java容器 类ArrayList源码分析
目录
简介
字段 capacity默认值,默认空数组,elementData数组,大小size
构造函数 3个,无参,int,collection
对数组大小的控制 trimToSize,ensureXXX(3个),grow,hugeCapacity
创建ArrayList和扩展内部数组总结
查询操作 size,isEmpty,contains,indexOf,lastIndexOf
克隆及生成数组 clone,toArray(2个)
单个的基于位置的操作 elementData,get,set,add(两个),remove(两个)
批量操作 clear,addAll(两个),removeRange,removeAll,retainAll,及各种辅助方法
序列化方法 writerObject,readObject
迭代器方法 iterator,listIterator, 内部类Itr,ListLtr
subList
spliterator
其余的批量方法 forEach,removeIf,replaceAll,sort
基本性质
jdk1.6/1.7/1.8之间ArrayList的区别
默认构造方法,ArrayList()
带初始容量的构造方法,public ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
Collection拷贝构造方法,public ArrayList(Collection c)
确保容量方法(扩容方法):ensureCapacity/ensureCapacityInternal
jdk1.6/1.7/1.8之间小结
ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList之前区别
简介
/**
* List接口的可变大小-数组的实现。
* 实现了所有的可选列表操作,允许所有的元素,包括null。
* 除了实现了List接口,这个类提供了一些方法,来操纵列表中内部存储的数组的大小。
* (这个类大致与Vector相同,除了他没有被同步)
*
*
size、isEmpty、get、set、iterator和listIterator操作在常量时间内运行。
* add操作在平摊的常量时间内允许,增加n个元素,需要O(n)的实际。
* 所有其他的现在在线性的时间内完成(大致上)
* 与LinkedList实现相比,常量因素要低。
*
*
每个ArrayList实例都有一个容量。
* 容量是列表中存放元素的数组的大小。它永远最小与列表的大小一样大。
* 当元素被添加到ArrayList中,它的容量自动增长。
* 除了添加一个元素,消耗平摊的常量时间外,没有对增长策略的指定细节。
*
*
应用程序可以增加ArrayList实例的容量,
* 在使用ensureCapacity增加一大堆元素之前。
* 这可以减少递增的重新分配的数量。
*
*
注意:这个实现是不同步的。
* 如果多线程并发地访问一个ArrayList实例,
* 并且至少一个线程结构上修改了这个列表,那么它必须在外面同步。
* (结构上的改变是增加,删除一个或多个元素,
* 或者显式地改变依赖数组的大小,仅仅改变元素的值不会是一个结构上的改变)
* 这通常是对封装列表的对象进行同步,来完成。
* 如果没有这样的对象,列表应该使用Collections.synchronizedList来包装它。
* 它通常该在创建时做,来防止意外对列表的非同步访问。
*
* List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...));
*
* 返回的Iterator和ListIterator是快速失败的。
* 如果Iterator创建后,列表在任何时间被结构上改变了,
* 除了迭代器自己的remove和add方法外,迭代器会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
* 因此,面对并发的改变,Iterator快速失败,十分干净,
* 而不是在将来某个不确定的时间,冒着风险,做任意的,不确定性的操作。
*
*
注意:不能保证Iterator的快速失败机制,
* 因为,通常地说,在存在非同步的并发修改的情况下,不可能做出严格的保证。
* 快速失败的迭代器基于最大努力抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
* 因此,依赖于这个异常,写程序来保证正确性是错的,
* 迭代器的快速失败机制,应该仅仅被用来探测bug
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Collection
* @see List
* @see LinkedList
* @see Vector
* @since 1.2
*/
public class ArrayList extends AbstractList
implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
两个迭代器
sublist
spliterator
字段 capacity默认值,默认空数组,elementData数组,大小size
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* 默认的初始容量,10
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* 共享的空数组实例,用于空的ArrayList实例。
* 对应于ArrayList(0)或者elementData对应空数组
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* 共享的空的数组实例,用于默认大小的空的数组实例。
* 对应于ArrayList()
* 将它与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA区别出来,来知道当第一个元素被加入时,膨胀多少。
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* 存储ArrayList的元素的数组缓冲。
* ArrayList的容量是这个数组缓冲的长度。
* 当加入第一个元素时,任何空的ArrayList,有着elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* 将被扩展到DEFAULT_CAPACITY。
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // 非私有化,来简化嵌套类来访问(如sublist,Iterator)
/**
* ArrayList的大小(包含元素的数量),初始为0
* @serial
*/
private int size;构造函数 3个,无参,int,collection
/**
* 使用指定的初始容量,创建一个空的列表。
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
//如果>0,缓冲数组的大小为initialCapacity,
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
//如果等于0,为{}
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* 创建一个空的类别,初始容量为10(但是add之前为{})
*/
public ArrayList() {
//默认为为{}
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* 创建一个包含指定集合元素的列表,顺序为集合迭代器返回的顺序。
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
//数组设定为c.toArray(),集合自己的变为数组的结果
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
//如果数组长度不为0
