Java代理实现方式详解
1. 简介
代理模式是常用的Java设计模式,其主要作用是为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。在某些情况下,一个对象不想或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象可以在调用对象和被调用对象起到中介的作用,代理模式的思想是为了提供额外的处理或者不同的操作。
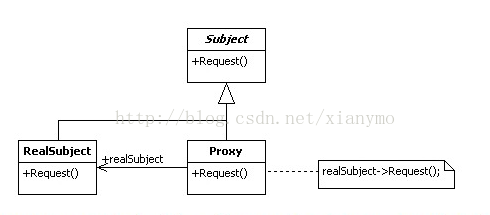
代理模式中,基本上有Subject角色,RealSubject角色,Proxy角色。其中:Subject角色负责定义RealSubject和Proxy角色应该实现的接口;RealSubject角色用来完成业务服务功能;Proxy角色负责调用RealSubject对应的方法完成业务功能。
按照代理的创建时期,代理可以分为两种:
- 静态代理:由程序创建或特定工具自动生成源代码,再对其编译。在程序运行前,代理类的.class文件就已经存在了。
- 动态代理:程序创建其不知道需要创建哪些类的代理类,代理类的定义,.class文件的生成需要在程序运行期动态创建。
2. 静态代理
在代码阶段确定了代理关系,Proxy类通过jdk编译器编译成class文件,当系统运行时,此class已经存在了。
下面简单实现静态代理:
a. 业务接口类
public interface Count {
public void count();
}
b. 业务实现类
public class CountImpl implements Count{
@Override
public void count() {
System.out.println("计算当前账户余额。。。。");
}
}c. 代理类
/**
*
* 项目名: java-proxy-statics
* 类名: CountProxy.java
* 类描述: 静态代理实现:由程序员创建或特定工具自动生成源代码,再对其编译。在程序运行前,代理类的.class文件就已经存在了
* 备注: 每个代理类只能为一个接口服务,这样就会导致代理类太多,代理类和实际类除了类名不一致,其他的都一致,重复代码太多,过于臃肿
* 创建日期:2015-6-26
* 创建时间:上午9:21:00
*
*/
public class CountProxy implements Count{
private Count count;
public CountProxy(Count count){
this.count = count;
}
@Override
public void count() {
System.out.println("开启事务。。。。");
count.count();
System.out.println("结束事务。。。。");
}
}
为了解决这个问题,就有了动态地创建Proxy的想法:在运行状态中,需要代理的地方,根据Subject和RealSubject,动态的创建一个Proxy,用完之后就会销毁,这样就可以避免了Proxy角色的class在系统中冗余的问题了。
3. 动态代理
与静态代理相对应的就是动态代理,动态代理类的字节码是在程序运行时动态生成,无需程序员手工编写它的源代码。动态代理类不仅简化了变成的功能,而且提供了软件系统的可扩展性。在这种模式之中:代理Proxy 和RealSubject 应该实现相同的功能,这一点相当重要。(我这里说的功能,可以理解为某个类的public方法)
在面向对象的编程之中,如果我们想要约定Proxy 和RealSubject可以实现相同的功能,有两种方式:
- 一个比较直观的方式,就是定义一个功能接口,然后让Proxy 和RealSubject来实现这个接口。
- 还有比较隐晦的方式,就是通过继承。因为如果Proxy 继承自RealSubject,这样Proxy则拥有了RealSubject的功能,Proxy还可以通过重写RealSubject中的方法,来实现多态。
3.1 JDK动态代理
JDK动态代理有两个很重要的类,Proxy和InvocationHandler。
3.1.1 Porxy类
Proxy类是JDK动态代理的核心累,提供了一个非常重要的方法:newProxyInstance,该方法能够在运行期动态创建实现了指定接口的类,具体得创建功能是由ProxyGenerator类来实现,这个类我们后面再讲述。
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException
ClassLoader loader:类加载器
Class interfaces:代理类需要实现的接口,也是目标类实现的接口
InvocationHandler h:实现InvocationHandler接口的实例。
3.1.2 InvocationHandler接口
每一个代理类都会关联一个实现InvocationHandler接口的子类对象,该子类对象是对目标类的又一层代理。InvocationHanlder只提供了一个方法:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable;参数说明:
Object proxy:生成的动态代理对象
Method method:需要代理的方法
Object[] args:代理方法调用的参数
