运维自动化之ANSIBLE
成功不易,加倍努力!
-
- 运维自动化之ANSIBLE
-
- 本章内容
- 1 自动化运维应用场景
-
- 1.1 云计算运维工程师核心职能
- 1.2 运维职业发展路线
- 1.3 企业实际应用场景分析
-
- 1.3.1 Dev开发环境
- 1.3.2 测试环境
- 1.3.3 预发布环境
- 1.3.4 发布环境
- 1.3.5 生产环境
- 1.3.6 灰度环境 属于生产环境的一部分
- 1.4 程序发布
- 1.5 自动化运维应用场景
- 1.6 常用自动化运维工具
- 2 Ansible 介绍和架构
-
- 2.1 Ansible发展史
- 2.2 Ansible 特性
- 2.3 Ansible 架构
-
- 2.3.1 Ansible 组成
- 2.3.2 Ansible 命令执行来源
- 2.3.3 注意事项
- 3 Ansible 安装和入门
-
- 3.1 Ansible安装
-
- 3.1.1 EPEL源的rpm包安装:
- 3.1.2 编译安装
- 3.1.3 Git方式
- 3.1.4 pip 安装
- 3.1.5 确认安装
- 3.2 Ansible 相关文件
-
- 3.2.1 配置文件
- 3.2.2 ansible主配置文件
- 3.2.3 inventory 主机清单
- 3.3 Ansible相关工具
-
- 3.3.1 ansible-doc
- 3.3.2 ansible
- 3.3.3 ansible-playbook
- 3.3.4 ansible-vault
- 3.3.5 ansible-console
- 3.3.6 ansible-galaxy
- 3.4 Ansible常用模块
-
- 3.4.1 Command 模块
- 3.4.2 Shell模块
- 3.4.3 Script模块
- 3.4.4 Copy模块
- 3.4.5 Fetch模块
- 3.4.6 File模块
- 3.4.7 unarchive模块
- 3.4.8 Archive模块
- 3.4.9 Hostname模块
- 3.4.10 Cron模块
- 3.4.11 Yum模块
- 3.4.12 Service模块
- 3.4.13 User模块
- 3.4.14 Group模块
- 3.4.15 Lineinfile模块
- 3.4.16 Replace模块
- 3.4.17 Setup模块
- 4 Playbook
-
- 4.1 playbook介绍
- 4.2 YAML 语言
-
- 4.2.1 YAMl 语言介绍
- 4.2.2 YAML 语言特性
- 4.2.3 YAML语法简介
- 4.2.4 三种常见的数据格式
- 4.3 Playbook 核心组件
-
- 4.3.1 hosts 组件
- 4.3.2 remote_user 组件
- 4.3.3 task列表和action组件
- 4.3.4 其它组件
- 4.3.5 ShellScripts VS Playbook 案例
- 4.4 playbook 命令
- 4.5 Playbook 初步
-
- 4.5.1 利用 playbook 创建 mysql 用户
- 4.5.2 利用 playbook 安装 nginx
- 4.5.3 利用 playbook 安装和卸载 httpd
- 4.5.4 利用 playbook 安装 mysql
- 4.6 Playbook中使用handlers和notify
- 4.7 Playbook中使用tags组件
- 4.8 Playbook中使用变量
-
- 4.8.1 使用 setup 模块中变量
- 4.8.2 在playbook 命令行中定义变量
- 4.8.3 在playbook文件中定义变量
- 4.8.4 使用变量文件
- 4.8.5 主机清单文件中定义变量
- 4.9 template 模板
-
- 4.9.1 jinja2语言
- 4.9.2 template
- 4.9.3 template中使用流程控制 for 和 if
- 4.10 playbook使用 when
- 4.11 playbook 使用迭代 with_items
- 4.12 管理节点过多导致的超时问题解决方法
- 5 roles角色
-
- 5.1 Ansible Roles目录编排
- 5.2 创建 role
- 5.3 playbook调用角色
- 5.4 roles 中 tags 使用
- 5.5 实战案例
-
- 5.5.1 案例1:实现 httpd 角色
- 5.5.2 案例2:实现 nginx 角色
- 5.5.3 案例3:实现 memcached 角色
- 5.5.4 案例4:实现 mysql 5.6 的角色
- 5.5.5 案例5 :实现多角色的选择
- 6 ansible 推荐学习资料
运维自动化之ANSIBLE
本章内容
- 运维自动化发展历程及技术应用
- Ansible命令使用
- Ansible常用模块详解
- YAML语法简介
- Ansible playbook基础
- Playbook变量、tags、handlers使用
- Playbook模板 templates
- Playbook条件判断 when
- Playbook字典 with_items
- Ansible Roles
1 自动化运维应用场景
1.1 云计算运维工程师核心职能
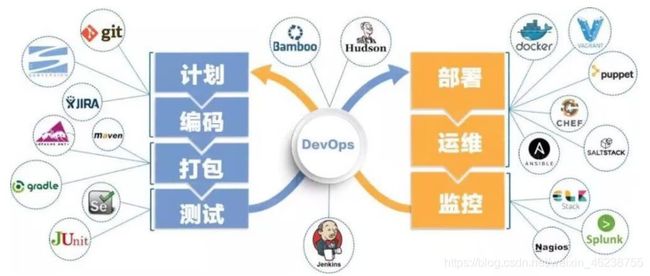
相关工具
- 代码管理(SCM):GitHub、GitLab、BitBucket、SubVersion
- 构建工具:maven、Ant、Gradle
- 自动部署:Capistrano、CodeDeploy
- 持续集成(CI):Jenkins、Travis
- 配置管理:Ansible、SaltStack、Chef、Puppet
- 容器:Docker、Podman、LXC、第三方厂商如AWS
- 编排:Kubernetes、Core、Apache Mesos
- 服务注册与发现:Zookeeper、etcd、Consul
- 脚本语言:python、ruby、shell
- 日志管理:ELK、Logentries
- 系统监控:Prometheus、Zabbix、Datadog、Graphite、Ganglia、Nagios
- 性能监控:AppDynamics、New Relic、Splunk
- 压力测试:JMeter、Blaze Meter、loader.io
- 应用服务器:Tomcat、JBoss、IIS
- Web服务器:Apache、Nginx
- 数据库:MySQL、Oracle、PostgreSQL等关系型数据库;mongoDB、redis等NoSQL数据库
- 项目管理(PM):Jira、Asana、Taiga、Trello、Basecamp、Pivotal Tracker
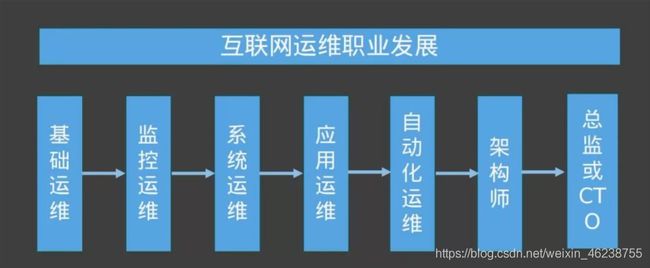
1.2 运维职业发展路线
运维的未来是什么?
一切皆自动化
“运维的未来是,让研发人员能够借助工具、自动化和流程,并且让他们能够在运维干预极少的情况下部署和运营服务,从而实现自助服务。每个角色都应该努力使工作实现自动化。”——《运维的未来》
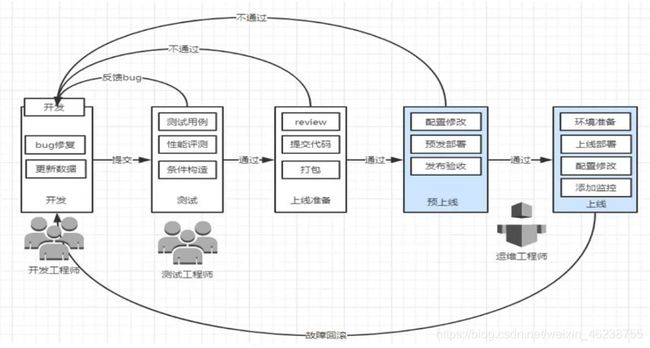
1.3 企业实际应用场景分析
1.3.1 Dev开发环境
使用者:程序员
功能:程序员个人的办公电脑或项目的开发测试环境,部署开发软件,测试个人或项目整体的BUG的环境
管理者:程序员
1.3.2 测试环境
使用者:QA测试工程师
功能:测试经过Dev环境测试通过的软件的功能和性能,判断是否达到项目的预期目标,生成测试报告
管理者:运维
说明:测试环境往往有多套,测试环境满足测试功能即可,不宜过多
1、测试人员希望测试环境有多套,公司的产品多产品线并发,即多个版本,意味着多个版本同步测试
2、通常测试环境有多少套和产品线数量保持一样
1.3.3 预发布环境
使用者:运维
功能:使用和生产环境一样的数据库,缓存服务等配置,测试是否正常
1.3.4 发布环境
包括代码发布机,有些公司为堡垒机(安全屏障)
使用者:运维
功能:发布代码至生产环境
管理者:运维(有经验)
发布机:往往需要有2台(主备)
1.3.5 生产环境
使用者:运维,少数情况开放权限给核心开发人员,极少数公司将权限完全开放给开发人员并其维护
功能:对用户提供公司产品的服务
管理者:只能是运维
生产环境服务器数量:一般比较多,且应用非常重要。往往需要自动工具协助部署配置应用
1.3.6 灰度环境 属于生产环境的一部分
使用者:运维
功能:在全量发布代码前将代码的功能面向少量精准用户发布的环境,可基于主机或用户执行灰度发布
案例:共100台生产服务器,先发布其中的10台服务器,这10台服务器就是灰度服务器
管理者:运维
灰度环境:往往该版本功能变更较大,为保险起见特意先让一部分用户优化体验该功能,待这部分用户使用没有重大问题的时候,再全量发布至所有服务器
1.4 程序发布
程序发布要求:
不能导致系统故障或造成系统完全不可用
不能影响用户体验
预发布验证:
新版本的代码先发布到服务器(跟线上环境配置完全相同,只是未接入到调度器)
灰度发布:
基于主机,用户,业务
发布路径:
/webapp/tuangou
/webapp/tuangou-1.1
/webapp/tuangou-1.2
发布过程:
- 在调度器上下线一批主机(标记为maintenance 状态)
- 关闭服务
- 部署新版本的应用程序
- 启动服务
- 在调度器上启用这一批服务器
自动化灰度发布:
- 脚本
- 发布平台
1.5 自动化运维应用场景
- 文件传输
- 应用部署
- 配置管理
- 任务流编排
1.6 常用自动化运维工具
- Ansible:python,Agentless,中小型应用环境
- Saltstack:python,一般需部署agent,执行效率更高
- Puppet:ruby, 功能强大,配置复杂,重型,适合大型环境
- Fabric:python,agentless
- Chef:ruby,国内应用少
- Cfengine
- func
| 自动化运维工 具 | Watch(关 注) | Star(点 赞) | Fork(复 制) | Contributors(贡献 者) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ansible | 1387 | 17716 | 5356 | 1428 |
| Saltstack | 530 | 6678 | 3002 | 1520 |
| Puppet | 463 | 4044 | 1678 | 425 |
| Chef | 383 | 4333 | 1806 | 464 |
| Fabric | 379 | 7334 | 1235 | 116 |
2 Ansible 介绍和架构
公司计划在年底做一次大型市场促销活动,全面冲刺下交易额,为明年的上市做准备。公司要求各业务组对年底大促做准备,运维部要求所有业务容量进行三倍的扩容,并搭建出多套环境可以共开发和测试人员做测试,运维老大为了在年底有所表现,要求运维部门同学尽快实现,当你接到这个任务时,有没有更快的解决方案?
