Android ThreadLocal理解及应用场景
前言
首先表明ThreadLocal并不是Thread,而是是一个线程内部的数据存储类。ThreadLocal是JDK 1.2的版本中开始提供的。ThreadLocal是以线程为关键字,因此通过它可以在指定的线程中存储数据,且只有在相应线程中才可以获取到相应存储的数据,其他线程来说是无法获取到数据。简单来说ThreadLocal是提供线程内的局部变量存储机制。总的来说ThreadLocal有两个个有点:
1、每个线程都有自己的局部变量,即每个线程都在ThreadLocal有一个独立的数据存储区域,且该线程的本地变量对其他线程是不可见的。
2、相应区域数据改变只与当前线程关联,线程之间互不干扰。
ThreadLocal使用场景
ThreadLocal设计初衷是为了解决线程并发的线程安全问题和某些特定场景的问题。ThreadLocal本身能够被多个线程共享使用,并且又能够达到线程安全的目的。ThreadLocal使用的场景大致分为以下两两种:
多线程中数据并发产生线程安全,即不同域(Thread)数据存取
ThreadLocal的原理就是为每个Thread提供数据提供一个副本,然后通过本身Thread访问副本来存取业务当数据。这样的形式减少了线程同步所带来的线程消耗,也减少了线程并发控制的复杂度。因此当以线程为作用域,并且不同线程拥有不同数据副本的时候,在该场景就可以使用ThreadLocal。以下通过例子更实质性的对该情景的理解:
public class TestClass {
//声明一个ThreadLocal变量,一会用于在单独Thread中存储相应Thread这个域中的数据;
final ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
//声明第一个线程,并在现在对threadLocal变量进行一个存储和取操作
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//在线程一种存储数据
threadLocal .set("threa1 data");
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);//将最后提取threadLocal数据
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
//在线程一种提取数据
System.out.println(threadLocal .get());
}
});
//声明第二个线程,并在现在对threadLocal变量进行一个存储和取操作
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//在线程二种存储数据
threadLocal .set("threa2 data");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);//将倒数第二位提取threadLocal数据
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
//在线程二种提取数据
System.out.println(threadLocal .get());
}
});
//声明第三个线程,并在现在对threadLocal变量进行一个存储和取操作
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//在线程三种存储数据
threadLocal .set("threa3 data");
//将第一个序提取threadLocal数据
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
//在线程三种提取数据
System.out.println(threadLocal .get());
}
});
public static void main(String[] args) {
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
}
//执行完main函数后输出结果如下
I/System.out: Thread-675 //为第三个线程
I/System.out: threa3 data
I/System.out: Thread-674 //为第二个线程
I/System.out: threa2 data
I/System.out: Thread-673 //为第一个线程
I/System.out: threa1 data
通过以上例子,可以发现虽然在不同线程中操作同一个ThreadLocal对象并存数据,但是在不同线程通过ThreadLocal来获取到的值却不是我们常规理解的先存先出的方式(链方式存储),而是在同一线程内存的数据,在同一线程取出的方式,这也就是我们前面提到的TheadLocal是指定的线程中存储数据,且只有在相应线程中才可以获取到相应存储的数据,其他线程来说是无法获取到数据。
复杂逻辑下对象传递,即解决共享参数
当函数调用栈比较深以或代码入口的多样性,又需要监听器能够贯穿整个线程的执行过程,这样就会将业务变的臃肿复杂化。常规操作就是将监听器通过参数的形式在函数调用栈中进行传递或将监听器作为静态变量供线程访问,这两种方式的结果就是:第一种将造成函数调用栈很深及;第二章将造成不具有可扩充性。而采用TheadLocal就解决这两种方式带来的问题。一下将例举常规方式和使用TheadLocal来解决这个问题。
常规方式:
如方法 metho1(),在该方法中调用了方法metho2(),而又在方法metho2() 中又调用了方法metho3(),现在都需要使用一个字符串参数 args。
//常规方式
public void metho1() {
String args = "data";
metho2(args);
}
public void metho2(String args) {
metho3(args);
}
public void metho3(String args) {
System.out.println(args);
}
TheadLocal方式
interface TestInterface {
ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
}
class Cl1 implements TestInterface {
public static void metho1(String args) {
threadLocal.set(args);
}
}
class Cl2 implements TestInterface {
public static void metho2() {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
}
}
class Cl3 implements TestInterface {
public static void metho3() {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
}
}
public class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cl1.metho1("Test Data");//将数据存储到ThreadLocal
Cl2.metho2(); //将数据ThreadLocal取出
Cl3.metho3(); //将数据ThreadLocal取出
}
}
//执行完main函数输出结果
I/System.out: Test Data
I/System.out: Test Data
ThreadLocal介绍
通过查看源码我们可以发现ThreadLocal类是一个泛型类,ThreadLocal传进来的泛型T的类型就是ThreadLocal需要保存的数据类型。一下将介绍几个主要方法,其他方法有兴趣的可以自行查看源码《ThreadLocal源码》
initialValue()方法,设置初始值该函数,每在一个新的线程中第一次调用get函数的时候都会调用;如果一开始就调用了set函数,则该函数不会被调用,除非调用了remove函数之后又调用get函数,这时候再get函数中还是会调用initialValue函数。
/**
* Returns the current thread's "initial value" for this
* thread-local variable. This method will be invoked the first
* time a thread accesses the variable with the {@link #get}
* method, unless the thread previously invoked the {@link #set}
* method, in which case the {@code initialValue} method will not
* be invoked for the thread. Normally, this method is invoked at
* most once per thread, but it may be invoked again in case of
* subsequent invocations of {@link #remove} followed by {@link #get}.
*
* This implementation simply returns {@code null}; if the
* programmer desires thread-local variables to have an initial
* value other than {@code null}, {@code ThreadLocal} must be
* subclassed, and this method overridden. Typically, an
* anonymous inner class will be used.
*
* @return the initial value for this thread-local
*/
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
由于该函数是protected类型的,因此建议在子类重载该函数的,所以通常该函数都会以匿名内部类的形式被重载,以指定初始值,如:
public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>() {
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
return "default Str";
}
};
}
set()方法
set函数主要用来在ThreadLocal中存储当前线程的下的值,通过传入的key的hashCode计算出索引的位置,从索引位置开始遍历,通过nextIndex方法来寻找下一个索引位置,如果找到某个Entry的key和传入的key相同,则用传入的value替换掉该Entry的value。如果遍历到某个Entry的key为空,则调用replaceStaleEntry方法;如果通过nextIndex寻找到一个空位置(代表没有找到key相同的),则将元素放在该位置上,调用cleanSomeSlots方法清理key为null的Entry,并判断是否需要扩容,如果需要则调用rehash方法进行扩容。set函数用来设置当前线程的该ThreadLocal的值,设置当前线程的ThreadLocal的值为value。
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
get()方法
该函数主要用来获取与当前线程关联的ThreadLocal的值,如果当前线程没有该ThreadLocal的值,则调用initialValue函数获取初始值且返回默认值,如果有重载则返回重载的值。
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
/**
* Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead
* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.
