MATLAB05:绘制高级图表
目录
二维图表
折线图
对数坐标系图线
双y轴图线
极坐标图线
统计图表
直方图
柱状图
饼图
阶梯图和针状图:绘制离散数字序列
其它统计图表
绘制图形
三维图表
二维图与三维图间的关系
二维图转为三维图
三维图转换为二维图
三维图的绘制
绘制三维图前的准备工作:使用meshgrid()生成二维网格
绘制三维线
绘制三维面
绘制三维图形的等高线
绘制三维体
三维图的视角与打光
调整视角
调整打光
学习一门技术最好的方式就是阅读官方文档,可以查看MATLAB官方文档
二维图表
折线图
| 函数 | 图形描述 |
|---|---|
loglog() |
x轴和y轴都取对数坐标 |
semilogx() |
x轴取对数坐标,y轴取线性坐标 |
semilogy() |
x轴取线性坐标,y轴取对数坐标 |
plotyy() |
带有两套y坐标轴的线性坐标系 |
ploar() |
极坐标系 |
对数坐标系图线
下面例子演示对数坐标系图线:
x = logspace(-1,1,100); y = x.^2;
subplot(2,2,1);
plot(x,y);
title('Plot');
subplot(2,2,2);
semilogx(x,y);
title('Semilogx');
subplot(2,2,3);
semilogy(x,y);
title('Semilogy');
subplot(2,2,4);
loglog(x, y);
title('Loglog');
![]()
对数坐标系可以加上网格,以区分线性坐标系与对数坐标系.
set(gca, 'XGrid','on');
![]()
双y轴图线
plotyy()的返回值为数组[ax,hlines1,hlines2],其中:
ax为一个向量,保存两个坐标系对象的句柄.hlines1和hlines2分别为两个图线的句柄.
x = 0:0.01:20;
y1 = 200*exp(-0.05*x).*sin(x);
y2 = 0.8*exp(-0.5*x).*sin(10*x);
[AX,H1,H2] = plotyy(x,y1,x,y2);
set(get(AX(1),'Ylabel'),'String','Left Y-axis')
set(get(AX(2),'Ylabel'),'String','Right Y-axis')
title('Labeling plotyy');
set(H1,'LineStyle','--'); set(H2,'LineStyle',':');
![]()
极坐标图线
% 螺旋线
x = 1:100; theta = x/10; r = log10(x);
subplot(1,4,1); polar(theta,r);
% 花瓣
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi); r = cos(4*theta);
subplot(1,4,2); polar(theta, r);
% 五边形
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi, 6); r = ones(1,length(theta));
subplot(1,4,3); polar(theta,r);
% 心形线
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi); r = 1-sin(theta);
subplot(1,4,4); polar(theta , r);
![]()
统计图表
| 函数 | 图形描述 |
|---|---|
hist() |
直方图 |
bar() |
二维柱状图 |
pie() |
饼图 |
stairs() |
阶梯图 |
stem() |
针状图 |
直方图
使用hist()绘制直方图,语法如下:
hist(x,nbins)
其中:
x表示原始数据nbins表示分组的个数
x = randn(1,1000);
subplot(2,1,1);
hist(x,10);
title('Bins = 10');
subplot(2,1,2);
hist(x,50);
title('Bins = 50');