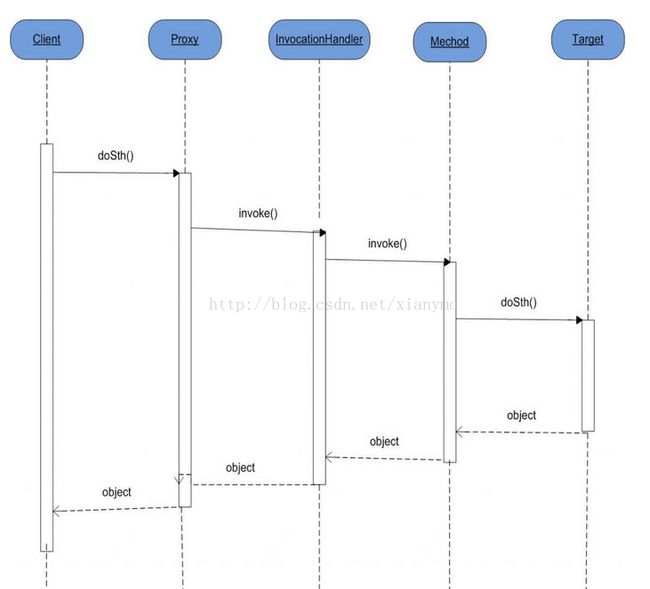
对于目标接口里的每个方法实现,都是通过调用InvocationHandler接口的子类对象的反射调用。也就是是说,动态代理类实际上是InvocationHandler子类对象的一个代理,InvocationHandler子类对象又是目标类的代理,通过这样层层代理就能够实现上述的功能了。之间的关系如下图示:
从上图可看出,JDK动态代理并不是简单的一层代理,而是通过层层代理,最终通过Method的反射来调用目标对象的方法,而需要额外添加的功能可放在InvocationHandler的实现类。
3.1.3 jdk动态代理实现
同样的,我们也来实现一个JDK动态代理的代理方式。
a. 接口类
public interface Count {
public void count();
}public interface Money {
public void update();
}b. 业务类
public class CountImpl implements Count, Money{
@Override
public void count(){
System.out.println("计算账户余额。。。");
}
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("更新账户余额。。。");
}
}c. 实现InvocationHanlder的子类对象
public class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{
private Object target;
public MyInvocationHandler(Object target){
this.target = target;
}
/**
* @param proxy:代理类的实例
* @param method:要调用的被代理类的方法
* @param args:被调用方法的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
System.out.println("开始记录日志。。。");
//反射调用目标对象的方法
method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("结束记录日志。。。");
return null;
}
}d. 获取代理类的工厂类
public class ProxyFactory {
public static Object getProxy(Object object){
MyInvocationHandler invocationHandler = new MyInvocationHandler(object);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(object.getClass().getClassLoader(), object.getClass().getInterfaces(), invocationHandler);
}
}e. 测试类
public class CountProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Count count = new CountImpl();
Count proxy = (Count) ProxyFactory.getProxy(count);
proxy.count();
}
}f. 输出结果
开始记录日志。。。
计算账户余额。。。
结束记录日志。。。从结果可以看到,我们已经在原有的业务功能上,通过动态代理的方式加入了日志功能,这就是spring aop的实现方式。代理类生成了,但这个代理的背后都是怎么样实现的呢?下面通过跟踪源码来一步步解析:
3.1.4 jdk动态代理源码分析
代理类是通过Proxy.newProxyInstance方法来完成,那么先看看newProxyInstance方法。
/**
* loader:类加载器
* interfaces:目标对象实现的接口
* h:InvocationHandler的实现类
*/
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
if (h == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
/*
* Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
*/
Class cl = getProxyClass(loader, interfaces);
/*
* Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
*/
try {
// 调用代理对象的构造方法(也就是$Proxy0(InvocationHandler h))
Constructor cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
// 生成代理类的实例并把MyInvocationHandler的实例传给它的构造方法
