Apollo项目类对象创建之工厂模式分析
前段时间写过这样一篇文章,因为CSDN的一个Bug,把原有文章覆盖了,咨询版务人员得知无法恢复,只能凭记忆再写一遍,供自己和可能需要帮助的人参考借鉴。
Apollo项目(https://github.com/apolloauto)的对象创建,大多使用直接法,例如:
// 在栈(stack)上直接创建对象
ADCTrajectory not_ready_pb;
// 在堆(heap)上直接创建对象
ZeroCopyOutputStream *output = new FileOutputStream(file_descriptor);还有部分对象使用单例(Singleton)模式创建,例如:
DECLARE_SINGLETON(AdapterManager);这里,DECLARE_SINGLETON(AdapterManager)是一个定义单例对象的宏,其定义如下:
#define DECLARE_SINGLETON(classname) \
public: \
static classname *instance() { \
static classname instance; \
return &instance; \
} \
DISALLOW_IMPLICIT_CONSTRUCTORS(classname) \
private:内嵌宏DISALLOW_IMPLICIT_CONSTRUCTORS(classname)的定义如下:
#define DISALLOW_IMPLICIT_CONSTRUCTORS(classname) \
private: \
classname(); \
DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname);继续看内嵌宏DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname)的定义:
#define DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname) \
private: \
classname(const classname &); \
classname &operator=(const classname &);于是,DECLARE_SINGLETON(AdapterManager)展开后的定义为:
public:
static AdapterManager *instance() {
static AdapterManager instance;
return &instance;
}
private:
AdapterManager();
private:
AdapterManager(const AdapterManager &);
AdapterManager &operator=(const AdapterManager &);
private:上述代码的意义一目了然,首先定义一个静态公有函数instance(),该函数在栈上创建一个AdapterManager类的静态对象,然后以指针形式将其返回。同时,将AdapterManager类的默认(或称缺省)构造函数、复制(或称拷贝)构造函数、复制赋值运算符(或称操作符)定义为私有函数,意即禁止进行隐式类型转换和复制操作。
还有部分对象,采用工厂模式创建,例如:
control_conf_ = control_conf;
for (auto controller_type : control_conf_->active_controllers()) {
auto controller = controller_factory_.CreateObject(
static_cast(controller_type));
if (controller) {
controller_list_.emplace_back(std::move(controller));
} else {
AERROR << "Controller: " << controller_type << "is not supported";
return Status(ErrorCode::CONTROL_INIT_ERROR,
"Invalid controller type:" + controller_type);
} 关于工厂模式的介绍,网上有很多文章,这篇文章讲得比较形象,值得参考:http://blog.csdn.net/linwh8/article/details/51232834,本文不再赘述。
使用工厂模式的必要性
很多人会问,我直接创建类对象就行了,为什么要使用工厂模式?不是脱裤子放屁,多此一举吗?其实不然,在很多应用中,需要创建哪些具体的类对象,事先根本无法知晓,只有在程序实际运行的那一刻,才能从配置文件、注册表或数据库获取需要创建的类对象,在此情形下,还能直接创建类对象吗?
另外,在许多应用中,我们希望通过改变配置文件、注册表或数据库来动态地使用不同的算法类,以期获得最优的性能,这种情形是不是也需要采用工厂模式动态创建类对象?
Apollo项目使用工厂模式创建类对象分析
Apollo项目使用的是抽象工厂模式,因为该项目使用模板定义工厂类,因此工厂模式经典定义中的抽象工厂类就不再需要了,下面看该类的具体定义:
#ifndef MODULES_COMMON_UTIL_FACTORY_H_
#define MODULES_COMMON_UTIL_FACTORY_H_
#include
#include CreateObjectOrNull(const IdentifierType &id,
Args... args) {
auto id_iter = producers_.find(id);
if (id_iter != producers_.end()) {
return std::unique_ptr(
(id_iter->second)(std::forward(args)...));
}
return nullptr;
}
/**
* @brief Creates and transfers membership of an object of type matching id.
* Need to register id before CreateObject is called.
