(t)) {
trem = this.chunkSize(t) - nb;
if (trem >= 0 && trem < rsize) {
rsize = trem;
v = t;
}
}
trem = this.designatedVictimSize - nb;
//比较 dv和 上一次获取到的节点的chunk哪个更接近nb,以下是chunk更接近nb的大小
if (v != -1 && (trem < 0 || rsize < trem)) {
if (!okAddress(v)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
r = v + nb;
Validation.validate(!VALIDATING || this.chunkSize(v) == rsize + nb);
if (okNext(v, r)) {
this.unlinkLargeChunk(v);
if (rsize < 16) {
this.setInUseAndPreviousInUse(v, rsize + nb);
} else {
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfInUseChunk(v, nb);
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfFreeChunk(r, rsize);
this.insertChunk(r, rsize);
}
return chunkToMem(v);
}
}
return -1;
}
splitFromDesignatedVictim
private int splitFromDesignatedVictim(int nb) {
//分配给用户后,dv剩余的内存大小
int rsize = this.designatedVictimSize - nb;
//内存地址指向当前dv地址
int p = this.designatedVictim;
int mem;
//如果剩余内存大于16字节
if (rsize >= 16) {
//更新dv的地址,大小
mem = this.designatedVictim = p + nb;
this.designatedVictimSize = rsize;
//设置对应chunk的使用状态及大小
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfFreeChunk(mem, rsize);
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfInUseChunk(p, nb);
} else {
//如果剩余内存小于16字节,直接分配给用户,并且dv销毁,更改dv相邻chunk中该dv的使用状态及大小
mem = this.designatedVictimSize;
this.designatedVictimSize = 0;
this.designatedVictim = -1;
this.setInUseAndPreviousInUse(p, mem);
}
mem = chunkToMem(p);
this.checkMallocedChunk(mem, nb);
return mem;
}
splitFromTop
private int splitFromTop(int nb) {
//top分配给用户后剩余的大小
int rSize = this.topSize -= nb;
//内存地址指向当前top地址
int p = this.top;
int r = this.top = p + nb;
//更新剩余chunk的头信息(分配给用户的内存是使用状态)
this.head(r, rSize | 1);
//更新待分配的chunk的头信息(分配给用户的内存是使用状态,前一个chunk也处于使用状态)
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfInUseChunk(p, nb);
int mem = chunkToMem(p);
this.checkTopChunk(this.top);
this.checkMallocedChunk(mem, nb);
return mem;
}
三.dlfree
流程图
代码分析
dlfree
private void dlfree(int mem, boolean shrink) {
int p = memToChunk(mem);
if (okAddress(p) && this.isInUse(p)) {
this.checkInUseChunk(p);
//待释放块的大小
int psize = this.chunkSize(p);
this.occupied -= psize;
//下一个内存块地址
int next = p + psize;
int nsize;
//如果pchunk是空闲状态
if (!this.previousInUse(p)) {
//找到pchunk的大小
nsize = this.prevFoot(p);
int previous = p - nsize;
//累加pchunk的大小
psize += nsize;
//标记前一个chunk的地址
p = previous;
if (!okAddress(previous)) {
throw new AssertionError();
}
//如果pchunk不是dv,从smallBins/treeBins移除pchunk
if (previous != this.designatedVictim) {
this.unlinkChunk(previous, nsize);
} else if ((this.head(next) & 3) == 3) {
//如果nchunk正在使用,就将当前的chunk合并到pchunk(因为pchunk是dv)设置为dv;更改nchunk的pchunk位空闲
this.designatedVictimSize = psize;
this.setFreeWithPreviousInUse(previous, psize, next);
return;
}
}
//以上是为了找到pchunk+chunk中的空闲块 ,所以以下psize可能包含待释放chunk的pchunk大小
if (okNext(p, next) && this.previousInUse(next)) {
//nchunk空闲
if (!this.chunkInUse(next)) {
//nchunk是topchunk,合并psize大小的空闲块(可能包含了pchunk),且设置topchunk的地址为p(可能是pchunk的地址)
if (next == this.top) {
nsize = this.topSize += psize;
this.top = p;
this.head(p, nsize | 1);
//如果p是dv,就要删除dv
if (p == this.designatedVictim) {
this.designatedVictim = -1;
this.designatedVictimSize = 0;
}
//真正回收top到系统中
if (shrink) {
this.storage.release((long)(p + TOP_FOOT_SIZE));
}
return;
}
//nchunk是dv,将当前的chunk合并到nchunk(因为nchunk是dv)设置为dv
if (next == this.designatedVictim) {
nsize = this.designatedVictimSize += psize;
this.designatedVictim = p;
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfFreeChunk(p, nsize);
return;
}
//合并nchunk
nsize = this.chunkSize(next);
psize += nsize;
//从bins移除nchunk
this.unlinkChunk(next, nsize);
//直接合并至dv
this.setSizeAndPreviousInUseOfFreeChunk(p, psize);
//检查p是不是dv,是就更新dvsize
if (p == this.designatedVictim) {
this.designatedVictimSize = psize;
return;
}
} else {
//设置当前chunk为空闲,且更改nchunk的pchunk为空闲
this.setFreeWithPreviousInUse(p, psize, next);
}
//插入chunk至smallBins/treeBins
if (isSmall(psize)) {
this.insertSmallChunk(p, psize);
} else {
this.insertLargeChunk(p, psize);
}
} else {
throw new AssertionError("Problem with next chunk [" + p + "][" + next + ":previous-inuse=" + this.previousInUse(next) + "]");
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Address " + mem + " has not been allocated");
}
}