SpringMVC启动原理
本文从API角度入手,带你了解SpringMVC启动的原理。
作者:南桥畂翊
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/57677a2c6ebd
來源:简书
简书著作权归作者所有,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处。
ServletContainerInitializer
在web容器启动时为提供给第三方组件机会做一些初始化的工作,例如注册servlet或者filtes等,servlet规范中通过ServletContainerInitializer实现此功能。
每个框架要使用ServletContainerInitializer就必须在对应的jar包的META-INF/services 目录创建一个名为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,文件内容指定具体的ServletContainerInitializer实现类,
那么,当web容器启动时就会运行这个初始化器做一些组件内的初始化工作。
一般伴随着ServletContainerInitializer一起使用的还有HandlesTypes注解,通过HandlesTypes可以将感兴趣的一些类注入到ServletContainerInitializerde的onStartup方法作为参数传入。
Tomcat容器的ServletContainerInitializer机制的实现,主要交由Context容器和ContextConfig监听器共同实现,
ContextConfig监听器负责在容器启动时读取每个web应用的WEB-INF/lib目录下包含的jar包的META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer,以及web根目录下的META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer,
通过反射完成这些ServletContainerInitializer的实例化,然后再设置到Context容器中,最后Context容器启动时就会分别调用每个ServletContainerInitializer的onStartup方法,并将感兴趣的类作为参数传入。
image.png
基本的实现机制如图,首先通过ContextConfig监听器遍历每个jar包或web根目录的META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件,根据读到的类路径实例化每个ServletContainerInitializer;然后再分别将实例化好的ServletContainerInitializer设置进Context容器中;最后Context容器启动时分别调用所有ServletContainerInitializer对象的onStartup方法。
假如读出来的内容为com.seaboat.mytomcat.CustomServletContainerInitializer,则通过反射实例化一个CustomServletContainerInitializer对象,这里涉及到一个@HandlesTypes注解的处理,被它标明的类需要作为参数值传入到onStartup方法。
如下例子:
@HandlesTypes({ HttpServlet.class,Filter.class })
public class CustomServletContainerInitializer implements
ServletContainerInitializer {
public void onStartup(Set> classes, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
for(Class c : classes)
System.out.println(c.getName());
}
}
其中@HandlesTypes标明的HttpServlet和Filter两个class被注入到了onStartup方法。
所以这个注解也是需要在ContextConfig监听器中处理。
前面已经介绍了注解的实现原理,由于有了编译器的协助,我们可以方便地通过ServletContainerInitializer的class对象中获取到HandlesTypes对象,进而再获取到注解声明的类数组,如
HandlesTypes ht =servletContainerInitializer.getClass().getAnnotation(HandlesTypes.class);
Class[] types = ht.value();
即可获取到HttpServlet和Filter的class对象数组,后面Context容器调用CustomServletContainerInitializer对象的onStartup方法时作为参数传入。
至此,即完成了servlet规范的ServletContainerInitializer初始化器机制。
SpringServletContainerInitializer
上面提到了META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer,在Springspring-web-4.3.0.RELEASE.jar Jar包中可以找到该文件,内容如下:
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
下面,我们就来详细讲解下SpringServletContainerInitializer。
首先看下API中的描述:
Servlet 3.0 ServletContainerInitializer被设计为使用Spring的WebApplicationInitializer SPI来支持Servlet容器的基于代码的配置,而不是传统的基于web.xml的配置(也可能两者结合使用)。
一、运作机制
假设类路径中存在spring-web模块的JAR包,SpringServletContainerInitializer将被加载并实例化,并且在容器启动期间由Servlet 3.0容器调用onStartup方法。
这是通过JAR Services API ServiceLoader.load(Class)方法(检测Spring-Web模块的META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer配置文件)实现的。
二、与web.xml结合使用
Web应用程序可以选择通过web.xml中的metadata-complete属性(它控制扫描Servlet注解的行为)
或通过web.xml中的web fragments(i.e. jars)被允许执行扫描ServletContainerInitializer)
来限制Servlet容器在启动时扫描的类路径。
当使用这个特性时,可以通过添加"spring_web"到web.xml里的web fragments列表来启用SpringServletContainerInitializer,
如下所示:
some_web_fragment
spring_web
servlet3.X中的metadata-complete属性
在Servlet3.X的web.xml中可以设置metadata-complete属性,例如:如果设置
metadata-complete="true",会在启动时不扫描注解(annotation)。如果不扫描注解的话,用注解进行的配置就无法生效,例如:@WebServlet
三、与Spring的WebApplicationInitializer的关系
Spring的WebApplicationInitializer SPI仅由一个方法组成:WebApplicationInitializer.onStartup(ServletContext)。声明与ServletContainerInitializer.onStartup(Set, ServletContext)非常相似:简单地说,SpringServletContainerInitializer负责将ServletContext实例化并委托给用户定义的WebApplicationInitializer实现。然后每个WebApplicationInitializer负责完成初始化ServletContext的实际工作。下面的onStartup文档中详细介绍了委托的具体过程。
四、注意事项
一般来说,这个类应该被视为WebApplicationInitializer SPI的支持。利用这个容器初始化器也是完全可选的:虽然这个初始化器在所有的Servlet 3.0+运行环境下被加载和调用,但用户可以选择是否提供WebApplicationInitializer实现。如果未检测到WebApplicationInitializer类型,则此SpringServletContainerInitializer将不起作用。
