转载 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI0NjUxNTY5Nw==&mid=2247483814&idx=1&sn=ddf49931d552e9b4553dcec457a84c51&scene=19#wechat_redirect
《深入理解Spring系列之一:开篇》中提到在Spring容器启动的过程中,会将Bean解析成Spring内部的BeanDefinition结构,本篇将深入分析这个BeanDefinition的内部结构。
直接看BeanDefinition源码,
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* Scope identifier for the standard singleton scope: "singleton".
* Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
/**
* Scope identifier for the standard prototype scope: "prototype".
*
Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a major part
* of the application. Typically corresponds to a user-defined bean.
*/
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a supporting
* part of some larger configuration, typically an outer
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* {@code SUPPORT} beans are considered important enough to be aware
* of when looking more closely at a particular
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition},
* but not when looking at the overall configuration of an application.
*/
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is providing an
* entirely background role and has no relevance to the end-user. This hint is
* used when registering beans that are completely part of the internal workings
* of a {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
*/
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2;
// Modifiable attributes
/**
* Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
void setParentName(String parentName);
/**
* Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
*/
String getParentName();
/**
* Specify the bean class name of this bean definition.
*
The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing,
* typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it.
* @see #setParentName
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName);
/**
* Return the current bean class name of this bean definition.
*
Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in
* case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent.
* Also, this may just be the class that a factory method is called on, or it may
* even be empty in case of a factory bean reference that a method is called on.
* Hence, do not consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but
* rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level.
* @see #getParentName()
* @see #getFactoryBeanName()
* @see #getFactoryMethodName()
*/
String getBeanClassName();
/**
* Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
void setScope(String scope);
/**
* Return the name of the current target scope for this bean,
* or {@code null} if not known yet.
*/
String getScope();
/**
* Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
*
If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean
* factories that perform eager initialization of singletons.
*/
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
/**
* Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not
* eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean.
*/
boolean isLazyInit();
/**
* Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized.
* The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
*/
void setDependsOn(String... dependsOn);
/**
* Return the bean names that this bean depends on.
*/
String[] getDependsOn();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*
Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring.
* It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even
* if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence,
* autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches.
*/
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
*
If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
*/
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
*/
boolean isPrimary();
/**
* Specify the factory bean to use, if any.
* This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on.
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setFactoryBeanName(String factoryBeanName);
/**
* Return the factory bean name, if any.
*/
String getFactoryBeanName();
/**
* Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with
* constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified.
* The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any,
* or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setBeanClassName
*/
void setFactoryMethodName(String factoryMethodName);
/**
* Return a factory method, if any.
*/
String getFactoryMethodName();
/**
* Return the constructor argument values for this bean.
*
The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null})
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
/**
* Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean.
*
The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null})
*/
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
// Read-only attributes
/**
* Return whether this a Singleton, with a single, shared instance
* returned on all calls.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
boolean isSingleton();
/**
* Return whether this a Prototype, with an independent instance
* returned for each call.
* @since 3.0
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
boolean isPrototype();
/**
* Return whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated.
*/
boolean isAbstract();
/**
* Get the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools with an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
int getRole();
/**
* Return a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*/
String getDescription();
/**
* Return a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
String getResourceDescription();
/**
* Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none.
* Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any.
*
Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the
* originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user.
*/
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}
可以看到上面的很多属性和方法都很熟悉,例如类名、scope、属性、构造函数参数列表、依赖的bean、是否是单例类、是否是懒加载等,其实就是将Bean的定义信息存储到这个BeanDefinition相应的属性中,后面对Bean的操作就直接对BeanDefinition进行,例如拿到这个BeanDefinition后,可以根据里面的类名、构造函数、构造函数参数,使用反射进行对象创建。
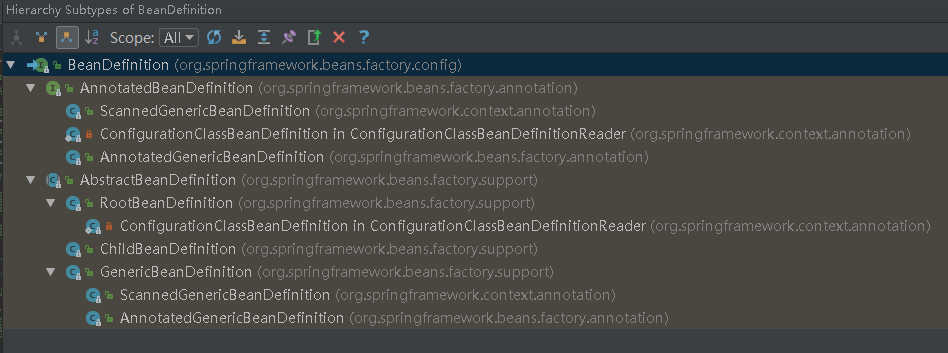
BeanDefinition是一个接口,是一个抽象的定义,实际使用的是其实现类,如 ChildBeanDefinition、RootBeanDefinition、GenericBeanDefinition等。
BeanDefinition继承了AttributeAccessor,说明它具有处理属性的能力;
BeanDefinition继承了BeanMetadataElement,说明它可以持有Bean元数据元素,作用是可以持有XML文件的一个bean标签对应的Object。