C#调用C++ DLL
一、创建C++ myDLL工程
1.myDLL.h头文件定义
#ifndef __MYDLL_H__
#define __MYDLL_H__
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif
#define ONEDLL_API __declspec(dllexport)
//Demo_01
ONEDLL_API int add(int a, int b);
//Demo_02
ONEDLL_API int __stdcall addA(int* a, int* b);
//Demo_03
ONEDLL_API void createInstance(void** ppInstance, int n);
ONEDLL_API void instanceAddN(void* pInstance, int n);
ONEDLL_API void deleteInstance(void** pInstance);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif知识点1:
为了避免同一个头文件被包含(include)多次,C/C++中有两种宏实现方式:一种是#ifndef方式;另一种是#pragma once方式。
//方式一:
#ifndef __MYDLL_H__
#define __MYDLL_H__
... ... // 声明、定义语句
#endif
//方式二:
#pragma once
... ... // 声明、定义语句#ifndef由C/C++语言标准支持,依赖于宏名字不能冲突,这不光可以保证同一个文件不会被包含多次,也能保证内容完全相同的两个文件不会被不小心同时包含。当然,缺点就是如果不同头文件的宏名不小心“撞车”,可能就会导致头文件明明存在,编译器却硬说找不到声明的状况
#pragma once则由编译器提供保证:同一个文件不会被包含多次。注意这里所说的“同一个文件”是指物理上的一个文件,而不是指内容相同的两个文件。带来的好处是,你不必再费劲想个宏名了,当然也就不会出现宏名碰撞引发的奇怪问题。对应的缺点就是如果某个头文件有多份拷贝,本方法不能保证他们不被重复包含。当然,相比宏名碰撞引发的“找不到声明”的问题,重复包含更容易被发现并修正。
参考资料:http://www.cppblog.com/szhoftuncun/archive/2012/03/13/35356.html
知识点2:
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif
... ... // 声明、定义语句
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif__cplusplus是cpp中的自定义宏,如果定义了这个宏,则表示这是一段cpp的代码;
extern "C"的主要作用就是为了能够正确实现C++代码调用其他C语言代码,加上extern "C"后, 会指示编译器这部分代码按C语言的进行编译,而不是C++的。
参考资料:http://blog.csdn.net/xupan_jsj/article/details/9028759
知识点3:
C 和C++ 对应不同的调用约定,产生的修饰符也各不相同,如下:
| 调用约定 | extern "C" 或 .c 文件 | .cpp、.cxx 或 /TP |
| C 命名约定 (__cdecl) | _test | ?test@@ZAXXZ |
| Fastcall 命名约定 (__fastcall) | @test@0 | ?test@@YIXXZ |
| 标准调用命名约定 (__stdcall) | _test@0 | ?test@@YGXXZ |
__cdecl 是C Declaration的缩写(declaration,声明),表示C语言默认的函数调用方法。
__stdcall是StandardCall的缩写,是C++的标准调用方式,经常在Windows API函数中使用。Windows .net平台默认使用__stdcall,C#默认方式亦如此。
//Demo_01
ONEDLL_API int add(int a, int b);
//Demo_02
ONEDLL_API int __stdcall addA(int* a, int* b);
//Demo_03
ONEDLL_API void createInstance(void** ppInstance, int n);
ONEDLL_API void instanceAddN(void* pInstance, int n);Demo_01是使用 __cdecl
Demo_02是使用 __stdcall
Demo_03也是使用 __cdecl
知识点4:
__declspec(dllexport) 声明DLL导出函数
参考资料:https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/a90k134d.aspx
2.myDLL.cpp文件定义
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "myDLL.h"
#include
class MyClass
{
public:
MyClass(int n):num(n){};
int num;
};
ONEDLL_API int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
ONEDLL_API int __stdcall addA(int* a, int* b)
{
(*a) ++;
(*b) ++;
int sum = *a + *b;
return sum;
}
ONEDLL_API void createInstance(void** ppInstance, int n)
{
*ppInstance = new MyClass(n);
MyClass* pInstance = (MyClass* )(*ppInstance);
printf("pInstance->num=%d\n", pInstance->num);
}
ONEDLL_API void instanceAddN(void* pInstance, int n)
{
((MyClass* )pInstance)->num += n;
