Java面向对象(下)
包
定义:为了便于管理大型软件系统中数目众多的类,解决类的命名冲突问题,Java引入包(package)机制,提供类的多重命名空间。
- package语句作为java源文件的第一条语句,指明该文件的中定义的类所在的包,若缺省该语句,则指定为无名包。
- java编译器把包对应于文件系统的目录管理,package语句中,用“.”来指明包目录的层次。
- 如:package com.sxt;则该文件中所有的类位于.\com\sxt目录下
- 如果想将一个类放入包中,在这个源文件第一句话写package
- 必须保证该类的class文件位于正确的目录下
- 必须将class文件的最上层包的父目录位于classpath下
- 执行一个类的时候也要写全包名
实例
package lee;
public class Hello{
public static void main(String [] args){
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
package lee;
import lee.sub.Apple;
public class HelloTest{
public static void main(String [] args){
Hello hello =new Hello();
Apple a = new Apple();
}
}
package lee.sub;
public class Apple{}
编译语句:javac -d . 类名.java
这样的好处是这个类里引入的包,直接就可以将先关的.class 文件生成到相应的文件夹下。
Java常用包
Java.lang:这个包下包含了java语言的核心类,如string、Math、System和Thread类,使用这个包下面的类无需使用import语句导入,系统会自动导入这个包下的所有类。
访问控制
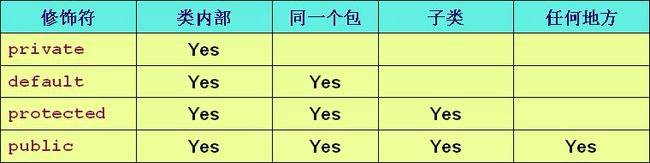
- java权限修饰符public、protected、private置于类的成员定义前,用来限制其他对象对该类对象成员的访问权限
- 对于class的权限修饰只可以用public(类可以在任意地方被访问)和default(类只可以被同一个包内部的类访问)
类的继承与权限访问
- java中使用extends关键字实现类的继承机制
- 通过继承,子类自动拥有了基类superclass的所有成员(成员变量和方法)
- java只支持单继承,不允许多继承
实例代码:
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age ){
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
}
class Student extends Person{
private String school;
public String getSchool(){
return school;
}
public void setSchool(String school){
this.school = school;
}
}
public class TestPerson{
public static void main(String args[]){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("Jason");
student.setAge(28);
student.setSchool("清华大学");
System.out.println(student.getName());
System.out.println(student.getAge());
System.out.println(student.getSchool());
}
}
输出结果:
继承中的构造方法
- 子类的构造过程中必须调用其基类的构造方法;
- 子类可以在自己的构造方法中使用super调用基类的构造方法;
- 如果调用super必须写在子类构造方法的第一行;
- 如果子类的构造方法中没有显示的调用基类的构造方法,则系统默认调用基类无参数的构造方法;
- 如果子类构造方法中既没有显示的调用基类的构造方法,而基类中又没有无参数的构造方法,则编译出错。
实例代码:
class SuperClass{
private int n;
SuperClass(){
System.out.println("SuperClass()");
}
SuperClass(int n){
System.out.println("SuperClass(" + n +")");
this.n = n;
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass{
private int n;
SubClass(int n){
System.out.println("SubClass(" + n +")");
this.n = n;
}
SubClass(){
super(300);
System.out.println("SubClass()");
}
}
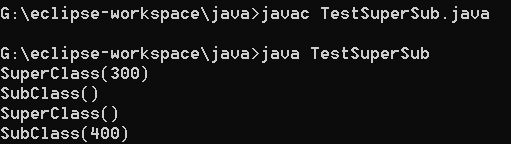
public class TestSuperSub{
public static void main(String arg[]){
SubClass sc1 = new SubClass();
SubClass sc2 = new SubClass(400);
}
}
输出结果:
方法的重写
- 在子类中可以根据需要对从基类中继承来的方法进行重写;
- 重写方法必须和被重写方法具有相同的方法名称、参数列表和返回类型;
- 重写方法不能使用比被重写方法更加严格的访问权限。
实例代码:
class Person{
public String name;
public int age;
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age ){
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "My Name: " + name + "\n" + "Age: " + age;
}
}
class Student extends Person{
private String school;
public String getSchool(){
return school;
}
public void setSchool(String school){
this.school = school;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "My name: " + name + "\n" + "Age: " + age + "\n" + "My school: " + school;
}
}
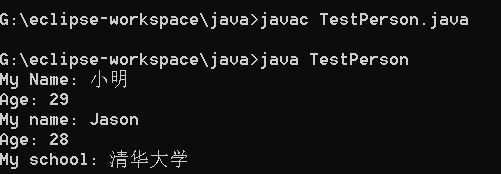
public class TestPerson{
public static void main(String args[]){
Student student = new Student();
Person person = new Person ();
person.setName("小明");
person.setAge(29);
