爬梯:JUC并发编程(一)
学习资源整理自:B站《狂神说》
JUC并发编程
1、基础概念
JUC 就是 java.util.concurrent
并发、并行
并发(多线程操作同一个资源)
- CPU单核,模拟出多条线程,快速切换
并行(多线程同行)
- CPU多核,同事执行:线程池
//获取CPU的核数
//CPU密集型、IO密集型
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
并发编程的本质:充分利用CPU资源
线程状态
源码:
public enum State {
//新生
NEW,
//运行
RUNNABLE,
//阻塞
BLOCKED,
//一直等待
WAITING,
//指定时间等待
TIMED_WAITING,
//终止
TERMINATED;
}
wait/sleep的异同
1、来自不同的类
wait—>Object
sleep—>Thread
2、关于锁的释放
wait会释放锁,sleep不会施放锁(抱着锁睡觉)
3、使用范围
wait 必须在同步代码块中使用
sleep 可以在任何地方
4、捕获异常
wait不需要捕获异常
sleep必须要捕获异常
2、Lock锁(重点)
真正的多线程开发,线程就是一个单独的资源类,没有附属操作。
1、属性、方法
传统synchronized
代码实现:
/**
* 原始方式synchronized实现并发
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-15 14:30
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String args[]){
//创建资源类实例,实现并发:多线程操作同一个资源
Tickets tickets = new Tickets();
//实现并发 买票
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
tickets.saleTicket();
}
},"小石").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
tickets.saleTicket();
}
},"小杰").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
tickets.saleTicket();
}
},"小伦").start();
}
}
/**
* 资源类
* 只含有属性、方法
*/
class Tickets{
int ticketCount = 30;
public synchronized void saleTicket(){
if(ticketCount>0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买到一张票,剩余"+ticketCount--);
}
}
}
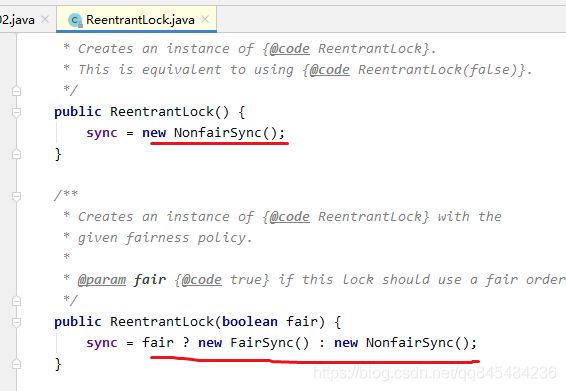
ReentrantLock
源码
FairSync:公平锁,先来后到
NonfairSync:非公平锁,可以插队(默认)
为什么默认是非公平锁呢?
因为有的线程执行完需要1个小时,而有些线程需要1分钟,为了“公平”可以允许:先执行1分钟,再执行1小时的情况
代码实现:
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* JUC ReentrantLock
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-15 15:01
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String args[]){
//创建资源类实例,实现并发:多线程操作同一个资源
Tickets tickets = new Tickets();
new Thread(()-> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) tickets.saleTicket();},"小石").start();
new Thread(()-> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) tickets.saleTicket();},"小杰").start();
new Thread(()-> {
for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) tickets.saleTicket();},"小伦").start();
}
}
/**
* Lock的三个步骤
* 1、new ReentrantLock()
* 2、lock.lock()
* 3、lock.unlock()
*/
class Tickets2{
int ticketCount = 30;
//创建可重入锁
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void saleTicket(){
lock.lock();//加锁
try {
if(ticketCount>0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买到一张票,剩余"+ticketCount--);
}
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
lock.unlock();//解锁
}
}
}
Synchronized和Lock的区别
| Synchronized | Lock |
|---|---|
| java内置关键字 | java的一个类 |
| 无法获取锁的状态 | 可以判断是否获取到了锁 |
| 自动释放锁 | 必须手动施放锁 |
| 若A获得锁后造成死锁,B将一直等待 | 拥有tryLock()方法,可以尝试获得锁 |
| 可重入锁,不可以中断的非公平锁 | 可重入锁,可以判断锁,可以设置公平锁或非公平锁 |
| 适合锁少量代码同步 | 适合锁大量代码同步 |
3、生产者和消费者场景
synchronized代码实现:
/**
* synchronized实现生产者消费者通信
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-15 16:00
*/
public class TestSychronized {
public static void main(String args[]){
Product product = new Product();//资源
//生产线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"小石1").start();
//生产线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"小石2").start();
//消费线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"阿伦1").start();
//消费线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"阿伦2").start();
}
}
class Product{
int pCount = 0;
//加仓
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
while(pCount!=0){
this.wait();//等待,让消费者先消费掉产品
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 生产了!当前库存:"+ ++pCount);
this.notifyAll();//解除消费者的等待
}
//减仓
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
while(pCount==0){
this.wait();//等待,让生产者先生产
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 消费了!当前库存:"+ --pCount);
this.notifyAll();//解除生产者的等待
}
}
结果:
小石1 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦1 消费了!当前库存:0
小石2 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦1 消费了!当前库存:0
小石1 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦1 消费了!当前库存:0
小石2 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦1 消费了!当前库存:0
小石1 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦1 消费了!当前库存:0
小石2 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦2 消费了!当前库存:0
......