请注意,除了这些类型是在spring-web模块JAR中提供的,使用这个SpringServletContainerInitializer和WebApplicationInitializer与Spring MVC没有任何“捆绑”。相反,它们可以被认为是通用的,以便于简化ServletContext基于代码的配置。换句话说,任何servlet, listener, 或者filter都可以在WebApplicationInitializer中注册,而不仅仅是Spring MVC特定的组件。
SpringServletContainerInitializer既不是为扩展而设计的。它应该被认为是一个内部类型,WebApplicationInitializer是面向用户的SPI。
好啦,现在对SpringServletContainerInitializer有了一个比较透彻的了解,下面我们来看一下唯一的onStartup方法。
将ServletContext委托给类路径中的WebApplicationInitializer实现。
因为这个类声明了@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class),所以
Servlet 3.0+容器会自动扫描类路径下Spring的WebApplicationInitializer接口的实现,并将所有这些类型的集合提供给这个方法的webAppInitializerClasses参数。
如果在类路径下找不到WebApplicationInitializer实现,则此方法不会有任何操作。将发出INFO级别的日志消息,通知用户ServletContainerInitializer确实已被调用,但没有找到WebApplicationInitializer实现。
假设检测到一个或多个WebApplicationInitializer类型,它们将被实例化(如果存在@Order注释或实现Ordered接口,则对其进行排序)。然后,将调用每个实例WebApplicationInitializer.onStartup(ServletContext)方法,并委派ServletContext,以便每个实例都可以注册和配置Servlet,例如Spring的DispatcherServlet,listeners(如Spring的ContextLoaderListener),或者其他Servlet API组件(如filters)。
下面是SpringServletContainerInitializer的源码:
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(Set> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
// WebApplicationInitializer实现如果存在`@Order`注释或实现`Ordered`接口,则对其进行排序,故这里使用LinkedList
List initializers = new LinkedList();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
// 有时候,Servlet容器提供给我们的可能是无效的webAppInitializerClass
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) waiClass.newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
WebApplicationInitializer
下面我们来看下WebApplicationInitializerAPI文档的相关介绍。
在Servlet 3.0+环境中实现该接口,以便以编程方式配置ServletContext,而不是以传统的基于web.xml的方法。WebApplicationInitializer SPI的实现将被SpringServletContainerInitializer(它本身是由Servlet 3.0容器自动引导的)自动检测到。
Example
基于XML的方式
大多数Spring用户构建Web应用程序时需要注册Spring的DispatcherServlet。作为参考,通常在WEB-INF/web.xml中按如下方式:
dispatcher
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml
1
dispatcher
/
基于代码的方式
DispatcherServlet注册逻辑与上述等效
public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
XmlWebApplicationContext appContext = new XmlWebApplicationContext();
appContext.setConfigLocation("/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml");
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher =
container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(appContext));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
}
}
作为上述的替代方法,您还可以继承自org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer。
正如您所看到的,使用Servlet 3.0的ServletContext.addServlet方法,我们注册了一个DispatcherServlet的实例。
这种风格简单明了。不用关心处理init-params等,只是普通的JavaBean风格的属性和构造函数参数。在将其注入到DispatcherServlet之前,您可以根据需要自由创建和使用Spring应用程序上下文。
大多数Spring Web组件已经更新,以支持这种注册方式。你会发现DispatcherServlet,FrameworkServlet,ContextLoaderListener和DelegatingFilterProxy现在都支持构造函数参数。Servlet 3.0 ServletContext API允许以编程方式设置init-params,context-params等。
完全基于代码的配置方法
在上面的例子中,WEB-INF/web.xml以WebApplicationInitializer形式的代码替换,但dispatcher-config.xml配置仍然是基于XML的。WebApplicationInitializer非常适合与Spring的基于代码的@Configuration类一起使用。以下示例演示了使用Spring的AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext代替XmlWebApplicationContext进行重构,以及使用用户定义的@Configuration类AppConfig和DispatcherConfig,而不是Spring XML文件。这个例子也超出了上面的例子来演示根应用上下文的典型配置和ContextLoaderListener的注册:
public class MyWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
// Create the 'root' Spring application context
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootContext =
new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
rootContext.register(AppConfig.class);
// Manage the lifecycle of the root application context
container.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootContext));
// Create the dispatcher servlet's Spring application context
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext dispatcherContext =
new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
dispatcherContext.register(DispatcherConfig.class);
// Register and map the dispatcher servlet
