在使用Entity Framework过程中,有时需要借助工具生成Code First的代码,而Entity Framework Reverse POCO Code First Generator是一款不错的工具
在Visual Studio中,通过“工具”→“扩展和更新...”来安装Entity Framework Reverse POCO Code First Generator
![]()
![]()
这里添加一个控制台项目,并在项目中添加POCO Code First Generator 生成模板(注意:添加项目后需要添加Entity Framework,POCO Code First Generator借助Entity Framework生成代码,可以使用Nuget添加)
![]()
![]()
默认的生成模板如下:
<#@ include file="EF.Reverse.POCO.Core.ttinclude" #>
<#
// v2.32.0
// Please make changes to the settings below.
// All you have to do is save this file, and the output file(s) is/are generated. Compiling does not regenerate the file(s).
// A course for this generator is available on Pluralsight at https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/code-first-entity-framework-legacy-databases
// Main settings **********************************************************************************************************************
ConnectionStringName = "MyDbContext"; // Searches for this connection string in config files listed below in the ConfigFilenameSearchOrder setting
// ConnectionStringName is the only required setting.
// As an alternative to ConnectionStringName above, which must match your app/web.config connection string name, you can override them below
//ConnectionString = "Data Source=(local);Initial Catalog=Northwind;Integrated Security=True;Application Name=EntityFramework Reverse POCO Generator";
//ProviderName = "System.Data.SqlClient";
// Namespace = ""; // Override the default namespace here
DbContextName = "MyDbContext"; // Note: If generating separate files, please give the db context a different name from this tt filename.
//DbContextInterfaceName = "IMyDbContext"; // Defaults to "I" + DbContextName or set string empty to not implement any interface.
DbContextInterfaceBaseClasses = "System.IDisposable"; // Specify what the base classes are for your database context interface
DbContextBaseClass = "System.Data.Entity.DbContext"; // Specify what the base class is for your DbContext. For ASP.NET Identity use "IdentityDbContext"
//DefaultConstructorArgument = "EnvironmentConnectionStrings.MyDbContext"; //defaults to "Name=" + ConnectionStringName
ConfigurationClassName = "Configuration"; // Configuration, Mapping, Map, etc. This is appended to the Poco class name to configure the mappings.
ConfigFilenameSearchOrder = new[] { "app.config", "web.config" }; // Add more here if required. The config files are searched for in the local project first, then the whole solution second.
GenerateSeparateFiles = false;
MakeClassesInternal = false;
MakeClassesPartial = false;
MakeDbContextInterfacePartial = false;
UseMappingTables = true; // If true, mapping will be used and no mapping tables will be generated. If false, all tables will be generated.
UsePascalCase = true; // This will rename the generated C# tables & properties to use PascalCase. If false table & property names will be left alone.
UseDataAnnotations = false; // If true, will add data annotations to the poco classes.
UseDataAnnotationsSchema = false; // UseDataAnnotations must also be true. If true, will add data annotations schema to the poco classes.
UsePropertyInitializers = false; // Removes POCO constructor and instead uses C# 6 property initialisers to set defaults
UseLazyLoading = true; // Marks all navigation properties as virtual or not, to support or disable EF Lazy Loading feature
IncludeComments = CommentsStyle.AtEndOfField; // Adds comments to the generated code
IncludeExtendedPropertyComments = CommentsStyle.InSummaryBlock; // Adds extended properties as comments to the generated code
IncludeConnectionSettingComments = true; // Add comments describing connection settings used to generate file
IncludeViews = true;
IncludeSynonyms = false;
IncludeStoredProcedures = true;
IncludeTableValuedFunctions = false; // If true, you must set IncludeStoredProcedures = true, and install the "EntityFramework.CodeFirstStoreFunctions" Nuget Package.
DisableGeographyTypes = false; // Turns off use of System.Data.Entity.Spatial.DbGeography and System.Data.Entity.Spatial.DbGeometry as OData doesn't support entities with geometry/geography types.
//CollectionInterfaceType = "System.Collections.Generic.List"; // Determines the declaration type of collections for the Navigation Properties. ICollection is used if not set.