如上while处,是因为有个“虚拟唤醒”的概念。
虚拟唤醒
当别的线程调用notifyAll之后,唤醒了全部等待的线程,而有的线程唤醒了之后,还没有真实轮到他干活(比如,当前pCount=1是需要生产的,但是他被唤醒干活了,这就叫做虚拟唤醒),常因为使用了if作为判断条件时产生,所以需要循环去判断:当线程被唤醒时:是否真的轮到我干活了?不然我继续等待~
JUC代码实现:
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* JUC 实现生产者消费者通信
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-15 17:00
*/
public class TestJUC {
public static void main(String args[]){
Product2 product = new Product2();//资源
//生产线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"小石1").start();
//生产线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"小石2").start();
//消费线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"阿伦1").start();
//消费线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"阿伦2").start();
}
}
class Product2{
int pCount = 0;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();//取代原监视器的方法(wait.notify.notifyAll)
//加仓
public void increment() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while(pCount!=0){
condition.await();//等待,让消费者先消费掉产品
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 生产了!当前库存:"+ ++pCount);
condition.signalAll();//解除消费者的等待
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//减仓
public void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while(pCount==0){
condition.await();//等待,让生产者先生产
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 消费了!当前库存:"+ --pCount);
condition.signalAll();//解除生产者的等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
结果:
小石1 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦1 消费了!当前库存:0
小石1 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦1 消费了!当前库存:0
小石2 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦2 消费了!当前库存:0
小石2 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦2 消费了!当前库存:0
小石2 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦2 消费了!当前库存:0
小石2 生产了!当前库存:1
阿伦2 消费了!当前库存:0
......
JUC实现精准唤醒:
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* JUC Condition实现精准唤醒
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-16 13:27
*/
public class TestJUC2 {
public static void main(String args[]){
Product3 product = new Product3();//资源
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.fun1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"石").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.fun2();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"似").start();
//消费线程
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
product.fun3();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"心").start();
}
}
class Product3{
int num = 0;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();//取代原监视器的方法(wait.notify.notifyAll)
Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();//取代原监视器的方法(wait.notify.notifyAll)
Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();//取代原监视器的方法(wait.notify.notifyAll)
public void fun1() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while(num!=0){
condition1.await();//等待
}
System.out.println(num++ +"==="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===");
condition2.signal();//解除指定的监控器条件器
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void fun2() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while(num!=1){
condition2.await();//等待
}
System.out.println(num++ +"==="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===");
condition3.signal();//解除指定的监控器条件器
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void fun3() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while(num!=2){
condition3.await();//等待
}
System.out.println(num +"==="+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===");
num=0;
condition1.signal();//解除指定的监控器条件器
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
结果:
0===石===
1===似===
2===心===
0===石===
1===似===
2===心===
0===石===
1===似===
2===心===
......
4、8锁现象
关于锁的8个问题
1、先执行哪个方法?为什么?(锁的对象)
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 8锁现象
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-16 13:46
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String args[]){
Cup cup = new Cup();
new Thread(()->{
cup.takeInWater();
},"A").start();
try {
//延迟500毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
cup.pourWater();
},"B").start();
}
}
/**
* 水杯
*/
class Cup{
public synchronized void takeInWater(){
System.out.println("装水--");
}
public synchronized void pourWater(){
System.out.println("倒水--");
}
}
完美回答:
装水方法先执行,因为主线程上有调用sleep方法,让主线程挂起500毫秒,再启动B线程执行倒水的方法,此时A线程先获得cup对象的锁。(回答先后顺序的答案都不对)
2、当装水方法延迟2秒,哪个线程先执行?