return (Object) cons.newInstance(new Object[] { h });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString());
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString());
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString());
}
}
再进getProxyClass方法内部
public static Class getProxyClass(ClassLoader loader,
Class... interfaces)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
// 如果目标类实现的接口数大于65535个则抛出异常
if (interfaces.length > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
}
// 声明代理对象所代表的Class对象(有点拗口)
Class proxyClass = null;
String[] interfaceNames = new String[interfaces.length];
Set interfaceSet = new HashSet(); // for detecting duplicates
// 遍历目标类所实现的接口
for (int i = 0; i < interfaces.length; i++) {
// 拿到目标类实现的接口的名称
String interfaceName = interfaces[i].getName();
Class interfaceClass = null;
try {
// 加载目标类实现的接口到内存中
interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
if (interfaceClass != interfaces[i]) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
interfaces[i] + " is not visible from class loader");
}
// 中间省略了一些无关紧要的代码 .......
// 把目标类实现的接口代表的Class对象放到Set中
interfaceSet.add(interfaceClass);
interfaceNames[i] = interfaceName;
}
// 把目标类实现的接口名称作为缓存(Map)中的key
Object key = Arrays.asList(interfaceNames);
Map cache;
synchronized (loaderToCache) {
// 从缓存中获取cache
cache = (Map) loaderToCache.get(loader);
if (cache == null) {
// 如果获取不到,则新建地个HashMap实例
cache = new HashMap();
// 把HashMap实例和当前加载器放到缓存中
loaderToCache.put(loader, cache);
}
}
synchronized (cache) {
do {
// 根据接口的名称从缓存中获取对象
Object value = cache.get(key);
if (value instanceof Reference) {
proxyClass = (Class) ((Reference) value).get();
}
if (proxyClass != null) {
// 如果代理对象的Class实例已经存在,则直接返回
return proxyClass;
} else if (value == pendingGenerationMarker) {
try {
cache.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
continue;
} else {
cache.put(key, pendingGenerationMarker);
break;
}
} while (true);
}
try {
// 中间省略了一些代码 .......
// 这里就是动态生成代理对象的最关键的地方
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(proxyName, interfaces);
try {
// 根据代理类的字节码生成代理类的实例
proxyClass = defineClass0(loader, proxyName,
proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
} catch (ClassFormatError e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
// add to set of all generated proxy classes, for isProxyClass
proxyClasses.put(proxyClass, null);
}
// 中间省略了一些代码 .......