// c.toArray 可能不返回(这是错误的)Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
//数组元素存入Ojbect数组中
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// 用空数组取代
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}对数组大小的控制 trimToSize,ensureXXX(3个),grow,hugeCapacity
/**
* 修剪ArrayList的容量,变为列表当前的大小。
* 应用程序能使用这个操作,来最小化ArrayList实例的存储空间
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
//size < elementData.length,修剪
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA //size==0 空数组
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); //否则数组大小为size
}
}
/**
* 增加ArrayList实例的容量,如果需要,
* 保证它能够持有数量最少为参数minCapacity指定的数量的元素。
* 注意:这个方法没有被ArrayList内部方法使用,基本没人使用它
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table 如果不是默认的元素数组,为0
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
//保证容量minCapacity
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
/** 这个方法被各种add调用,还有readObject方法使用,这个操作增加modCount
*
* @param minCapacity
*/
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//如果是空的默认数组,ArrayList(),大小为max(10,minCapacity),即至少为10,ensureExplicitCapacity(max(10,minCapacity))
//注意:如果调用ArrayList(0),数组为EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,不进入这个if,直接ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
//保证容量minCapacity
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// 如果minCapacity确实超出了数组长度,grow(minCapacity)
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* 数组分配的最大长度。
* 一些虚拟机在数组中存放头字段。分配更大的数组可能导致OutOfMemoryError:要求的数组大小超过了虚拟器限制
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* 增加容量,保证它能够持有数量最少为参数minCapacity指定的数量的元素。
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新长度为1.5倍的旧容量
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
//如果新长度 0)
//如果新长度大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,新长度为hugeCapacity(minCapacity),为MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
//或Integer.MAX_VALUE(当minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 最小容量通常与大小接近,所以这是赚的:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); //复制到大小为newCapacity的数组
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
//如果minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,返回Integer.MAX_VALUE,否则返回MAX_ARRAY_SIZE(即增加到MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
} 创建ArrayList和扩展内部数组总结
如果无参构造器,赋值elementaData为DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA这个空数组。
有参构造器,initialCapacity为0,赋值elementaData为EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA这个空数组。
initialCapacity大于0,赋值elementaData为initialCapacity大小的Object数组。
构造器参数为集合,赋值elementaData为c的size大小的Object数组,里面放置c的元素,如果没有元素,赋值EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA。
add方法,首先调用ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1)。
ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity)方法内,如果elementData 为DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,minCapacity是10和minCapacity的max。(即,如果调用无参构造器,第一次创建的数组大小至少为10)如果不是,则不变。然后调用ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity)
ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity)内,如果minCapacity确实超出了数组长度,调用grow(minCapacity)
grow(int minCapacity)方法内,新长度最大是Integer.MAX_VALUE,是旧长度的1.5倍,或者是minCapacity(看哪个大,即至少是旧长度的1.5倍),然后elementData复制到大小为newCapacity的数组,赋值给elementData
查询操作 size,isEmpty,contains,indexOf,lastIndexOf
/**
* 返回列表元素数量,直接返回size字段。
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* 根据size字段是否为0,返回列表是否为空
*
* @return true if this list contains no elements
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/**
* 如果集合包含指定元素,返回true。
* 更正式地,当且仅当集合至少有一个这样的元素时,返回true。
* (o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e)).