//主方法同上
/**
* 水杯
*/
class Cup{
public synchronized void takeInWater(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("装水--");
}
public synchronized void pourWater(){
System.out.println("倒水--");
}
}
完美回答:
装水方法先执行,因为装水方法想获得cup对象的锁,执行了sleep方法,锁住对象挂起等待,所以需要装水方法执行完才能执行倒水方法。
3、增加一个普通方法后,先执行哪个线程?
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String args[]){
Cup cup = new Cup();
new Thread(()->{
cup.takeInWater();
},"A").start();
try {
//延迟500毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
cup.washCup();
},"B").start();
}
}
/**
* 水杯
*/
class Cup{
public synchronized void takeInWater(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("装水--");
}
public synchronized void pourWater(){
System.out.println("倒水--");
}
public void washCup(){
System.out.println("洗杯子--");
}
}
完美回答:
先执行洗杯子方法,因为洗杯子是普通方法,不是同步代码,不受锁限制。
4、两个对象的情况下,哪个线程先执行,为什么?
/**
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-16 14:23
*/
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String args[]){
Cup4 cup1 = new Cup4();
Cup4 cup2 = new Cup4();
new Thread(()->{
cup1.takeInWater();
},"A").start();
try {
//延迟500毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
cup2.pourWater();
},"B").start();
}
}
/**
* 水杯
*/
class Cup4{
public synchronized void takeInWater(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("装水--");
}
public synchronized void pourWater(){
System.out.println("倒水--");
}
}
完美答案:
先执行倒水方法,两个对象就有两个锁,互不影响。
5、静态同步方法,哪个线程先执行?
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String args[]){
Cup5 cup1 = new Cup5();
new Thread(()->{
cup1.takeInWater();
},"A").start();
try {
//延迟500毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
cup1.pourWater();
},"B").start();
}
}
/**
* 水杯
*/
class Cup5{
public static synchronized void takeInWater(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("装水--");
}
public static synchronized void pourWater(){
System.out.println("倒水--");
}
}
完美答案:
装水方法先执行,先获得锁的对象先执行,而且static修饰的方法是在类加载的时候生成的,也就在class文件中,所以此时的锁是所在了class对象上。(若只回答先获得锁先执行则不能得全分)
6、两个对象的情况下,静态同步方法,哪个先执行?
public static void main(String args[]){
Cup6 cup1 = new Cup6();
Cup6 cup2 = new Cup6();
new Thread(()->{
cup1.takeInWater();
},"A").start();
try {
//延迟500毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
cup2.pourWater();
},"B").start();
}
//资源类代码同上
完美答案:
装水方法先执行,因为静态方法上的锁是锁在了class对象上,全局唯一。
7、一个静态同步方法和一个普通同步方法,哪个先执行?
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String args[]){
Cup7 cup1 = new Cup7();
new Thread(()->{
cup1.takeInWater();
},"A").start();
try {
//延迟500毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
cup1.pourWater();
},"B").start();
}
}
/**
* 水杯
*/
class Cup7{
public static synchronized void takeInWater(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("装水--");
}
public synchronized void pourWater(){
System.out.println("倒水--");
}
}
完美答案:
先执行倒水方法,因为倒水方法的锁锁的是对象,而装水锁的是class类模板,
8、两个对象,一个调用静态同步方法,一个调用同步方法,哪个先执行?