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher =
container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(dispatcherContext));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
}
}
作为上述的替代方法,您还可以继承自org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer。注意,WebApplicationInitializer的实现类会被自动检测到。
Ordering WebApplicationInitializer execution
WebApplicationInitializer实现类可以有选择地在类上使用Spring的@Order注解,也可以实现Spring的Ordered接口。如果是这样,初始化程序将在调用之前排序。这为用户提供了确保Servlet容器初始化顺序的机制。使用此功能的情况很少,因为典型的应用程序可能会将所有容器初始化集中在一个WebApplicationInitializer中。
注意事项
web.xml版本
WEB-INF/web.xml和WebApplicationInitializer的使用不是互斥的; 例如,web.xml可以注册一个servlet,而WebApplicationInitializer可以注册另一个。 Initializer甚至可以通过诸如ServletContext.getServletRegistration(String)之类的方法来修改在web.xml中执行的注册。但是,如果应用程序中存在WEB-INF/web.xml,则其版本属性必须设置为"3.0"或更高,否则Servlet容器将忽略ServletContainerInitializer的引导。
下面我们来看一组WebApplicationInitializer的实现类:
继承关系如下:
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
|
| —— AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer
|
| —— AbstractContextLoaderInitializer
|
| —— WebApplicationInitializer
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer实现类的基类,用于注册配置了@Configuration/@Component注解标记的配置类的DispatcherServlet。
具体的实现类需要实现getRootConfigClasses()和getServletConfigClasses()以及getServletMappings()方法。更多的方法由AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer提供。这是使用基于Java配置应用程序的首选方法。
下面是AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer的源码:
public abstract class AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
/**
* 创建要提供给`ContextLoaderListener`的**根应用程序上下文**。
*
* 返回的上下文委托给`ContextLoaderListener.ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)`,
* 并将作为`DispatcherServlet`应用程序上下文的父上下文来建立。
*
* 因此,它通常包含中间层服务,数据源等。
*
* 该方法创建一个`AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext`,并为其提供由`getRootConfigClasses()`返回的配置类。如果`getRootConfigClasses()`返回Null,则不会创建根应用上下文。
*/
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
Class[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
rootAppContext.register(configClasses);
return rootAppContext;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 创建一个**Servlet应用上下文**以提供给`DispatcherServlet`。
*
* 返回的上下文被委托给Spring的`DispatcherServlet.DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)`方法。
*
* 因此,它通常包含控制器,视图解析器,locale解析器和其他Web相关的bean。
*
* 该实现创建一个`AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext`,为其提供由`getServletConfigClasses()`返回的配置类。
*/
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext servletAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
Class[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
servletAppContext.register(configClasses);
}
return servletAppContext;
}
/**
* 指定要提供给根应用上下文的`@Configuration`或`@Component`注解标记的配置类。
*/
protected abstract Class[] getRootConfigClasses();
/**
* 指定要提供给Dispatcher Servlet应用上下文的`@Configuration`或`@Component`注解标记的配置类。
*/
protected abstract Class[] getServletConfigClasses();
}
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer
org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer实现的基类,在ServletContext中注册DispatcherServlet。
具体的实现类需要实现createServletApplicationContext()和getServletMappings()方法,两者都由registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)调用。
进一步的自定义可以通过重写customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic)方法来实现。
由于此类继承了AbstractContextLoaderInitializer抽象类,具体实现类也需要实现createRootApplicationContext()来设置父级根应用上下文。如果不需要根应用上下文,createRootApplicationContext()返回null即可。
下面看下源码:
public abstract class AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractContextLoaderInitializer {
/**
* The default servlet name. Can be customized by overriding {@link #getServletName}.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME = "dispatcher";
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
super.onStartup(servletContext);
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}
/**
* 针对给定的Servlet上下文注册一个`DispatcherServlet`。
*
* 该方法将创建一个名称为由`getServletName()`指定的`DispatcherServlet`,