2.1 Ansible发展史
作者:Michael DeHaan( Cobbler 与 Func 作者)
ansible 的名称来自科幻小说《安德的游戏》中跨越时空的即时通信工具,使用它可以在相距数光年的距离,远程实时控制前线的舰队战斗。
2012-03-09,发布0.0.1版,2015-10-17,Red Hat宣布1.5亿美元收购
官网:https://www.ansible.com/
官方文档:https://docs.ansible.com/
2.2 Ansible 特性
- 模块化:调用特定的模块完成特定任务,支持自定义模块,可使用任何编程语言写模块
- Paramiko(python对ssh的实现),PyYAML,Jinja2(模板语言)三个关键模块
- 基于Python语言实现
- 部署简单,基于python和SSH(默认已安装),agentless,无需代理不依赖PKI(无需ssl)
- 安全,基于OpenSSH
- 幂等性:一个任务执行1遍和执行n遍效果一样,不因重复执行带来意外情况
- 支持playbook编排任务,YAML格式,编排任务,支持丰富的数据结构
- 较强大的多层解决方案 role
2.3 Ansible 架构
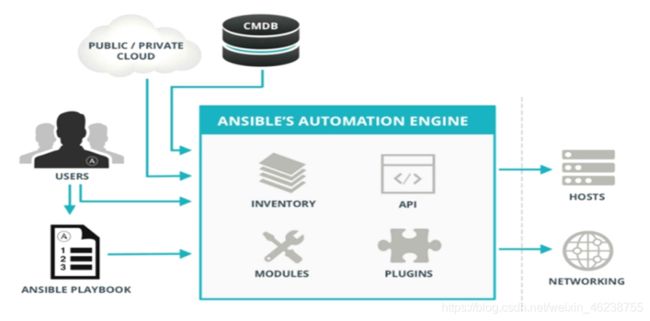
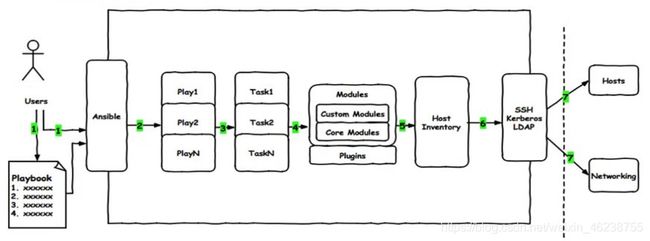
2.3.1 Ansible 组成
组合INVENTORY、API、MODULES、PLUGINS的绿框,为ansible命令工具,其为核心执行工具
- INVENTORY:Ansible管理主机的清单/etc/anaible/hosts
- MODULES:Ansible执行命令的功能模块,多数为内置核心模块,也可自定义
- PLUGINS:模块功能的补充,如连接类型插件、循环插件、变量插件、过滤插件等,该功能不常用
- API:供第三方程序调用的应用程序编程接口
2.3.2 Ansible 命令执行来源
- USER 普通用户,即SYSTEM ADMINISTRATOR
- PLAYBOOKS:任务剧本(任务集),编排定义Ansible任务集的配置文件,由Ansible顺序依次执行,通常是JSON格式的YML文件
- CMDB(配置管理数据库) API 调用
- PUBLIC/PRIVATE CLOUD API调用
- USER-> Ansible Playbook -> Ansibile
2.3.3 注意事项
- 执行ansible的主机一般称为主控端,中控,master或堡垒机
- 主控端Python版本需要2.6或以上
- 被控端Python版本小于2.4,需要安装python-simplejson
- 被控端如开启SELinux需要安装libselinux-python
- windows 不能做为主控端
3 Ansible 安装和入门
3.1 Ansible安装
ansible的安装方法有多种
3.1.1 EPEL源的rpm包安装:
[root@ansible ~]#yum install ansible
3.1.2 编译安装
yum -y install python-jinja2 PyYAML python-paramiko python-babel python-crypto
tar xf ansible-1.5.4.tar.gz
cd ansible-1.5.4
python setup.py build
python setup.py install
mkdir /etc/ansible
cp -r examples/* /etc/ansible
3.1.3 Git方式
git clone git://github.com/ansible/ansible.git --recursive
cd ./ansible
source ./hacking/env-setup
3.1.4 pip 安装
pip 是安装Python包的管理器,类似 yum
yum install python-pip python-devel
yum install gcc glibc-devel zibl-devel rpm-bulid openssl-devel
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install ansible --upgrade
3.1.5 确认安装
[root@ansible ~]#ansible --version
ansible 2.9.5
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = ['/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 3.6.8 (default, Nov 21 2019, 19:31:34) [GCC 8.3.1 20190507 (Red Hat 8.3.1-4)]
3.2 Ansible 相关文件
3.2.1 配置文件
- /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg 主配置文件,配置ansible工作特性
- /etc/ansible/hosts 主机清单
- /etc/ansible/roles/ 存放角色的目录
3.2.2 ansible主配置文件
Ansible 的配置文件 /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg ,其中大部分的配置内容无需进行修改
[defaults]
#inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts # 主机列表配置文件
#library = /usr/share/my_modules/ # 库文件存放目录
#remote_tmp = $HOME/.ansible/tmp #临时py命令文件存放在远程主机目录
#local_tmp = $HOME/.ansible/tmp # 本机的临时命令执行目录
#forks = 5 # 默认并发数
#sudo_user = root # 默认sudo 用户
#ask_sudo_pass = True #每次执行ansible命令是否询问ssh密码
#ask_pass = True
#remote_port = 22
#host_key_checking = False # 检查对应服务器的host_key,建议取消注释
#log_path=/var/log/ansible.log #日志文件,建议启用
#module_name = command #默认模块,可以修改为shell模块
3.2.3 inventory 主机清单
ansible的主要功用在于批量主机操作,为了便捷地使用其中的部分主机,可以在inventory file中将其分组命名
默认的inventory file为 /etc/ansible/hosts
inventory file可以有多个,且也可以通过Dynamic Inventory来动态生成
主机清单文件格式
inventory文件遵循INI文件风格,中括号中的字符为组名。可以将同一个主机同时归并到多个不同的组中
此外,当如若目标主机使用了非默认的SSH端口,还可以在主机名称之后使用冒号加端口号来标明
如果主机名称遵循相似的命名模式,还可以使用列表的方式标识各主机
范例:
ntp.magedu.com
[webservers]
www1.magedu.com:2222
www2.magedu.com
[dbservers]
db1.magedu.com
db2.magedu.com
db3.magedu.com
[websrvs]
www[1:100].example.com
[dbsrvs]
db-[a:f].example.com
[appsrvs]
10.0.0.[1:100]
#范例
[websrvs]
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.7
[appsrvs]
10.0.0.6
10.0.0.100
[dbsrvs]
10.0.0.8
3.3 Ansible相关工具
- /usr/bin/ansible 主程序,临时命令执行工具
- /usr/bin/ansible-doc 查看配置文档,模块功能查看工具,相当于man
- /usr/bin/ansible-playbook 定制自动化任务,编排剧本工具,相当于脚本
- /usr/bin/ansible-pull 远程执行命令的工具
- /usr/bin/ansible-vault 文件加密工具
- /usr/bin/ansible-console 基于Console界面与用户交互的执行工具
- /usr/bin/ansible-galaxy 下载/上传优秀代码或Roles模块的官网平台
利用ansible实现管理的主要方式:
- Ad-Hoc 即利用ansible命令,主要用于临时命令使用场景
- Ansible-playbook 主要用于长期规划好的,大型项目的场景,需要有前期的规划过程
3.3.1 ansible-doc
此工具用来显示模块帮助
格式
ansible-doc [options] [module...]
-l, --list #列出可用模块
-s, --snippet #显示指定模块的playbook片段
范例:
#列出所有模块
ansible-doc -l
#查看指定模块帮助用法
ansible-doc ping
#查看指定模块帮助用法
ansible-doc -s ping
范例:
[root@ansible ~]#date
Wed Jun 17 16:08:09 CST 2020
[root@ansible ~]#ansible --version
ansible 2.9.9
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = ['/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 3.6.8 (default, May 21 2019, 23:51:36) [GCC 8.2.1 20180905 (Red Hat 8.2.1-3)]
[root@ansible ~]#ansible-doc -l|wc -l
3387
[root@ansible ~]#ansible-doc -s ping
- name: Try to connect to host, verify a usable python and return `pong' on success
ping:
data: # Data to return for the `ping' return value. If this parameter is set to `crash', the module will cause an exception.
