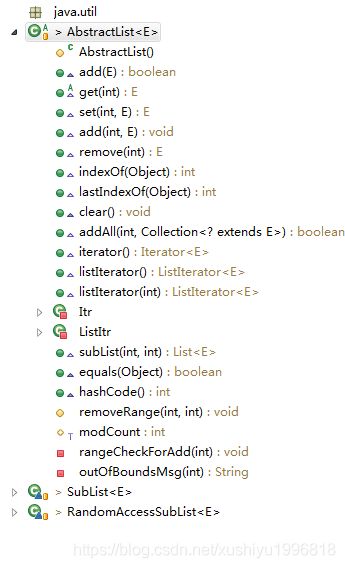
java容器 抽象类AbstractList源码分析
目录
简介
构造器
基于index的方法-两个add,get,remove,set
查找元素-indexOf,lastIndexOf
块操作-addAll,clear
辅助操作-removeRange,rangeCheckForAdd,outOfBoundsMsg
字段-modCount
比较和哈希-equals,hashCode
迭代器-Iterator,ListIterator,对应的两个内部类Itr,ListItr
分段列表 subList,两个内部类 SubList,RandomAccessSubList
简介
/**
* 这个类提供了一个List接口的骨架似的实现,
* 来最小化实现List接口的努力,而且这个实现支持随机访问的数据存储(类似数组)。
* 对于一个顺序访问的数据(例如链表),AbstractSequentialList应该被优先使用。
*
*
为了实现一个不可更改的列表,编程者仅仅需要继承这个类,
* 提供get(int)和size()方法的实现即可。
*
*
为了实现一个可更改的列表,编程者需要额外覆盖set(int, Object)方法。
* 如果列表是可变大小的,编程者需要额外覆盖add(int, Object)和remove(int)方法
*
*
编程者通常需要提供一个无参构造器,和集合作为参数的构造器,作为Collection接口的规范的建议。
*
*
不像其他抽象集合实现,编程者不一定要提供一个Iterator的实现。
* 这个类实现了Iterator和ListIterator,它们位于随机访问方法之上:
* get(int), set(int, E), add(int, E) , remove(int).
*
*
文档中,这个类的每个非抽象方法详细地描述了它的实现。
* 如果正在实现的集合有更有效的实现,这种方法可以被覆盖。
*
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @since 1.2
*/
public abstract class AbstractList extends AbstractCollection implements List
构造器
/**
* Sole constructor. (For invocation by subclass constructors, typically
* implicit.)
*
* 唯一的构造器(通过子类构造器调用,通常是隐式的)
*/
protected AbstractList() {
}基于index的方法-两个add,get,remove,set
//修改操作
/**
* 在列表的最后加入一个指定元素(可选操作)
*
*
支持此操作的列表可能会限制加入到列表的元素。
* 尤其是,一些列表拒绝添加null元素,一些对元素的类型做限制。
* 列表类应该明确地在他们的文档中,指定对可以添加的元素,做出哪些限制。
*
*
这个实现称为add(size(), e)
*
*
注意:这个实现会抛出UnsupportedOperationException,
* 除非add(int, Object)被覆盖
*
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code add} operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element
* prevents it from being added to this list
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//调用add的重载方法,在末尾加入e
add(size(), e);
return true;
}
//基于位置的操作
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
abstract public E get(int index);
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
*
This implementation always throws an
* {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
*
This implementation always throws an
* {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
*
This implementation always throws an
* {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
查找元素-indexOf,lastIndexOf
// 查找操作
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* 这个实现一开始得到一个ListIterator(调用listIterator),
* 然后遍历列表,直到指定元素被找到,或者碰到列表末尾。
*
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
//得到ListIterator
ListIterator it = listIterator();
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasNext())
if (it.next()==null)
return it.previousIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasNext())
if (o.equals(it.next()))
//因为调用了next,游标已经在对应元素右边,所以返回previousIndex
return it.previousIndex();
}
return -1;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* 这个实现一开始得到一个ListIterator,指向列表末尾(调用listIterator(size()))。
* 然后向后遍历列表,直到指定元素被找到,或者碰到列表开始。
*
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
//一开始,游标在列表最后元素的右边
ListIterator it = listIterator(size());
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (it.previous()==null)
return it.nextIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasPrevious())
//不断向左
if (o.equals(it.previous()))
//因为调用了previous,游标已经在对应元素左边,所以返回nextIndex
return it.nextIndex();
}
return -1;
}
块操作-addAll,clear
// Bulk Operations
/**
* 移除列表中所有的元素(可选操作)。这个方法返回后,列表为空。
*
* 这个实现调用removeRange(0, size())
*
*
注意这个实现会抛出UnsupportedOperationException,除非remove(int index)或者
* removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)被覆盖。
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code clear} operation
* is not supported by this list
*/
public void clear() {
