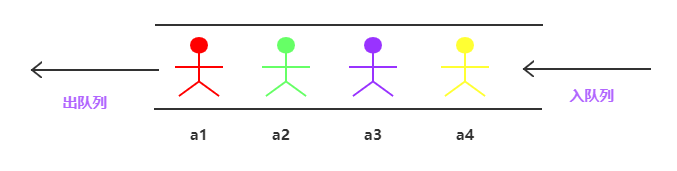【Java】数据结构——队列(图文)
文章目录
-
- 简介
- 一、顺序队列(循环队列)
-
- 介绍
-
- 1.存储结构
- 2.初始化队列
- 3.入队
- 4.出队
- 5.查看队头
- 6.遍历队列
- 7.通过下标查看
- 8.队列长度
- 9.判满
- 10.判空
- 完整代码
- 测试
- 二、链式队列
-
- 介绍
-
- 1.存储结构和初始化
- 2. 入队列
- 3. 出队列
- 4. 队列长度
- 5. 判空
- 6. 查看队头
- 7.通过索引删除结点
- 8.通过索引访问结点
- 9.遍历结点
- 完整代码
- 测试
简介
1.定义:队列是一种操作受限的的线性表,只允许在表的一端进行插入,在另一端进行删除。
2.特性: 先进先出
3.关键字:
3.1.队头(head):允许删除的一端,又称队首。
3.2.队尾(tail):允许插入的一端。
3.3.空队列:不含任何元素的空表。
一、顺序队列(循环队列)
介绍
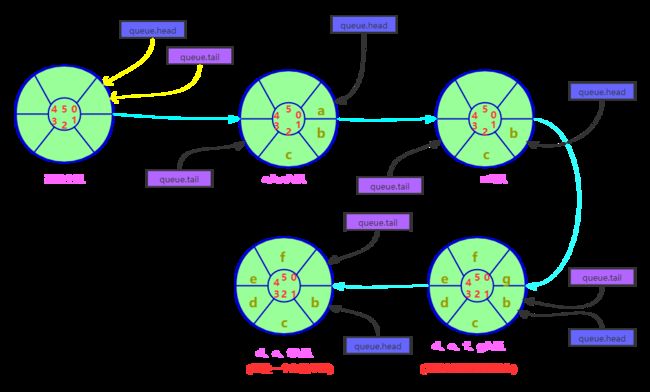
初始时:Q.head=Q.tail队首指针加1:Q.head=(Q.head+1)%capacity
队尾指针减1:Q.tail=(Q.tail+1)%capacity
队列长度:(Q.head+capacity-Q.tail)%capacity
队满条件:(Q.head+1)%capacity==Q.tail
队空条件:Q.head=Q.tail
队列元素个数:(Q.tail-Q.head+capacity)%capacity
(注:capacity为容量、head为队头指针、tail为队尾指针)
1.存储结构
public class ArrayQueue<T> {
//容量
private int capacity;
//队列头部
private int head;
//队列尾部
private int tail;
//队列数组(用户存储结点)
private T[]queue;
}
2.初始化队列
代码:
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity+1;
this.queue= newArray(capacity+1);
this.head=0;
this.tail=0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T[] newArray(int size) {
return (T[]) new Object[size];
}
3.入队
代码:
public boolean add(T o){
queue[tail]=o;
if (this.isFull()){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue full");
}
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
4.出队
代码:
public T remove(int i) {
if (i != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can only remove head of queue");
if (this.isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
T removed = queue[head];
queue[head] = null;
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
return removed;
}
5.查看队头
思路:
返回head 下标对应的值即可。
代码:
public T peek(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
}
return queue[head];
}
6.遍历队列
思路:
遍历打印数组。
初始下标为:head
队列长度:(tail+capacity-head)%capacity+1
代码:
public void list(){
if (isEmpty()){
System.err.println("the queue is empty!");
return;
}
for (int i = head; i <this.size()+head ; i++) {
System.out.println(queue[i%this.capacity]);
}
}
7.通过下标查看
代码:
public T get(int i) {
int size = size();
if (i < 0 || i >= size) {
final String msg = "Index " + i + ", queue size " + size;
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(msg);
}
int index = (head + i) % capacity;
return queue[index];
}
8.队列长度
代码:
public int size(){
return (this.tail+this.capacity-this.head)%this.capacity;
}
9.判满
代码:
public boolean isFull(){
return (tail+1)%this.capacity==head;
}
10.判空
代码:
public boolean isEmpty(){
return tail==head;
}
完整代码
package com.qingfeng.queue.template;
/**
* @param
*/
public class ArrayQueue<T> {
private int capacity;
private int head;
private int tail;
private T[] queue;
/**
* @param capacity
*/
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity + 1;
this.queue = newArray(capacity + 1);
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
/**
* @param size
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T[] newArray(int size) {
return (T[]) new Object[size];
}
/**
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return (tail + 1) % this.capacity == head;
}
/**
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return tail == head;
}
/**
* @param o
*/
public boolean add(T o) {
queue[tail] = o;
if (this.isFull()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue full");
}
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
/**
* @return
*/
public T remove(int i) {
if (i != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can only remove head of queue");
if (this.isEmpty())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
T removed = queue[head];
queue[head] = null;
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
return removed;
}
/**
*
*/
public void list() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.err.println("the queue is empty!");
return;
}
for (int i = head; i < this.size() + head; i++) {
System.out.println(queue[i % this.capacity]);
}
}
/**
* @return
*/
public T peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
}
return queue[head];
}
public int size() {
return (this.tail + this.capacity - this.head) % this.capacity;
}
public T get(int i) {
int size = size();
if (i < 0 || i >= size) {
final String msg = "Index " + i + ", queue size " + size;
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(msg);
}
int index = (head + i) % capacity;
return queue[index];
}
}
测试
代码:
public class ArrayQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User liuxin = new User(2018, "liuxin");
User yanghai = new User(2019, "yanghai");
User dahai = new User(2020, "dahai");
/*----------------------------------------------------------*/
ArrayQueue<User> queue = new ArrayQueue<User>(5);
queue.add(liuxin);
queue.add(yanghai);
queue.add(dahai);
queue.list();
/*----------------------------------------------------------*/
System.out.println();
System.out.println(queue.get(1));
