简单介绍Java中的Unsafe类
概述
sun.misc.Unsafe类旨在仅由核心Java库(JUC包下的类)而非标准用户使用的底层机制,即不推荐开发者使用,但并不妨碍我们对该类的了解。Unsafe可以使Java直接进行内存的操作、实例化类与对实例进行属性操作、提供CAS操作等底层操作,下文将对这些功能进行简单的案例演示,实际开发中依旧不推荐使用,只作为Java体系中的一个知识点了解即可。
Unsafe实例构建
内部类创建Unsafe类实例时都是调用其静态方法getUnsafe(),具体源码如下:
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
Class var0 = Reflection.getCallerClass();
// 通过ClassLoader判断时内部还是外部调用
if (!VM.isSystemDomainLoader(var0.getClassLoader())) {
throw new SecurityException("Unsafe");
} else {
return theUnsafe;
}
}
由于Unsafe是为了内部使用而设计的,所以如果我们直接在程序中调用getUnsafe()时会检测类加载器是内部还是外部,外部将直接报SecurityException异常。当然,我们可以使用反射来获得实例:
Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
f.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) f.get(null);
Unsafe对象操作
Java中开发构建实例的方法主要有构造函数、反射、实现Cloneable接口及序列化4种,而Unsafe构建属于官方不推荐使用的,例子如下:
public class UnsafeTest {
private int number;
public UnsafeTest() {
this.number = 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
instanceOperate();
}
public static void instanceOperate() throws InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
UnsafeTest test = (UnsafeTest) unsafe.allocateInstance(UnsafeTest.class);
// 输出0
System.out.println(test.number);
}
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
try {
Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
f.setAccessible(true);
return (Unsafe) f.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
除了实例化对象外,Unsafe还可直接操作类属性,如下:
public static void instanceOperate() throws InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
UnsafeTest test = (UnsafeTest) unsafe.allocateInstance(UnsafeTest.class);
// 输出0
System.out.println(test.number);
Field numberField = UnsafeTest.class.getDeclaredField("number");
unsafe.putInt(test, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(numberField), 1);
// 输出1
System.out.println(test.number);
}
上例中的UnsafeTest类是没有get与set方法的,Unsafe对属性number的操作是直接到内存根据对象字段元数据获取偏移,找到实例number的属性数据进行操作的,实例数据可参考对象布局(JOL)。
Unsafe操作堆外内存
当应用程序用完了JVM上的可用内存,最终可能会迫使GC进程过于频繁地运行。理想情况下,我们需要一个特殊的内存区域,堆外且不受GC控制。Unsafe类中的allocateMemory()方法能够从堆中分配大对象,这意味着GC和JVM将不会看到并考虑此内存。不过该方法分配的内存需要手动管理,并在不再需要时使用freeMemory()方法正确回收。
例:通过Unsafe直接在内存上创建数组UnsafeTest.OffHeapArray
static class OffHeapArray {
private final static int BYTE = 1;
private long size;
// 内存起始地址
private long address;
/**
* 创建内存数组
*
* @param size 分配的内存大小
*/
public OffHeapArray(long size) {
this.size = size;
// 分配内存地址
address = getUnsafe().allocateMemory(size * BYTE);
}
/**
* 设置起始内存偏移指定下标后的位置值
*
* @param i 数组下标,内存偏移量
* @param value
*/
public void set(long i, byte value) {
getUnsafe().putByte(address + i * BYTE, value);
}
/**
* 根据数组下标idx计算在内存中的位置,然后获取数组值
*
* @param idx 数组下标,用于计算元素内存相对数组起始地址的偏移量
* @return
*/
public int get(long idx) {
return getUnsafe().getByte(address + idx * BYTE);
}
public long size() {
return size;
}
public void freeMemory() {
getUnsafe().freeMemory(address);
}
}
// 堆外内存测试方法
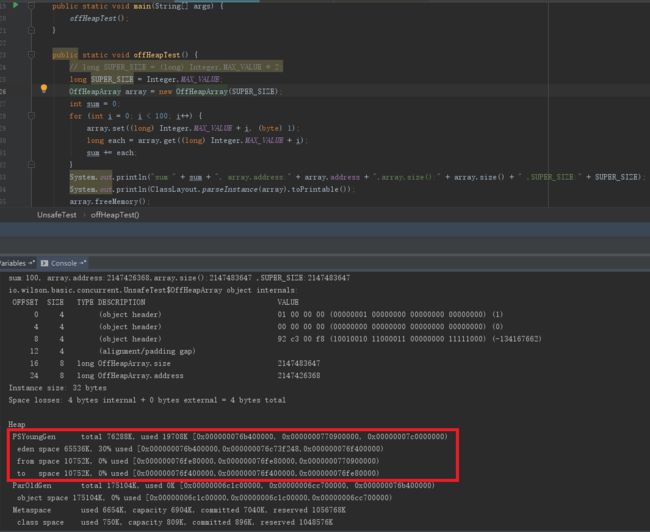
public static void offHeapTest() {
// long SUPER_SIZE = (long) Integer.MAX_VALUE * 2;
long SUPER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
OffHeapArray array = new OffHeapArray(SUPER_SIZE);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
array.set((long) Integer.MAX_VALUE + i, (byte) 1);
long each = array.get((long) Integer.MAX_VALUE + i);
sum += each;
}
System.out.println("sum:" + sum + ", array.address:" + array.address + ",array.size():" + array.size() + " ,SUPER_SIZE:" + SUPER_SIZE);
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(array).toPrintable());
array.freeMemory();
}
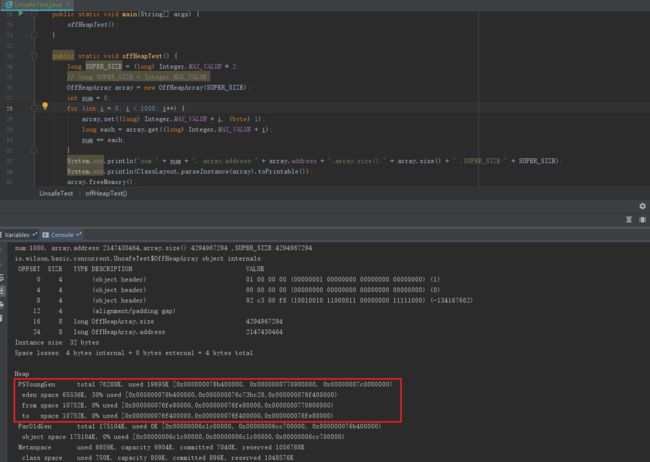