public static void main(String args[]){
Cup8 cup1 = new Cup8();
Cup8 cup2 = new Cup8();
new Thread(()->{
cup1.takeInWater();
},"A").start();
try {
//延迟500毫秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
cup2.pourWater();
},"B").start();
}
//资源类代码同上
完美答案:
先执行倒水方法,因为倒水方法锁的是对象,不需要等待class类模板施放锁。
3、集合类线程不安全
List
/**
* 集合类不安全
* java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 并发修改异常
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-16 16:29
*/
public class TestList {
public static void main(String args[]){
/**
* 并发下的ArrayList不安全
* 解决方案:
* 1、List list = new Vector(); 查看Vector.add()源码得知,add方法由synchronized修饰
* 2、List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()); 使用集合工具类,创建线程安全的ArrayList
* 3、List list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
*/
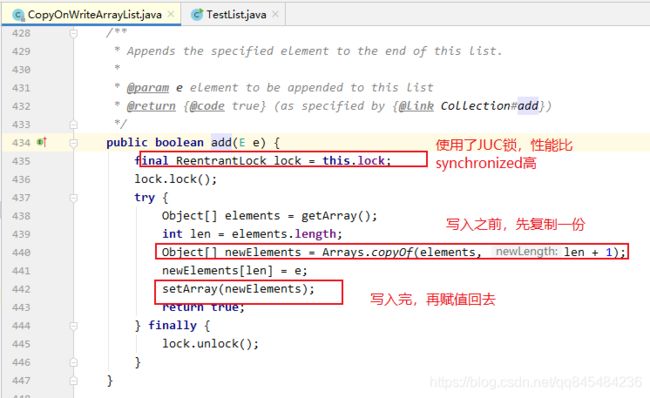
// CopyOnWrite 写入时复制 COW 计算机程序设计领域的一种优化策略:
// 在写入是复制一份出来写入,写入完再复制回原来的数组里,避免写入时覆盖造成数据问题!
List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//十个线程去修改list
new Thread(()->{
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,5));
System.out.println(list);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
源码:
Set
/**
* Set 线程不安全 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-16 17:16
*/
public class TestSet {
public static void main(String args[]){
/**
* 并发下的HashSet不安全
* 解决方案:
* 1、Set set = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<>()); 使用集合工具类
* 2、Set set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet();
*/
Set<String> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
set.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,5));
System.out.println(set);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
Set基础补充:
Set和List一样,继承自Collection
源码:
所以HashSet底层就是一个MashMap的key,没有value无序不重复
HashMap
/**
* Map 线程不安全 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-16 17:35
*/
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String args[]){
Map<String,String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<String,String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
map.put(Thread.currentThread().getName(),UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,5));
System.out.println(map);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
4、Callable
官方文档:
细节:1、有缓存;2、等待结果时会阻塞;
代码实现:
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 使用Callable
* 相比Runnable,Callable能抛出异常,并且有返回值
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-16 17:59
*/
public class TestCallable {
public static void main(String args[]) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask(myThread);//适配器
new Thread(futureTask,"A").start();//结果会被写入缓存
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
new Thread(futureTask,"B").start();
System.out.println(futureTask.get());//执行耗时任务时,可能会阻塞
}
}
class MyThread implements Callable<String>{
@Override
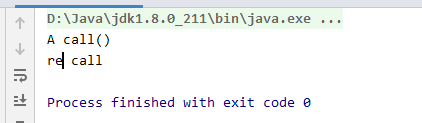
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" call()");
return "re call";
}
}
5、常用辅助类
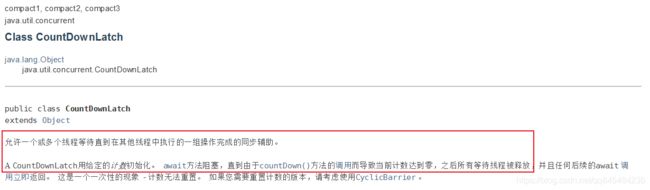
CountDownLatch
计数器,官方文档:
代码实现:
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
/**
* 计数器,初始化时给定一个统计数
* 在需要某些任务必须完成时使用,设置成必须倒数完,主流程才能继续走下去
*/
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
countDownLatch.countDown();//-1
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();//等待计数器倒数完毕
System.out.println("主流程任务--");
}
控制台:
0
1
4
3
2
主流程任务--
Process finished with exit code 0
CyclicBarrier
代码实现:
public static void main(String args[]){
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(7,()->{
System.out.println("集齐七颗龙珠召唤神龙!~");
});
for (int i = 1; i <= 7 ; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("收集到第"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"颗龙珠");
try {
//设置屏障点,需要等全部线程走到这一步才能继续执行
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
控制台:
收集到第1颗龙珠
收集到第3颗龙珠
收集到第2颗龙珠
收集到第4颗龙珠
收集到第5颗龙珠
收集到第6颗龙珠
收集到第7颗龙珠
集齐七颗龙珠召唤神龙!~
Process finished with exit code 0
Semaphore
信号量
官方文档:
代码实现:
public static void main(String args[]){
/**
* 模拟抢车位场景、限流
* 只有3个车位,但是有7台车,轮流停车
*/
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();//线程进入,获取
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进入停车位》》》》");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);//停车1s
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"离开停车位《《《《");
semaphore.release();//线程执行完毕,施放信号
}
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
控制台:
3进入停车位》》》》
1进入停车位》》》》
2进入停车位》》》》
2离开停车位《《《《
3离开停车位《《《《