removeRange(0, size());
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
*
这个实现得到一个指定集合的Iterator,并且遍历它,
* 插入从Iterator获取的元素到列表中的合适的位置,一次一次,使用add(int, E)。
* 许多实现会为了效率覆盖这个方法。
*
*
注意:这个实现会抛出UnsupportedOperationException,
* 除非add(int, E)被覆盖
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
//保证index的范围
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
boolean modified = false;
for (E e : c) {
//得到集合的每个元素
//调用add(int, E)
add(index++, e);
modified = true;
}
return modified;
}
辅助操作-removeRange,rangeCheckForAdd,outOfBoundsMsg
/**
* 移除这个列表中所有index在fromIndex(包含)到toIndex(不包含)的元素。
* 将后继的元素移到左边(减去index)。
* 这种调用减少了列表toIndex - fromIndex个元素。
* 如果toIndex==fromIndex,操作啥都不干。
*
* 这个方法被clear操作调用于这个列表和subList。
* 覆盖这个方法,来利用列表实现的内部机制能充分地提高clear操作的性能,在这个列表和subList。
*
*
这个实现得到一个ListIterator,在fromIndex之前,重复调用ListIterator.next,
* 和 ListIterator.remove ,直到整个范围都被移除了。
* 注意:如果 ListIterator.remove需要线性时间,实现需要二次方的时间
*
* @param fromIndex index of first element to be removed
* @param toIndex index after last element to be removed
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
ListIterator it = listIterator(fromIndex);
for (int i=0, n=toIndex-fromIndex; i
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size())
//index范围为[0,size()-1]
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
//返回列表大小和列表要的index,说明哪里超出范围了
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size();
}字段-modCount
/**
* 这个列表在结构上被改变的次数。
* 结构上的改变是那些改变列表的大小,或者一个扰乱列表的方式,这种方式能让迭代过程中,可能产生错误的结果。
*
* 这个字段由iterator和listIterator方法返回的Iterator和ListIterator使用。
* 如果这个字段的值没有按照预期改变,Iterator或者ListIterator会在
* next,remove,previous,set,add操作中抛出ConcurrentModificationException.
* 这提供快速失败的机制,而不是在迭代过程中,面对并发修改的行为,产生不确定性的行为。
*
*
子类使用这个字段是可选的。
* 如果一个子类希望提供一个快速失败的Iterator(和ListIterator),
* 那么它只需要在add(int, E),remove(int)方法
* (或者其他覆盖的,会导致列表的结构改变的方法)中,递增这个字段。
* 一次调用add(int, E)或remove(int)一定不超让这个字段增加超过1,
* 否则Iterator(和ListIterator)会抛出假的ConcurrentModificationExceptions。
* 如果一个实现不希望提供快速失败的Iterator,这个字段可以忽略。
*
*/
protected transient int modCount = 0;
比较和哈希-equals,hashCode
// 比较和哈希
/**
* 将指定对象与这个列表进行相等性的比较。
* 当且仅当指定对象也是一个列表,两个列表有相同的大小,两个列表所有对应的元素对,都是相同的,返回true。
* e1和e2两个元素相等,如果(e1==null ? e2==null : e1.equals(e2))。
* 换言而之,两个列表被定义为相同的,如果它们有同样的顺序的同样的元素。
*
* 这个实现首先检查指定对象是否是这个列表自己。
* 如果是,返回true。如果不是,检查指定对象是否是列表。
* 如果不是返回false。如果是,遍历两个列表,比较元素对。
* 如果有一个比较返回false,方法返回false。
* 如果有一个迭代器在另一个迭代器前耗完元素,返回false(两个列表长度不同)
* 否则在操作完成后,返回true
*
*
* @param o the object to be compared for equality with this list
* @return {@code true} if the specified object is equal to this list
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
//检验是否是自己
return true;
if (!(o instanceof List))
//检验是否是列表
return false;
ListIterator e1 = listIterator();
ListIterator e2 = ((List) o).listIterator();
//调用两者的ListIterator
while (e1.hasNext() && e2.hasNext()) {
E o1 = e1.next();
Object o2 = e2.next();
if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2)))
//有一个不同,返回false
return false;
}
//如果有一个有next,返回false,否则都耗尽元素,返回true
return !(e1.hasNext() || e2.hasNext());
}
/**
* 返回列表的hashcode
*
* 此实现使用的正是用于在List接口文档中描述hashCode方法。
*
* @return the hash code value for this list
*/
public int hashCode() {
int hashCode = 1;
for (E e : this)
//类似于string的hashcode,只是将char的hash变成每个元素的hash
hashCode = 31*hashCode + (e==null ? 0 : e.hashCode());
return hashCode;
}
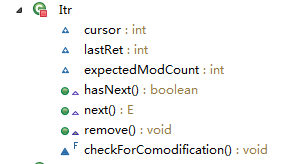
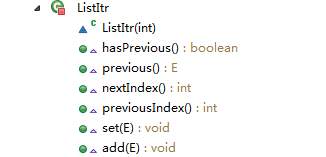
迭代器-Iterator,ListIterator,对应的两个内部类Itr,ListItr
// Iterators
/**
* 返回一个覆盖列表中元素的Iterator,以适当的顺序
* 这个实现返回了一个Iterator接口的直接实现,依赖于列表的size(),get(int),remove(int)方法
*
*
注意:方法返回的Iterator的remove方法会抛出UnsupportedOperationException,