CollectionType = "System.Collections.Generic.List"; // Determines the type of collection for the Navigation Properties. "ObservableCollection" for example. Add "System.Collections.ObjectModel" to AdditionalNamespaces if setting the CollectionType = "ObservableCollection".
NullableShortHand = true; //true => T?, false => Nullable
AddUnitTestingDbContext = true; // Will add a FakeDbContext and FakeDbSet for easy unit testing
IncludeQueryTraceOn9481Flag = false; // If SqlServer 2014 appears frozen / take a long time when this file is saved, try setting this to true (you will also need elevated privileges).
IncludeCodeGeneratedAttribute = true; // If true, will include the GeneratedCode attribute, false to remove it.
UsePrivateSetterForComputedColumns = true; // If the columns is computed, use a private setter.
AdditionalNamespaces = new[] { "" }; // To include extra namespaces, include them here. i.e. "Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework"
AdditionalContextInterfaceItems = new[] // To include extra db context interface items, include them here. Also set MakeClassesPartial=true, and implement the partial DbContext class functions.
{
"" // example: "void SetAutoDetectChangesEnabled(bool flag);"
};
// If you need to serialize your entities with the JsonSerializer from Newtonsoft, this would serialize
// all properties including the Reverse Navigation and Foreign Keys. The simplest way to exclude them is
// to use the data annotation [JsonIgnore] on reverse navigation and foreign keys.
// For more control, take a look at ForeignKeyAnnotationsProcessing() further down
AdditionalReverseNavigationsDataAnnotations = new string[] // Data Annotations for all ReverseNavigationProperty.
{
// "JsonIgnore" // Also add "Newtonsoft.Json" to the AdditionalNamespaces array above
};
AdditionalForeignKeysDataAnnotations = new string[] // Data Annotations for all ForeignKeys.
{
// "JsonIgnore" // Also add "Newtonsoft.Json" to the AdditionalNamespaces array above
};
ColumnNameToDataAnnotation = new Dictionary
{
// This is used when UseDataAnnotations = true;
// It is used to set a data annotation on a column based on the columns name.
// Make sure the column name is lowercase in the following array, regardless of how it is in the database
// Column name DataAnnotation to add
{ "email", "EmailAddress" },
{ "emailaddress", "EmailAddress" },
{ "creditcard", "CreditCard" },
{ "url", "Url" },
{ "phone", "Phone" },
{ "phonenumber", "Phone" },
{ "mobile", "Phone" },
{ "mobilenumber", "Phone" },
{ "telephone", "Phone" },
{ "telephonenumber", "Phone" },
{ "password", "DataType(DataType.Password)" },
{ "username", "DataType(DataType.Text)" }
};
// Migrations *************************************************************************************************************************
MigrationConfigurationFileName = ""; // null or empty to not create migrations
MigrationStrategy = "MigrateDatabaseToLatestVersion"; // MigrateDatabaseToLatestVersion, CreateDatabaseIfNotExists or DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges
ContextKey = ""; // Sets the string used to distinguish migrations belonging to this configuration from migrations belonging to other configurations using the same database. This property enables migrations from multiple different models to be applied to applied to a single database.
AutomaticMigrationsEnabled = true;
AutomaticMigrationDataLossAllowed = true; // if true, can drop fields and lose data during automatic migration
// Pluralization **********************************************************************************************************************
// To turn off pluralization, use:
// Inflector.PluralizationService = null;
// Default pluralization, use:
// Inflector.PluralizationService = new EnglishPluralizationService();
// For Spanish pluralization:
// 1. Intall the "EF6.Contrib" Nuget Package.
// 2. Add the following to the top of this file and adjust path, and remove the space between the angle bracket and # at the beginning and end.
// < #@ assembly name="your full path to \EntityFramework.Contrib.dll" # >
// 3. Change the line below to: Inflector.PluralizationService = new SpanishPluralizationService();
Inflector.PluralizationService = new EnglishPluralizationService();
// If pluralisation does not do the right thing, override it here by adding in a custom entry.
//Inflector.PluralizationService = new EnglishPluralizationService(new[]
//{
// // Create custom ("Singular", "Plural") forms for one-off words as needed.
