JWT在Java中的使用
这里简要总结一下JWT的使用流程,以及其实现的原理。
1 JWT是什么?
直接看官方解释:https://jwt.io/introduction/
JWT全称是JSON Web Tokens ,也就是JSON格式数据使用加密算法加密后按照一定规则生成的一个字符串token 。
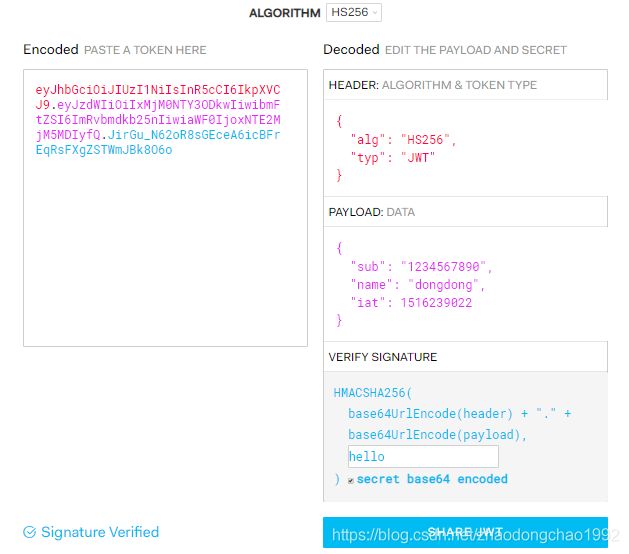
既然是一个JSON,那么它就有一定的格式,它由Header,Payload,Signature三部分组成,然后使用“.”连接,最后token格式如:A.B.C
- Header JWT的头,一般主要包含两个信息,JWT使用的加密算法和类型申明。这一部分使用Base64转换为密文。作为A
格式如下:
{
"alg": "HS256", //使用HS256加密算法
"typ": "JWT" //表面自己是JWT
}
- Payload 信息负载,这部分主要记录主要的信息,通信用户以及一些其他的自定义申明。
申明分为三中:-
Registered claims 注册申明
包含用户登陆注册的一些信息,如:iss(发出者),exp(到期时间),sub(主题),aud(受众)等。 -
Public claims 公共申明
这些可以由使用JWT的人员随意定义。 但是为避免冲突,应在IANA JSON Web令牌注册表中定义它们,或将其定义为包含抗冲突名称空间的URI。 -
Private claims 私有申明
这些是自定义声明,旨在在同意使用它们的各方之间共享信息,既不是注册声明也不是公共声明。
-
格式如:
{
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "John Doe",
"admin": true
}
- Signature 签名
第三部分,它的值使用的是在Header中定义的加密算法,加密前两部分的内容。前两部分按照如下格式组装:
String signature = HMACSHA256(base64UrlEncode(header)+"."+
base64UrlEncode(payload),
secret)
Signature的作用是校验Header和Payload在传输的过程中有没有改变。secret是自定义的签名的私钥,保存在服务端,用于校验token的合法性
最后JWT的完整形式是:
String jwtToken = Header +"."+ Payload + "." + Signature ;
在官方网站:在https://jwt.io/可以在线编译JWT。
如下:
在Java应用程序中使用
JWT说到底是一个安全规范的协议,现在它在Java中有很多比较好的实现。其中用的很多的就有https://github.com/jwtk/jjwt
下面就用jjwt来演示一下怎么实现JWT。
新建一个Maven项目,添加如下依赖:
<!-- JWT依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>${
jwt.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-impl</artifactId>
<version>${
jwt.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-jackson</artifactId>
<version>${
jwt.version}</version>
</dependency>
创建一个JWT:
/**
* 生成一个JWT
*
* @param audience 用户
* @param privateClaims 可以由使用JWT的人随意定义。但为避免冲突,推荐参考:https://www.iana.org/assignments/jwt/jwt.xhtml
* @param effectiveMillis 生效时间,单位为毫秒
* @param singKey 签名算法密钥
* @return JWT字符串
*/
public static String createToken(String audience, Map<String, Object> privateClaims, long effectiveMillis, String singKey) {
//jwt主题
String subject = "Authentication";
//jwt生效时间
Date createTime = new Date();
//根据给定的生效时间长度,生成jwt的失效时间点
Date expiredTime = new Date(createTime.getTime() + effectiveMillis);
//生成签名密钥,基于HMAC-SHA算法
Key key = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(SecureUtil.sha256(singKey).getBytes());
//发行人,取服务器的信息与应用信息
String issuer = "sun-" + SystemUtil.getHostInfo().getAddress();
//设置申明信息
Claims claims = new DefaultClaims();
claims.setId(IDWorker.getIdStr());
claims.setIssuer(issuer);
claims.setSubject(subject);
claims.setAudience(audience);
claims.setIssuedAt(createTime);
claims.setExpiration(expiredTime);
//添加自定义申明
claims.putAll(privateClaims);
return Jwts.builder()
.setClaims(claims)
.setHeaderParam("author", "ZHAODC")
.signWith(key, SignatureAlgorithm.HS256)
.compact();
}
这样就能生成了一个JWT。
然后就是解析JWT ,代码如下:
/**
* 获取JWT的JSON格式对象
*
* @param jwtStr token
* @param signKey 密钥
* @return json格式的明文
*/
public static JsonObject getJwt(String jwtStr, String signKey) {
Jwt jwt = Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey(Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(SecureUtil.sha256(signKey).getBytes()))
.parse(jwtStr);
Gson gson = new Gson();
String str = gson.toJson(jwt);
return gson.fromJson(str, JsonObject.class);
}
再获取JWT对象中申明Claims:
/**
* 解析JWT,获取JWT中的有效载荷
*
* @param jwtStr JWT字符串
* @param singKey 签名密钥
* @return 有效载荷
*/
public static Claims getClaims(String jwtStr, String singKey) {
Key key = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(SecureUtil.sha256(singKey).getBytes());
return Jwts.parser()
.setSigningKey(key)
.parseClaimsJws(jwtStr)
.getBody();
}
再看一下这个申明Claims对象是如何定义的:
先看顶级接口:
/**
* Mutation (modifications) to a {@link io.jsonwebtoken.Claims Claims} instance.
*
* @param the type of mutator
* @see io.jsonwebtoken.JwtBuilder
* @see io.jsonwebtoken.Claims
* @since 0.2
*/
public interface ClaimsMutator<T extends ClaimsMutator> {
/**
* Sets the JWT
* iss (issuer) value. A {@code null} value will remove the property from the JSON map.
*
* @param iss the JWT {@code iss} value or {@code null} to remove the property from the JSON map.
* @return the {@code Claims} instance for method chaining.
*/
T setIssuer(String iss);
/**
* Sets the JWT
* sub (subject) value. A {@code null} value will remove the property from the JSON map.
*
* @param sub the JWT {@code sub} value or {@code null} to remove the property from the JSON map.
* @return the {@code Claims} instance for method chaining.
*/
T setSubject(String sub);
/**
* Sets the JWT
* aud (audience) value. A {@code null} value will remove the property from the JSON map.
*
* @param aud the JWT {@code aud} value or {@code null} to remove the property from the JSON map.
* @return the {@code Claims} instance for method chaining.
*/
T setAudience(String aud);
/**
* Sets the JWT
* exp (expiration) timestamp. A {@code null} value will remove the property from the JSON map.
*
* A JWT obtained after this timestamp should not be used.
*
* @param exp the JWT {@code exp} value or {@code null} to remove the property from the JSON map.
* @return the {@code Claims} instance for method chaining.
*/
T setExpiration(Date exp);
/**
* Sets the JWT
* nbf (not before) timestamp. A {@code null} value will remove the property from the JSON map.
*
* A JWT obtained before this timestamp should not be used.
*
* @param nbf the JWT {@code nbf} value or {@code null} to remove the property from the JSON map.
* @return the {@code Claims} instance for method chaining.
*/
T setNotBefore(Date nbf);
/**
* Sets the JWT
* iat (issued at) timestamp. A {@code null} value will remove the property from the JSON map.
*
* The value is the timestamp when the JWT was created.
*
* @param iat the JWT {@code iat} value or {@code null} to remove the property from the JSON map.
* @return the {@code Claims} instance for method chaining.
*/
T setIssuedAt(Date iat);
/**
* Sets the JWT
* jti (JWT ID) value. A {@code null} value will remove the property from the JSON map.
*
* This value is a CaSe-SenSiTiVe unique identifier for the JWT. If specified, this value MUST be assigned in a
* manner that ensures that there is a negligible probability that the same value will be accidentally
* assigned to a different data object. The ID can be used to prevent the JWT from being replayed.
*
* @param jti the JWT {@code jti} value or {@code null} to remove the property from the JSON map.
* @return the {@code Claims} instance for method chaining.