return proxyClass;
} 上面我们提到了ProxyGenerator是完成动态代理类class字节码功能的类,这里就调用了它的静态方法generateProxyClass,进入该方法:
public static byte[] generateProxyClass(final String name,
Class[] interfaces)
{
ProxyGenerator gen = new ProxyGenerator(name, interfaces);
// 这里动态生成代理类的字节码
final byte[] classFile = gen.generateClassFile();
// 如果saveGeneratedFiles的值为true,则会把所生成的代理类的字节码保存到硬盘上
if (saveGeneratedFiles) {
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new java.security.PrivilegedAction() {
public Void run() {
try {
FileOutputStream file =
new FileOutputStream(dotToSlash(name) + ".class");
file.write(classFile);
file.close();
return null;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InternalError(
"I/O exception saving generated file: " + e);
}
}
});
}
// 返回代理类的字节码
return classFile;
} 看到这里就清楚了,是通过调用generateProxyClass方法来实现代理类字节码的创建的。好了,通过上述源码的分析,对于如何创建代理的流程就很清晰了,但是最后生成的代理类的结构是怎么样的呢,而且InvocationHandler又是怎么被调用的呢,下面我们先生成一个代理类,保存到磁盘,然后查看class文件。
public class ProxyGeneratorUtils {
/**
* 把代理类的字节码写到硬盘上
* @param path 保存路径
*/
public static void writeProxyClassToHardDisk(String path) {
// 第一种方法,这种方式在刚才分析ProxyGenerator时已经知道了
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", true);
// 第二种方法
// 获取代理类的字节码
byte[] classFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass("$Proxy11", CountImpl.class.getInterfaces());
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(path);
out.write(classFile);
out.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
public void test(){
writeProxyClassToHardDisk("D:/proxy/$Proxy11.class");
}
}执行测试,代理类就保存在d:/proxy目录下了,用JD-Gui工具打开class文件:
/**
* 代理类实现了与目标类Count相同的接口,并继承了Proxy
*
*/
public final class $Proxy11 extends Proxy implements Count, Money {
private static Method m1;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m0;
private static Method m4;
private static Method m2;
/**
* 代理类的构造方法需要一个InvocationHanlder作为参数
*
* @param paramInvocationHandler
*/
public $Proxy11(InvocationHandler paramInvocationHandler) {
super(paramInvocationHandler);
}
/**
* 实现了目标类Count的equals方法
*/
public final boolean equals(Object paramObject) {
try {
// 实际上是通过调用InvaocationHandler.invoke(proxy, equals, args)来调用目标类Count的equals方法
return ((Boolean) this.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[] { paramObject })).booleanValue();
} catch (Error | RuntimeException localError) {
throw localError;
} catch (Throwable localThrowable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
/**
* 实现了目标类Count的count方法
*/
public final void count() {
try {
// 实际上是通过调用InvaocationHandler.invoke(this, count, args)来调用目标类Count的count方法
this.h.invoke(this, m3, null);
return;
} catch (Error | RuntimeException localError) {
throw localError;
} catch (Throwable localThrowable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
/**
* 实现了目标类Count的hashCode方法
*/
public final int hashCode() {
try {
// 实际上是通过调用InvaocationHandler.invoke(this, hashCode, args)来调用目标类Count的count方法
return ((Integer) this.h.invoke(this, m0, null)).intValue();
} catch (Error | RuntimeException localError) {
throw localError;
} catch (Throwable localThrowable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
/**
* 实现了目标类Count的update方法
*/
public final void update() {
try {
// 实际上是通过调用InvaocationHandler.invoke(this, update, args)来调用目标类Count的count方法
this.h.invoke(this, m4, null);
return;
} catch (Error | RuntimeException localError) {
throw localError;
} catch (Throwable localThrowable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
/**
* 实现了目标类Count的toString方法
*/
public final String toString() {
try {
// 实际上是通过调用InvaocationHandler.invoke(this, toString, args)来调用目标类Count的count方法