student.setName("Jason");
student.setAge(28);
student.setSchool("清华大学");
System.out.println(person.getInfo());
System.out.println(student.getInfo());
}
}
输出结果:
Object类
- Object类是所有java类的根基类;
- 如果在类的声明中未使用extends关键字指明其基类,则默认基类为Object类
toString方法
- Object类中定义有public String toString()方法,其返回值是String类型,描述当前对象的有关信息;
- 在进行String与其他类型数据的连接操作时,如:System.out.println();将自动调用该对象的toString()方法;
- 可以根据需要在用户自定义类型中重写toString()方法。
实例代码:
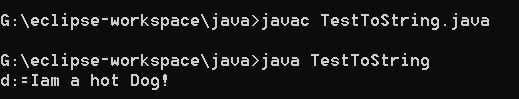
public class TestToString{
public static void main(String [] args){
Dog d = new Dog();
System.out.println("d:=" + d);
}
}
class Dog{
public String toString(){
return "Iam a hot Dog!";
}
}
输出结果:
equals方法
- Object类中定义有
- Public boolean equals(Object obj)方法,提供定义对象是否“相等”的逻辑;
- Object的equals方法定义为:X.equals(y)当x和y是同一个对象的应用时返回true否则返回false;
- jdk提供了一些类,如String、Date等,重写了Object的equals方法,调用这些类的equals方法,X.equals(y),当x和y所引用的对象是同一类对象且属性内容相等时,返回true否则返回false;
- 可以根据需要在用户自定义类型中重写equals方法。
实例代码:
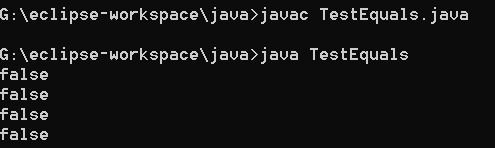
public class TestEquals{
public static void main(String [] args){
Cat c1 = new Cat(1,2,3);
Cat c2 = new Cat(1,2,5);
System.out.println(c1 == c2);
System.out.println(c1.equals(c2));
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(c1.equals(c2));
}
}
class Cat{
int color;
int height;
int weight;
public Cat(int color, int height, int weight){
this.color = color;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == null)return false;
else{
if(obj instanceof Cat){
Cat c = (Cat)obj;
if(c.color == this.color && c.height == this.height && c.weight == this.weight){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
输出结果:
对象转型(casting)
- 一个基类的引用类型变量可以“指定”其子类的对象;
- 一个基类的引用不可以访问其子类对象新增加的成员(属性和方法);
- 可以使用引用变量instanceof类名来判断该引用类型变量所“指向”的对象是否属于该类或该类的子类;
- 子类的对象可以当做基类的对象来使用称作向上转型(upcasting),反之称为向下转型(downcasting)。
动态绑定(多态)
- 动态绑定是指在执行期间而非编译期间判断所引用对象的实际类型,根据其实际的类型调用相应的方法
三个必要条件:
- 要有继承;
- 要有重写;
- 父类引用指向子类对象;
实例代码:
class Animal{
private String name;
Animal(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void enjoy(){
System.out.println("叫声...");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
private String eyesColor;
Cat(String n, String c){
super(n);
eyesColor = c;
}
public void enjoy(){
System.out.println("猫叫声...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
private String furColor;
Dog(String n, String c){
super(n);
furColor = c;
}
public void enjoy(){
System.out.println("狗叫声...");
}
}
class Lady{
private String name;
private Animal pet;
Lady(String name, Animal pet){
this.name = name;
this.pet = pet;
}
public void myPetEnjoy(){
pet.enjoy();
}
}
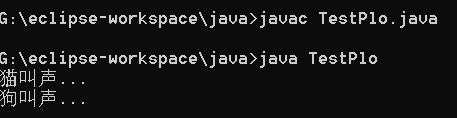
public class TestPlo{
public static void main(String args[]){
Cat c = new Cat("Catname","blue");
Dog d = new Dog("Dogname","black");
Lady l1 = new Lady("11",c);
Lady l2 = new Lady("12",d);
l1.myPetEnjoy();
l2.myPetEnjoy();
}
}输出结果:
抽象类
- 用abstract关键字来修饰一个类的时候,这个类叫做抽象类,用abstract来修饰一个方法的时候,这个方法叫做抽象方法;
- 含有抽象方法的类必须被声明为抽象类,抽象类必须被继承,抽象方法必须被重写;
- 抽象类不能被实例化;
- 抽象方法只需声明,而不需实现。
接口
- 接口是抽象方法和常量值的定义的集合;
- 从本质上讲,接口是一种特殊的抽象类;
- 多个无关类可以实现同一个接口;
- 一个类可以实现多个无关类的接口;
- 与继承关系类似,接口与实现类之间存在多态性;
- 用interface修饰的原因是解决多重继承(一个子类有多个父类)的问题,每个父类之间有多个并且重复的成员变量;
- 接口是由static修饰的变量就不属于专门对象;
- 修饰符可以是public或省略,如果省略了public访问控制符,则默认采用包权限访问控制符,即只有在相同包结构下才可以访问该接口;
- 如果一个变量是静态而且是final类型的就可以定义为一个接口。