3.3.2 ansible
此工具通过ssh协议,实现对远程主机的配置管理、应用部署、任务执行等功能
建议:使用此工具前,先配置ansible主控端能基于密钥认证的方式联系各个被管理节点
范例:利用sshpass批量实现基于key验证脚本1
[root@centos8 ~]#vim /etc/ssh/ssh_config
#修改下面一行
StrictHostKeyChecking no
[root@centos8 ~]#cat hosts.list
10.0.0.18
10.0.0.28
[root@centos8 ~]#vim push_ssh_key.sh
#!/bin/bash
rpm -q sshpass &> /dev/null || yum -y install sshpass
[ -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa ] || ssh-keygen -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa -P ''
export SSHPASS=magedu
while read IP;do
sshpass -e ssh-copy-id -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no $IP
done < hosts.list
范例: 实现基于key验证的脚本2
IPLIST="
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.18
10.0.0.7
10.0.0.6
10.0.0.200"
rpm -q sshpass &> /dev/null || yum -y install sshpass
[ -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa ] || ssh-keygen -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa -P ''
export SSHPASS=centos
for IP in $IPLIST;do
sshpass -e ssh-copy-id -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no $IP
done
格式:
ansible <host-pattern> [-m module_name] [-a args]
主机清单列表 模块 参数
选项说明:
--version #显示版本
-m module #指定模块,默认为command
-v #详细过程 –vv -vvv更详细
--list-hosts #显示主机列表,可简写 --list
-k, --ask-pass #提示输入ssh连接密码,默认Key验证
-C, --check #检查,并不执行
-T, --timeout=TIMEOUT #执行命令的超时时间,默认10s
-u, --user=REMOTE_USER #执行远程执行的用户
-b, --become #代替旧版的sudo 切换
--become-user=USERNAME #指定sudo的runas用户,默认为root
-K, --ask-become-pass #提示输入sudo时的口令
ansible的Host-pattern
用于匹配被控制的主机的列表
All :表示所有Inventory中的所有主机
范例
ansible all –m ping
[root@ansible ~]#ansible all --list
hosts (5):
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.7
10.0.0.6
10.0.0.100
10.0.0.18
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs --list
hosts (2):
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.7
*:通配符
ansible "*” -m ping
ansible 192.168.1.* -m ping
ansible "srvs” -m ping
或关系
ansible "websrvs:appsrvs" -m ping
ansible "192.168.1.10:192.168.1.20" -m ping
逻辑与
#在websrvs组并且在dbsrvs组中的主机
ansible "websrvs:&dbsrvs" –m ping
逻辑非
#在websrvs组,但不在dbsrvs组中的主机
#注意:此处为单引号
ansible 'websrvs:!dbsrvs' –m ping
综合逻辑
ansible 'websrvs:dbsrvs:&appsrvs:!ftpsrvs' –m ping
正则表达式
ansible "websrvs:dbsrvs" –m ping
ansible "~(web|db).*\.magedu\.com" –m ping
范例:
[root@kube-master1 ~]#ansible 'kube*:etcd:!10.0.0.101' -a reboot
ansible命令执行过程
- 加载自己的配置文件 默认/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
- 加载自己对应的模块文件,如:command
- 通过ansible将模块或命令生成对应的临时py文件,并将该文件传输至远程服务器的对应执行用户
$HOME/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-数字/XXX.PY文件 - 给文件+x执行
- 执行并返回结果
- 删除临时py文件,退出
ansible 的执行状态:
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -A 14 '\[colors\]' /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
[colors]
#highlight = white
#verbose = blue
#warn = bright purple
#error = red
#debug = dark gray
#deprecate = purple
#skip = cyan
#unreachable = red
#ok = green
#changed = yellow
#diff_add = green
#diff_remove = red
#diff_lines = cyan
- 绿色:执行成功并且不需要做改变的操作
- 黄色:执行成功并且对目标主机做变更
- 红色:执行失败
ansible使用范例
#以wang用户执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang -k
#以wang sudo至root执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang -k -b
#以wang sudo至mage用户执行ping存活检测
ansible all -m ping -u wang -k -b --become-user=mage
#以wang sudo至root用户执行ls
ansible all -m command -u wang -a 'ls /root' -b --become-user=root -k -K
3.3.3 ansible-playbook
此工具用于执行编写好的 playbook 任务
范例:
ansible-playbook hello.yml
cat hello.yml
---
#hello world yml file
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: hello world
command: /usr/bin/wall hello world
3.3.4 ansible-vault
此工具可以用于加密解密yml文件
格式:
ansible-vault [create|decrypt|edit|encrypt|rekey|view]
范例
ansible-vault encrypt hello.yml #加密
ansible-vault decrypt hello.yml #解密
ansible-vault view hello.yml #查看
ansible-vault edit hello.yml #编辑加密文件
ansible-vault rekey hello.yml #修改口令
ansible-vault create new.yml #创建新文件
3.3.5 ansible-console
此工具可交互执行命令,支持tab,ansible 2.0+新增
提示符格式:
执行用户@当前操作的主机组 (当前组的主机数量)[f:并发数]$
常用子命令:
- 设置并发数: forks n 例如: forks 10
- 切换组: cd 主机组 例如: cd web
- 列出当前组主机列表: list
- 列出所有的内置命令: ?或help
范例
[root@ansible ~]#ansible-console
Welcome to the ansible console.
Type help or ? to list commands.
root@all (3)[f:5]$ list
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.7
10.0.0.6
root@all (3)[f:5]$ cd websrvs
root@websrvs (2)[f:5]$ list
10.0.0.7
10.0.0.8
root@websrvs (2)[f:5]$ forks 10
root@websrvs (2)[f:10]$ cd appsrvs
root@appsrvs (2)[f:5]$ yum name=httpd state=present
root@appsrvs (2)[f:5]$ service name=httpd state=started
3.3.6 ansible-galaxy
此工具会连接 https://galaxy.ansible.com 下载相应的roles
范例:
#列出所有已安装的galaxy
ansible-galaxy list
#安装galaxy
ansible-galaxy install geerlingguy.mysql
ansible-galaxy install geerlingguy.redis
#删除galaxy
ansible-galaxy remove geerlingguy.redis
3.4 Ansible常用模块
2015年底270多个模块,2016年达到540个,2018年01月12日有1378个模块,2018年07月15日1852个模块,2019年05月25日(ansible 2.7.10)时2080个模块,2020年03月02日有3387个模块
虽然模块众多,但最常用的模块也就2,30个而已,针对特定业务只用10几个模块
常用模块帮助文档参考:
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/modules/modules_by_category.html
3.4.1 Command 模块
功能:在远程主机执行命令,此为默认模块,可忽略-m选项
注意:此命令不支持 $VARNAME < > | ; & 等,用shell模块实现
范例:
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m command -a 'chdir=/etc cat centos-release'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core)
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
CentOS Linux release 8.1.1911 (Core)
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m command -a 'chdir=/etc creates=/data/f1.txt
cat centos-release'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core)
10.0.0.8 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
skipped, since /data/f1.txt exists
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m command -a 'chdir=/etc removes=/data/f1.txt
cat centos-release'
10.0.0.7 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
skipped, since /data/f1.txt does not exist
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
CentOS Linux release 8.1.1911 (Core)
ansible websrvs -m command -a ‘service vsftpd start’
ansible websrvs -m command -a ‘echo magedu |passwd --stdin wang’
ansible websrvs -m command -a 'rm -rf /data/'
ansible websrvs -m command -a 'echo hello > /data/hello.log'
ansible websrvs -m command -a "echo $HOSTNAME"
3.4.2 Shell模块
功能:和command相似,用shell执行命令
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#ansible websrvs -m shell -a "echo $HOSTNAME"
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
centos8
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
centos8
[root@centos8 ~]#ansible websrvs -m shell -a 'echo $HOSTNAME'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Centos7.8
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
centos8.1.cuiqinghe.com
[root@centos8 ~]#ansible websrvs -m shell -a 'echo centos | passwd --stdin cui'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Changing password for user cui.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Changing password for user cui.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@centos8 ~]#ansible websrvs -m shell -a 'ls -l /etc/shadow'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
---------- 1 root root 806 Jun 18 16:17 /etc/shadow
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
---------- 1 root root 868 Jun 19 16:17 /etc/shadow
[root@centos8 ~]#ansible websrvs -m shell -a 'echo hello > /data/hello.log'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@centos8 ~]#ansible websrvs -m shell -a 'cat /data/hello.log'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
hello
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
hello
注意:调用bash执行命令 类似 cat /tmp/test.md | awk -F‘|’ ‘{print $1,$2}’ &> /tmp/example.txt 这些复杂命令,即使使用shell也可能会失败,解决办法:写到脚本时,copy到远程,执行,再把需要的结果拉回执行命令的机器
范例:将shell模块代替command,设为模块
[root@ansible ~]#vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
#修改下面一行
module_name = shell
3.4.3 Script模块
功能:在远程主机上运行ansible服务器上的脚本(无需执行权限)
范例:
ansible websrvs -m script -a /data/test.sh
3.4.4 Copy模块
功能:从ansible服务器主控端复制文件到远程主机
#如目标存在,默认覆盖,此处指定先备份
ansible websrvs -m copy -a "src=/root/test1.sh dest=/tmp/test2.sh owner=wang mode=600 backup=yes"
#指定内容,直接生成目标文件
ansible websrvs -m copy -a "content='test line1\ntest line2' dest=/tmp/test.txt"
#复制/etc目录自身,注意/etc/后面没有/ 类似于rsync
ansible websrvs -m copy -a "src=/etc dest=/backup"
#复制/etc/下的文件,不包括/etc/目录自身,注意/etc/后面有/
ansible websrvs -m copy -a "src=/etc/ dest=/backup"
3.4.5 Fetch模块
功能:从远程主机提取文件至ansible的主控端,copy相反,目前不支持目录
范例:
ansible websrvs -m fetch -a 'src=/root/test.sh dest=/data/scripts'
范例:
[root@ansible ~]#ansible all -m fetch -a 'src=/etc/os-release
dest=/data/os'
[root@ansible ~]#tree /data/os/
/data/
├── 10.0.0.7
│ └── etc
│ └── os-release
└── 10.0.0.8
└── etc
└── os-release
4 directories, 2 files
3.4.6 File模块
功能:设置文件属性
范例:
#创建空文件
ansible all -m file -a 'path=/data/test.txt state=touch'
ansible all -m file -a 'path=/data/test.txt state=absent'
ansible all -m file -a "path=/root/test.sh owner=wang mode=755"
#创建目录
ansible all -m file -a "path=/data/mysql state=directory owner=mysql
group=mysql"
#创建软链接
ansible all -m file -a 'src=/data/testfile dest=/data/testfile-link state=link’
3.4.7 unarchive模块
功能:解包解压缩
实现有两种用法:
1、将ansible主机上的压缩包传到远程主机后解压缩至特定目录,设置copy=yes
2、将远程主机上的某个压缩包解压缩到指定路径下,设置copy=no
常见参数:
- copy:默认为yes,当copy=yes,拷贝的文件是从ansible主机复制到远程主机上,如果设置为copy=no,会在远程主机上寻找src源文件
- remote_src:和copy功能一样且互斥,yes表示在远程主机,不在ansible主机,no表示文件在ansible主机上
- src:源路径,可以是ansible主机上的路径,也可以是远程主机(被管理端或者第三方主机)上的路径,如果是远程主机上的路径,则需要设置copy=no
- dest:远程主机上的目标路径
- mode:设置解压缩后的文件权限
范例:
#默认copy时yes,故省略
ansible all -m unarchive -a 'src=/data/foo.tgz dest=/var/lib/foo owner=wang group=bin'
#源包不在absible主机上,就要把copy设成no
ansible all -m unarchive -a 'src=/tmp/foo.zip dest=/data copy=no mode=0777'
ansible all -m unarchive -a 'src=https://example.com/example.zip dest=/data copy=no'
范例:
[root@ansible ~]#tar Jcvf etc.tar.xz /etc/
[root@ansible ~]#ll -h
-rw-------. 1 root root 1.6K Mar 11 22:26 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3.8M Jun 20 09:27 etc.tar.xz
[root@ansible ~]#ansible all --list
hosts (4):
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.7
10.0.0.6
10.0.0.100
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs --list
hosts (2):
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.7
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m unarchive -a 'src=/root/etc.tar.xz dest=/data owner=cui group=bin'
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/data",
"extract_results": {
"cmd": [
"/usr/bin/gtar",
"--extract",
"-C",
"/data",
"--owner=cui",
"--group=bin",
"-f",
"/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1592616801.5587249-8032-36480135360957/source"
],
"err": "",
"out": "",
"rc": 0
},
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"handler": "TarArchive",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"size": 17,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1592616801.5587249-8032-36480135360957/source",
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/data",
"extract_results": {
"cmd": [
"/usr/bin/gtar",
"--extract",
"-C",
"/data",
"--owner=cui",
"--group=bin",
"-f",
"/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1592616801.5619113-8034-100361774048645/source"
],
"err": "",
"out": "",
"rc": 0
},
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"handler": "TarArchive",
"mode": "0755",
"owner": "root",
"size": 17,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1592616801.5619113-8034-100361774048645/source",
"state": "directory",
"uid": 0
}
#目标主机
[root@centos8 ~]#ll /data/
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 134 cui bin 8192 Jun 20 08:48 etc
[root@Centos7 ~]#ll /data/
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 134 cui bin 8192 Jun 20 08:48 etc
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -a 'rm -rf /data/*'
[WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=absent rather than running
'rm'. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you can add 'warn:
false' to this command task or set 'command_warnings=False' in ansible.cfg to get
rid of this message.