*/
T setId(String jti);
}
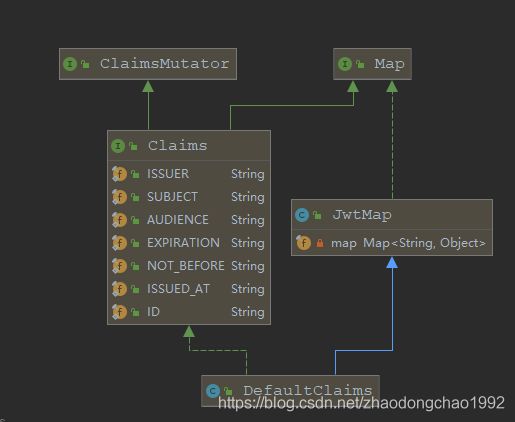
可以看到,Claims继承了Map,然后里面包含了以下这些内置的基本字段:
| 规范编码 | 对应Claims属性 | 值 |
|---|---|---|
| iss | issuer | 用户,JWT的签发者 |
| sub | subject | 主题,值为这个JWT的主题,入登录用户信息认证 |
| aud | audience | 受众群体,记录JWT的接受者 |
| exp | expiration | JWT的过期时间 |
| nbf | notBefore | 时间,表示JWT在这个时间之前是不可用的 |
| iat | issuedAt | JWT的签发时间 |
| jti | id | JWT的ID,唯一标识 |
这一段可以参考:https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-json-web-token-25#section-4
再来看一下它的默认实现DefaultClaims 。
可以看到,它的构造函数里面就传了Map ,其实这个就是自定义的申明。
JWT接口的定义:
/**
* An expanded (not compact/serialized) JSON Web Token.
*
* @param the type of the JWT body contents, either a String or a {@link Claims} instance.
*
* @since 0.1
*/
public interface Jwt<H extends Header, B> {
/**
* Returns the JWT {@link Header} or {@code null} if not present.
*
* @return the JWT {@link Header} or {@code null} if not present.
*/
H getHeader();
/**
* Returns the JWT body, either a {@code String} or a {@code Claims} instance.
*
* @return the JWT body, either a {@code String} or a {@code Claims} instance.
*/
B getBody();
}
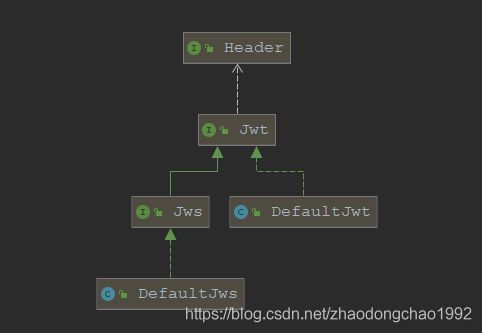
可以看到,JWT接口里面定了Header和Body(对应的是Payload)
/**
* An expanded (not compact/serialized) Signed JSON Web Token.
*
* @param the type of the JWS body contents, either a String or a {@link Claims} instance.
*
* @since 0.1
*/
public interface Jws<B> extends Jwt<JwsHeader,B> {
String getSignature();
}
Jws里面定义了Signature对应的就是JWT标准中的Signature ,类型是String
默认实现DefaultJws :
public class DefaultJws<B> implements Jws<B> {
private final JwsHeader header;
private final B body;
private final String signature;
public DefaultJws(JwsHeader header, B body, String signature) {
this.header = header;
this.body = body;
this.signature = signature;
}
@Override
public JwsHeader getHeader() {
return this.header;
}
@Override
public B getBody() {
return this.body;
}
@Override
public String getSignature() {
return this.signature;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "header=" + header + ",body=" + body + ",signature=" + signature;
}
}
可以看到这里面就刚好包含了JWT中的三个部分header ,body(Payload) ,signature
再来看Header的实现:
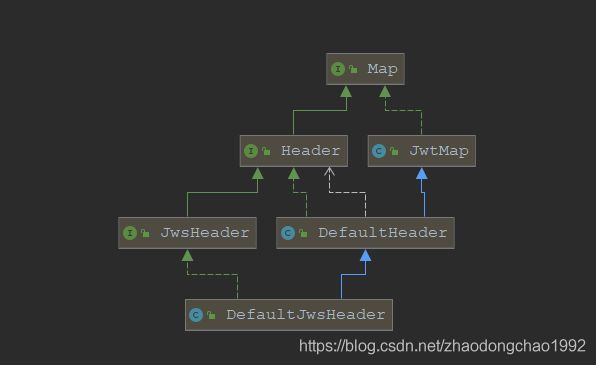
Header接口源码:
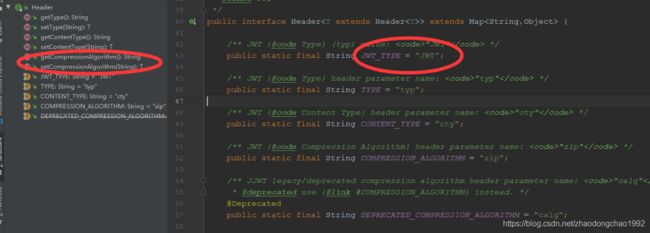
可以看到Header接口中定义了JWT规范中的类型和加密算法两个字段。具体的源码实现可以自己查阅。
下面将重点了,JWT的构建过程
JWT的构建是通过io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts这个工具类完成,看代码:
/**
* Factory class useful for creating instances of JWT interfaces. Using this factory class can be a good
* alternative to tightly coupling your code to implementation classes.