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return true if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
//是否o的index>=0
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
/**
* 返回列表中第一次出现指定元素的位置,或者如果列表中不包含这个元素,返回-1。
* 更正式地,返回最小的index i,
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i))),
* 或者如果没有这样的index,返回-1
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
//直接根据下标,遍历elementData数组
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 返回列表中最后一次出现指定元素的位置,或者如果列表中不包含这个元素,返回-1。
* 更正式地,返回最大的index i,
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i))),
* 或者如果没有这样的index,返回-1
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}克隆及生成数组 clone,toArray(2个)
/**
* 返回ArrayList实例的一个浅复制(元素自身不被复制)
*
* @return a clone of this ArrayList instance
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
ArrayList v = (ArrayList) super.clone();
//将元素的引用复制过去,数组大小为size,而不是当前的容量
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
v.modCount = 0;
return v;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
/**
* 返回一个包含这个列表所有元素的数组。(从第一个到最后一个元素)
*
* 返回的数组是安全的,因为列表没有维持对它的引用
* (换言而之,这个方法必须分配一个新的数组,即使列表内部已经有一个数组了)。
* 因此调用者修改返回的数组是安全的。
*
*
这个方法是基于数组和基于列表的API之间的桥梁。
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list in
* proper sequence
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
//数组为elementData
//大小为size
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
/**
*
返回一个包含这个列表所有元素的数组。(从第一个到最后一个元素)
* 返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。
* 如果列表适合这个指定的数组的大小,她就在里面返回。
* 否则,创建一个新数组,类型为指定数组的运行时类型,大小为这个列表的大小。
*
*
如果该列表适应指定的数组,有着剩余的空间(数组比列表有更多的元素),
* 数组中的元素在列表的末尾的,被设置为null。
* (如果调用者知道列表确实没有任何null元素,这才有助于决定列表的长度)
*
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of the list
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
// 如果size比a.length大,返回一个a.getClass()类型的新数组,内容为elementData,大小为size
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass());
//否则,复制在a的[0,size)处复制元素,后面的size处设置为null,之后的不管
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
单个的基于位置的操作 elementData,get,set,add(两个),remove(两个)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
//返回数组中index位置的元素,强转为E
return (E) elementData[index];
}
/**
* 返回列表中指定位置的元素。
* index范围[0,size()-1]
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
//先检查范围,再在数组中根据下标,直接获取元素
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* 用指定元素替代列表中指定位置的元素,返回旧元素
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
//得到旧元素,设置新元素,返回旧元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 在列表的最后加入一个指定元素
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return true (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//保证大小size=1,这个方法增加modCount
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//size处为e,然后size++
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* 插入指定元素到列表的指定位置。elementData[index] = element。
* 在这个位置的元素(如果有)和任何后边的元素被移动到右边(将它们的index+1)
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index); //检查范围[0,size]
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // 保证size+1的容量,modCount++
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);//index和随后size-index个,放到index+1去
elementData[index] = element; //index处为指定元素
size++;
}
/**
* 删除列表中指定位置的元素
* 移动后面的元素到左边(index-1)。
* 返回被移除的元素。
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index); //指定位置的旧元素
int numMoved = size - index - 1; //需要被移动的元素的数量
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved); //index+1和随后size-index-1个,放到index去
elementData[--size] = null; // 将size--位,设置为null,清理多出来的空间
return oldValue; // 返回被移除的元素
}
/**
* 如果指定元素存在,从列表中移除指定元素。如果列表不包含这个元素,列表不变。
* 更正式地说,移除一个index最小的这样的元素(如果这样的元素存在) ,
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))
* 如果列表包含指定元素,返回true。(如果列表因为调用而改变,返回true)
* 被移除的元素,可以认为被调用了remove(int)
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return true if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
//从前往后找
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
//可以视为快速的remove(int)
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/*
* 私有的remove方法,被remove(Object)使用,跳过边界检查,不返回移除的元素,其余的和remove(int)一样
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}批量操作 clear,addAll(两个),removeRange,removeAll,retainAll,及各种辅助方法
/**
* 移除列表中所有的元素。这个方法返回后,列表为空。
*/
public void clear() {
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
//数组内部元素的引用,全部设置为null
elementData[i] = null;
//size设置为0
size = 0;
}
/**
* 将指定列表的所有元素加入到这个列表的最后,顺序为指定列表的迭代器的返回顺序。
* 当执行操作时,如果修改指定列表,操作的结果未知。
* (这意味着,如果如果指定列表是这个列表,而且列表是非空的,调用的结果未知)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return true if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray(); // c.toArray 根据c的Iterator的顺序,返回的数组