printf("pInstance->num=%d\n", ((MyClass* )pInstance)->num);
}
ONEDLL_API void deleteInstance(void** pInstance)
{
delete *pInstance;
*pInstance = NULL;
} 二、创建C# invokeDLL工程
1.MyDLL.cs文件定义
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace invokeDLL
{
unsafe class MyDLL
{
[DllImport(@"E:/VS2012/myDLL/Debug/myDLL.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern int add(int a, int b);
[DllImport(@"E:/VS2012/myDLL/Debug/myDLL.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.StdCall)]
public static extern int addA(ref int a, ref int b);
[DllImport(@"E:/VS2012/myDLL/Debug/myDLL.dll", EntryPoint = "addA")]
public static extern int addAA(ref int a, ref int b);
[DllImport(@"E:/VS2012/myDLL/Debug/myDLL.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void createInstance(IntPtr* pInstance, int n);
[DllImport(@"E:/VS2012/myDLL/Debug/myDLL.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void instanceAddN(IntPtr pInstance, int n);
[DllImport(@"E:/VS2012/myDLL/Debug/myDLL.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void deleteInstance(IntPtr* pInstance);
}
}
知识点1:
unsafe 关键字表示不安全上下文,该上下文是任何涉及指针的操作所必需的。unsafe可以用来修饰类、类的成员函数、类的全局变量,但不能用来修饰类成员函数内的局部变量。
unsafe在C#程序中的使用场合:
1)实时应用,采用指针来提高性能;
2)引用非.net DLL提供的如C++编写的外部函数,需要指针来传递该函数;
3)调试,用以检测程序在运行过程中的内存使用状况。
知识点2:
C#使用DLLImport调用DLL基本格式:
[DllImport("文件路径")]DLLImport会按照如下顺序查找DLL文件:程序当前目录 -> System32目录 -> 环境变量Path所设置路径
也可指定DLL文件绝对路径,如:
[DllImport(@"E:/myDLL/myDLL.dll")]DLLImport其他属性:
| 字段 |
说明 |
| BestFitMapping |
启用或禁用最佳匹配映射。 |
| CallingConvention |
指定用于传递方法参数的调用约定。 默认值为 WinAPI,该值对应于基于 32 位 Intel 的平台的 __stdcall。 |
| CharSet |
控制名称重整以及将字符串参数封送到函数中的方式。 默认值为 CharSet.Ansi。 |
| EntryPoint |
指定要调用的 DLL 入口点。 |
| ExactSpelling |
控制是否应修改入口点以对应于字符集。 对于不同的编程语言,默认值将有所不同。 |
| PreserveSig |
控制托管方法签名是否应转换成返回 HRESULT 并且返回值有一个附加的 [out, retval] 参数的非托管签名。 默认值为 true(不应转换签名)。 |
| SetLastError |
允许调用方使用 Marshal.GetLastWin32Error API 函数来确定执行该方法时是否发生了错误。 在 Visual Basic 中,默认值为 true;在 C# 和 C++ 中,默认值为 false。 |
| ThrowOnUnmappableChar |
控件引发的异常,将无法映射的 Unicode 字符转换成一个 ANSI"?"字符。 |
EntryPoint字段按名称或序号指定 DLL 函数。如果函数在方法定义中的名称与入口点在 DLL 的名称相同,则不必用 EntryPoint 字段来显式地标识函数。
CallingConvention字段指定调用DLL中函数的方式,必须指定与DLL中定义相同的方式。
参考资料:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/w4byd5y4.aspx
http://blog.csdn.net/ycl295644/article/details/48239759
知识点3:
C#调用DLL文件时参数对应表
| Wtypes.h 中的非托管类型 | 非托管 C 语言类型 | 托管类名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HANDLE | void* | System.IntPtr | 32 位 |
| BYTE | unsigned char | System.Byte | 8 位 |
| SHORT | short | System.Int16 | 16 位 |
| WORD | unsigned short | System.UInt16 | 16 位 |
| INT | int | System.Int32 | 32 位 |
| UINT | unsigned int | System.UInt32 | 32 位 |
| LONG | long | System.Int32 | 32 位 |
| BOOL | long | System.Int32 | 32 位 |
| DWORD | unsigned long | System.UInt32 | 32 位 |
| ULONG | unsigned long | System.UInt32 | 32 位 |