* 并使用从`createServletApplicationContext()`返回的Servlet应用上下文对其进行初始化,
* 并将其映射到从`getServletMappings()`返回的`pattern`。
*
* 进一步的自定义可以通过重写`customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic)`或`createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)`来实现。
*
* @param servletContext 注册servlet的上下文
*/
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
// DispatcherServlet被注册的名称
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return empty or null");
// 创建Servlet应用上下文,参见AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer的实现
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext,
"createServletApplicationContext() did not return an application " +
"context for servlet [" + servletName + "]");
// 将Servlet应用上下文以委托给DispatcherServlet
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
Assert.notNull(registration,
"Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'." +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
customizeRegistration(registration);
}
/**
* 返回`DispatcherServlet`被注册的名称。 默认值为DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME。
*
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected String getServletName() {
return DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME;
}
/**
* 创建一个Servlet应用上下文以提供给`DispatcherServlet`。
* 返回的上下文被委托给Spring的`DispatcherServlet.DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)`。
*
* 因此,它通常包含控制器,视图解析器,locale解析器和其他Web相关的bean。
*
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected abstract WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext();
/**
* 使用指定的`WebApplicationContext`Servlet应用上下文创建`DispatcherServlet`(或由`FrameworkServlet`派生的其他类型的`dispatcher`)。
*
* 注意:从4.2.3开始允许返回任意`FrameworkServlet`的子类。
* 以前,它必须要返回一个`DispatcherServlet`或其子类。
*/
protected FrameworkServlet createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) {
return new DispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
}
/**
* Specify application context initializers to be applied to the servlet-specific
* application context that the {@code DispatcherServlet} is being created with.
*
* @see #createServletApplicationContext()
* @see DispatcherServlet#setContextInitializers
* @see #getRootApplicationContextInitializers()
* @since 4.2
*/
protected ApplicationContextInitializer[] getServletApplicationContextInitializers() {
return null;
}
/**
* 指定`DispatcherServlet`的servlet映射 - 例如"/", "/app"等
*
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected abstract String[] getServletMappings();
/**
* 指定添加到`ServletContext`,并映射到`DispatcherServlet`的过滤器。
*
* @return an array of filters or {@code null}
* @see #registerServletFilter(ServletContext, Filter)
*/
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
return null;
}
/**
* 将给定的过滤器添加到`ServletContext`并将其映射到`DispatcherServlet`,如下所示:
*
* - 1. 根据具体的类型选择默认的过滤器名称;
*
- 2. 异步支持是根据`asyncSupported`的返回值设置的;
*
- 3. 使用`dispatcher`类型为REQUEST,FORWARD,INCLUDE和ASYNC(取决于asyncSupported的返回值)创建过滤器映射
*
*
* 如果上面的默认值不合适,重写这个方法并直接用`ServletContext`注册过滤器。
*
* @param servletContext the servlet context to register filters with
* @param filter the filter to be registered
* @return the filter registration
*/
protected FilterRegistration.Dynamic registerServletFilter(ServletContext servletContext, Filter filter) {
// 获取要注册的filter的名称
String filterName = Conventions.getVariableName(filter);
Dynamic registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName, filter);
if (registration == null) {// 注册失败,名称追加序号并重试
int counter = -1;
while (counter == -1 || registration == null) {
counter++;
registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName + "#" + counter, filter);
Assert.isTrue(counter < 100,
"Failed to register filter '" + filter + "'." +
"Could the same Filter instance have been registered already?");
}
}
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
registration.addMappingForServletNames(getDispatcherTypes(), false, getServletName());
return registration;
}
private EnumSet getDispatcherTypes() {
return (isAsyncSupported() ?
EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.INCLUDE, DispatcherType.ASYNC) :
EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.INCLUDE));
}
/**
* `DispatcherServlet`和通过`getServletFilters()`添加的所有过滤器的异步支持标记位
*/
protected boolean isAsyncSupported() {
return true;
}
/**
* Optionally perform further registration customization once
* {@link #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)} has completed.
*
* @param registration the {@code DispatcherServlet} registration to be customized
* @see #registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext)
*/
protected void customizeRegistration(ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration) {
}
}
? 补充:registration.addMappingForServletNames
为当前FilterRegistration所代表的Filter添加一个具有指定Servlet名称和dispatcher类型的过滤器映射。过滤器映射按照添加的顺序进行匹配。根据isMatchAfter参数的值,来确定给定的过滤器映射在ServletContext(从中获取当前FilterRegistration)的任何声明的过滤器映射之前或之后匹配。如果这个方法被多次调用,每个连续的调用都会作用于前者。
Parameters:
dispatcherTypes - 过滤器映射的
dispatcher类型,如果要使用默认的DispatcherType.REQUEST,则为nullisMatchAfter - 如果给定的过滤器映射在任何声明的过滤器映射之后匹配,则为true;如果在从中获取此
FilterRegistration的ServletContext的任何声明的过滤器映射之前匹配,则为falseservletNames - 过滤器映射的Servlet名称
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer
WebApplicationInitializer实现类的基类,在ServletContext中注册ContextLoaderListener。需要由子类实现的唯一方法是createRootApplicationContext(),它在registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext)中被调用。
public abstract class AbstractContextLoaderInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
/** Logger available to subclasses */
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
/**
* 针对给定的`ServletContext`注册一个`ContextLoaderListener`。
* `ContextLoaderListener`使用从`createRootApplicationContext()`方法返回的根应用上下文进行初始化。
*
* @param servletContext the servlet context to register the listener against
*/
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
/**
* Create the "root" application context to be provided to the
* {@code ContextLoaderListener}.
* The returned context is delegated to
* {@link ContextLoaderListener#ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)} and will
* be established as the parent context for any {@code DispatcherServlet} application
* contexts. As such, it typically contains middle-tier services, data sources, etc.
* @return the root application context, or {@code null} if a root context is not
* desired
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer
*/
protected abstract WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext();
/**
* Specify application context initializers to be applied to the root application
* context that the {@code ContextLoaderListener} is being created with.