1离开停车位《《《《
6进入停车位》》》》
4进入停车位》》》》
5进入停车位》》》》
6离开停车位《《《《
4离开停车位《《《《
5离开停车位《《《《
7进入停车位》》》》
7离开停车位《《《《
Process finished with exit code 0
acquire():获取,若信号量满了的时候则挂起等待。
release():释放,当前线程执行完毕,释放信号。
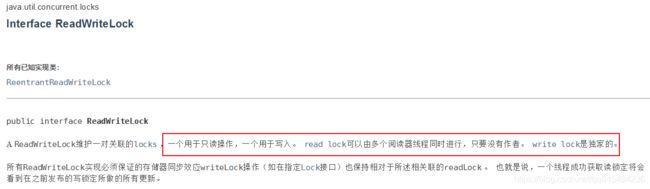
6、读写锁
官方文档:
写锁:一次只能被一个线程占有;
读锁:多个线程可以同时占有;
代码实现:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
/**
* @author: stone
* @create: 2020-08-16 22:27
*/
public class readWriteLockDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
MyCacheLock myCacheLock = new MyCacheLock();//资源类
//模拟5个写入线程
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
final int tempI = i;
new Thread(()->{
myCacheLock.write(String.valueOf(tempI),"石似心"+tempI);
}).start();
}
//模拟5个读取线程
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
final int tempI = i;
new Thread(()->{
myCacheLock.read(String.valueOf(tempI));
}).start();
}
}
}
class MyCacheLock {
private volatile Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//读写锁:相较于普通的可重入锁,细粒度更高,读写分开控制
ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public void write(String key,Object value){
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();//加写锁
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入"+key);
map.put(key,value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入完毕。。。");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();//释放
}
}
public void read(String key){
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();//加读锁
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取"+key);
map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取完毕。。。");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();//释放
}
}
}
7、阻塞队列
BlockingQueue
家族关系:
什么情况下使用阻塞队列:多线程并发处理,线程池。
四组API:
| 方式 | 抛出异常 | 返回值 | 阻塞等待 | 超时等待 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 添加 | add | offer | put | offer(val,time,unit) |
| 移除 | remove | poll | take | poll(time,unit) |
| 检测队首 | element | peek |
抛出异常
/**
* 抛出异常 add remove
*/
public static void test1(){
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(2);
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.add("A"));
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.add("B"));
/*Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full*/
//System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.add("C")); //
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
/*检测队首元素,返回 A */
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.element());
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
/*先进先出*/
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.remove());
/*Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException*/
//System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.remove());
}
返回值
/**
* 有返回值,无异常
*/
public static void test2(){
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(2);
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("A"));
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("B"));
/*超出队列范围,返回false,不会报错 */
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("C"));
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
/*检测队首元素 返回A
* 若无则返回 null 不会报错
*/
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.peek());
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
/*先进先出*/
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
/*超出队列范围,返回null,不会报错*/
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
}
阻塞等待
/**
* 阻塞 等待
*/
public static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(2);
arrayBlockingQueue.put("A");
arrayBlockingQueue.put("B");
/*超出队列范围: 阻塞线程,一直等待,不会报错没有返回值 */
//arrayBlockingQueue.put("C");
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
/*先进先出*/
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.take());
/*超出队列范围: 阻塞线程,一直等待,不会报错没有返回值*/
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.take());
}
超时等待
/**
* 超时 等待
*/
public static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue arrayBlockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(2);
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("A"));
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("B"));
/*超出队列范围: 阻塞线程,两秒内若仍无位置,则施放线程,返回false */
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.offer("C", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
/*先进先出*/
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll());
/*超出队列范围: 阻塞线程,一直等待,不会报错没有返回值*/
System.out.println(arrayBlockingQueue.poll(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
篇幅太长,拆分下一篇