![]()
柱状图
-
使用
bar()和bar3()函数分别绘制二维和三维直方图x = [1 2 5 4 8]; y = [x;1:5]; subplot(1,3,1); bar(x); title('A bargraph of vector x'); subplot(1,3,2); bar(y); title('A bargraph of vector y'); subplot(1,3,3); bar3(y); title('A 3D bargraph');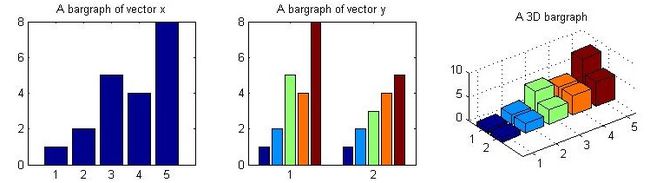
hist主要用于查看变量的频率分布,而bar主要用于查看分立的量的统计结果. -
使用
barh()函数可以绘制纵向排列的柱状图x = [1 2 5 4 8]; y = [x;1:5]; barh(y); title('Horizontal');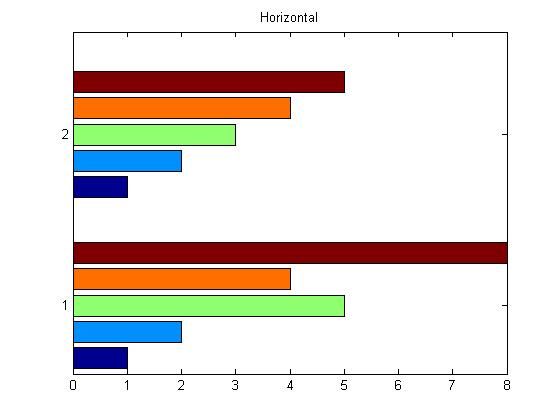
-
向
bar()传入'stack'参数可以让柱状图以堆栈的形式画出.x = [1 2 5 4 8]; y = [x;1:5]; bar(y,'stacked'); title('Stacked');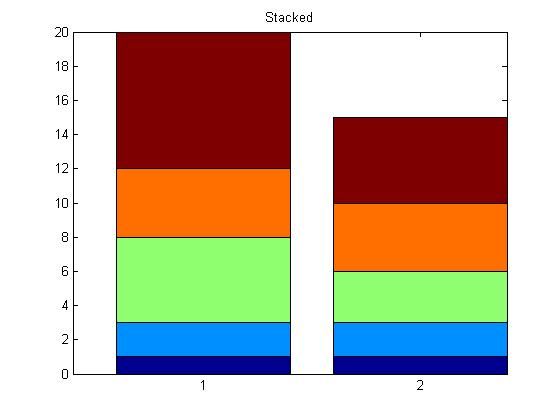
饼图
使用pie()和pie3()可以绘制二维和三维的饼图.向其传入一个bool向量表示每一部分扇区是否偏移.
a = [10 5 20 30];
subplot(1,3,1); pie(a);
subplot(1,3,2); pie(a, [0,0,0,1]);
subplot(1,3,3); pie3(a, [0,0,0,1]);
![]()
阶梯图和针状图:绘制离散数字序列
stairs()和stem()函数分别用来绘制阶梯图和针状图,用于表示离散数字序列.
x = linspace(0, 4*pi, 40); y = sin(x);
subplot(1,2,1); stairs(y);
subplot(1,2,2); stem(y);
![]()
其它统计图表
-
boxplot()load carsmall boxplot(MPG, Origin);
![]()
-
errorbar()x=0:pi/10:pi; y=sin(x); e=std(y)*ones(size(x)); errorbar(x,y,e)
![]()
绘制图形
MATLAB也可以绘制简单的图形,使用fill()函数可以对区域进行填充.
t =(1:2:15)'*pi/8; x = sin(t); y = cos(t);
fill(x,y,'r'); axis square off;
text(0,0,'STOP','Color', ...
'w', 'FontSize', 80, ...
'FontWeight','bold', ...
'HorizontalAlignment', 'center');
![]()
三维图表
二维图与三维图间的关系
二维图转为三维图
在MATLAB中,所有的图都是三维图,二维图只不过是三维图的一个投影.点击图形窗口的Rotate 3D按钮,即可通过鼠标拖拽查看该图形的三维视图.
![]()
三维图转换为二维图
使用imagesc()函数可以将三维图转换为二维俯视图,通过点的颜色指示高度.
[x, y] = meshgrid(-3:.2:3,-3:.2:3); z = x.^2 + x.*y + y.^2;
subplot(1, 2, 1)
surf(x, y, z);
subplot(1, 2, 2)
imagesc(z);
![]()
使用colorbar命令可以在生成的二维图上增加颜色与高度间对应关系的图例,使用colormap命令可以改变配色方案.具体细节请参考官方文档
![]()
三维图的绘制
绘制三维图前的准备工作:使用meshgrid()生成二维网格
我们对一个二维网格矩阵应用函数z=f(x,y)z=f(x,y)z=f(x,y)才能得到三维图形,因此在得到三维数据之前我们应当使用meshgrid()函数生成二维网格矩阵.
meshgrid()函数将输入的两个向量进行相应的行扩充和列扩充以得到两个增广矩阵,对该矩阵可应用二元函数.