*
* @since 0.1
*/
public final class Jwts {
private static final Class[] MAP_ARG = new Class[]{
Map.class};
private Jwts() {
}
/**
* Creates a new {@link Header} instance suitable for plaintext (not digitally signed) JWTs. As this
* is a less common use of JWTs, consider using the {@link #jwsHeader()} factory method instead if you will later
* digitally sign the JWT.
*
* @return a new {@link Header} instance suitable for plaintext (not digitally signed) JWTs.
*/
public static Header header() {
return Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultHeader");
}
/**
* Creates a new {@link Header} instance suitable for plaintext (not digitally signed) JWTs, populated
* with the specified name/value pairs. As this is a less common use of JWTs, consider using the
* {@link #jwsHeader(java.util.Map)} factory method instead if you will later digitally sign the JWT.
*
* @return a new {@link Header} instance suitable for plaintext (not digitally signed) JWTs.
*/
public static Header header(Map<String, Object> header) {
return Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultHeader", MAP_ARG, header);
}
/**
* Returns a new {@link JwsHeader} instance suitable for digitally signed JWTs (aka 'JWS's).
*
* @return a new {@link JwsHeader} instance suitable for digitally signed JWTs (aka 'JWS's).
* @see JwtBuilder#setHeader(Header)
*/
public static JwsHeader jwsHeader() {
return Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultJwsHeader");
}
/**
* Returns a new {@link JwsHeader} instance suitable for digitally signed JWTs (aka 'JWS's), populated with the
* specified name/value pairs.
*
* @return a new {@link JwsHeader} instance suitable for digitally signed JWTs (aka 'JWS's), populated with the
* specified name/value pairs.
* @see JwtBuilder#setHeader(Header)
*/
public static JwsHeader jwsHeader(Map<String, Object> header) {
return Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultJwsHeader", MAP_ARG, header);
}
/**
* Returns a new {@link Claims} instance to be used as a JWT body.
*
* @return a new {@link Claims} instance to be used as a JWT body.
*/
public static Claims claims() {
return Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultClaims");
}
/**
* Returns a new {@link Claims} instance populated with the specified name/value pairs.
*
* @param claims the name/value pairs to populate the new Claims instance.
* @return a new {@link Claims} instance populated with the specified name/value pairs.
*/
public static Claims claims(Map<String, Object> claims) {
return Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultClaims", MAP_ARG, claims);
}
/**
* Returns a new {@link JwtParser} instance that can be configured and then used to parse JWT strings.
*
* @return a new {@link JwtParser} instance that can be configured and then used to parse JWT strings.
*/
public static JwtParser parser() {
return Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultJwtParser");
}
/**
* Returns a new {@link JwtBuilder} instance that can be configured and then used to create JWT compact serialized
* strings.
*
* @return a new {@link JwtBuilder} instance that can be configured and then used to create JWT compact serialized
* strings.
*/
public static JwtBuilder builder() {
return Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultJwtBuilder");
}
}
可以看到io.jsonwebtoken.impl.DefaultJwtBuilder是真正构建JWT的类,看它的源码:
public class DefaultJwtBuilder implements JwtBuilder {
private Header header;
private Claims claims;
private String payload;
private SignatureAlgorithm algorithm;
private Key key;
private Serializer<Map<String,?>> serializer;
private Encoder<byte[], String> base64UrlEncoder = Encoders.BASE64URL;
private CompressionCodec compressionCodec;
...
