【LeetCode】498. 对角线遍历 & 1424. 对角线遍历 II
I、498. 对角线遍历(蛇形)
一、题目描述
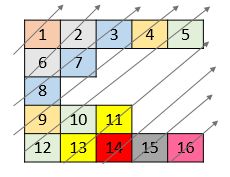
给定一个含有 M x N 个元素的矩阵(M 行,N 列),请以对角线遍历的顺序返回这个矩阵中的所有元素,对角线遍历如下图所示。
示例:
输入:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ]
]
输出: [1,2,4,7,5,3,6,8,9]
说明:
给定矩阵中的元素总数不会超过 100000 。
二、解题思路 & 代码
2.1 对角线迭代和翻转
算法
- 初始化数组
result,用于存储最后结果。 - 使用一个外层循环遍历所有的对角线。第一行和最后一列的元素都是对角线的起点。
- 使用一个内层 while 循环遍历对角线上的所有元素。可以计算指定对角线上的元素数量,也可以简单迭代直到索引超出范围。
- 因为不知道每条对角线上的元素数量,需要为每条对角线分配一个列表或动态数组。但是同样也可以通过计算得到当前对角线上的元素数量。
- 对于奇数编号的对角线,只需要将迭代结果翻转再加入结果数组即可。
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
if not matrix or not matrix[0]:
return []
N, M = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
result, intermediate = [], []
for d in range(N + M - 1):
# Clear the intermediate array everytime we start
# to process another diagonal
intermediate.clear()
# We need to figure out the "head" of this diagonal
# The elements in the first row and the last column
# are the respective heads.
r, c = 0 if d < M else d - M + 1, d if d < M else M - 1
# Iterate until one of the indices goes out of scope
# Take note of the index math to go down the diagonal
while r < N and c > -1:
intermediate.append(matrix[r][c])
r += 1
c -= 1
# Reverse even numbered diagonals. The
# article says we have to reverse odd
# numbered articles but here, the numbering
# is starting from 0 :P
if d % 2 == 0:
result.extend(intermediate[::-1])
else:
result.extend(intermediate)
return result
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( N ⋅ M ) O(N⋅M) O(N⋅M),数组有 N 行 M 列。对于所有奇数对角线上的元素,需要两次处理,迭代和翻转。为了节省空间,需要遍历新对角线之前清除中间使用的空间,该操作需要 O ( K ) O(K) O(K) 的复杂度度,其中 K 是数组长度。因此至少处理两次数组中的元素,渐进复杂度为 O ( N ⋅ M ) O(N⋅M) O(N⋅M)。
- 空间复杂度: O ( m i n ( N , M ) ) O(min(N,M)) O(min(N,M)),额外空间用于存储每条对角线的中间数组,该数组长度为 N 和 M 的最小值。注意:对角线延伸到索引超出范围结束。
2.2 模拟
算法
- 初始化一个布尔变量 direction 表示当前对角线的方向。根据当前方向和尾部位置确定下一条对角线首部。最初 direction 为 1,方向向上。每条对角线遍历完成后更新 direction。
- 假设当前对角线首部为 m a t r i x [ i ] [ j ] matrix[i][j] matrix[i][j],根据方向遍历该对角线。
1)向上的对角线,下一个元素是 m a t r i x [ i − 1 ] [ j + 1 ] matrix[i−1][j+1] matrix[i−1][j+1]。
2)向下的对角线,下一个元素是 m a t r i x [ i + 1 ] [ j − 1 ] matrix[i+1][j−1] matrix[i+1][j−1]。 - 遍历当前对角线元素直到到达矩阵边界结束。
- 假设现在到达当前对角线的最后一个元素,寻找下一条对角线首部。注意:下面伪代码中方向是当前对角线方向。如果当前对角线方向是向上的,则下一条对角线是向下的;否则是下一条对角线是向上的。
tail = [i, j]
if direction == up, then {
if [i, j + 1] is within bounds, then {
next_head = [i, j + 1]
} else {
next_head = [i + 1, j]
}
} else {
if [i + 1, j] is within bounds, then {
next_head = [i + 1, j]
} else {
next_head = [i, j + 1]
}
}
- 继续处理对角线元素,当前对角线遍历结束时,使用当前方向和尾部位置找出下一条对角线首部。然后翻转方向,处理下一条对角线。
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
if not matrix or not matrix[0]:
return []
N, M = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
row, column = 0, 0
direction = 1
result = []
while row < N and column < M:
result.append(matrix[row][column])
# Move along in the current diagonal depending upon
# the current direction.[i, j] -> [i - 1, j + 1] if
# going up and [i, j] -> [i + 1][j - 1] if going down.
new_row = row + (-1 if direction == 1 else 1)
new_column = column + (1 if direction == 1 else -1)
# Checking if the next element in the diagonal is within the
# bounds of the matrix or not. If it's not within the bounds,
# we have to find the next head.
if new_row < 0 or new_row == N or new_column < 0 or new_column == M:
# If the current diagonal was going in the upwards
# direction.
if direction:
# For an upwards going diagonal having [i, j] as its tail
# If [i, j + 1] is within bounds, then it becomes
# the next head. Otherwise, the element directly below
# i.e. the element [i + 1, j] becomes the next head
row += (column == M - 1)
column += (column < M - 1)
else:
# For a downwards going diagonal having [i, j] as its tail
# if [i + 1, j] is within bounds, then it becomes
# the next head. Otherwise, the element directly below
# i.e. the element [i, j + 1] becomes the next head
column += (row == N - 1)
row += (row < N - 1)
# Flip the direction
direction = 1 - direction
else:
row = new_row
column = new_column
return result
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O ( N ⋅ M ) O(N⋅M) O(N⋅M),每个元素只处理一次。
- 空间复杂度: O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),不使用额外空间。注意:输出数组空间不计入空间复杂度,因为这是题目要求的空间。空间复杂度应该指除了最终数组以外的空间。上一个方法中是中间数组,该方法中只有几个变量。
参考:
- LeetCode官方题解
===============================================================================================================================
II、1424. 对角线遍历 II(同向)
给你一个列表 nums ,里面每一个元素都是一个整数列表。请你依照下面各图的规则,按顺序返回 nums 中对角线上的整数。
输入:nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[1,4,2,7,5,3,8,6,9]
输入:nums = [[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7],[8],[9,10,11],[12,13,14,15,16]]
输出:[1,6,2,8,7,3,9,4,12,10,5,13,11,14,15,16]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [[1,2,3],[4],[5,6,7],[8],[9,10,11]]
输出:[1,4,2,5,3,8,6,9,7,10,11]
示例 4:
输入:nums = [[1,2,3,4,5,6]]
输出:[1,2,3,4,5,6]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
1 <= nums[i].length <= 10^5
1 <= nums[i][j] <= 10^9
nums 中最多有 10^5 个数字。
二、解题思路 & 代码
n u m s [ i ] [ j ] nums[i][j] nums[i][j] 必然在第(i + j)次斜线的结果中。i 越小,结果越靠后。
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
sub_result = []
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(len(nums[i])):
if i + j >= len(sub_result):
sub_result.append([])
sub_result[i + j].append(nums[i][j])
result = []
for sub in sub_result:
result += sub[::-1]
return result