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // 保证数量size+a.length Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); // 将a的从0开始,numNew个,放到数组的size处
size += numNew; //size增加numNew个
return numNew != 0;
}
/**
* 将指定列表的所有元素加入到这个列表的指定位置。
* 在这个位置的元素(如果有)和任何这个元素右边的元素,被移动到右边(增加它们的index)
* 新的元素出现的顺序为指定列表的迭代器的返回顺序。
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return true if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length; // 被加入的数量
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
int numMoved = size - index; // 被移动的数量
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved); //先将数组的index处,numMoved个,放到index+numNew处
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); // 将a的0处,numNew个,放到数组的index处
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
/**
* 移除这个列表中所有index在fromIndex(包含)到toIndex(不包含)的元素。
* 将后继的元素移到左边(减去index)。
* 这种调用减少了列表toIndex - fromIndex个元素。
* 如果toIndex==fromIndex,操作啥都不干。
*
* 这个方法被ArrayList的sublist的removeRange引用
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code fromIndex} or
* {@code toIndex} is out of range
* ({@code fromIndex < 0 ||
* fromIndex >= size() ||
* toIndex > size() ||
* toIndex < fromIndex})
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - toIndex;
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex,
numMoved); //数组的toIndex,numMoved个,移动到数组的fromIndex
// clear to let GC do its work
int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex);
for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) {
elementData[i] = null; //后面的设置为null
}
size = newSize;
}
/**
* 检查给定的index是否在范围内。给get,remove,set使用
* 如果不,抛出适当的运行时异常。
* 方法不检查index是否为负数:方法总是在任何数组访问前被使用,如果数组为负,会抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
*
检查范围(-无穷,size)
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* 对add和addAll使用的rangeCheck版本。检查范围[0,size]
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* 创建一个IndexOutOfBoundsException的详细信息。
* 在错误处理代码的许多可能重构中,这种“大纲”在服务器和客户机vm上都表现得最好。
*
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
/**
* 删除这个列表中,所有已经包含在指定列表的元素
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (optional)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (optional),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
*/
public boolean removeAll(Collection c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, false);
}
/**
* 列表中只保留指定列表包含的元素。
* 换言而之,列表中移除所有不被指定列表包含的元素。
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (optional)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (optional),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see Collection#contains(Object)
*/
public boolean retainAll(Collection c) {
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
return batchRemove(c, true);
}
/** 根据c.contains(elementData[r]),批量删除elementData的元素。
* 使用双指针算法,直接覆盖,而不是一个个删除
* @param c
* @param complement
* @return
*/
private boolean batchRemove(Collection c, boolean complement) {
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
int r = 0, w = 0; //r和w是数组中读取,写入的指针,双指针算法
boolean modified = false;
try {
for (; r < size; r++) //读取指针,不断递增到size
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)
//remove,complement为false,即集合不包含r对应的元素,依次写入(即包含时,就不写入数组了)
//retain,为true,包含时写入,不包含时,不写入
//写入后,w++
elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
} finally {
// 保持AbstractCollection的兼容性
// 如果c.contains() 抛出异常,此时r不为size
if (r != size) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, r,
elementData, w,
size - r); // 将数组的r开始,size-r个(即未被读取的),复制到w
w += size - r;
}
if (w != size) {
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
//将w之后的,设置为null
elementData[i] = null;
modCount += size - w;
size = w;
modified = true;
}
}
return modified;
}
序列化方法 writerObject,readObject
/**
* 保存ArrayList实例的状态,到一个流。(序列化)
*
* @serialData The length of the array backing the ArrayList
* instance is emitted (int), followed by all of its elements
* (each an Object) in the proper order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException{
// 写出元素计数和任何隐藏的东西
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// 输出size,作为容量,为了与clone方法兼容
s.writeInt(size);
// 以适当的顺序输出所有元素
for (int i=0; i 0) {
// 像clone方法,基于大小而不是容量分配数组
ensureCapacityInternal(size); // 保证容量size
Object[] a = elementData;
// 以适当的顺序读入所有元素
for (int i=0; i 迭代器方法 iterator,listIterator, 内部类Itr,ListLtr
/**
* 返回一个覆盖列表中元素的ListIterator(以适当的顺序),
* 以列表中指定位置开始。
* 指定位置的元素是第一次调用ListIterator的next方法返回的元素。
* 第一次调用ListIterator的previous方法返回的元素是指定index-1对应的元素。
*
* The returned list iterator is fail-fast.
