2019.5.8,总结下今天学的知识:
python数据类型,最常用的有 int 和 float,python中对数据进行运算如果超了数值范围,不会报错,而会自动转换成能表示数值范围更大的数据类型。所以,在python中进行数据运算时,并不用担心数值的范围,算就完了。值得注意的是,整除运算是:// ,如:5//4 = 1; 次方运算可以用pow()函数运算,也可以用**号运算。如求2的3次方,可以用pow(2,3)计算,2**3也行。还有就是虚数了,2+3j表示一个虚数,2是实部,3是虚部。之所以用 j 不用 i 是因为在工程领域中虚数是用 j 表示的,而不是数学中常用的 i 。运算时有加法减法和乘法,“实部+实部,虚部+虚部”即可。
列表的使用,直接附上代码:
1 # Author:K 2 3 names = ["zhangsan","lisi","wangwu","zhaoliu"] 4 5 print(names) 6 print(names[0]) #查找列表第一个位置的数据 7 print(names.index("zhangsan")) #根据数据找到index 8 9 names.insert(2,"aaa") #将“aaa”插入到位置2中 10 print(names) 11 12 names.insert(names.index("aaa")+1,"bbb") #将“bbb”插入到“aaa”的后面 13 print(names) 14 15 names.remove("aaa") #删除“aaa” 16 print(names) 17 18 names.pop(names.index("bbb")) #删除“bbb” 19 print(names) 20 21 names.append("wuqi") #添加“wuqi”到列表末端 22 print(names) 23 24 print(names[1:3]) #取names[1] names[2] “左闭右开” 25 print(names[:len(names)-1]) #除了倒数第一个不取,其他全取出来 26 print(names[:]) #取列表的全部数据,冒号前省略是从0开始,冒号后省略是默认取到最后一位 27 28 names.insert(names.index("lisi")+1,"lisi") 29 print(names) 30 print(names.count("lisi")) #count函数计算列表中指定数据有多少个 31 print(len(names)) #len函数计算列表长度 32 33 import copy 34 names2 = copy.deepcopy(names) #深copy,完全克隆一份。 35 # names2 = names[:] #浅copy 36 print(names2) 37 38 print(names2[0:-1:2]) #步长为2进行切片 39 40 for i in names2: #循环打印列表的数据 41 print(i) 42 43 #浅copy用处 44 person = ["name",["saving",100]] 45 p1 = person[:] 46 p2 = person[:] 47 48 p1[0] = "Husband" 49 p2[0] = "Wife" 50 51 p1[1][1] = 50 52 print(person) 53 print(p1) 54 print(p2)
元祖和列表的区别:
元祖只能“查”,不能“增删改”,也叫只读列表。只有两个方法 count() 和 index()。
列表的应用之“购物车程序”:
1 # Author:K 2 shopping_list = [["thinkpad x1",11000],["dell XPS13",10000],["HUAWEI P30",6000]] 3 4 while True: 5 salary = input("Your salary:") 6 if salary.isdigit(): #判断输入的是否是一个数字 7 salary = int(salary) #转成整型数据,方便与价格进行比较 8 buying_list = [] #创建已买商品列表 9 balance = salary 10 while True: 11 print("-----shopping list-----") 12 for index,commodity in enumerate(shopping_list): #enumerate方法可以取列表的下标 13 print(index, commodity) 14 print() 15 user_choice = input("Please choose commodity index you want to buy:") 16 if user_choice.isdigit(): 17 user_choice = int(user_choice) 18 if user_choice >= 0 and user_choice < len(shopping_list): 19 if balance >= shopping_list[user_choice][1]: 20 buying_list.append(shopping_list[user_choice]) 21 print("added [{name}] to your shopping cart!".format(name=shopping_list[user_choice][0])) 22 balance = balance - shopping_list[user_choice][1] #求出余额 23 print("Your current balance is \033[41;1m %s \033[0m" % balance) # \033[31;1m %s \033[0m 将%s显示为红色,41为红底 24 print("Your buying_list: {name}\n".format(name = buying_list)) #打印已购买商品 25 else: 26 exit("\033[31;1m Not sufficient funds! \033[0m") #余额不足 27 else: 28 print("The commodity index is not exist!") 