* 除非列表的remove(int)方法被覆盖。
*
*
这个实现可以在并发修改时,抛出运行时异常,如protected的modCount字段的描述。
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* 这个实现返回listIterator(0)
* @see #listIterator(int)
*/
public ListIterator listIterator() {
return listIterator(0);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* 这个实现返回一个实现ListIterator接口的实现,它继承了Iterator方法返回的Iterator类。
* ListIterator实现依赖于列表的get(int),set(int, E),add(int, E),remove(int),size()方法
*
*
注意:调用返回的ListIterator的remove,set,add方法会抛出UnsupportedOperationException,
* 除非set(int, E),add(int, E),remove(int)方法被覆盖
*
*
这个实现当面对并发修改会抛出运行时异常,如protected的modCount字段描述的规范。
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public ListIterator listIterator(final int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class Itr implements Iterator {
/**
* 下一次调用next,返回的元素的index
*/
int cursor = 0;
/**
* 最近一次调用next或者previous返回的元素的index。
* 如果这个元素被remove删除了,重新设置为 -1
*/
int lastRet = -1;
/**
* Iterator相信依赖的列表应该有的modCount。
* 如果预期被违背了,Iterator已经探测到并发修改。
*/
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
//如果cursor到size(),就没有next的元素了
return cursor != size();
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
//返回的是cursor的元素,通过get方法得到
E next = get(i);
//设置上一个next或者previous返回的元素的index
lastRet = i;
//cursor递增
cursor = i + 1;
return next;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
//如果已经remove过了,就不能再remove了
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
//调用自身实现的remove方法
AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);
if (lastRet < cursor)
//游标减少
cursor--;
//重新设置lastRet
lastRet = -1;
//重新设置expectedModCount(这个和自己的remove的结果相关)
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
//检查当前的modCount是否与预期的modCount相同
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//继承了Itr,由原来的的三个属性和4个方法
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator {
ListItr(int index) {
//设置cursor
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
//如果cursor不,0,previous的index不为-1,就一定有previous
return cursor != 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor - 1;
//返回cursor-1的元素
E previous = get(i);
//cursor和lastRet都变成cursor-1
lastRet = cursor = i;
return previous;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor-1;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
//调用主体队列的set方法,对lastRet重新设定
AbstractList.this.set(lastRet, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
//在cursor处插入元素,原有的cursor及之后的被移到右边
AbstractList.this.add(i, e);
lastRet = -1;
//下一次next返回的是原来cursor处,现在的cursor+1处的
//下一次previous返回的是现在的cursor处,被插入的元素e
cursor = i + 1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
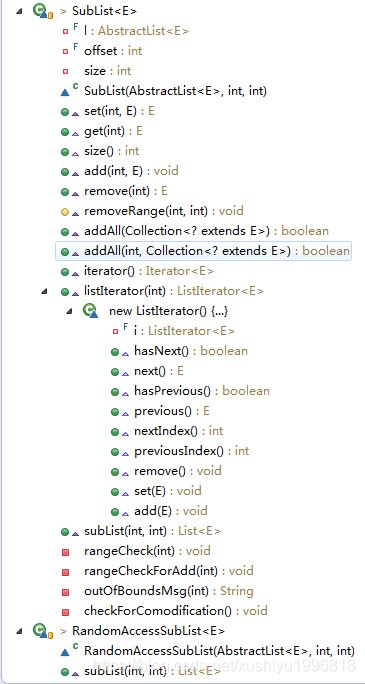
} 分段列表 subList,两个内部类 SubList,RandomAccessSubList
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* 这个实现返回了一个继承了AbstractList的列表。
* 子类在私有字段内,存储了依赖列表的偏移量,大小(在生命周期内能改变)和预期的modCount。
* 子类有两个变体,一个实现了RandomAccess接口。
* 如果这个列表实现了RandomAccess,返回的列表会是实现了RandomAccess接口的子类的实例。
*
*
*
子类的set(int, E), get(int), add(int, E), remove(int),
* addAll(int, Collection)和removeRange(int, int)方法
* 在检查index的大小,然后根据偏移量调整后,将方法委托给依赖的abstract list。
* addAll(int, Collection)方法仅仅返回addAll(size, c)。
*
*
listIterator(int)方法返回了一个基于依赖的列表的ListIterator的包装对象,
* 它以依赖的列表的对应方法创建。
* Iterator方法仅仅返回了一个ListIterator,
* size方法仅仅返回子类的size字段。
*
*
所有的方法首先检查依赖的列表的modCount是否与预期值相同,
* 如果不同,抛出ConcurrentModificationException
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if an endpoint index value is out of range
* {@code (fromIndex < 0 || toIndex > size)}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the endpoint indices are out of order
* {@code (fromIndex > toIndex)}
*/