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -a 'ls /data/*'
10.0.0.7 | FAILED | rc=2 >>
ls: cannot access /data/*: No such file or directorynon-zero return code
10.0.0.8 | FAILED | rc=2 >>
ls: cannot access '/data/*': No such file or directorynon-zero return code
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m copy -a 'src=etc.tar.xz dest=/root/'
[root@ansible ~]#mv etc.tar.xz /opt/
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m unarchive -a 'src=/root/etc.tar.xz dest=/data copy=no'
[root@centos8 ~]#ll /data/
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 134 root root 8192 Jun 20 08:48 etc
3.4.8 Archive模块
功能:打包压缩保存在被管理节点
范例:
ansible websrvs -m archive -a 'path=/var/log/ dest=/data/log.tar.bz2 format=bz2 owner=wang mode=0600'
3.4.9 Hostname模块
功能:管理主机名,一般是针对一台主机设,对多个主机设不合理
范例:
ansible node1 -m hostname -a “name=websrv”
ansible 192.168.100.18 -m hostname -a 'name=node18.magedu.com'
[root@ansible ~]#ansible 10.0.0.6 -m hostname -a 'name=centos66.cuiqinghe.com'
[root@centos6 ~]#hostname
centos66.cuiqinghe.com
[root@centos6 ~]#cat /etc/sysconfig/network #直接写到配置文件中了
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=centos66.cuiqinghe.com
#扩展:centos7,centos8,ubuntu的主机名都放在/etc/hostname中
3.4.10 Cron模块
功能:计划任务 (分时日月周)
支持时间:minute,hour,day,month,weekday
范例:
#备份数据库脚本
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /root/mysql_backup.sh
#!/bin/bash
mysqldump -A -F --single-transaction --master-data=2 -q -uroot |gzip > /data/mysql_`date +%F_%T`.sql.gz
#-A全部数据库备份 -F刷新日志 --single-transaction启用事务 --master-data=2 记录备份点 -q快速备份
#创建任务
ansible 10.0.0.8 -m cron -a 'hour=2 minute=30 weekday=1-5 name="backup mysql" job=/root/mysql_backup.sh'
ansible websrvs -m cron -a "minute=*/5 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp.aliyun.com
&>/dev/null' name=Synctime"
#避免产生大量垃圾文件
#ntpdate ntp.aliyun.com 命令只有centos7和之前的版本有
#禁用计划任务
ansible websrvs -m cron -a "minute=*/5 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp.aliyun.com
&>/dev/null' name=Synctime disabled=yes"
#启用计划任务
ansible websrvs -m cron -a "minute=*/5 job='/usr/sbin/ntpdate ntp.aliyun.com
&>/dev/null' name=Synctime disabled=no"
#删除任务
ansible websrvs -m cron -a "name='backup mysql' state=absent"
ansible websrvs -m cron -a 'state=absent name=Synctime'
范例:
[root@ansible ~]#cat mysql_backup.sh
#!/bin/bash
mysqldump -A -F --single-transaction --master-data=2 -q -uroot |gzip > /data/mysql_`date +%F_%T`.sql.gz
[root@ansible ~]#chmod +x mysql_backup.sh
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m copy -a 'src=/root/mysql_backup.sh dest=/opt/'
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -a 'ls -l /opt/'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
total 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 541 Jun 20 10:12 mysql_backup.sh
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
total 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 541 Jun 20 10:12 mysql_backup.sh
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m cron -a 'hour=2 minute=30 weekday=1-5 name="backup mysql" job=/opt/mysql_backup.sh'
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -a 'crontab -l'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: backup mysql
30 2 * * 1-5 /opt/mysql_backup.sh
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: backup mysql
30 2 * * 1-5 /opt/mysql_backup.sh
[root@Centos7 ~]#cat /var/spool/cron/root
#Ansible: backup mysql
30 2 * * 1-5 /opt/mysql_backup.sh
3.4.11 Yum模块
功能:管理软件包,只支持RHEL,CentOS,fedora,不支持Ubuntu其它版本
范例:
ansible websrvs -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=present' #安装
ansible websrvs -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=absent' #删除
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -m yum -a 'name=iotop,cowsay'
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -a 'rpm -q iotop cowsay'
3.4.12 Service模块
功能:管理服务
范例:
#设为开机启动
ansible all -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=yes'
#查看状态
ansible websrvs -a 'systemctl is-enabled httpd'
ansible all -m service -a 'name=httpd state=stopped'
ansible all -m service -a 'name=httpd state=reloaded'
ansible all -m service -a 'name=httpd state=restarted'
#修改端口
ansible all -m shell -a "sed -i 's/^Listen 80/Listen 8080/' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf"
[root@ansible ~]#ansible websrvs -a "grep Listen /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf"
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
# Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or
# Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen 8080
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
# Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or
# Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen 8080
3.4.13 User模块
功能:管理用户
范例
#创建用户
ansible all -m user -a 'name=user1 comment="test user" uid=2048 home=/app/user1 group=root'
ansible all -m user -a 'name=nginx comment=nginx uid=88 group=nginx
groups="root,daemon" shell=/sbin/nologin system=yes create_home=no
home=/data/nginx non_unique=yes'
#remove=yes表示删除用户及家目录等数据,默认remove=no
ansible all -m user -a 'name=nginx state=absent remove=yes'
3.4.14 Group模块
功能:管理组
范例:
#创建组
ansible websrvs -m group -a 'name=nginx gid=88 system=yes'
#删除组
ansible websrvs -m group -a 'name=nginx state=absent'
3.4.15 Lineinfile模块
ansible在使用sed进行替换时,经常会遇到需要转义的问题,而且ansible在遇到特殊符号进行替换时,存在问题,无法正常进行替换 。其实在ansible自身提供了两个模块:lineinfile模块和replace模块,可以方便的进行替换
功能:相当于sed,可以修改文件内容,若需要修改的行数较多,就用copy模块
范例:
ansible websrvs -m lineinfile -a "path=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
regexp='^Listen' line='Listen 80'"
ansible all -m lineinfile -a "path=/etc/selinux/config regexp='^SELINUX=' line='SELINUX=disabled'"
ansible all -m lineinfile -a 'dest=/etc/fstab state=absent regexp="^#"
3.4.16 Replace模块
该模块有点类似于sed命令,主要也是基于正则进行匹配和替换,建议使用
范例:
ansible all -m replace -a "path=/etc/fstab regexp='^(UUID.*)' replace='#\1'"
ansible all -m replace -a "path=/etc/fstab regexp='^#(.*)' replace='\1'"
3.4.17 Setup模块
功能: setup 模块来收集主机的系统信息,这些 facts 信息可以直接以变量的形式使用,但是如果主机较多,会影响执行速度,可以使用 gather_facts: no 来禁止 Ansible 收集 facts 信息
范例:
ansible all -m setup
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_nodename"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_hostname"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_domain"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_memtotal_mb"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_memory_mb"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_memfree_mb"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_os_family"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_distribution_major_version"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_distribution_version"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_processor_vcpus"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_architecture"
ansible all -m setup -a "filter=ansible_processor*"
范例:
[root@ansible ~]#ansible all -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_python_version'
10.0.0.7 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_python_version": "2.7.5",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
10.0.0.6 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_python_version": "2.6.6",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
10.0.0.8 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_python_version": "3.6.8",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false
}
10.0.0.100 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_python_version": "3.6.9",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"changed": false
}
范例:取IP地址
#取所有IP
ansible 10.0.0.100 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses'
10.0.0.100 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"10.0.0.100"
],
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"changed": false
}
#取默认IP
[root@ansible ~]#ansible 10.0.0.8 -m setup -a 'filter="ansible_default_ipv4"'
10.0.0.8 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_default_ipv4": {
"address": "10.0.0.8",
"alias": "eth0",
"broadcast": "10.0.0.255",
"gateway": "10.0.0.2",
"interface": "eth0",
"macaddress": "00:0c:29:30:80:0a",
"mtu": 1500,
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"network": "10.0.0.0",
"type": "ether"
},
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false
}
4 Playbook
4.1 playbook介绍
playbook 剧本是由一个或多个"play"组成的列表
play的主要功能在于将预定义的一组主机,装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。Task实际是调用ansible的一个module,将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让它们联合起来,按事先编排的机制执行预定义的动作
Playbook 文件是采用YAML语言编写的
4.2 YAML 语言
4.2.1 YAMl 语言介绍
YAML是一个可读性高的用来表达资料序列的格式。YAML参考了其他多种语言,包括:XML、C语言、Python、Perl以及电子邮件格式RFC2822等。Clark Evans在2001年在首次发表了这种语言,另外Ingy döt Net与Oren Ben-Kiki也是这语言的共同设计者,目前很多软件中采有此格式的文件,如:ubuntu,anisble,docker,k8s等
YAML:YAML Ain’t Markup Language,即YAML不是XML。不过,在开发的这种语言时,YAML的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)
YAML 官方网站:http://www.yaml.org
4.2.2 YAML 语言特性
- YAML的可读性好
- YAML和脚本语言的交互性好
- YAML使用实现语言的数据类型
- YAML有一个一致的信息模型
- YAML易于实现
- YAML可以基于流来处理
- YAML表达能力强,扩展性好
4.2.3 YAML语法简介
- 在单一文件第一行,用连续三个连字号"-" 开始,还有选择性的连续三个点号( … )用来表示文件的结尾
- 次行开始正常写Playbook的内容,一般建议写明该Playbook的功能
- 使用#号注释代码
- 缩进必须是统一的,不能空格和tab混用
- 缩进的级别也必须是一致的,同样的缩进代表同样的级别,程序判别配置的级别是通过缩进结合换行来实现的
- YAML文件内容是区别大小写的,key/value的值均需大小写敏感
- 多个key/value可同行写也可换行写,同行使用,分隔
- v可是个字符串,也可是另一个列表
- YAML文件扩展名通常为yml或yaml