@Override
public JwtBuilder signWith(Key key, SignatureAlgorithm alg) throws InvalidKeyException {
Assert.notNull(key, "Key argument cannot be null.");
Assert.notNull(alg, "SignatureAlgorithm cannot be null.");
alg.assertValidSigningKey(key); //since 0.10.0 for https://github.com/jwtk/jjwt/issues/334
this.algorithm = alg;
this.key = key;
return this;
}
@Override
public JwtBuilder signWith(SignatureAlgorithm alg, byte[] secretKeyBytes) throws InvalidKeyException {
Assert.notNull(alg, "SignatureAlgorithm cannot be null.");
Assert.notEmpty(secretKeyBytes, "secret key byte array cannot be null or empty.");
Assert.isTrue(alg.isHmac(), "Key bytes may only be specified for HMAC signatures. If using RSA or Elliptic Curve, use the signWith(SignatureAlgorithm, Key) method instead.");
SecretKey key = new SecretKeySpec(secretKeyBytes, alg.getJcaName());
return signWith(key, alg);
}
@Override
public JwtBuilder signWith(SignatureAlgorithm alg, String base64EncodedSecretKey) throws InvalidKeyException {
Assert.hasText(base64EncodedSecretKey, "base64-encoded secret key cannot be null or empty.");
Assert.isTrue(alg.isHmac(), "Base64-encoded key bytes may only be specified for HMAC signatures. If using RSA or Elliptic Curve, use the signWith(SignatureAlgorithm, Key) method instead.");
byte[] bytes = Decoders.BASE64.decode(base64EncodedSecretKey);
return signWith(alg, bytes);
}
@Override
public JwtBuilder signWith(SignatureAlgorithm alg, Key key) {
return signWith(key, alg);
}
...
@Override
public String compact() {
if (this.serializer == null) {
//try to find one based on the runtime environment:
InstanceLocator<Serializer<Map<String,?>>> locator =
Classes.newInstance("io.jsonwebtoken.impl.io.RuntimeClasspathSerializerLocator");
this.serializer = locator.getInstance();
}
if (payload == null && Collections.isEmpty(claims)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Either 'payload' or 'claims' must be specified.");
}
if (payload != null && !Collections.isEmpty(claims)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Both 'payload' and 'claims' cannot both be specified. Choose either one.");
}
Header header = ensureHeader();
JwsHeader jwsHeader;
if (header instanceof JwsHeader) {
jwsHeader = (JwsHeader) header;
} else {
//noinspection unchecked
jwsHeader = new DefaultJwsHeader(header);
}
if (key != null) {
jwsHeader.setAlgorithm(algorithm.getValue());
} else {
//no signature - plaintext JWT:
jwsHeader.setAlgorithm(SignatureAlgorithm.NONE.getValue());
}
if (compressionCodec != null) {
jwsHeader.setCompressionAlgorithm(compressionCodec.getAlgorithmName());
}
String base64UrlEncodedHeader = base64UrlEncode(jwsHeader, "Unable to serialize header to json.");
byte[] bytes;
try {
bytes = this.payload != null ? payload.getBytes(Strings.UTF_8) : toJson(claims);
} catch (SerializationException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to serialize claims object to json: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
if (compressionCodec != null) {
bytes = compressionCodec.compress(bytes);
}
String base64UrlEncodedBody = base64UrlEncoder.encode(bytes);
//拼接JWT字符串 header+"."+body
String jwt = base64UrlEncodedHeader + JwtParser.SEPARATOR_CHAR + base64UrlEncodedBody;
if (key != null) {
//jwt must be signed:
//通过加密算法名称和加密秘钥,构建一个签名器
JwtSigner signer = createSigner(algorithm, key);
//使用签名器对header和body进行签名,
String base64UrlSignature = signer.sign(jwt);
// 使用"."隔开将结果添加到jwt的后面,最后得到的格式就是jwtStr = header.body.signature
jwt += JwtParser.SEPARATOR_CHAR + base64UrlSignature;
} else {
// no signature (plaintext), but must terminate w/ a period, see
// https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-json-web-token-25#section-6.1
jwt += JwtParser.SEPARATOR_CHAR;
}
return jwt;
}
/*
* @since 0.5 mostly to allow testing overrides
*/
protected JwtSigner createSigner(SignatureAlgorithm alg, Key key) {
return new DefaultJwtSigner(alg, key, base64UrlEncoder);
}
}
这里最终实现Header, payload, Signature的加密和拼接的逻辑在compact()方法中,里面有主要的注释。到此,JWT的使用就讲完了。