public List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return (this instanceof RandomAccess ?
//根据实现是否实现RandomAccess接口,返回两个类的构造函数的结果
new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex) :
new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex));
}
//继承abstractlist
class SubList extends AbstractList {
//依赖的列表
private final AbstractList l;
//偏移量,就是fromIndex,以后传入index,实际操作的是依赖列表的fromIndex+index
private final int offset;
//大小,就是toIndex - fromIndex
private int size;
SubList(AbstractList list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > list.size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
l = list;
offset = fromIndex;
size = toIndex - fromIndex;
//sublist的modCount目前为依赖的列表的modCount
this.modCount = l.modCount;
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
//在依赖列表的index+offset位进行对应操作
return l.set(index+offset, element);
}
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
return l.get(index+offset);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
//返回sublist大小
return size;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
l.add(index+offset, element);
//更新modCount
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size++;
}
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E result = l.remove(index+offset);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size--;
return result;
}
//给clear调用
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
l.removeRange(fromIndex+offset, toIndex+offset);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size -= (toIndex-fromIndex);
}
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
//在自己的size处,add
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
//在依赖的列表处增加
l.addAll(offset+index, c);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
//增加size
size += cSize;
return true;
}
public Iterator iterator() {
//其实继承的方法,调用了下面的listIterator(0)
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator listIterator(final int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListIterator() {
//i是在依赖的列表的ListIterator,在index+offset处开始
private final ListIterator i = l.listIterator(index+offset);
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex() < size;
}
public E next() {
if (hasNext())
//调用依赖列表的ListIterator的next
return i.next();
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return previousIndex() >= 0;
}
public E previous() {
if (hasPrevious())
调用依赖列表的ListIterator的next
return i.previous();
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public int nextIndex() {
//返回依赖列表元素的nextIndex-offset,是自身的index
return i.nextIndex() - offset;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return i.previousIndex() - offset;
}
public void remove() {
i.remove();
SubList.this.modCount = l.modCount;
size--;
}
public void set(E e) {
i.set(e);
}
public void add(E e) {
i.add(e);
SubList.this.modCount = l.modCount;
size++;
}
};
}
public List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
//保证index在sublist的范围内
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
private void checkForComodification() {
if (this.modCount != l.modCount)
//检查sublist的modCount与依赖列表的modCount是否相同
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//继承SubList,在 SubList 之外加了个 RandomAccess 的标识,表明他可以支持随机访问而已,和它没啥区别
//告诉调用者这个sublist,实现了RandomAccess(即实现了RandomAccess的列表的sublist也实现了RandomAccess)
class RandomAccessSubList extends SubList implements RandomAccess {
RandomAccessSubList(AbstractList list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
super(list, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
public List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
}