// new CustomPluralizationEntry("Course", "Courses"),
// new CustomPluralizationEntry("Status", "Status") // Use same value to prevent pluralisation
//});
// Elements to generate ***************************************************************************************************************
// Add the elements that should be generated when the template is executed.
// Multiple projects can now be used that separate the different concerns.
ElementsToGenerate = Elements.Poco | Elements.Context | Elements.UnitOfWork | Elements.PocoConfiguration;
// Use these namespaces to specify where the different elements now live. These may even be in different assemblies.
// Please note this does not create the files in these locations, it only adds a using statement to say where they are.
// The way to do this is to add the "EntityFramework Reverse POCO Code First Generator" into each of these folders.
// Then set the .tt to only generate the relevant section you need by setting
// ElementsToGenerate = Elements.Poco; in your Entity folder,
// ElementsToGenerate = Elements.Context | Elements.UnitOfWork; in your Context folder,
// ElementsToGenerate = Elements.PocoConfiguration; in your Maps folder.
// PocoNamespace = "YourProject.Entities";
// ContextNamespace = "YourProject.Context";
// UnitOfWorkNamespace = "YourProject.Context";
// PocoConfigurationNamespace = "YourProject.Maps";
// You also need to set the following to the namespace where they now live:
PocoNamespace = "";
ContextNamespace = "";
UnitOfWorkNamespace = "";
PocoConfigurationNamespace = "";
// Schema *****************************************************************************************************************************
// If there are multiple schemas, then the table name is prefixed with the schema, except for dbo.
// Ie. dbo.hello will be Hello.
// abc.hello will be AbcHello.
PrependSchemaName = true; // Control if the schema name is prepended to the table name
// Table Suffix ***********************************************************************************************************************
// Prepends the suffix to the generated classes names
// Ie. If TableSuffix is "Dto" then Order will be OrderDto
// If TableSuffix is "Entity" then Order will be OrderEntity
TableSuffix = null;
// Filtering **************************************************************************************************************************
// Use the following table/view name regex filters to include or exclude tables/views
// Exclude filters are checked first and tables matching filters are removed.
// * If left null, none are excluded.
// * If not null, any tables matching the regex are excluded.
// Include filters are checked second.
// * If left null, all are included.
// * If not null, only the tables matching the regex are included.
// For clarity: if you want to include all the customer tables, but not the customer billing tables.
// TableFilterInclude = new Regex("^[Cc]ustomer.*"); // This includes all the customer and customer billing tables
// TableFilterExclude = new Regex(".*[Bb]illing.*"); // This excludes all the billing tables
//
// Example: TableFilterExclude = new Regex(".*auto.*");
// TableFilterInclude = new Regex("(.*_FR_.*)|(data_.*)");
// TableFilterInclude = new Regex("^table_name1$|^table_name2$|etc");
// ColumnFilterExclude = new Regex("^FK_.*$");
SchemaFilterExclude = null;
SchemaFilterInclude = null;
TableFilterExclude = null;
TableFilterInclude = null;
ColumnFilterExclude = null;
// Filtering of tables using a function. This can be used in conjunction with the Regex's above.
// Regex are used first to filter the list down, then this function is run last.
// Return true to include the table, return false to exclude it.
TableFilter = (Table t) =>
{
// Example: Exclude any table in dbo schema with "order" in its name.
//if(t.Schema.Equals("dbo", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase) && t.NameHumanCase.ToLowerInvariant().Contains("order"))
// return false;
return true;
};
// Stored Procedures ******************************************************************************************************************
// Use the following regex filters to include or exclude stored procedures
StoredProcedureFilterExclude = null;
StoredProcedureFilterInclude = null;
// Filtering of stored procedures using a function. This can be used in conjunction with the Regex's above.
// Regex are used first to filter the list down, then this function is run last.
// Return true to include the stored procedure, return false to exclude it.
StoredProcedureFilter = (StoredProcedure sp) =>
{
// Example: Exclude any stored procedure in dbo schema with "order" in its name.