29 elif user_choice == 'q': #输入q退出程序,并打印已买商品列表 30 exit("Your buying_list is :{name}\n".format(name = buying_list)) 31 else: 32 print("Invalid data!") 33 else: 34 print("Please input int number!!!") 35 continue
字符串常用操作:
1 # Author:K 2 string = 'ABC DEFG HIII' 3 4 print(string.isalpha()) #不包含空格。纯英文字符 5 print(string[string.find("DEFG"):]) 6 print("33.33".isdigit()) 7 print("\nKisI") 8 print("KisI".lstrip()) 9 10 p = str.maketrans("abcdefghijk","1234567890-") #加密 11 print("abcdeffffffg".translate(p))
字典的使用:
1 # Author:K 2 dict = dict.fromkeys([1,2,3],"Test") #创建一个字典,对应的值都为Test,但创建嵌套字典的时候不建议使用 3 print(dict) 4 5 info = { 6 "广东省":{ 7 "广州市":["番禺区","花都区","天河区"], 8 "云浮市":["郁南县","新兴县"] 9 }, 10 "甘肃省":{ 11 "兰州市":["榆中县","和平县"] 12 } 13 } 14 15 info["北京市"] = ["沙河区"] #添加以“北京市”为key的值,这个值是列表 16 print(info) 17 18 del info["北京市"] #删除“北京市” 19 print(info) 20 21 info["广东省"] = ["深圳市"] #将“广东省”下的市改成“深圳市”,之前的数据全部删除 22 print(info) 23 24 print(info.get("广东省")) #取key为“广东省”的值 25 26 b = {1:2,3:4,"广东省":{"深圳市":"南山区"}} 27 info.update(b) #合并 info 字典和 b 字典,若 b 字典有与 info 相同的关键字,则更新,其他不同的关键字则添加到 info 字典中 28 print(info) 29 30 print(info.items()) #将字典转换成列表并打印
上回的作业2:
三级菜单
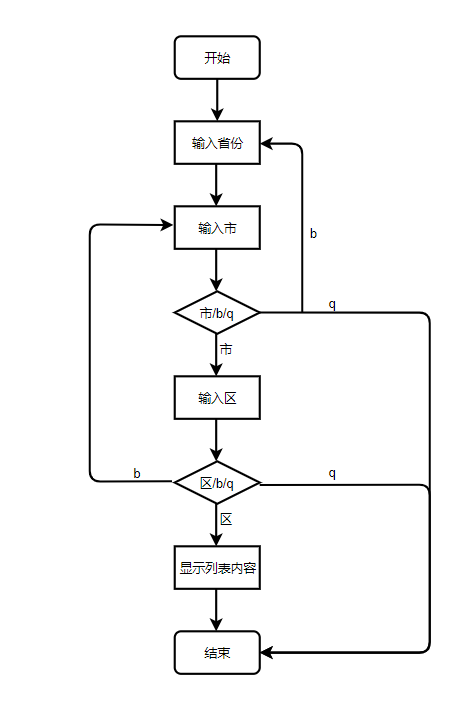
需求:按要求输入,找到省,然后找到市,再找到区,再找到对应区的列表按b返回上一级菜单,按q退出程序。
流程图如下:
1 # Author:K 2 info = { 3 "广东省":{ 4 "广州市":{ 5 "番禺区":["吃的","喝的"], 6 "花都区":["玩的","工作"], 7 "天河区":[] 8 }, 9 "云浮市":{ 10 "城中区":["吃的","喝的"], 11 } 12 }, 13 "甘肃省":{ 14 "兰州市":{ 15 "城关区":[], 16 "安宁区":[] 17 }, 18 } 19 } 20 21 while True: 22 for information in info: 23 print(information) 24 choice_province = input("请输入要查询的省:") 25 while True: 26 for city in info[choice_province]: 27 print(city) 28 choice_city = input("请输入要查询的市:") 29 if choice_city == 'b': 30 break 31 elif choice_city == 'q': 32 exit("已退出程序!") 33 while True: 34 for district in info[choice_province][choice_city]: 35 print(district) 36 choice_district = input("请输入要查询的区:") 37 if choice_district == 'b': 38 break 39 elif choice_district == 'q': 40 exit("已退出程序!") 41 while True: 42 for things in info[choice_province][choice_city][choice_district]: 43 print(things) 44 lastlevel_choice = input("最后一层,按b返回,按q退出") 45 if lastlevel_choice == 'b': 46 break 47 elif lastlevel_choice == 'q': 48 exit("已退出程序!")
这段代码太low,后续学了函数之后应该可以优化!
作业:购物车的优化
用户入口:
1.商品信息存在文件里
2.已购商品,余额记录。
商家入口:
1.可以添加商品,修改商品价格