*
* @return the initial value
*/
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
remove()方法
该函数用来将当前线程的ThreadLocal绑定的值删除,最好手动调用该函数,防止内存泄露。
/**
* Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local
* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently
* {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be
* reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method,
* unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread
* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the
* {@code initialValue} method in the current thread.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
ThreadLocalMap 内部类
内容部类之Entry类(存储结构)
ThreadLocalMap内部类自定义了一个哈希映射(类似map哈希链表形式的存储)Entry,Entry就是ThreadLocal的内部类ThreadLocalMap用来存储的静态内部类,用于维护线程本地变量值。Entry的key为ThreadLocal,value为ThreadLocal对应的值。每个线程都有一个ThreadLocalMap类型的threadLocals变量。且Entry的key是一个弱引用。
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
内容部类getEntry方法
该方法主要用来从ThreadLocalMap类中的Entry数组变量中获取相应线程值。
根据hash code计算出索引位置
如果该索引位置Entry的key和传入的key相等,则为目标Entry,直接返回
否则,e不是目标Entry,调用getEntryAfterMiss方法(见下文代码块6详解)继续遍历。
/**
* Get the entry associated with key. This method
* itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing
* key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is
* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part
* by making this method readily inlinable.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
//计算出索引位置
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
//如果该索引位置Entry的key和传入的key相等,即为目标Entry,返回相应值
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
//否则,调用getEntryAfterMiss方法继续遍历。
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
内容部类getEntryAfterMiss方法
该方法主要变量Entry数组中对应线程的值,如果遇到key为null的元素,调用expungeStaleEntry方法(见下文expungeStaleEntry方法详解)进行清除;否则,遍历到Entry为null时,结束遍历,返回null。
/**
* Version of getEntry method for use when key is not found in
* its direct hash slot.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @param i the table index for key's hash code
* @param e the entry at table[i]
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
//从元素e开始向后遍历,如果找到目标Entry直接返回,相反全部遍历完没有找到则返回null。
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//遍历到Entry为null时,结束遍历,返回null
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
//如果遇到key为null的元素,调用expungeStaleEntry方法进行清除
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
内容部类expungeStaleEntry方法
该方法主要是用于清除key为null的Entry。并将不为空的元素放到合适的位置,最后遍历到Entry为空的元素时,跳出循环返回当前索引位置。
/**
* Expunge a stale entry by rehashing any possibly colliding entries
* lying between staleSlot and the next null slot. This also expunges
* any other stale entries encountered before the trailing null. See
* Knuth, Section 6.4
*
* @param staleSlot index of slot known to have null key
* @return the index of the next null slot after staleSlot
* (all between staleSlot and this slot will have been checked
* for expunging).
*/
//从staleSlot开始遍历
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);(e = tab[i]) != null;i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
//重新计算该Entry的索引位置,用于判断是否重新安排该Entry的位置
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
//如果索引位置不为当前索引位置,则将当前位置i的Entry清空,且重新布置Entry位置
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
内容部类rehash方法
在ThreadLocalMap类中,我们发现一开给Entry[] table数组开辟的空间INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16,如果在存储的过程中发现size超过阈值的3/4,则通过该方法进行拓展。
/**
* Re-pack and/or re-size the table. First scan the entire
* table removing stale entries. If this doesn't sufficiently
* shrink the size of the table, double the table size.
*/
private void rehash() {
expungeStaleEntries();
// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}
ThreadLocal内在原理
ThreadLocal的原理还是很简单的,就是自定义了一个哈希映射存储,然后用线程作为哈希存储的Key,需要存储的值为哈希存存储的Value,如下图:
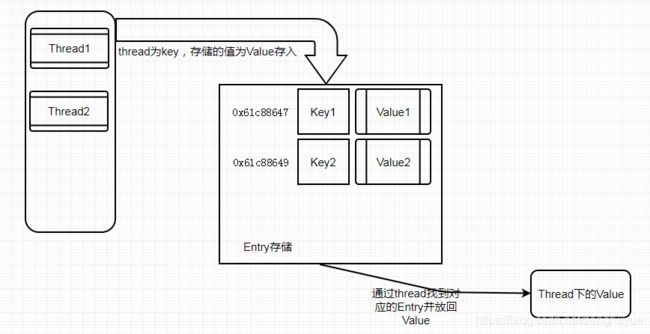
ThreadLocal需要注意的
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap.Entry中的key是弱引用的,但是value是基于强引用的,当某个ThreadLocal对象不存在强引用时,且GC后,key会被回收,但是value还存强引用时,因此就会出现内存的泄露情况。目前最好的解决方式就是在使用完ThreadLocal及时调remove方法。