//if(sp.Schema.Equals("dbo", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase) && sp.NameHumanCase.ToLowerInvariant().Contains("order"))
// return false;
return true;
};
// Table renaming *********************************************************************************************************************
// Use the following function to rename tables such as tblOrders to Orders, Shipments_AB to Shipments, etc.
// Example:
TableRename = (string name, string schema, bool isView) =>
{
// Example
//if (name.StartsWith("tbl"))
// name = name.Remove(0, 3);
//name = name.Replace("_AB", "");
//if(isView)
// name = name + "View";
// If you turn pascal casing off (UsePascalCase = false), and use the pluralisation service, and some of your
// tables names are all UPPERCASE, some words ending in IES such as CATEGORIES get singularised as CATEGORy.
// Therefore you can make them lowercase by using the following
// return Inflector.MakeLowerIfAllCaps(name);
// If you are using the pluralisation service and you want to rename a table, make sure you rename the table to the plural form.
// For example, if the table is called Treez (with a z), and your pluralisation entry is
// new CustomPluralizationEntry("Tree", "Trees")
// Use this TableRename function to rename Treez to the plural (not singular) form, Trees:
// if (name == "Treez") return "Trees";
return name;
};
// Column modification*****************************************************************************************************************
// Use the following list to replace column byte types with Enums.
// As long as the type can be mapped to your new type, all is well.
//EnumsDefinitions.Add(new EnumDefinition { Schema = "dbo", Table = "match_table_name", Column = "match_column_name", EnumType = "name_of_enum" });
//EnumsDefinitions.Add(new EnumDefinition { Schema = "dbo", Table = "OrderHeader", Column = "OrderStatus", EnumType = "OrderStatusType" }); // This will replace OrderHeader.OrderStatus type to be an OrderStatusType enum
// Use the following function if you need to apply additional modifications to a column
// eg. normalise names etc.
UpdateColumn = (Column column, Table table) =>
{
// Rename column
//if (column.IsPrimaryKey && column.NameHumanCase == "PkId")
// column.NameHumanCase = "Id";
// .IsConcurrencyToken() must be manually configured. However .IsRowVersion() can be automatically detected.
//if (table.NameHumanCase.Equals("SomeTable", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase) && column.NameHumanCase.Equals("SomeColumn", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
// column.IsConcurrencyToken = true;
// Remove table name from primary key
//if (column.IsPrimaryKey && column.NameHumanCase.Equals(table.NameHumanCase + "Id", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
// column.NameHumanCase = "Id";
// Remove column from poco class as it will be inherited from a base class
//if (column.IsPrimaryKey && table.NameHumanCase.Equals("SomeTable", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
// column.Hidden = true;
// Apply the "override" access modifier to a specific column.
// if (column.NameHumanCase == "id")
// column.OverrideModifier = true;
// This will create: public override long id { get; set; }
// Perform Enum property type replacement
var enumDefinition = EnumsDefinitions.FirstOrDefault(e =>
(e.Schema.Equals(table.Schema, StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase)) &&
(e.Table.Equals(table.Name, StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase) || e.Table.Equals(table.NameHumanCase, StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase)) &&
(e.Column.Equals(column.Name, StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase) || e.Column.Equals(column.NameHumanCase, StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase)));
if (enumDefinition != null)
{
column.PropertyType = enumDefinition.EnumType;
if(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(column.Default))
column.Default = "(" + enumDefinition.EnumType + ") " + column.Default;
}
return column;
};
// StoredProcedure renaming ************************************************************************************************************
// Use the following function to rename stored procs such as sp_CreateOrderHistory to CreateOrderHistory, my_sp_shipments to Shipments, etc.
// Example:
/*StoredProcedureRename = (sp) =>
{
if (sp.NameHumanCase.StartsWith("sp_"))
return sp.NameHumanCase.Remove(0, 3);
return sp.NameHumanCase.Replace("my_sp_", "");
};*/
StoredProcedureRename = (sp) => sp.NameHumanCase; // Do nothing by default
// Use the following function to rename the return model automatically generated for stored procedure.
// By default it's ReturnModel.