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public ListIterator listIterator(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
/**
* 返回一个覆盖列表中元素的ListIterator(以适当的顺序)
*
* The returned list iterator is fail-fast.
*
* @see #listIterator(int)
*/
public ListIterator listIterator() {
return new ListItr(0);
}
/**
* 返回一个覆盖列表中元素的Iterator(以适当的顺序)
*
* The returned iterator is fail-fast.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* AbstractList.Itr 的优化版本
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator {
int cursor; // 下一个返回元素的index,初始为0
int lastRet = -1; // 上一次返回元素的index,如果没有,为-1
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
//检查cursor是否超出size和length
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
//返回elementData[cursor],设置lastRet = cursor,cursor++,
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
//调用ArrayList.remove(lastRet)
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
//cursor倒退为lastRet,lasetRet重设为-1,重设expectedModCount
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer consumer) {
//重写forEachRemaining
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
//i范围[cursor,size)
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// 在while循环后,更新,减少堆的写入流量
//如果正常结束,i=size,cursor=size,lastRet=size-1,modCount == expectedModCount
//非正常结束,i就不为size,modCount != expectedModCount,后面会报错
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* AbstractList.ListItr的优化版本
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index; //设置cursor
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
// 返回cursor-1,cursor--,lastRet=cursor-1
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
//在lastRet处set
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
//add(cursor,e)
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
//cursor++,重设lastRet
//从而 下次next的元素不变,previous的是新的元素 e
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
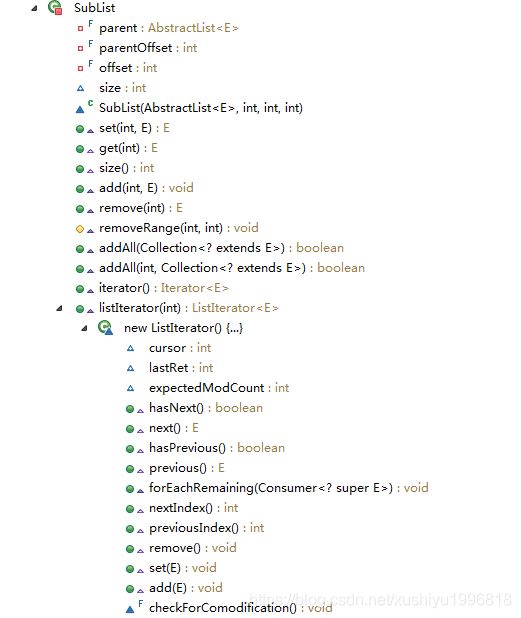
subList
/**
* 返回list一部分的视图,从指定的fromIndex(包含)到toIndex(不包含)。
* (如果fromIndex和toIndex相等,返回的list为空)
* 返回的列表有该列表支持,所以返回的列表的非结构性的改变会反映在这个列表中,反之亦然。
* 返回的列表支持所有由这个列表支持的可选list操作。
*
*
这个方法不需要显示的范围操作(数组中常见的那种)。
* 任何需要列表用作范围操作的操作,都可以传入一个subList视图,而不是一整个列表。
* 例如:从列表中删除一个范围的元素:
*
*
{@code
* list.subList(from, to).clear();
* }
*
*
* 可以用indexOf和lastIndexOf来构造类似的习语,
* 所有Collections的语法能适用于一个subList
*
*
如果支持的列表被结构性的改变了,而不是通过返回的列表改变,返回的列表的语义未知。
* (结构性的改变是改变这个列表的大小或者以一种正则进行的迭代的方式扰乱列表)
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
/** 0 <= fromIndex <= toIndex <= size
* @param fromIndex
* @param toIndex
* @param size
*/
static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
private class SubList extends AbstractList implements RandomAccess {
private final AbstractList parent;
// 在父亲list(ArrayList或sublist)的偏移量
// add,remove的位置是parentOffset + index,这个是调用parent的add和remove方法
// 可以发现sublist套sublist时,也是如abstractlist的sublist,一层套一层
// 调用上一层的sublist的add方法,直到最上层ArrayList时,真正调用
// 重要:之所以要一层层调用,是因为涉及到结构的变化,要让一层层的sublist都知道变化,所以要一层层调用,而不是直接对数组操作
private final int parentOffset;
// 自身在内部类SubList的外部类ArrayList的数组的偏移量,offset处为sublist开始的地方
// get,set的位置为offset+index,这个是直接对数组进行操作
private final int offset;
// size为to-from
int size;
// sublist的sublist
// 最初 return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
// 之后 return new SubList(this, offset, fromIndex2, toIndex2);
// 等于 return new SubList(this, 0 + fromIndex, fromIndex2, toIndex2);