| CHAR | char | System.Char | 用 ANSI 修饰。 |
| LPSTR | char* | System.String 或 System.StringBuilder | 用 ANSI 修饰。 |
| LPCSTR | Const char* | System.String 或 System.StringBuilder | 用 ANSI 修饰。 |
| LPWSTR | wchar_t* | System.String 或 System.StringBuilder | 用 Unicode 修饰。 |
| LPCWSTR | Const wchar_t* | System.String 或 System.StringBuilder | 用 Unicode 修饰。 |
| FLOAT | Float | System.Single | 32 位 |
| DOUBLE | Double | System.Double | 64 位 |
参考资料:
https://www.cnblogs.com/toto0473/archive/2013/01/14/2860281.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/rwzhou/p/5961095.html
http://blog.csdn.net/superhackerzhang/article/details/7648360
比较常用的:
int * ——ref int
int & ——ref int
void * ——IntPtr
void ** ——IntPtr *
2.Progams.cs文件定义
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace invokeDLL
{
class Program
{
unsafe static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("====== add ======");
int sum = MyDLL.add(1, 2);
Console.WriteLine("sum={0}", sum);
Console.WriteLine("====== addA ======");
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
sum = MyDLL.addA(ref a, ref b);
Console.WriteLine("a={0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("b={0}", b);
Console.WriteLine("sum={0}", sum);
Console.WriteLine("====== addAA ======");
sum = MyDLL.addA(ref a, ref b);
Console.WriteLine("a={0}", a);
Console.WriteLine("b={0}", b);
Console.WriteLine("sum={0}", sum);
Console.WriteLine("====== createInstance ======");
IntPtr pInstance = IntPtr.Zero;
MyDLL.createInstance(&pInstance, 1);
Console.WriteLine("====== instanceAddN ======");
MyDLL.instanceAddN(pInstance, 1);
Console.WriteLine("====== deleteInstance ======");
MyDLL.deleteInstance(&pInstance);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Demo_01,Demo_02不再做详细解释,现主要分析下Demo_3中的createInstance、instanceAddN方法。
createInstance过程
IntPtr pInstance = IntPtr.Zero;
C#新建变量pInstance
pInstance变量的值为0,
pInstance变量在内存中的地址为0x05F6E72C,
即内存中地址为0x05F6E72C的区域存储的内容为0
MyDLL.createInstance(&pInstance, 1);
↓↓
调用
↓↓
ONEDLL_API void createInstance(void** ppInstance, int n)
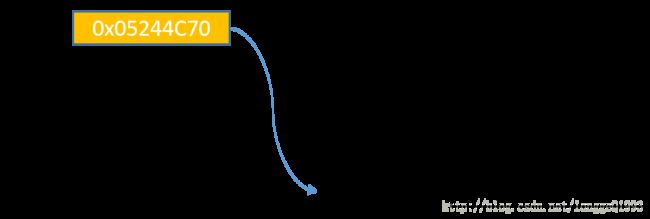
主调函数(即C#)会将pInstance的地址作为参数值传递给被调函数(即DLL),被调函数的形参(ppInstance)作为局部变量在栈中开辟了临时内存空间,存放的是由主调函数放进来的实参的值即0x05F6E72C。*ppInstance = new MyClass(n);通过C++ 构造函数,在堆内存中新建MyClass对象,该对象在内存中的地址为0x05244C70,将该值(0x05244C70)存储至于 地址为0x05F6E72C的内存区域。
DLL中被调函数执行完毕,自动释放为存储局部变量申请的栈空间,返回C#中主调函数,此时变量pInstance的值已从调用DLL前的0,变为0x05244C70。
instanceAddN过程
MyDLL.instanceAddN(pInstance, 1);
↓↓
调用
↓↓
ONEDLL_API void instanceAddN(void* pInstance, int n)
主调函数(即C#)会将pInstance的值(0x05244C70)作为参数值传递给被调函数(即DLL),被调函数的形参作为局部变量在栈中开辟了内存空间,存放的是由主调函数放进来的实参的值即0x05244C70 。
总结
1. 由于C#端保存着对MyClass对象的一份引用,故C#可调用DLL对MyClass对象进行多次修改。 使用完毕后,务必释放对象,指针置为空。参考资料:https://www.cnblogs.com/dragon2012/p/3847966.html
2. 该例子适用于C#端不依赖于DLL中对象数据,DLL端自行管理自身数据的场景,减小了C#与DLL之间的耦合程度。