// Example:
/*StoredProcedureReturnModelRename = (name, sp) =>
{
if (sp.NameHumanCase.Equals("ComputeValuesForDate", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
return "ValueSet";
if (sp.NameHumanCase.Equals("SalesByYear", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
return "SalesSet";
return name;
};*/
StoredProcedureReturnModelRename = (name, sp) => name; // Do nothing by default
// StoredProcedure return types *******************************************************************************************************
// Override generation of return models for stored procedures that return entities.
// If a stored procedure returns an entity, add it to the list below.
// This will suppress the generation of the return model, and instead return the entity.
// Example: Proc name Return this entity type instead
//StoredProcedureReturnTypes.Add("SalesByYear", "SummaryOfSalesByYear");
// Callbacks **********************************************************************************************************************
// This method will be called right before we write the POCO header.
Action WritePocoClassAttributes = t =>
{
if (UseDataAnnotations)
{
foreach (var dataAnnotation in t.DataAnnotations)
{
WriteLine(" [" + dataAnnotation + "]");
}
}
// if(t.ClassName.StartsWith("Order"))
// WriteLine(" [SomeAttribute]");
};
// Writes optional base classes
Func WritePocoBaseClasses = t =>
{
//if (t.ClassName == "User")
// return ": IdentityUser";
// Or use the maker class to dynamically build more complex definitions
/* Example:
var r = new BaseClassMaker("POCO.Sample.Data.MetaModelObject");
r.AddInterface("POCO.Sample.Data.IObjectWithTableName");
r.AddInterface("POCO.Sample.Data.IObjectWithId",
t.Columns.Any(x => x.IsPrimaryKey && !x.IsNullable && x.NameHumanCase.Equals("Id", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase) && x.PropertyType == "long"));
r.AddInterface("POCO.Sample.Data.IObjectWithUserId",
t.Columns.Any(x => !x.IsPrimaryKey && !x.IsNullable && x.NameHumanCase.Equals("UserId", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase) && x.PropertyType == "long"));
return r.ToString();
*/
return "";
};
// Writes any boilerplate stuff
Action WritePocoBaseClassBody = t =>
{
// Do nothing by default
// Example:
// WriteLine(" // " + t.ClassName);
};
Func WritePocoColumn = c =>
{
bool commentWritten = false;
if((IncludeExtendedPropertyComments == CommentsStyle.InSummaryBlock || IncludeComments == CommentsStyle.InSummaryBlock) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(c.SummaryComments))
{
WriteLine(string.Empty);
WriteLine(" ///");
WriteLine(" /// {0}", System.Security.SecurityElement.Escape(c.SummaryComments));
WriteLine(" /// ");
commentWritten = true;
}
if (UseDataAnnotations)
{
if(c.Ordinal > 1 && !commentWritten)
WriteLine(string.Empty); // Leave a blank line before the next property
foreach (var dataAnnotation in c.DataAnnotations)
{
WriteLine(" [" + dataAnnotation + "]");
}
}
// Example of adding a [Required] data annotation attribute to all non-null fields
//if (!c.IsNullable)
// return " [System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Required] " + c.Entity;
return " " + c.Entity;
};
ForeignKeyFilter = (ForeignKey fk) =>
{
// Return null to exclude this foreign key, or set IncludeReverseNavigation = false
// to include the foreign key but not generate reverse navigation properties.