x = -2:1:2;
y = -2:1:2;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y)
Z = X.^2 + Y.^2
我们得到了生成的二维网格矩阵如下:
X =
-2 -1 0 1 2
-2 -1 0 1 2
-2 -1 0 1 2
-2 -1 0 1 2
-2 -1 0 1 2
Y =
-2 -2 -2 -2 -2
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1
0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2 2
Z =
8 5 4 5 8
5 2 1 2 5
4 1 0 1 4
5 2 1 2 5
8 5 4 5 8
绘制三维线
使用plot3()函数即可绘制三维面,输入应为三个向量.
x=0:0.1:3*pi; z1=sin(x); z2=sin(2.*x); z3=sin(3.*x);
y1=zeros(size(x)); y3=ones(size(x)); y2=y3./2;
plot3(x,y1,z1,'r',x,y2,z2,'b',x,y3,z3,'g'); grid on;
xlabel('x-axis'); ylabel('y-axis'); zlabel('z-axis');
![]()
下面例子绘制了两个螺旋线:
subplot(1, 2, 1)
t = 0:pi/50:10*pi;
plot3(sin(t),cos(t),t)
grid on; axis square;
subplot(1, 2, 2)
turns = 40*pi;
t = linspace(0,turns,4000);
x = cos(t).*(turns-t)./turns;
y = sin(t).*(turns-t)./turns;
z = t./turns;
plot3(x,y,z); grid on;
![]()
绘制三维面
使用mesh()和surf()命令可以绘制三维面,前者不会填充网格而后者会.
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5; y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
subplot(1,2,1); mesh(X,Y,Z);
subplot(1,2,2); surf(X,Y,Z);
![]()
绘制三维图形的等高线
使用contour()和contourf()函数可以绘制三维图形的等高线,前者不会填充网格而后者会.
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y);
Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
subplot(1,2,1);
mesh(X,Y,Z); axis square;
subplot(1,2,2);
contour(X,Y,Z); axis square;
![]()
向contour()函数传入参数或操作图形句柄可以改变图像的细节:
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5; y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y); Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
subplot(1,3,1); contour(Z,[-.45:.05:.45]); axis square;
subplot(1,3,2); [C,h] = contour(Z); clabel(C,h); axis square;
subplot(1,3,3); contourf(Z); axis square;
![]()
使用meshc()和surfc()函数可以在绘制三维图形时绘制其等高线.
x = -3.5:0.2:3.5; y = -3.5:0.2:3.5;
[X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y); Z = X.*exp(-X.^2-Y.^2);
subplot(1,2,1); meshc(X,Y,Z);
subplot(1,2,2); surfc(X,Y,Z);
![]()
绘制三维体
使用patch()函数可以绘制三维体.
v = [0 0 0; 1 0 0 ; 1 1 0; 0 1 0; 0.25 0.25 1; 0.75 0.25 1; 0.75 0.75 1; 0.25 0.75 1];
f = [1 2 3 4; 5 6 7 8; 1 2 6 5; 2 3 7 6; 3 4 8 7; 4 1 5 8];
subplot(1,2,1);
patch('Vertices', v, 'Faces', f, 'FaceVertexCData', hsv(6), 'FaceColor', 'flat');
view(3); axis square tight; grid on;
subplot(1,2,2);
patch('Vertices', v, 'Faces', f, 'FaceVertexCData', hsv(8), 'FaceColor','interp');
view(3); axis square tight; grid on
![]()
三维图的视角与打光
调整视角
使用view()函数可以调整视角,view()函数接受两个浮点型参数,分别表示两个方位角azimuth和elevation.
![]()
sphere(50); shading flat;
material shiny;
axis vis3d off;
view(-45,20);
![]()
调整打光
使用light()函数可以对三维图形进行打光,并返回光源的句柄.
[X, Y, Z] = sphere(64); h = surf(X, Y, Z);
axis square vis3d off;
reds = zeros(256, 3); reds(:, 1) = (0:256.-1)/255;
colormap(reds); shading interp; lighting phong;
set(h, 'AmbientStrength', 0.75, 'DiffuseStrength', 0.5);
L1 = light('Position', [-1, -1, -1])
通过对光源的句柄进行操作可以修改光源的属性
set(L1, 'Position', [-1, -1, 1]);
set(L1, 'Color', 'g');
![]()