* @since 4.2
* @see #createRootApplicationContext()
* @see ContextLoaderListener#setContextInitializers
*/
protected ApplicationContextInitializer[] getRootApplicationContextInitializers() {
return null;
}
}
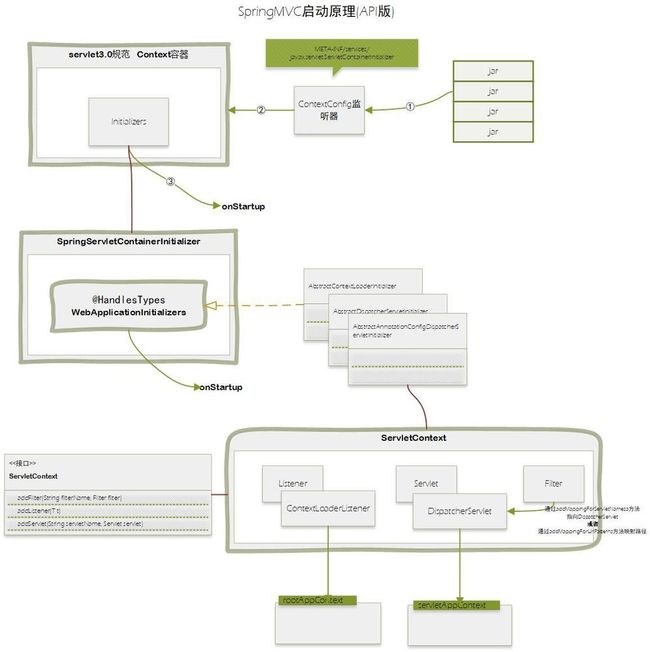
上面说了这么多,简单总结下。
如图所示:
SpringMVC启动原理(API版).jpg
ContextLoaderListener
上面提到了ContextLoaderListener,下面来说下这个类的作用。
ServletContextListener
首先看下javax.servlet.ServletContextListener
ServletContextListener为一个接口,声明如下:
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
ServletContextListener接口用于接收有关javax.servlet.ServletContext生命周期改变的通知事件。
为了接收这些通知事件,其实现类有如下三种方式声明:
- Web应用程序的部署描述符(deployment descriptor of the web application,web.xml)中声明
- 使用
javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener进行注释 - 通过
javax.servlet.ServletContext上定义的javax.servlet.ServletContext.addListener方法注册
这个接口实现类的contextInitialized方法按照它们的声明顺序被调用, 而contextDestroyed方法则以相反的顺序被调用。
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import java.util.EventListener;
/**
* 用于接收有关{@link javax.servlet.ServletContext}生命周期改变的通知事件的接口。
*
* 为了接收这些通知事件,实现类必须
* 在Web应用程序的部署描述符(deployment descriptor of the web application)中声明、
* 使用{@link javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener}进行注释,
* 或者通过{@link javax.servlet.ServletContext}上定义的{@link javax.servlet.ServletContext#addListener}方法注册。
*
* 这个接口实现类的{@link #contextInitialized}方法按照它们的声明顺序被调用,
* 而{@link #contextDestroyed}方法则以相反的顺序被调用。
*
* @see ServletContextEvent
* @since Servlet 2.3
*/
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
/**
* 接收Web应用程序初始化过程正在启动的通知。
*
* 在Web应用程序中的任何一个filter或servlet被初始化之前,所有ServletContextListeners都会收到上下文初始化的通知。
*
* @param sce 包含正在初始化的ServletContext的ServletContextEvent
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce);
/**
* 接收ServletContext即将关闭的通知。
*
* 在任何ServletContextListeners收到上下文销毁通知之前,所有servlet和filter都将被销毁。
*
* @param sce 包含正在被销毁的ServletContext的ServletContextEvent
*/
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce);
}
ContextLoaderListener
然后再看下ContextLoaderListener
声明如下:
public class ContextLoaderListener
extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
引导listener启动和关闭Spring的根WebApplicationContext。它只是
简单地委托给ContextLoader(继承)以及ContextCleanupListener(在contextDestroyed方法中调用)。
该listener应该在web.xml中的org.springframework.web.util.Log4jConfigListener(该类已标记过时)之后进行注册。
从Spring 3.1开始,ContextLoaderListener支持通过ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)构造函数注入根Web应用程序上下文, 从而允许在Servlet 3.0+环境中进行编程式配置。
ContextLoaderListener()
创建一个新的ContextLoaderListener, 它将基于"contextClass"和"contextConfigLocation" Servlet
当在web.xml中声明ContextLoaderListener为
创建的应用程序上下文将被注册到ServletContext属性WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE下, 并且当在此listener上调用contextDestroyed方法时,Spring应用程序上下文将被关闭。
ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context)
用给定的应用程序上下文创建一个新的ContextLoaderListener。 这个构造函数用于Servlet 3.0+,通过javax.servlet.ServletContext.addListener API可以实现基于实例的listeners注册。
上下文可能或尚未刷新。 如果
- (a)是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的实现.