YAML的语法和其他高阶语言类似,并且可以简单表达清单、散列表、标量等数据结构。其结构(Structure)通过空格来展示,序列(Sequence)里的项用"-“来代表,Map里的键值对用”:"分隔,下面介绍常见的数据结构。
4.2.3.1 List列表
列表由多个元素组成,每个元素放在不同行,且元素前均使用"-"打头,并且 - 后有一个空格, 或者将所有元素用 [ ] 括起来放在同一行
范例:
#不同行,行以-开头,后面有一个空格
# A list of tasty fruits
- Apple
- Orange
- Strawberry
- Mango
#同一行
[Apple,Orange,Strawberry,Mango]
4.2.3.2 Dictionary字典
字典由多个key与value构成,key和value之间用 :分隔, 并且 : 后面有一个空格,所有k/v可以放在一行,或者每个 k/v 分别放在不同行
范例:
#不同行
# An employee record
name: Example Developer
job: Developer
skill: Elite
#同一行,也可以将key:value放置于{}中进行表示,用,分隔多个key:value
# An employee record
{
name: "Example Developer", job: "Developer", skill: "Elite"}
范例:YAML 表示一个家庭
name: John Smith
age: 41
gender: Male
spouse:
name: Jane Smith
age: 37
gender: Female
children:
- name: Jimmy Smith
age: 17
gender: Male
- {
name: Jenny Smith, age: 13, gender: Female}
- {
name: hao Smith, age: 20, gender: Male }
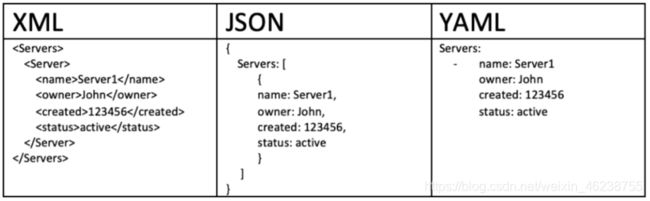
4.2.4 三种常见的数据格式
- XML:Extensible Markup Language,可扩展标记语言,可用于数据交换和配置
- JSON:JavaScript Object Notation, JavaScript 对象表记法,主要用来数据交换传输或配置,不支持注释
- YAML:YAML Ain’t Markup Language YAML 不是一种标记语言, 主要用来配置,大小写敏感,不支持tab
可以用工具互相转换,参考网站:
https://www.json2yaml.com/
http://www.bejson.com/json/json2yaml/
4.3 Playbook 核心组件
一个playbook 中由列表组成,其中所用到的常见组件类型如下:
- Hosts 执行的远程主机列表
- Tasks 任务集,由多个task的元素组成的列表实现,每个task是一个字典
- Variables 内置变量或自定义变量在playbook中调用
- Templates 模板,可替换模板文件中的变量并实现一些简单逻辑的文件
- Handlers 和 notify 结合使用,由特定条件触发的操作,满足条件方才执行,否则不执行
- tags 标签 指定某条任务执行,用于选择运行playbook中的部分代码。ansible具有幂等性,因此会自动跳过没有变化的部分,即便如此,有些代码为测试其确实没有发生变化的时间依然会非常地长。此时,如果确信其没有变化,就可以通过tags跳过此些代码片断
- 一个完整的代码块功能需最少元素需包括 name 和 task,一个name只能包括一个task
4.3.1 hosts 组件
Hosts:playbook中的每一个play的目的都是为了让特定主机以某个指定的用户身份执行任务。hosts用于指定要执行指定任务的主机,须事先定义在主机清单中
one.example.com
one.example.com:two.example.com
192.168.1.50
192.168.1.*
Websrvs:dbsrvs #或者,两个组的并集
Websrvs:&dbsrvs #与,两个组的交集
webservers:!phoenix #在websrvs组,但不在dbsrvs组
案例:
- hosts: websrvs:appsrvs hosts元素
4.3.2 remote_user 组件
remote_user: 可用于Host和task中。也可以通过指定其通过sudo的方式在远程主机上执行任务,其可用于play全局或某任务;此外,甚至可以在sudo时使用sudo_user指定sudo时切换的用户
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root #键值对
tasks:
- name: test connection
ping:
remote_user: magedu
sudo: yes #默认sudo为root
sudo_user:wang #sudo为wang
4.3.3 task列表和action组件
play的主体部分是task list,task list中有一个或多个task,各个task 按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个task后,再开始第二个task
task的目的是使用指定的参数执行模块,而在模块参数中可以使用变量。模块执行是幂等的,这意味着多次执行是安全的,因为其结果均一致
每个task都应该有其name,用于playbook的执行结果输出,建议其内容能清晰地描述任务执行步骤。如果未提供name,则action的结果将用于输出
task两种格式:
action: module arguments
module: arguments 建议使用
注意:shell和command模块后面跟命令,而非key=value
范例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
4.3.4 其它组件
某任务的状态在运行后为changed时,可通过"notify"通知给相应的handlers
任务可以通过"tags"打标签,可在ansible-playbook命令上使用-t指定进行调用
4.3.5 ShellScripts VS Playbook 案例
#SHELL脚本实现
#!/bin/bash
# 安装Apache
yum install --quiet -y httpd
# 复制配置文件
cp /tmp/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
cp/tmp/vhosts.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/
# 启动Apache,并设置开机启动
systemctl enable --now httpd
#Playbook实现
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: "安装Apache"
yum: name=httpd
- name: "复制配置文件"
copy: src=/tmp/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
- name: "复制配置文件"
copy: src=/tmp/vhosts.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/
- name: "启动Apache,并设置开机启动"
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
4.4 playbook 命令
格式
ansible-playbook <filename.yml> ... [options]
常见选项
-C --check #只检测可能会发生的改变,但不真正执行操作
--list-hosts #列出运行任务的主机
--list-tags #列出tag
--list-tasks #列出task
--limit 主机列表 #只针对主机列表中的特定主机执行
-v -vv -vvv #显示过程
范例:
[root@ansible ansible]#cat hello.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
tasks:
- name: hello
command: echo "hello ansible"
[root@ansible ansible]#ansible-playbook hello.yml
[root@ansible ansible]#ansible-playbook -v hello.yml
[root@ansible ansible]#ansible-playbook --list-tasks hello.yml
playbook: hello.yml
play #1 (websrvs): websrvs TAGS: []
tasks:
是否存活 TAGS: []
清理/data/ TAGS: []
[root@ansible ansible]#ansible-playbook --list-hosts hello.yml
playbook: hello.yml
play #1 (websrvs): websrvs TAGS: []
pattern: ['websrvs']
hosts (2):
10.0.0.8
10.0.0.7
范例
ansible-playbook file.yml --check #只检测
ansible-playbook file.yml
ansible-playbook file.yml --limit websrvs
4.5 Playbook 初步
4.5.1 利用 playbook 创建 mysql 用户
范例:mysql_user.yml
---
- hosts: dbsrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- {
name: create group, group: name=mysql system=yes gid=306}
- name: create user
user: name=mysql shell=/sbin/nologin system=yes group=mysql uid=306 home=/data/mysql create_home=no
4.5.2 利用 playbook 安装 nginx
范例:install_nginx.yml
---
# install nginx
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add group nginx
user: name=nginx state=present
- name: add user nginx
user: name=nginx state=present group=nginx
- name: Install Nginx
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: web page
copy: src=files/index.html dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
- name: Start Nginx
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
4.5.3 利用 playbook 安装和卸载 httpd
范例:install_httpd.yml
---
#install httpd
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: Install configure file
copy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
- name: modify config
lineinfile: path=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf regexp='^Listen' line='Listen 8080'
- name: mkdir website dir
file: path=/data/html state=directory
- name: web html
copy: src=files/index.html dest=/data/html/
- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
ansible-playbook install_httpd.yml --limit 10.0.0.8 #
范例:remove_httpd.yml
#remove_httpd.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: remove httpd package
yum: name=httpd state=absent
- name: remove apache user
user: name=apache state=absent
- name: remove config file
file: name=/etc/httpd state=absent
- name: remove web html
file: name=/data/html/ state=absent
4.5.4 利用 playbook 安装 mysql
范例:安装mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12
[root@ansible ~]#ls -l /data/ansible/files/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 403177622 Dec 4 13:05 /data/ansible/files/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/files/my.cnf
[mysqld]
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
user=mysql
symbolic-links=0
datadir=/data/mysql
innodb_file_per_table=1
log-bin
pid-file=/data/mysql/mysqld.pid
[client]
port=3306
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
[mysqld_safe]
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
#安全加固脚本,设密码
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/files/secure_mysql.sh
#!/bin/bash
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql_secure_installation <<EOF
y
magedu
magedu
y
y
y
y
EOF
[root@ansible ~]#tree /data/ansible/files/
/data/ansible/files/
├── my.cnf
├── mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
└── secure_mysql.sh
0 directories, 3 files
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/install_mysql.yml
---
# install mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
- hosts: dbsrvs
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: install packages
yum: name=libaio,perl-Data-Dumper,perl-Getopt-Long
- name: create mysql group
group: name=mysql gid=306
- name: create mysql user
user: name=mysql uid=306 group=mysql shell=/sbin/nologin system=yes
create_home=no home=/data/mysql
- name: copy tar to remote host and file mode
unarchive: src=/data/ansible/files/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-
x86_64.tar.gz dest=/usr/local/ owner=root group=root
- name: create linkfile /usr/local/mysql
file: src=/usr/local/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64
dest=/usr/local/mysql state=link
- name: data dir
shell: chdir=/usr/local/mysql/ ./scripts/mysql_install_db --
datadir=/data/mysql --user=mysql
tags: data
- name: config my.cnf
copy: src=/data/ansible/files/my.cnf dest=/etc/my.cnf
- name: service script
shell: /bin/cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
- name: enable service
shell: /etc/init.d/mysqld start;chkconfig --add mysqld;chkconfig mysqld on
tags: service
- name: PATH variable
copy: content='PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH' dest=/etc/profile.d/mysql.sh
- name: secure script
script: /data/ansible/files/secure_mysql.sh
tags: script
---
#Installing MariaDB Binary
安装MySQL错误问题整理:
[root@ansible ansible]#ansible-playbook install_mysql5.6.yml --limit 10.0.0.8
TASK [secure script] **************************************************************
fatal: [10.0.0.8]: FAILED! => {
"changed": true, "msg": "non-zero return code", "rc": 29, "stderr": "Shared connection to 10.0.0.8 closed.\r\n", "stderr_lines": ["Shared connection to 10.0.0.8 closed."], "stdout": "Can't find a 'mysql' client in PATH or ./bin\r\nCleaning up...\r\nWarning: Could not unlink .my.cnf.3304: No such file or directory\r\nWarning: Could not unlink .mysql.3304: No such file or directory\r\n", "stdout_lines": ["Can't find a 'mysql' client in PATH or ./bin", "Cleaning up...", "Warning: Could not unlink .my.cnf.3304: No such file or directory", "Warning: Could not unlink .mysql.3304: No such file or directory"]}
PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************
10.0.0.8 : ok=10 changed=10 unreachable=0 failed=1 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