// Example, to exclude all foreign keys for the Categories table, use:
// if (fk.PkTableName == "Categories")
// return null;
// Example, to exclude reverse navigation properties for tables ending with Type, use:
// if (fk.PkTableName.EndsWith("Type"))
// fk.IncludeReverseNavigation = false;
return fk;
};
ForeignKeyProcessing = (foreignKeys, fkTable, pkTable, anyNullableColumnInForeignKey) =>
{
var foreignKey = foreignKeys.First();
// If using data annotations and to include the [Required] attribute in the foreign key, enable the following
//if (!anyNullableColumnInForeignKey)
// foreignKey.IncludeRequiredAttribute = true;
return foreignKey;
};
ForeignKeyName = (tableName, foreignKey, foreignKeyName, relationship, attempt) =>
{
string fkName;
// 5 Attempts to correctly name the foreign key
switch (attempt)
{
case 1:
// Try without appending foreign key name
fkName = tableName;
break;
case 2:
// Only called if foreign key name ends with "id"
// Use foreign key name without "id" at end of string
fkName = foreignKeyName.Remove(foreignKeyName.Length-2, 2);
break;
case 3:
// Use foreign key name only
fkName = foreignKeyName;
break;
case 4:
// Use table name and foreign key name
fkName = tableName + "_" + foreignKeyName;
break;
case 5:
// Used in for loop 1 to 99 to append a number to the end
fkName = tableName;
break;
default:
// Give up
fkName = tableName;
break;
}
// Apply custom foreign key renaming rules. Can be useful in applying pluralization.
// For example:
/*if (tableName == "Employee" && foreignKey.FkColumn == "ReportsTo")
return "Manager";
if (tableName == "Territories" && foreignKey.FkTableName == "EmployeeTerritories")
return "Locations";
if (tableName == "Employee" && foreignKey.FkTableName == "Orders" && foreignKey.FkColumn == "EmployeeID")
return "ContactPerson";
*/
// FK_TableName_FromThisToParentRelationshipName_FromParentToThisChildsRelationshipName
// (e.g. FK_CustomerAddress_Customer_Addresses will extract navigation properties "address.Customer" and "customer.Addresses")
// Feel free to use and change the following
/*if (foreignKey.ConstraintName.StartsWith("FK_") && foreignKey.ConstraintName.Count(x => x == '_') == 3)
{
var parts = foreignKey.ConstraintName.Split('_');
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(parts[2]) && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(parts[3]) && parts[1] == foreignKey.FkTableName)
{
if (relationship == Relationship.OneToMany)
fkName = parts[3];
else if (relationship == Relationship.ManyToOne)
fkName = parts[2];
}
}*/
return fkName;
};
ForeignKeyAnnotationsProcessing = (Table fkTable, Table pkTable, string propName) =>
{
/* Example:
// Each navigation property that is a reference to User are left intact
if (pkTable.NameHumanCase.Equals("User") && propName.Equals("User"))
return null;
// all the others are marked with this attribute
return new[] { "System.Runtime.Serialization.IgnoreDataMember" };
*/
return null;
};
// Return true to include this table in the db context
ConfigurationFilter = (Table t) =>
{
return true;
};
// That's it, nothing else to configure ***********************************************************************************************
// Read schema
var factory = GetDbProviderFactory();
var tables = LoadTables(factory);
var storedProcs = LoadStoredProcs(factory);
// Generate output
if (tables.Count > 0 || storedProcs.Count > 0)
{
#>
<#@ include file="EF.Reverse.POCO.ttinclude" #>
<#@ import namespace="System.Xml.Schema" #>
<# } #>
在App.config中添加数据库连接字符串,如果是Web项目,则是Web.config,这里name与POCO 模板指定的Name一致(可以修改模板或配置文件,随便一处,保持一致就行)

在模板中Ctrl + S,这时提示运行模板,点击“确定”

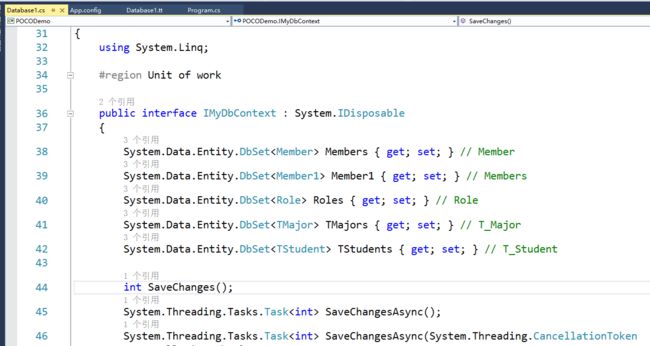
这是生成的代码:
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/sjqq/p/7523588.html
你可能感兴趣的:(Entity Framework工具POCO Code First Generator的使用(参考链接:https://github.com/sjh37/EntityFramework-Reverse...)