- (b)尚未刷新(推荐的方法)
满足上面两个条件,则会发生以下情况:
- 如果给定的上下文还没有被分配一个id,则将被分配一个
ServletContext和ServletConfig对象将被委托给应用程序上下文customizeContext将被调用- 任何通过"contextInitializerClasses"
init-param指定的ApplicationContextInitializers将被应用。 refresh()将被调用
如果上下文已经被刷新或者没有实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,上述任何一种情况都不会发生。
创建的应用程序上下文将被注册到ServletContext属性WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE下, 并且当在此listener上调用contextDestroyed方法时,Spring应用程序上下文将被关闭。
import org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.ContextCleanupListener;
import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
/**
* 引导listener启动和关闭Spring的根{@link WebApplicationContext}。
* 简单地委托给{@link ContextLoader}以及{@link ContextCleanupListener}。
*
* 该listener应该在{@code web.xml}中的{@link org.springframework.web.util.Log4jConfigListener}之后进行注册,如果使用它的话。
*
* 从Spring 3.1开始,{@code ContextLoaderListener}支持通过{@link ContextLoaderListener#ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)}构造函数注入根Web应用程序上下文,
* 从而允许在Servlet 3.0+环境中进行编程式配置。
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @see #setContextInitializers
* @see org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer
* @see org.springframework.web.util.Log4jConfigListener
* @since 17.02.2003
*/
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
/**
* 创建一个新的{@code ContextLoaderListener},
* 它将基于"contextClass"和"contextConfigLocation" Servlet {@code }参数创建一个Web应用程序上下文。
* 请参阅{@link ContextLoader}父类文档以获取详细信息。
*
* 当在{@code web.xml}中声明{@code ContextLoaderListener}为{@code }时,通常使用这个构造函数。
*
* 创建的应用程序上下文将被注册到ServletContext属性{@link WebApplicationContext#ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE}下,
* 并且当在此listener上调用{@link #contextDestroyed}方法时,Spring应用程序上下文将被关闭。
*
* @see ContextLoader
* @see #ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent)
* @see #contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent)
*/
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
/**
* 用给定的应用程序上下文创建一个新的{@code ContextLoaderListener}。
* 这个构造函数用于Servlet 3.0+,通过{@link javax.servlet.ServletContext#addListener} API可以实现基于实例的listeners注册。
*
* 上下文可能或尚未{@linkplain org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh() 刷新}。
* 如果(a)是{@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext}的实现,并且(b)尚未刷新(推荐的方法),则会发生以下情况:
*
* - 如果给定的上下文还没有被分配一个{@linkplain org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#setId id},则将被分配一个
*
- {@code ServletContext}和{@code ServletConfig}对象将被委托给应用程序上下文
*
- {@link #customizeContext}将被调用
*
- 任何通过"contextInitializerClasses" init-param指定的{@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer ApplicationContextInitializer}s将被应用。
*
- {@link org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh refresh()}将被调用
*
*
* 如果上下文已经被刷新或者没有实现{@code ConfigurableWebApplicationContext},上述任何一种情况都不会发生。
*
* 创建的应用程序上下文将被注册到ServletContext属性{@link WebApplicationContext#ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE}下,
* 并且当在此listener上调用{@link #contextDestroyed}方法时,Spring应用程序上下文将被关闭。
*
* @param context the application context to manage
* @see #contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent)
* @see #contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent)
*/
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
ContextLoader
声明如下:
public class ContextLoader {
为给定的servlet上下文初始化Spring的Web应用程序上下文,
使用构造时提供的应用程序上下文, 或者根据"contextClass" 和"contextConfigLocation"
方式1 通过web.xml配置
在web.xml org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext。
默认,指定的任何上下文类都需要实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口。
处理web.xml
注意:在多个配置文件的情况下,后面的bean定义将覆盖之前加载的文件中的定义,至少在使用Spring的默认ApplicationContext实现时是这样。 这可以用来通过一个额外的XML文件重写某些bean定义。
方式2 通过Java Config配置
从Spring 3.1开始,ContextLoader支持通过ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)构造函数注入根Web应用程序上下文, 从而允许在Servlet 3.0+环境中进行编程式配置。 有关使用示例,请参阅org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer。