#打开目标主机,mysql端口已打开,但是命令找不到,别着急,退出重进
[root@centos8 ~]#ss -ntl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:5355 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 80 *:3306 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:5355 [::]:*
[root@centos8 ~]#mysql
-bash: mysql: command not found
[root@centos8 ~]#exit
#再次执行命令显示缺包
[root@centos8 ~]#mysql
mysql: error while loading shared libraries: libncurses.so.5: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
[root@centos8 ~]#yum -y install libaio numactl-libs ncurses-compat-libs libncurses.so.5
#登陆成功
[root@centos8 ~]#mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1
Server version: 5.6.47-log MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
范例:install_mariadb.yml
---
#Installing MariaDB Binary Tarballs
- hosts: dbsrvs
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: create group
group: name=mysql gid=27 system=yes
- name: create user
user: name=mysql uid=27 system=yes group=mysql shell=/sbin/nologin home=/data/mysql create_home=no
- name: mkdir datadir
file: path=/data/mysql owner=mysql group=mysql state=directory
- name: unarchive package
unarchive: src=/data/ansible/files/mariadb-10.2.27-linux-x86_64.tar.gz dest=/usr/local/ owner=root group=root
- name: link
file: src=/usr/local/mariadb-10.2.27-linux-x86_64 path=/usr/local/mysql state=link
- name: install database
shell: chdir=/usr/local/mysql ./scripts/mysql_install_db -- datadir=/data/mysql --user=mysql
- name: config file
copy: src=/data/ansible/files/my.cnf dest=/etc/ backup=yes
- name: service script
shell: /bin/cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
- name: start service
service: name=mysqld state=started enabled=yes
- name: PATH variable
copy: content='PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH' dest=/etc/profile.d/mysql.sh
4.6 Playbook中使用handlers和notify
Handlers本质是task list ,类似于MySQL中的触发器触发的行为,其中的task与前述的task并没有本质上的不同,主要用于当关注的资源发生变化时,才会采取一定的操作。而Notify对应的action可用于在每个play的最后被触发,这样可避免多次有改变发生时每次都执行指定的操作,仅在所有的变化发生完成后一次性地执行指定操作。在notify中列出的操作称为handler,也即notify中调用handler中定义的操作
案例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: Install configure file
copy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
notify: restart httpd
- name: ensure apache is running
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
案例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: add group nginx
user: name=nginx state=present
- name: add user nginx
user: name=nginx state=present group=nginx
- name: Install Nginx
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: config
copy: src=/root/config.txt dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify:
- Restart Nginx
- Check Nginx Process
handlers:
- name: Restart Nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted enabled=yes
- name: Check Nginx process
shell: killall -0 nginx &> /tmp/nginx.log
4.7 Playbook中使用tags组件
在playbook文件中,可以利用tags组件,为特定 task 指定标签,当在执行playbook时,可以只执行特定tags的task,而非整个playbook文件
案例:
vim httpd.yml
---
# tags example
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=present
- name: Install configure file
copy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/
tags: conf
- name: start httpd service
tags: service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
ansible-playbook –t conf,service httpd.yml
4.8 Playbook中使用变量
变量名:仅能由字母、数字和下划线组成,且只能以字母开头
变量定义:
variable=value
范例:
http_port=80
变量调用方式:
通过{ { variable_name }} 调用变量,且变量名前后建议加空格,有时用"{ { variable_name }}"才生效
变量来源:
-
ansible 的 setup facts 远程主机的所有变量都可直接调用
-
通过命令行指定变量,优先级最高
ansible-playbook -e varname=value test.yml -
在playbook文件中定义
vars: - var1: value1 - var2: value2 -
在独立的变量YAML文件中定义
- hosts: all vars_files: - vars.yml -
在 /etc/ansible/hosts 中定义主机(普通)变量:主机组中主机单独定义,优先级高于公共变量组(公共)变量:针对主机组中所有主机定义统一变量
-
在role中定义
4.8.1 使用 setup 模块中变量
本模块自动在playbook调用,不要用ansible命令调用
案例:使用setup变量
ansible 10.0.0.101 -m setup -a 'filter="ansible_default_ipv4"'
10.0.0.101 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_default_ipv4": {
"address": "10.0.0.101",
"alias": "eth0",
"broadcast": "10.0.0.255",
"gateway": "10.0.0.2",
"interface": "eth0",
"macaddress": "00:0c:29:e8:c7:9b",
"mtu": 1500,
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"network": "10.0.0.0",
"type": "ether"
}
},
"changed": false
}
范例:
---
#var1.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
gather_facts: yes
tasks:
- name: create log file
file: name=/data/{
{
ansible_nodename }}.log state=touch owner=cui mode=600
ansible-playbook var.yml
4.8.2 在playbook 命令行中定义变量
范例:
vim var2.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={
{
pkname }} state=present
ansible-playbook –e pkname=httpd var2.yml
4.8.3 在playbook文件中定义变量
范例:
vim var3.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
- username: user1
- groupname: group1
tasks:
- name: create group
group: name={
{
groupname }} state=present
- name: create user
user: name={
{
username }} group={
{
groupname }} state=present
ansible-playbook -e "username=user2 groupname=group2" var3.yml
#-e的优先级比playbook中高
范例:
cat var4.yaml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars: #变量的定义方式,值从setup模块中来,生成一个和IP地址同名的文件夹
collect_info: "/data/test/{
{ansible_default_ipv4['address']}}/"
tasks:
- name: create IP directory
file: name="{
{collect_info}}" state=directory
#执行结果
tree /data/test/
/data/test/
└── 10.0.0.102
1 directory, 0 files
4.8.4 使用变量文件
可以在一个独立的playbook文件中定义变量,在另一个playbook文件中引用变量文件中的变量,比playbook中定义的变量优化级高
vim vars.yml #只负责定义变量
---
# variables file
package_name: mariadb-server
service_name: mariadb
vim var5.yml
---
#install package and start service
- hosts: dbsrvs
remote_user: root
vars_files:
- vars.yml
tasks:
- name: install package
yum: name={
{
package_name }}
tags: install
- name: start service
service: name={
{
service_name }} state=started enabled=yes
范例:
cat vars2.yml
---
var1: httpd
var2: nginx
cat var6.yml
---
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
vars_files:
- vars2.yml
tasks:
- name: create httpd log
file: name=/app/{
{
var1 }}.log state=touch
- name: create nginx log
file: name=/app/{
{
var2 }}.log state=touch
4.8.5 主机清单文件中定义变量
4.8.5.1 主机变量
在inventory 主机清单文件中为指定的主机定义变量以便于在playbook中使用
范例:
[websrvs]
www1.magedu.com http_port=80 maxRequestsPerChild=808
www2.magedu.com http_port=8080 maxRequestsPerChild=909
4.8.5.2 组(公共)变量
在inventory 主机清单文件中赋予给指定组内所有主机上的在playbook中可用的变量,如果和主机变是同名,优先级低于主机变量
范例:
[websrvs]
www1.magedu.com http_port=8080
www2.magedu.com
[websrvs:vars]
http_port=80
ntp_server=ntp.magedu.com
nfs_server=nfs.magedu.com
范例: 通过变量生成主机名
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[websrvs]
10.0.0.8 hname=www1 domain=magedu.io
10.0.0.7 hname=www2
[websvrs:vars]
mark="-"
domain=magedu.org
[root@ansible ansible]#ansible websrvs -m hostname -a 'name={
{ hname }}{
{ mark }}{
{ domain }}'
10.0.0.7 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_domain": "org",
"ansible_fqdn": "www2-magedu.org",
"ansible_hostname": "www2-magedu",
"ansible_nodename": "www2-magedu.org",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "www2-magedu.org"
}
10.0.0.8 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_domain": "io",
"ansible_fqdn": "www1-magedu.io",
"ansible_hostname": "www1-magedu",
"ansible_nodename": "www1-magedu.io",
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": true,
"name": "www1-magedu.io"
}
bash
#命令行指定变量:
ansible websvrs –e domain=magedu.cn –m hostname –a 'name={
{ hname }}{
{ mark
}}{
{ domain }}'
4.9 template 模板
模板是一个文本文件,可以做为生成文件的模版,并且模板文件中还可嵌套jinja语法
4.9.1 jinja2语言
官方网站:
http://jinja.pocoo.org/
https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/2.11.x/
jinja2 语言使用字面量,有下面形式:
字符串:使用单引号或双引号
数字:整数,浮点数
列表:[item1, item2, …]
元组:(item1, item2, …)
字典:{key1:value1, key2:value2, …}
布尔型:true/false
算术运算:+, -, *, /, //, %, **
比较操作:==, !=, >, >=, <, <=
逻辑运算:and,or,not
流表达式:For,If,When
字面量:
表达式最简单的形式就是字面量。字面量表示诸如字符串和数值的 Python 对象。如"Hello World"
双引号或单引号中间的一切都是字符串。无论何时你需要在模板中使用一个字符串(比如函数调用、过滤器或只是包含或继承一个模板的参数),如42,42.23 数值可以为整数和浮点数。如果有小数点,则为浮点数,否则为整数。在 Python 里, 42 和 42.0 是不一样的
算术运算:
Jinja 允许用计算值。支持下面的运算符
+:把两个对象加到一起。通常对象是素质,但是如果两者是字符串或列表,你可以用这 种方式来衔接它们。无论如何这不是首选的连接字符串的方式!连接字符串见 ~ 运算符。 { { 1 + 1 }} 等于 2
-:用第一个数减去第二个数。 { { 3 - 2 }} 等于 1
/:对两个数做除法。返回值会是一个浮点数。 { { 1 / 2 }} 等于 0.5
//:对两个数做除法,返回整数商。 { { 20 // 7 }} 等于 2
%:计算整数除法的余数。 { { 11 % 7 }} 等于 4
*:用右边的数乘左边的操作数。 { { 2 * 2 }} 会返回 4 。也可以用于重 复一个字符串多次。 { { ‘=’ * 80 }}会打印 80 个等号的横条
**:取左操作数的右操作数次幂。 { { 2**3 }} 会返回 8
比较操作符
== 比较两个对象是否相等
!= 比较两个对象是否不等
> 如果左边大于右边,返回 true
>= 如果左边大于等于右边,返回 true
< 如果左边小于右边,返回 true
<= 如果左边小于等于右边,返回 true
逻辑运算符
对于 if 语句,在 for 过滤或 if 表达式中,它可以用于联合多个表达式
and 如果左操作数和右操作数同为真,返回 true
or 如果左操作数和右操作数有一个为真,返回 true
not 对一个表达式取反
(expr)表达式组
true / false true 永远是 true ,而 false 始终是 false
4.9.2 template
template功能:可以根据和参考模块文件,动态生成相类似的配置文件
template文件必须存放于templates目录下,且命名为 .j2 结尾
yaml/yml 文件需和templates目录平级,目录结构如下示例:
./
├── temnginx.yml
└── templates
└── nginx.conf.j2
范例:利用template 同步nginx配置文件
#准备templates/nginx.conf.j2文件
vim temnginx.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: template config to remote hosts
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
ansible-playbook temnginx.yml
template变更替换
范例:
#修改文件nginx.conf.j2
mkdir templates
vim templates/nginx.conf.j2
worker_processes {
{
ansible_processor_vcpus }}; #cpu颗数
vim temnginx2.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx
- name: template config to remote hosts
