Fetch 跨域
一.Fetch 实现跨域
实现其实直接在 fetch 的配置项里面添加 mode :‘cors’ 就可以了,例子如下:
fetch('http://localhost:3000/myWebSite/praise', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
id: '5e42b22161478f3750fb48e9'}),
mode:'cors'
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(res => console.log(res));
以上就能实现跨域。
二.可能会产生的问题:
然而实际应用中可能会出现一些问题,所以我们首先应该学习下这个设置有什么用,请看下图:

可以看到 mode 可以设置以上属性:
- same-origin:也就是还有有同源政策。
- cors:允许跨域,且报文的正文可读,头文件里面的属性可能不会暴露完全。
- no-cors:允许跨域,但是一些请求头可能就不会发送出去了,且 JS 可能访问不到响应的属性(说白了就是服务端不跨域)。
- navigate:(笔者还未掌握,掌握之后再补上)。
看了上面的知识,对此模式的运作有了初步的了解,那接下来说明一下我遇到的问题:
1. 设置了跨域仍然不能跨域
那么你可能报了如下错误:

报错: Access-Control-Allow-Origin 这个属性没有在已请求的资源上(响应头)。如果一个不透明的响应服务满足您的需求,把 mode 设置为 ‘no-cors’ 来获取 ‘cors’ 获取失败的资源。
看上面这句话,解决方式有两个,设置响应头 ’ Access-Control-Allow-Origin’,或者设置 mode:‘cors’。
- 设置响应头的方式,其实还是服务端开启跨域。我们添加了 ‘cors’(不添加响应头) 跨域失败的原因应该是 fetch 是 JavaScript 执行的,但请求是浏览器发起的,浏览器接收响应,响应头没有 ’ Access-Control-Allow-Origin’,浏览器就报同源政策的错误,从而 fetch 也接收不到之后的响应。
- 设置 ‘no-cors’ 这种模式跨域是特殊的跨域,如果不添加响应头 ’ Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ ,后台是可以接收到请求的,但是因为服务端不能跨域,响应数据并不能被接收到。如果你添加响应头 ’ Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ ,浏览器的控制台可以看到响应的数据,但是 fetch 并不能接收到(请看属性第三点)。
二. 服务端接收不到参数的问题
fetch('http://localhost:3000/myWebSite/praise', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
id: '5e42b22161478f3750fb48e9'}),
mode:'cors'
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(res => console.log(res));
出现这种原因,首先确认一下后台有没有使用 bodyparser 这类模块,导致body无法获取。
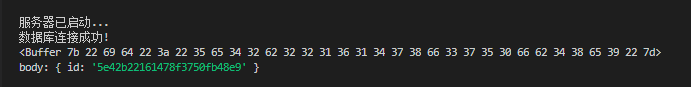
如果使用了 bodyparser 仍然没有数据,这时候您要注意 body 的传输方式是不是以数据流的形式传输。
出现这种情况的原因很可能是您以为 cors 已经开启了跨域,实际上并没有跨域成功,然后您根据提示,设置为 no-cors 发现后台可以响应,但是body接收不到数据。因为,现在 body 是以数据流的形式传输。
1.解决方式一(最优)
经过本人实验,可以使用 cors ,后端也开启跨域(设置响应头),这时可以正常接收到 body。
2.解决方式二
使用 no-cors,后端开启跨域,这时是数据流形式的传输 body,需要用以下代码来获取 body。
app.post('/myWebSite/praise', (req, res) => {
let body = '';
req.on('data', data => {
console.log(data);
body += data;
});
req.on('end', () => console.log('body:',JSON.parse(body)))
})
3. 解决方式三
以 x-www-form-urlencoded 转码的方法让 body 被编码为key/value格式发送到服务端,这种方式不会以数据流的形式传输。前端代码:
fetch('http://localhost:3000/myWebSite/praise', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
},
body: "id=5e42b22161478f3750fb48e9"
// 如果是多个参数的话,以 xx=xx?xx=xx的形式写,很常用的
mode:'cors'
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(res => console.log(res));
总结,如果后台接收不到 body(或是说 params ,query都没有),那么先查看是否是使用 bodyparser 这类工具,如果使用,则确认 body 是否通过数据流的形式传输。