总结
介绍了这么多类,这里做一个简短的总结。
Servlet3.0+规范后,允许Servlet,Filter,Listener不必声明在web.xml中,而是以Java Config的方式编码存在,实现容器的零配置。
ServletContainerInitializer启动容器时负责加载相关配置。
package javax.servlet;
import java.util.Set;
public interface ServletContainerInitializer {
void onStartup(Set> var1, ServletContext var2) throws ServletException;
}
Servlet容器启动时会自动扫描当前服务中ServletContainerInitializer的实现类。并调用其onStartup方法,其参数Set可通过在实现类上声明注解javax.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes(xxx.class)注解自动注入。@HandlesTypes会自动扫描项目中所有的xxx.class的实现类,并将其全部注入Set。
Spring为其提供了一个实现类:SpringServletContainerInitializer类。通过查看源码可以看出,WebApplicationInitializer才是我们需要关心的接口。
我们只需要将相应的Servlet,Filter,Listener等硬编码到该接口的实现类中即可。
Spring为我们提供了一些WebApplicationInitializer的抽象类,我们只需要继承并按需修改即可。常见的实现类有:
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer
AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer
对于一个web应用,其部署在web容器中,web容器提供其一个全局的上下文环境,这个上下文就是ServletContext,其为后面的Spring IoC容器提供宿主环境;
其次,在web.xml中会提供有ContextLoaderListener。
在web容器启动时,会触发容器初始化事件,此时ContextLoaderListener会监听到这个事件,其contextInitialized方法会被调用。
package org.springframework.web.context;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
在contextInitialized这个方法中,spring会初始化一个启动上下文,这个上下文被称为根上下文,即WebApplicationContext,这是一个接口类。
确切的说,其实现类是XmlWebApplicationContext(基于web.xml配置)或者上面提及的AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(基于JavaConfig配置)。
这个就是Spring IoC容器,其对应的自定义的配置由web.xml中的
在这个IoC容器初始化完毕后,TODO Spring以WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE为属性Key,将其存储到ServletContext中,便于获取。
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
}
public class ContextLoader {
...
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
...
// 以`WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE`为属性Key,将根上下文存储到ServletContext中
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
...
}
...
}
再次,ContextLoaderListener监听器初始化完毕后,开始初始化web.xml中配置的Servlet,这个servlet可以配置多个,以最常见的DispatcherServlet为例,
这个servlet实际上是一个标准的前端控制器,用以转发、匹配、处理每个servlet请求。
DispatcherServlet上下文在初始化的时候会建立自己的IoC上下文,用以持有spring mvc相关的bean。
在建立DispatcherServlet自己的IoC上下文时,TODO 会利用WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE先从ServletContext中获取之前的根上下文(即WebApplicationContext)作为自己上下文的parent上下文。
有了这个parent上下文之后,再初始化自己持有的上下文。
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX = FrameworkServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT.";
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
...
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
...
}
}
这个DispatcherServlet初始化自己上下文的工作在其initStrategies方法中可以看到,大概的工作就是初始化处理器映射、视图解析等。
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initMultipartResolver(context);
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
}
}
这个servlet自己持有的上下文默认实现类也是XmlWebApplicationContext,当然也可以基于JavaConfig方式配置AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext。
初始化完毕后,TODO spring以与servlet的名字相关(此处不是简单的以servlet名为Key,而是通过一些转换)的属性为属性Key,也将其存到ServletContext中,以便后续使用。
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX = FrameworkServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT.";
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
...
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
...
}
/**
* Return the ServletContext attribute name for this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
* The default implementation returns
* {@code SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX + servlet name}.
* @see #SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX
* @see #getServletName
*/
public String getServletContextAttributeName() {
return SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX + getServletName();
}
}
这样每个servlet就持有自己的上下文,即拥有自己独立的bean空间,同时各个servlet共享相同的bean,即根上下文定义的那些bean。