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #这一步并不会原装复制,而是把目标文件调整修改之后生成新的conf文件
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
ansible-playbook temnginx2.yml
#扩展:cpu颗数查看
[root@ansible ansible]#ansible websrvs -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_processor_vcpus'
10.0.0.7 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_processor_vcpus": 2,
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false
}
10.0.0.8 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_processor_vcpus": 1,
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"
},
"changed": false
}
template算术运算
范例:
vim nginx.conf.j2
worker_processes {
{
ansible_processor_vcpus**2 }}; #2次方
worker_processes {
{
ansible_processor_vcpus+2 }};
以下为二次方的执行结果:
[root@ansible ansible]#vim templates/nginx.conf.j2
worker_processes {
{
ansible_processor_vcpus**3 }};
[root@ansible ansible]#cat templnginx.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx
- name: template config to remote hosts
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: restart nginx
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
ansible-playbook templnginx.yml --limit 10.0.0.8
4.9.3 template中使用流程控制 for 和 if
template中也可以使用流程控制 for 循环和 if 条件判断,实现动态生成文件功能
范例
#temlnginx2.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts: #定义一个变量:由三个元素组成的一个列表
- 81
- 82
- 83
tasks:
- name: template config
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/data/nginx.conf
#templates/nginx2.conf.j2
{
% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %} #vhost会自动取81,82,83
server {
listen {
{
vhost }}
}
{
% endfor %}
ansible-playbook -C templnginx2.yml --limit 10.0.0.8
#生成的结果:
server {
listen 81
}
server {
listen 82
}
server {
listen 83
}
范例:
#temlnginx3.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- listen: 8080
tasks:
- name: config file
template: src=nginx3.conf.j2 dest=/data/nginx3.conf
#templates/nginx3.conf.j2
{
% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {
{
vhost.listen }}
}
{
% endfor %}
ansible-playbook templnginx3.yml --limit 10.0.0.8
#生成的结果
server {
listen 8080
}
范例:
#templnginx4.yml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- listen: 8080
server_name: "web1.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web1/"
- listen: 8081
server_name: "web2.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web2/"
- {
listen: 8082, server_name: "web3.magedu.com", root: "/var/www/nginx/web3/"}
tasks:
- name: template config
template: src=nginx4.conf.j2 dest=/data/nginx4.conf
# templates/nginx.conf4.j2
{
% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {
{
vhost.listen }}
server_name {
{
vhost.server_name }}
root {
{
vhost.root }}
}
{
% endfor %}
ansible-playbook templnginx4.yml --limit 10.0.0.8
#生成结果:
server {
listen 8080
server_name web1.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web1/
}
server {
listen 8081
server_name web2.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web2/
}
server {
listen 8082
server_name web3.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web3/
}
在模版文件中还可以使用 if条件判断,决定是否生成相关的配置信息
范例:
#templnginx5.yml
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
vars:
nginx_vhosts:
- web1:
listen: 8080
root: "/var/www/nginx/web1/"
- web2:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web2.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web2/"
- web3:
listen: 8080
server_name: "web3.magedu.com"
root: "/var/www/nginx/web3/"
tasks:
- name: template config to
template: src=nginx.conf5.j2 dest=/data/nginx5.conf
#templates/nginx.conf5.j2
#如果vhost.server_name定义过了,就生成server_name的值,没定义就不生成;即根据变量存在与否,来决定是否生成server_name
{
% for vhost in nginx_vhosts %}
server {
listen {
{
vhost.listen }}
{
% if vhost.server_name is defined %}
server_name {
{
vhost.server_name }}
{
% endif %}
root {
{
vhost.root }}
}
{
% endfor %}
#生成的结果
server {
listen 8080
root /var/www/nginx/web1/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_name web2.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web2/
}
server {
listen 8080
server_name web3.magedu.com
root /var/www/nginx/web3/
}
4.10 playbook使用 when
when语句,可以实现条件测试。如果需要根据变量、facts或此前任务的执行结果来做为某task执行与否的前提时要用到条件测试,通过在task后添加when子句即可使用条件测试,jinja2的语法格式
范例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: "shutdown RedHat flavored systems"
command: /sbin/shutdown -h now
when: ansible_os_family == "RedHat"
范例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add group nginx
tags: user
user: name=nginx state=present
- name: add user nginx
user: name=nginx state=present group=nginx
- name: Install Nginx
yum: name=nginx state=present
- name: restart Nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
范例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install conf file to centos7
template: src=nginx.conf.c7.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
- name: install conf file to centos6
template: src=nginx.conf.c6.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
4.11 playbook 使用迭代 with_items
迭代:当有需要重复性执行的任务时,可以使用迭代机制
对迭代项的引用,固定变量名为"item"
要在task中使用with_items给定要迭代的元素列表
列表元素格式:
- 字符串
- 字典
范例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add several users
user: name={
{
item }} state=present groups=wheel
with_items: #下面的列表会自动嵌入到上面的item
- testuser1
- testuser2
- testuser3
#上面语句的功能等同于下面的语句
- name: add several users
user: name=testuser1 state=present groups=wheel
- name: add several users
user: name=testuser2 state=present groups=wheel
- name: add several users
user: name=testuser3 state=present groups=wheel
#执行结果
[root@centos8 ~]#getent passwd
testuser1:x:1001:1001::/home/testuser1:/bin/bash
testuser2:x:1002:1002::/home/testuser2:/bin/bash
testuser3:x:1003:1003::/home/testuser3:/bin/bash
范例:卸载 mariadb
---
#remove mariadb server
- hosts: appsrvs:!10.0.0.8
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: stop service
shell: /etc/init.d/mysqld stop
- name: delete files and dir
file: path={
{
item}} state=absent
with_items:
- /usr/local/mysql
- /usr/local/mariadb-10.2.27-linux-x86_64
- /etc/init.d/mysqld
- /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh
- /etc/my.cnf
- /data/mysql
- name: delete user
user: name=mysql state=absent remove=yes
范例:
---
- hosts:websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks
- name: install some packages
yum: name={
{
item }} state=present
with_items:
- nginx
- memcached
- php-fpm
范例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy file
copy: src={
{
item }} dest=/tmp/{
{
item }}
with_items:
- file1
- file2
- file3
- name: yum install httpd
yum: name={
{
item }} state=present
with_items:
- apr
- apr-util
- httpd
迭代嵌套子变量:在迭代中,还可以嵌套子变量,关联多个变量在一起使用
示例:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add some groups
group: name={
{
item }} state=present
with_items:
- nginx
- mysql
- apache
- name: add some users
user: name={
{
item.name }} group={
{
item.group }} state=present
with_items:
- {
name: 'nginx', group: 'nginx' }
- {
name: 'mysql', group: 'mysql' }
- {
name: 'apache', group: 'apache' }
范例:
cat with_item2.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: add some groups
group: name={
{
item }} state=present
with_items:
- g1
- g2
- g3
- name: add some users
user: name={
{
item.name }} group={
{
item.group }} home={
{
item.home }}
create_home=yes state=present
with_items:
- {
name: 'user1', group: 'g1', home: '/data/user1' }
- {
name: 'user2', group: 'g2', home: '/data/user2' }
- {
name: 'user3', group: 'g3', home: '/data/user3' }
#最终结果如下:
[root@centos8 ~]#getent passwd user1
user1:x:1001:1001::/data/user1:/bin/bash
[root@centos8 ~]#id user1
uid=1001(user1) gid=1001(g1) groups=1001(g1)
[root@centos8 ~]#ll /data/
total 12
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 264 Jun 21 10:49 nginx4.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 238 Jun 21 11:25 nginx5.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 72 Jun 21 10:44 nginx.conf
drwx------ 2 user1 g1 62 Jun 21 11:53 user1
drwx------ 2 user2 g2 62 Jun 21 11:53 user2
drwx------ 2 user3 g3 62 Jun 21 11:54 user3
4.12 管理节点过多导致的超时问题解决方法
默认情况下,Ansible将尝试并行管理playbook中所有的机器。对于滚动更新用例,可以使用serial关键字定义Ansible一次应管理多少主机,还可以将serial关键字指定为百分比,表示每次并行执行的主机数占总数的比例
范例:
#vim test_serial.yml
---
- hosts: all
serial: 2 #每次只同时处理2个主机
gather_facts: False
tasks:
- name: task one
comand: hostname
- name: task two
command: hostname
范例:
- name: test serail
hosts: all
serial: "20%" #每次只同时处理20%的主机
5 roles角色
角色是ansible自1.2版本引入的新特性,用于层次性、结构化地组织playbook。roles能够根据层次型结构自动装载变量文件、tasks以及handlers等。要使用roles只需要在playbook中使用include指令即可。简单来讲,roles就是通过分别将变量、文件、任务、模板及处理器放置于单独的目录中,并可以便捷地include它们的一种机制。角色一般用于基于主机构建服务的场景中,但也可以是用于构建守护进程等场景中
运维复杂的场景:建议使用 roles,代码复用度高
roles:多个角色的集合, 可以将多个的role,分别放至roles目录下的独立子目录中
roles/
mysql/
nginx/
tomcat/
redis/
5.1 Ansible Roles目录编排
roles目录结构如下所示 ( 圆圈代表文件,方框代表文件夹 )
每个角色,以特定的层级目录结构进行组织
角色写好之后就固定了,想要调用哪些角色就另外写yaml文件,其实也就是原来写的yaml文件拆开放到不同文件夹里,实现模块化
roles目录结构:
playbook.yml
roles/
project/
tasks/
files/
vars/
templates/
handlers/
default/ #默认变量
meta/ #元数据
Roles各目录作用
roles/project/ :项目名称,有以下子目录
- files/ :存放由copy或script模块等调用的文件
- templates/:template模块查找所需要模板文件的目录
- tasks/:定义task,role的基本元素,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
- handlers/:至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
- vars/:定义变量,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要在此文件中通过include进行包含
- meta/:定义当前角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系,至少应该包含一个名为main.yml的文件,其它文件需在此文件中通过include进行包含
- default/:设定默认变量时使用此目录中的main.yml文件,比vars的优先级低
