使用yolo3自己训练的模型加上deep_sort实现多目标跟踪
使用yolo3自己训练的模型加上deep_sort实现多目标跟踪
本文章用于记录自己多目标跟踪调试代码的过程。
我的部分环境如下
python 3.6.10
keras 2.3.1
scikit-learn 0.19.0
tensorflow 1.14.0
opencv 3.3.1
1.使用yolo3模型训练自己的数据集
可以参照训练自己的yolo3模型用于识别机动车及部分道路信息或者训练自己的yolo3模型用于识别机动车及部分道路信息
得到自己训练出来的模型
2.下载yolo3+deep_sort的模型deep_sort_yolov3
- 下载地址https://github.com/Qidian213/deep_sort_yolov3
将自己训练的模型weights.h5复制到model_data文件夹中。 - 生成mars-small128.pb文件,下载地址https://github.com/nwojke/deep_sort,下载下来,在cmd中cd到下载的文件目录,运行命令
python tools/freeze_model.py
生成mars-small128.pb文件,把mars-small128.pb文件复制到deep_sort_yolov3模型的model_data文件夹中。如果运行命令失败也可以就使用原mars-small128.pb文件。 - 在deep_sort_yolov3中找到yolo3.cfg文件并打开,ctrl+f搜 yolo, 总共会搜出3个含有yolo的地方,将classes改为自己模型识别类别的个数,filters改为如图的样子。一共要改三处。

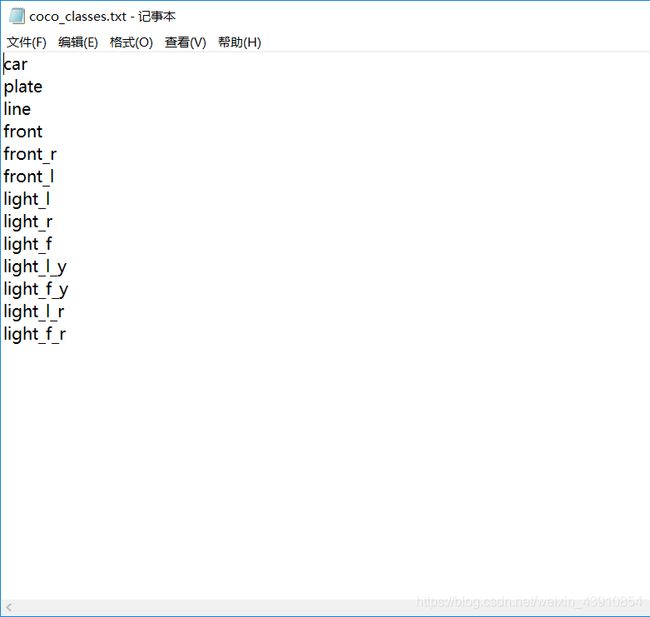
在model_data文件夹中找到voc_classes.txt将内容改为自己的类别如图所示。
- 找到yolo.py将内容替换为如下代码 。目的是为了更改权重trained_weights.h5的打开方式,model_path改为自己的权重名称。
import colorsys
import os
import random
from timeit import time
from timeit import default_timer as timer ### to calculate FPS
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import load_model
from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
from yolo3.model import yolo_eval, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body
from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
class YOLO(object):
def __init__(self):
self.model_path = 'model_data/trained_weights.h5'
self.anchors_path = 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt'
self.classes_path = 'model_data/coco_classes.txt'
self.score = 0.5
self.iou = 0.5
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.model_image_size = (416, 416) # fixed size or (None, None)
self.is_fixed_size = self.model_image_size != (None, None)
self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
def _get_class(self):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def _get_anchors(self):
anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
anchors = np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
return anchors
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model must be a .h5 file.'
# Load model, or construct model and load weights.
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
is_tiny_version = num_anchors == 6 # default setting
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None, None, 3)), num_anchors // 2, num_classes) \
if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None, None, 3)), num_anchors // 3, num_classes)
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
num_anchors / len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
# Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
return boxes, scores, classes
def detect_image(self, image):
if self.is_fixed_size:
assert self.model_image_size[0]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
assert self.model_image_size[1]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)))
else:
new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
image.height - (image.height % 32))
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
#print(image_data.shape)
image_data /= 255.
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
return_boxs = []
return_scores = []
for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
predicted_class = self.class_names[c]
if predicted_class != 'person' :
continue
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
x = int(box[1])
y = int(box[0])
w = int(box[3]-box[1])
h = int(box[2]-box[0])
if x < 0 :
w = w + x
x = 0
if y < 0 :
h = h + y
y = 0
return_boxs.append([x,y,w,h])
return_scores.append(score)
return return_boxs, return_scores
def close_session(self):
self.sess.close()
找到yolo3文件夹下的model.py在最后增加一个函数,代码如下。
def tiny_yolo_body(inputs, num_anchors, num_classes):
'''Create Tiny YOLO_v3 model CNN body in keras.'''
x1 = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(16, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(32, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(64, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (3,3)))(inputs)
x2 = compose(
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(512, (3,3)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(1,1), padding='same'),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(1024, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (1,1)))(x1)
y1 = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(512, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D(num_anchors*(num_classes+5), (1,1)))(x2)
x2 = compose(
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (1,1)),
UpSampling2D(2))(x2)
y2 = compose(
Concatenate(),
DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (3,3)),
DarknetConv2D(num_anchors*(num_classes+5), (1,1)))([x2,x1])
return Model(inputs, [y1,y2])
- 最后在demo.py里面修改一下视频路径,直接运行即可。
- 过程中可能会遇见版本不兼容的问题,耐心一点百度就好了根据错误提示具体解决。其中如果scikit-learn版本>0.19,
from sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ import linear_assignment代码报错如下
No module named 'sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_'
有人说,linear_assignment 函数从0.21开始被弃用了,并且将在0.23版本中移除,官方提升将用scipy.optimize.linear_sum_assignment 进行替代。但相同的函数名称linear_assignment用法却完全不相同,所以必须将scikit-learn库版本降到0.19或以下。
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment as linear_assignment
与
from sklearn.utils.linear_assignment_ import linear_assignment