return (String) this.h.invoke(this, m2, null);
} catch (Error | RuntimeException localError) {
throw localError;
} catch (Throwable localThrowable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
/**
* 代理类需要代理目标类的方法,包括父类,接口,目标类自己的所有公共方法
*/
static {
try {
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[] { Class.forName("java.lang.Object") });
m3 = Class.forName("cn.test.proxy.Count").getMethod("count", new Class[0]);
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]);
m4 = Class.forName("cn.test.proxy.Money").getMethod("update", new Class[0]);
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]);
return;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException localNoSuchMethodException) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(localNoSuchMethodException.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException localClassNotFoundException) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(localClassNotFoundException.getMessage());
}
}
}
仔细观察可以看出生成的动态代理类有以下特点:
1.继承自 java.lang.reflect.Proxy,实现了 Count,MONEY 这两个CountImp实现的接口;
2.类中的所有方法都是final 的;
3.所有的方法功能的实现都统一调用了InvocationHandler的invoke()方法。
3.2 Cglib动态代理
JDK的动态代理机制只能代理实现了接口的类,而没有实现接口的类就不能实现JDK的动态代理,cglib是针对此类来实现代理的,它的原理就是对指定的目标类生成一个子类,并覆盖其中的方法来实现增强功能,但因为采用的是继承,所以不能对final修饰的类进行代理。
3.2.1 什么是Cglib
CGLIB是一个强大的高性能的代码生成包。
- 广泛的被许多AOP的框架使用,例如:Spring AOP和dynaop,为他们提供方法的interception(拦截);
- hibernate使用CGLIB来代理单端single-ended(多对一和一对一)关联(对集合的延迟抓取,是采用其他机制实现的);
- EasyMock和jMock是通过使用模仿(moke)对象来测试java代码的包。
它们都通过使用CGLIB来为那些没有接口的类创建模仿(moke)对象。
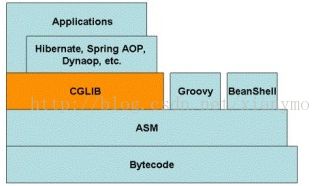
CGLIB包的底层是通过使用一个小而快的字节码处理框架ASM(Java字节码操控框架),来转换字节码并生成新的类。除了CGLIB包,脚本语言例如 Groovy和BeanShell,也是使用ASM来生成java的字节码。当不鼓励直接使用ASM,因为它要求你必须对JVM内部结构包括class文件的格式和指令集都很熟悉。所以cglib包要依赖于asm包,需要一起导入。下图为cglib与一些框架和语言的关系(CGLIB Library and ASM Bytecode Framework)。
Spring AOP和Hibernate同时使用JDK的动态代理和CGLIB包。Spring AOP,如果不强制使用CGLIB包,默认情况是使用JDK的动态代理来代理接口。
3.2.2 Cglib动态代理实现
a. 业务类
public class CountImpl {
public void count(){
System.out.println("计算账户余额。。。");
}
}
public class MyMethodIntercaptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args,
MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("开始记录日志。。。");
proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
System.out.println("结束记录日志。。。");
return null;
}
}
c. 代理类生成工厂
public class ProxyFactory {
public static Object getProxy(Object target){
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = new MyMethodIntercaptor();
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());
enhancer.setCallback(methodInterceptor);
return enhancer.create();
}
}d. 测试类
public class CountProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
CountImpl countImpl = new CountImpl();
CountImpl countProxy = (CountImpl) ProxyFactory.getProxy(countImpl);
countProxy.count();
}
}e. 输出结果
开始记录日志。。。
计算账户余额。。。
结束记录日志。。。
Cglib的源码分析暂不分析了。
3.3 javassist实现动态代理
动态代理本质上就是在程序运行期间根据目标类重新创建一个代理类,而通过代理类去反射调用目标类的业务逻辑。理解了这个,我们就很容易用javassist来实现动态代理,
关于javassist的介绍,前面文章有介绍:Javassist详解。
3.3.1 javassist实现动态代理
a. 业务类接口
public interface Count {
public void count();
public void sayHello();
}b. 业务类实现类
public class CountImpl implements Count{
@Override
public void count() {
System.out.println("计算账户余额。。。");
}
@Override
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("你好。。。。");
}
}c. 自定义Interacptor
public interface Interceptor {
public int intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] Args);
}d. 代理类生成工厂
/**
* 基于Javassist动态生成字节码实现简单的动态代理
**/
public class Proxy {
/**
* 动态生成的代理类名前缀
* */
private static final String PACKAGE_NAME = Proxy.class.getPackage().getName();