* @param id The identifier of the class we which to instantiate
* @param args the object construction arguments
*/
template <typename... Args>
std::unique_ptr CreateObject(const IdentifierType &id,
Args... args) {
auto result = CreateObjectOrNull(id, args...);
AERROR_IF(!result) << "Factory could not create Object of type : " << id;
return result;
}
private:
MapContainer producers_;
};
} // namespace util
} // namespace common
} // namespace apollo
#endif // MODULES_COMMON_UTIL_FACTORY_H_ Factory类包含了Register()、Unregister()、Empty()、CreateObjectOrNull()、CreateObject()等公有函数,其中Register()、Unregister()函数用于注册和反注册产品类,其作与经典模式中抽象工厂接口类的功能类似,Empty()函数用于判断当前工厂类中是否包含产品创建函数,CreateObjectOrNull()、CreateObject()函数用于创建可能包含空指针和不包含空指针的产品类对象。
Apollo项目中对Factory类实例化的情形包括但不限于:
apollo::common::util::Factory<
ControlConf::ControllerType,
Controller,
std::mapapollo::common::util::Factory<
LocalizationConfig::LocalizationType,
LocalizationBase,
std::mapapollo::common::util::Factory<
PlanningConfig::PlannerType,
Planner,
std::mapapollo::common::util::Factory<
TaskType,
Task,
std::map具体类图如下所示:
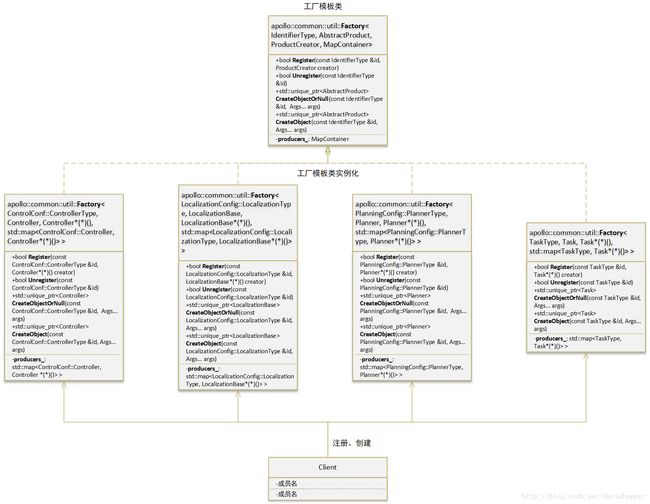
下面以apollo::common::util::Factory为例进行说明(其他示例不再一一讲解),类图如下:

注册产品类代码为:
void EMPlanner::RegisterTasks() {
task_factory_.Register(TRAFFIC_DECIDER,
[]() -> Task* { return new TrafficDecider(); });
task_factory_.Register(DP_POLY_PATH_OPTIMIZER,
[]() -> Task* { return new DpPolyPathOptimizer(); });
task_factory_.Register(PATH_DECIDER,
[]() -> Task* { return new PathDecider(); });
task_factory_.Register(DP_ST_SPEED_OPTIMIZER,
[]() -> Task* { return new DpStSpeedOptimizer(); });
task_factory_.Register(SPEED_DECIDER,
[]() -> Task* { return new SpeedDecider(); });
task_factory_.Register(QP_SPLINE_ST_SPEED_OPTIMIZER, []() -> Task* {
return new QpSplineStSpeedOptimizer();
});
task_factory_.Register(POLY_ST_SPEED_OPTIMIZER,
[]() -> Task* { return new PolyStSpeedOptimizer(); });
}代码中的产品创建函数ProductCreator=Task* (*)()全部采用简洁的Lambda表达式实现。
创建具体产品类对象的代码为:
Status EMPlanner::Init(const PlanningConfig& config) {
AINFO << "In EMPlanner::Init()";
RegisterTasks();
for (const auto task : config.em_planner_config().task()) {
tasks_.emplace_back(
task_factory_.CreateObject(static_cast(task)));
AINFO << "Created task:" << tasks_.back()->Name();
}
// ...
return Status::OK();
} 配置文件为:modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt,Apollo 2.0配置的任务类型如下所示:
planner_type : EM
em_planner_config {
task : TRAFFIC_DECIDER
task : DP_POLY_PATH_OPTIMIZER
task : PATH_DECIDER
task : DP_ST_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
task : SPEED_DECIDER
task : QP_SPLINE_ST_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
// ...上述配置文件表明,EMPlanner类中动态生成了TrafficDecider、DpPolyPathOptimizer、
PathDecider、DpStSpeedOptimizer、
SpeedDecider、QpSplineStSpeedOptimizer等优化任务类对象。