Spring 关于bean的获取以及自定义注解的起始注入和获取
最近有收获了一点东西,特来记录。假设一个场景,一个学生的学习计划根据其不同的人,和学习内容有不同的结果,和处理方式。按照我们正常的写法,应该是就是构造一个’内容‘接口。例如
public interface PersonAnnotationService {
public String testPrint();
}接下来我们应该制造很多实现类,区分人和学习内容来根据不同的情况获取不同的实现类。这就麻烦了,一,我们怎么区分这两个条件呢,二,区分了我们怎么能简单的,不模糊的获取对应的实现类呢
方法一:如果用一对一架构关系的话,也是有办法的。比如我们,创建一个子接口去继承内容接口
public interface PersonZxyCoding extends PersonAnnotationService{
}@Service
public class PersonZxyCodingImpl implements PersonZxyCoding{
@Override
public String testPrint() {
System.err.println("这里是son:PersonZxyCodingImpl");
return null;
}
} @Autowired
private PersonZxyCoding personZxyCoding;这是实现的第一种办法,很简单。现在回归我们的主题,我们需要注意的是,如果,我有一个班五十二个人,每个人都有dancing和coding两种或者更多的同样内容细节要编写,那就很可怕了。那就是至少52*2=104个类。在这种情况下,也许我们可以考虑换个方法。
方法二:所有的内容实现类继承一个接口。如
xx extends PersonAnnotationService 详细说下这个过程就是,
1.创建一个有关接口
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Service
public @interface personInfo {
String personInfo() default "0";
String value() default "";
}
@Service
@personInfo(personInfo=config.personInfoCoding)
public class PersonCodingServiceimpl implements PersonAnnotationServiceps:此处业务分析,详细代码在最后面给出
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
//全局保存相关的personBean实现对象
public static Map getPersonbeanmap = new HashMap();
// 获取Spring的application到该类
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0) throws BeansException {
getContent.applicationContext = arg0;
}
// 通过反射操作获取对应的类
public static Object getTarget(Object proxy) throws Exception {
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(proxy)) {
return proxy;// 不是代理对象
}
// 根据jdk进行反射操作
if (AopUtils.isJdkDynamicProxy(proxy)) {
return getJdkDynamicProxyTargetObject(proxy);
} else { // 根据cglib进行反射操作
return getCglibProxyTargetObject(proxy);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static T getBean(String beanName) {
cheakApplicationContext();
return (T) applicationContext.getBean(beanName);
}
public static T getBean(Class clazz) {
cheakApplicationContext();
return (T) applicationContext.getBean(clazz);
}
// 根据传入的自定义注解的类,从Application获取有此注解的所有类
public static Map getMapbeanwithAnnotion(Class cls) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map = applicationContext.getBeansWithAnnotation(cls);
return map;
} 4.现在我们可以想象的是,Spring启动的时候,有关注解的实现类,将会以bean的形式存入容器中,而我们也编写了获取bean和获取相关类的方法。那么接下来,我们需要做的,是在启动时候,把实现类,放在map中,通过,Map<'人+内容',‘实现类’>的形式保存。在需要的时候直接getKey获取有关的实现类。
在这里我们需要实现ApplicationListener
所有我们可以把需要spring执行的有关方法放在这里面,在本环境,我们需要做的事,把map处理成上述的格式。
@Service
public class initContent implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
// 通过注解获取相关的类
Map map = getContent.getMapbeanwithAnnotion(personInfo.class);
for (Map.Entry entrymap : map.entrySet()) {
try {
// 通过反射获取相关的实现类的Object
Object object = getContent.getTarget(entrymap.getValue());
if (object != null) {
PersonAnnotationService annotationService = (PersonAnnotationService) object;
// 不为空的情况下,获取实现类的注解对象
// 并把注解对象的注解字段当做map的Key,实现类Object当做值
personInfo info = annotationService.getClass().getAnnotation(personInfo.class);
getContent.getPersonbeanmap.put(info.personInfo(), object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Autowired
private PersonService personService;
@Autowired
private PersonZxyCoding personZxyCoding;
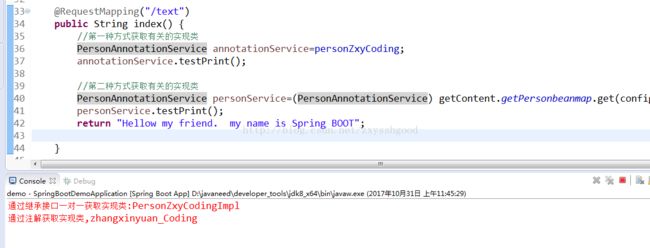
@RequestMapping("/text")
public String index() {
//第一种方式获取有关的实现类
PersonAnnotationService annotationService=personZxyCoding;
annotationService.testPrint();
//第二种方式获取有关的实现类
PersonAnnotationService personService=(PersonAnnotationService) getContent.getPersonbeanmap.get(config.personInfoCoding);
personService.testPrint();
return "Hellow my friend. my name is Spring BOOT";
}结果:
附:getContent详细代码
@Service
public class getContent implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
//全局保存相关的personBean实现对象
public static Map getPersonbeanmap = new HashMap();
// 获取Spring的application到该类
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0) throws BeansException {
getContent.applicationContext = arg0;
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static T getBean(String beanName) {
cheakApplicationContext();
return (T) applicationContext.getBean(beanName);
}
public static T getBean(Class clazz) {
cheakApplicationContext();
return (T) applicationContext.getBean(clazz);
}
// 根据传入的自定义注解的类,从Application获取有此注解的所有类
public static Map getMapbeanwithAnnotion(Class cls) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map = applicationContext.getBeansWithAnnotation(cls);
return map;
}
// 空值检测
private static void cheakApplicationContext() {
if (applicationContext == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("applicaitonContext未注入,请在applicationContext.xml中定义SpringContextHolder");
}
}
// 通过反射操作获取对应的类
public static Object getTarget(Object proxy) throws Exception {
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(proxy)) {
return proxy;// 不是代理对象
}
// 根据jdk进行反射操作
if (AopUtils.isJdkDynamicProxy(proxy)) {
return getJdkDynamicProxyTargetObject(proxy);
} else { // 根据cglib进行反射操作
return getCglibProxyTargetObject(proxy);
}
}
private static Object getCglibProxyTargetObject(Object proxy) throws Exception {
Field h = proxy.getClass().getDeclaredField("CGLIB$CALLBACK_0");
h.setAccessible(true);
Object dynamicAdvisedInterceptor = h.get(proxy);
Field advised = dynamicAdvisedInterceptor.getClass().getDeclaredField("advised");
advised.setAccessible(true);
Object target = ((AdvisedSupport) advised.get(dynamicAdvisedInterceptor)).getTargetSource().getTarget();
return target;
}
private static Object getJdkDynamicProxyTargetObject(Object proxy) throws Exception {
Field h = proxy.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField("h");
h.setAccessible(true);
AopProxy aopProxy = (AopProxy) h.get(proxy);
Field advised = aopProxy.getClass().getDeclaredField("advised");
advised.setAccessible(true);
Object target = ((AdvisedSupport) advised.get(aopProxy)).getTargetSource().getTarget();
return target;
}
}