/*----------------------------------------------------------*/
System.out.println();
queue.remove(0);
queue.list();
}
}
运行结果:
User{
id=2018, name='liuxin'}
User{
id=2019, name='yanghai'}
User{
id=2020, name='dahai'}
User{
id=2019, name='yanghai'}
User{
id=2019, name='yanghai'}
User{
id=2020, name='dahai'}
Process finished with exit code 0
二、链式队列
介绍
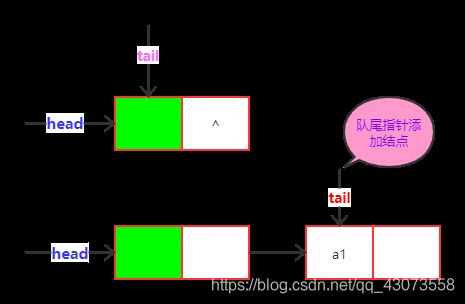
1.队列的链式表示称为链队列。
2.适用场合:适合数据变动比较大的情形。
3.优点:不会存在溢出的现象。
1.存储结构和初始化
代码:
public class LinkedQueue<T> {
private Node head;//队头
private Node tail;//队尾
public LinkedQueue() {
this.head = new Node(null);//初始化队头为空
this.tail = this.head;
}
private class Node {
private T element;//保存结点
private Node next;//存放下一个结点
public Node(T element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
}
2. 入队列
代码:
public boolean add(T o) {
if (o == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("the pointer is null!");
}
Node newNode = new Node(o);
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
return true;
}
3. 出队列
代码:
public T deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty!");
}
Node del = this.head.next;
Node temp = this.head.next;
temp = head;
head = temp.next;
return del.element;
}
4. 队列长度
代码:
public int size() {
Node temp = head.next;
int length = 0;
while (temp != null) {
length++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return length;
}
5. 判空
代码:
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.head == this.tail;
}
6. 查看队头
代码:
public T peek() {
return (T) this.head.next.element;
}
7.通过索引删除结点
代码:
public T remove(int i) {
Node temp = head;
int j = 1;
while (temp.next != null && j < i) {
temp = temp.next;
j++;
}
Node remove = temp.next;
temp.next = temp.next.next;
return remove.element;
}
8.通过索引访问结点
代码:
public T get(int i) {
Node temp = head;
int j = 1;
while (temp.next != null && j <= i) {
temp = temp.next;
j++;
}
return temp.element;
}
9.遍历结点
代码:
public void list() {
for (int i = 1; i <= this.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(this.get(i));
}
}
完整代码
package com.qingfeng.queue.template;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class LinkedQueue<T> {
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public LinkedQueue() {
this.head = new Node(null);
this.tail = this.head;
}
/**
* @param o
* @return
*/
public boolean add(T o) {
if (o == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("the pointer is null!");
}
Node newNode = new Node(o);
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
return true;
}
/**
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.head == this.tail;
}
public int size() {
Node temp = head.next;
int length = 0;
while (temp != null) {
length++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return length;
}
/**
* @return
*/
public T deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty!");
}
Node del = this.head.next;
Node temp = this.head.next;
temp = head;
head = temp.next;
return del.element;
}
/**
* @param i
* @return
*/
public T remove(int i) {
Node temp = head;
int j = 1;
while (temp.next != null && j < i) {
temp = temp.next;
j++;
}
Node remove = temp.next;
temp.next = temp.next.next;
return remove.element;
}
/**
* @param i
* @return
*/
public T get(int i) {
Node temp = head;
int j = 1;
while (temp.next != null && j <= i) {
temp = temp.next;
j++;
}
return temp.element;
}
/**
*
*/
public void list() {
for (int i = 1; i <= this.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(this.get(i));
}
}
/**
* @return
*/
public T peek() {
return (T) this.head.next.element;
}
private class Node {
private T element;
private Node next;
public Node(T element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
}
测试
代码:
public class LinkedQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedQueue<String> queue = new LinkedQueue<>();
/*-------------------------------------------------------*/
System.out.println("-----testEnQueue-----");
queue.add("1");
queue.add("2");
queue.add("3");
queue.add("4");
queue.list();
/*-------------------------------------------------------*/
System.out.println("-----testSize-----");
System.out.println("the size of queue is:"+queue.size());
/*-------------------------------------------------------*/
System.out.println("-----testRemove-----");
String s = queue.remove(3);
System.out.println("remove:"+s);
queue.list();
/*-------------------------------------------------------*/
System.out.println("-----testGet-----");
String s2 = queue.get(2);
System.out.println(s2);
/*-------------------------------------------------------*/
System.out.println("-----testDeQueue-----");
System.out.println(queue.deQueue());
System.out.println(queue.deQueue());
System.out.println(queue.deQueue());
}
}
运行结果:
-----testEnQueue-----
1
2
3
4
-----testSize-----
the size of queue is:4
-----testRemove-----
remove:3
1
2
4
-----testGet-----
2
-----testDeQueue-----
1
2
4
Process finished with exit code 0