Linux网络编程——tcp实例
题目
1、通过TCP协议实现多个client端可以并发连接到server,client可获得server指定目录下的文件列表。
/*
* client.c
*
* Created on: 2016年11月3日
* Author: Administrator
*/
#include /*
============================================================================
Name : CS-opendir.c
Author : Allen
Version :
Copyright : Your copyright notice
Description : Hello World in C, Ansi-style
============================================================================
*/
#include .SUFFIXES: .c .o
CC=gcc
SRCS1=server.c
SRCS2=client.c
OBJS1=$(SRCS1:.c=.o)
OBJS2=$(SRCS2:.c=.o)
EXEC1=server
EXEC2=client
all: $(OBJS1) $(OBJS2)
$(CC) -o $(EXEC1) $(OBJS1)
$(CC) -o $(EXEC2) $(OBJS2)
@echo '-------------ok--------------'
.c.o:
$(CC) -Wall -g -o $@ -c $<
clean:
rm -f $(OBJS1) $(OBJS2)
rm -f core*
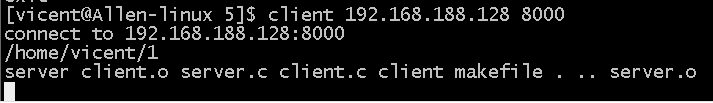
运行结果
今天没时间为代码注释啦,改天补齐.