OffHeapArray是一个通过直接在内存上存取数组的实现类,通过Unsafe的allocateMemory(size)方法获取到分配的内存起始地址,根据分配的内存起始地址计算数组下标在内存中的实际地址。单看以上程序是无法看出分配的内存是在堆上还是堆外的,可以通过参数-VM:-PrintGCDetails并更改分配的内存大小size后对比size更改前后的堆大小变化。
CAS操作
java.concurrent包中的CAS操作(如AtomicInteger)使用了Unsafe中的compareAndSwap()方法以提供最佳性能。与Java中的标准悲观同步机制相比,该操作广泛用于无锁算法中,该算法可以利用CAS处理器指令提供极大的加速。以下为使用Unsafe的CAS操作实现的一个计数器范例:
public class CASCounter {
private Unsafe unsafe;
private volatile long val = 0;
// 字段val在对象实例内存起始地址的偏移量
private long offset;
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, InterruptedException {
CASCounter casCounter = new CASCounter();
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1000);
IntStream.range(0, 1000)
.forEach(i -> executorService.execute(casCounter::increment));
executorService.shutdown();
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 输出1000
System.out.println(casCounter.val);
}
private Unsafe getUnsafe() {
try {
Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
f.setAccessible(true);
return (Unsafe) f.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public CASCounter() throws NoSuchFieldException {
unsafe = getUnsafe();
// objectFieldOffset:获取
offset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(CASCounter.class.getDeclaredField("val"));
}
public void increment() {
long oldVal = val;
while (!unsafe.compareAndSwapLong(this, offset, oldVal, oldVal + 1)) {
oldVal = val;
}
}
public long getVal() {
return val;
}
}
Unsafe线程切换
Unsafe类中提供了park()与unpark()两个方法让JVM用来进行上下文切换线程。当线程正在等待某个操作时,JVM可以使用不安全类中的park()方法来阻塞该线程,该方法类似于Object.wait()方法,不过它调用的是本地操作系统代码,因此利用某些体系结构细节来获得最佳性能。当线程被阻塞并需要再次使其可运行时,JVM使用unpark()方法。可以在一些线程池应用中看到这些方法调用,如ForkJoinPool、LockSupport、Exchanger等。
附代码代码
public class UnsafeTest {
private int number;
public UnsafeTest() {
this.number = 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
offHeapTest();
}
public static void offHeapTest() {
// long SUPER_SIZE = (long) Integer.MAX_VALUE * 2;
long SUPER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
OffHeapArray array = new OffHeapArray(SUPER_SIZE);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
array.set((long) Integer.MAX_VALUE + i, (byte) 1);
long each = array.get((long) Integer.MAX_VALUE + i);
sum += each;
}
System.out.println("sum:" + sum + ", array.address:" + array.address + ",array.size():" + array.size() + " ,SUPER_SIZE:" + SUPER_SIZE);
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(array).toPrintable());
array.freeMemory();
}
public static void instanceOperate() throws InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
UnsafeTest test = (UnsafeTest) unsafe.allocateInstance(UnsafeTest.class);
// 输出0
System.out.println(test.number);
Field numberField = UnsafeTest.class.getDeclaredField("number");
unsafe.putInt(test, unsafe.objectFieldOffset(numberField), 1);
// 输出1
System.out.println(test.number);
}
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
try {
Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
f.setAccessible(true);
return (Unsafe) f.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
static class OffHeapArray {
private final static int BYTE = 1;
private long size;
// 内存起始地址
private long address;
/**
* 创建内存数组
*
* @param size 分配的内存大小
*/
public OffHeapArray(long size) {
this.size = size;
// 分配内存地址
address = getUnsafe().allocateMemory(size * BYTE);
}
/**
* 设置起始内存偏移指定下标后的位置值
*
* @param i 数组下标,内存偏移量
* @param value
*/
public void set(long i, byte value) {
getUnsafe().putByte(address + i * BYTE, value);
}
/**
* 根据数组下标idx计算在内存中的位置,然后获取数组值
*
* @param idx 数组下标,用于计算元素内存相对数组起始地址的偏移量
* @return
*/
public int get(long idx) {
return getUnsafe().getByte(address + idx * BYTE);
}
public long size() {
return size;
}
public void freeMemory() {
getUnsafe().freeMemory(address);
}
}
}