5.2 创建 role
创建role的步骤
1 创建以roles命名的目录
2 在roles目录中分别创建以各角色名称命名的目录,如webservers等
3 在每个角色命名的目录中分别创建files、handlers、meta、tasks、templates和vars目录;用不到
的目录可以创建为空目录,也可以不创建
4 在playbook文件中,调用各角色
针对大型项目使用Roles进行编排
范例:roles的目录结构
nginx-role.yml
roles/
└── nginx
├── files
│ └── main.yml
├── tasks
│ ├── groupadd.yml
│ ├── install.yml
│ ├── main.yml
│ ├── restart.yml
│ └── useradd.yml
└── vars
└── main.yml
5.3 playbook调用角色
调用角色方法1:
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- mysql
- memcached
- nginx
调用角色方法2:
键role用于指定角色名称,后续的k/v用于传递变量给角色
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
roles:
- mysql
- {
role: nginx, username: nginx }
调用角色方法3:
还可基于条件测试实现角色调用
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
roles:
- {
role: nginx, username: nginx, when: ansible_distribution_major_version
== '7' }
#只有7版本时才调用
5.4 roles 中 tags 使用
#nginx-role.yml, 贴标签后挑标签来执行
---
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- {
role: nginx ,tags: [ 'nginx', 'web' ] ,when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6" }
- {
role: httpd ,tags: [ 'httpd', 'web' ] }
- {
role: mysql ,tags: [ 'mysql', 'db' ] }
- {
role: mariadb ,tags: [ 'mariadb', 'db' ] } ansible-playbook --tags="nginx,httpd,mysql" nginx-role.yml
5.5 实战案例
5.5.1 案例1:实现 httpd 角色
#创建角色相关的目录,默认在/etc/ansible/roles
mkdir -pv /data/ansible/roles/httpd/{
tasks,handlers,files}
#创建角色相关的文件
cd /data/ansible/roles/httpd/
#main.yml 是task的入口文件
vim tasks/main.yml
- include: group.yml
- include: user.yml
- include: install.yml
- include: config.yml
- include: index.yml
- include: service.yml
vim tasks/group.yml
- name: create apache group
group: name=apache system=yes gid=80
vim tasks/user.yml
- name: create apache user
user: name=apache system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin home=/var/www/ uid=80 group=apache
vim tasks/install.yml
- name: install httpd package
yum: name=httpd
vim tasks/config.yml
- name: config file
copy: src=httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/ backup=yes
notify: restart
vim tasks/index.yml
- name: index.html
copy: src=index.html dest=/var/www/html/
vim tasks/service.yml
- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
vim handlers/main.yml
- name: restart
service: name=httpd state=restarted
#在files目录下准备两个文件
ls files/
httpd.conf index.html
tree /data/ansible/roles/httpd/
/data/ansible/roles/httpd/
├── files
│ ├── httpd.conf
│ └── index.html
├── handlers
│ └── main.yml
└── tasks
├── config.yml
├── group.yml
├── index.yml
├── install.yml
├── main.yml
├── service.yml
└── user.yml
3 directories, 10 files
#在playbook中调用角色
vim /data/ansible/role_httpd.yml
---
# httpd role
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- httpd
#运行playbook
ansible-playbook /data/ansible/role_httpd.yml
mkdir -pv /data/ansible
5.5.2 案例2:实现 nginx 角色
mkdir -pv /data/ansible/roles/nginx/{
tasks,handlers,templates,vars}
#创建task文件
cd /data/ansible/roles/nginx/
vim tasks/main.yml
- include: install.yml
- include: config.yml
- include: index.yml
- include: service.yml
vim tasks/install.yml
- name: install
yum: name=nginx
vim tasks/config.yml
- name: config file for centos7
template: src=nginx7.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
when: ansible_distribution_major_version=="7"
notify: restart
- name: config file for centos8
template: src=nginx8.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
when: ansible_distribution_major_version=="8"
notify: restart
vim tasks/index.yml
- name: index.html
copy: src=roles/httpd/files/index.html dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/
vim tasks/service.yml
- name: start service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
#创建handler文件
cat handlers/main.yml
- name: restart
service: name=nginx state=restarted
#创建两个template文件
cat templates/nginx7.conf.j2
...省略...
user {
{
user}};
worker_processes {
{
ansible_processor_vcpus+3}}; #修改此行
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
...省略...
cat templates/nginx8.conf.j2
...省略...
user nginx;
worker_processes {
{
ansible_processor_vcpus**3}}; #修改此行
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
...省略...
#创建变量文件
vim vars/main.yml
user: daemon
#目录结构如下
tree /data/ansible/roles/nginx/
/data/ansible/roles/nginx/
├── handlers
│ └── main.yml
├── tasks
│ ├── config.yml
│ ├── file.yml
│ ├── install.yml
│ ├── main.yml
│ └── service.yml
├── templates
│ ├── nginx7.conf.j2
│ └── nginx8.conf.j2
└── vars
└── main.yml
4 directories, 9 files
#在playbook中调用角色
vim /data/ansible/role_nginx.yml
---
#nginx role
- hosts: websrvs
roles:
- role: nginx
#运行playbook
ansible-playbook /data/ansible/role_nginx.yml
5.5.3 案例3:实现 memcached 角色
mkdir -pv /data/ansible/roles/memcached/{
tasks,templates}
cd /data/ansible/roles/memcached
vim tasks/main.yml
- include: install.yml
- include: config.yml
- include: service.yml
vim tasks/install.yml
- name: install
yum: name=memcached
vim tasks/config.yml
- name: config file
template: src=memcached.j2 dest=/etc/sysconfig/memcached
vim tasks/service.yml
- name: service
service: name=memcached state=started enabled=yes
#//整除
vim templates/memcached.j2
PORT="11211"
USER="memcached"
MAXCONN="1024"
CACHESIZE="{
{ansible_memtotal_mb//4}}"
OPTIONS=""
tree /data/ansible/roles/memcached/
/data/ansible/roles/memcached/
├── tasks
│ ├── config.yml
│ ├── install.yml
│ ├── main.yml
│ └── service.yml
└── templates
└── memcached.j2
2 directories, 5 files
vim /data/ansible/role_memcached.yml
---
- hosts: appsrvs
roles:
- role: memcached
ansible-play /data/ansible/role_memcached.yml
5.5.4 案例4:实现 mysql 5.6 的角色
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/files/my.cnf
[mysqld]
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
user=mysql
symbolic-links=0
datadir=/data/mysql
innodb_file_per_table=1
log-bin
pid-file=/data/mysql/mysqld.pid
[client]
port=3306
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
[mysqld_safe]
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/files/secure_mysql.sh
#!/bin/bash
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql_secure_installation <[root@ansible ~]#chmod +x /data/ansible/roles/mysql/files/secure_mysql.sh
[root@ansible ~]#ls /data/ansible/roles/mysql/files/
my.cnf mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz secure_mysql.sh
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/main.yml
- include: install.yml
- include: group.yml
- include: user.yml
- include: unarchive.yml
- include: link.yml
- include: data.yml
- include: config.yml
- include: service.yml
- include: path.yml
- include: secure.yml
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/install.yml
- name: install packages
yum: name=libaio,perl-Data-Dumper,perl-Getopt-Long
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/group.yml
- name: create mysql group
group: name=mysql gid=306
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/user.yml
- name: create mysql user
user: name=mysql uid=306 group=mysql shell=/sbin/nologin system=yes
create_home=no home=/data/mysql
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/unarchive.yml
- name: copy tar to remote host and file mode
unarchive: src=mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz dest=/usr/local/
owner=root group=root
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/link.yml
- name: mkdir /usr/local/mysql
file: src=/usr/local/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 dest=/usr/local/mysql state=link
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/data.yml
- name: data dir
shell: chdir=/usr/local/mysql/ ./scripts/mysql_install_db --
datadir=/data/mysql --user=mysql
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/config.yml
- name: config my.cnf
copy: src=my.cnf dest=/etc/my.cnf
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/service.yml
- name: service script
shell: /bin/cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server
/etc/init.d/mysqld;chkconfig --add mysqld;chkconfig mysqld on;/etc/init.d/mysqld start
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/path.yml
- name: PATH variable
copy: content='PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH' dest=/etc/profile.d/mysql.sh
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/roles/mysql/tasks/secure.yml
- name: secure script
script: secure_mysql.sh
[root@ansible ~]#tree /data/ansible/roles/mysql/
/data/ansible/roles/mysql/
├── files
│ ├── my.cnf
│ ├── mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
│ └── secure_mysql.sh
└── tasks
├── config.yml
├── data.yml
├── group.yml
├── install.yml
├── link.yml
├── main.yml
├── path.yml
├── secure.yml
├── service.yml
├── unarchive.yml
└── user.yml
2 directories, 14 files
[root@ansible ~]#cat /data/ansible/mysql_roles.yml
- hosts: dbsrvs
remote_user: root
roles:
- {
role: mysql,tags: ["mysql","db"]}
- {
role: nginx,tage: ["nginx","web"]}
[root@ansible ~]#ansible-playbook -t mysql /data/ansible/mysql_roles.yml
5.5.5 案例5 :实现多角色的选择
vim /data/ansible/role_httpd_nginx.yml
---
- hosts: websrvs
roles:
- {
role: httpd,tags: [httpd,web], when:
ansible_distribution_major_version=="7" }
- {
role: nginx,tags: [nginx,web], when:
ansible_distribution_major_version=="8" }
ansible-playbook -t nginx /data/ansible/role_httpd_nginx.yml
6 ansible 推荐学习资料
http://galaxy.ansible.com
https://galaxy.ansible.com/explore#/
http://github.com/
http://ansible.com.cn/
https://github.com/ansible/ansible
https://github.com/ansible/ansible-examples