/**
* 代理类名索引 用于标示一个唯一的代理类(具体的代理类名为PACKAGE_NAME$n)
* class
* */
private static final AtomicLong PROXY_CLASS_COUNTER = new AtomicLong(0);
/**
* 代理拦截器(利用继承减少动态构造的字节码)
* */
protected Interceptor interceptor;
protected Proxy(Interceptor interceptor) {
this.interceptor = interceptor;
}
/**
* 创建动态代理的工厂方法 static factory method for create proxy
*
* @param targetClass:被代理的类型
* @param interceptor:拦截器实例
* @return 返回动态代理实例 它实现了targerClass的所有接口。 因此可以向上转型为这些之中的任意接口
* */
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static Object createProxy(Class targetClass, Interceptor interceptor) {
int index = 0;
/* 获得运行时类的上下文 */
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
/* 动态创建代理类 */
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass(PACKAGE_NAME + ".$proxy" + PROXY_CLASS_COUNTER.getAndIncrement());
try {
/* 获得Proxy类作为代理类的父类 */
CtClass superclass = pool.get(Proxy.class.getName());
ctClass.setSuperclass(superclass);
/* 获得被代理类的所有接口 */
CtClass[] interfaces = pool.get(targetClass.getName()).getInterfaces();
for (CtClass i : interfaces) {
/* 动态代理实现这些接口 */
ctClass.addInterface(i);
/* 获得结构中的所有方法 */
CtMethod[] methods = i.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int n = 0; n < methods.length; n++) {
CtMethod m = methods[n];
/* 构造这些Method参数 以便传递给拦截器的interceptor方法 */
StringBuilder fields = new StringBuilder();
fields.append("private static java.lang.reflect.Method method"+ index);
fields.append("=Class.forName(\"");
fields.append(i.getName());
fields.append("\").getDeclaredMethods()[");
fields.append(n);
fields.append("];");
/* 动态编译之 */
CtField cf = CtField.make(fields.toString(), ctClass);
ctClass.addField(cf);
GenerateMethods(pool, ctClass, m, index);
index++;
}
}
/* 创建构造方法以便注入拦截器 */
CtConstructor cc = new CtConstructor(new CtClass[] { pool.get(Interceptor.class.getName()) }, ctClass);
cc.setBody("{super($1);}");
ctClass.addConstructor(cc);
ctClass.writeFile("d:/proxy/"+ctClass.getSimpleName());
return ctClass.toClass().getConstructor(Interceptor.class).newInstance(interceptor);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 动态生成生成方法实现(内部调用)
* */
private static void GenerateMethods(ClassPool pool, CtClass proxy,
CtMethod method, int index) {
try {
CtMethod cm = new CtMethod(method.getReturnType(),method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes(), proxy);
/* 构造方法体 */
StringBuilder mbody = new StringBuilder();
mbody.append("{super.interceptor.intercept(this,method");
mbody.append(index);
mbody.append(",$args);}");
cm.setBody(mbody.toString());
proxy.addMethod(cm);
} catch (CannotCompileException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}e. 测试程序
public class CountProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Count count = new CountImpl();
Count countProxy = (Count) Proxy.createProxy(count.getClass(), new MyInterceptor(count));
countProxy.count();
countProxy.sayHello();
}
}f. 输出结果
开始记录日志。。。。
计算账户余额。。。
结束记录日志。。。。
开始记录日志。。。。
你好。。。。
结束记录日志。。。。
从结果可以看到,我们已经用javassist实现了一个动态代理,然后我们查看生成的代理类字节码文件:
public class $proxy0 extends Proxy implements Count
{
private static Method method0 = java.lang.Class.forName("cn.test.proxy.Count").getDeclaredMethods()[0];
private static Method method1 = java.lang.Class.forName("cn.test.proxy.Count").getDeclaredMethods()[1];
public void count()
{
this.interceptor.intercept(this, method0, new Object[0]);
}
public void sayHello()
{
this.interceptor.intercept(this, method1, new Object[0]);
}
public $proxy0(Interceptor paramInterceptor)
{
super(paramInterceptor);
}
}生成的代理类和jdk动态代理形式差不多,实现了目标类的接口,继承了我们自定义的Proxy类以及实现了目标类的所有公共方法。