// 之后 return new SubList(this, fromIndex + fromIndex2, fromIndex3, toIndex3);
SubList(AbstractList parent,
int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
this.parent = parent;
this.parentOffset = fromIndex;
this.offset = offset + fromIndex;
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
}
public E set(int index, E e) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e;
return oldValue;
}
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);
}
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return this.size;
}
public void add(int index, E e) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
parent.add(parentOffset + index, e);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size++;
}
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size--;
return result;
}
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex,
parentOffset + toIndex);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(this.size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c);
this.modCount = parent.modCount;
this.size += cSize;
return true;
}
public Iterator iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
public ListIterator listIterator(final int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
final int offset = this.offset;
return new ListIterator() {
// next和previous返回的元素是外部类数组的cursor+offset
// remove和add是调用外部subList的remove(lastRet)和add(cursor)方法
int cursor = index;
int lastRet = -1;
int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != SubList.this.size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = SubList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[offset + (i++)]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
lastRet = cursor = i;
checkForComodification();
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
SubList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(offset + lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
SubList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
};
}
public List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, offset, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size;
}
private void checkForComodification() {
if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public Spliterator spliterator() {
checkForComodification();
return new ArrayListSpliterator(ArrayList.this, offset,
offset + this.size, this.modCount);
}
}
spliterator
/**
* 创建一个迟绑定和快速失败的spliterator,覆盖这个列表的元素
*
* 这个spliterator报告是SIZED,SUBSIZED,ORDERED。
* 覆盖的实现应该报告额外的特征值。
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator spliterator() {
return new ArrayListSpliterator<>(this, 0, -1, 0);
}
/** 基于index,一次分割成两个,懒初始化的spliterator*/
static final class ArrayListSpliterator implements Spliterator {
/*
* 如果ArrayList是不可变的,或者结构不可变的(没有add,remove等待),
* 我们能用Arrays.spliterator来实现他们的分割器。
* 相反,我们再遍历过程中,检测出足够多的干扰,不牺牲太多的性能。
* 我们主要依赖modCount。
* 这些不能保证检测出太多的并发违背,并且有时对线程内的干扰过于保守,
* 但在实践中能探测出足够的问题。
* 为了实现这一点,
* 1 我们懒初始化fence和expectedModCount,直到最迟的时刻,
* 即我们需要提交我们正在检查的状态,直到提高精度。
* (这不适用于SubList,那会创建非懒的spliterator)
* 2 我们只在forEach的末尾进行ConcurrentModificationException检查
* (性能最敏感的方法)
* 当时用forEach(与迭代器相反),我们通常仅仅在action后,探测干扰,而不是在之前。
* 进一步ConcurrentModificationException触发的检查适用于所有其他可能违反假设的情况,
* 例如null或给定其size()的过小的elementData数组,这只可能由于干扰而发生。
* 这允许forEach的内部循环可以在没有进一步检查的情况下运行,简化了lambda解析。
* 虽然这确实需要很多检查,注意:在常见情况list.stream().forEach(a),
* 除了forEach内部,不会有其他地方进行检查或者计算。
* 其他更少使用的方法不能利用大部分的流线型。
*
*/
//list就是外层的ArrayList,分割出去的spliterator也是外层的
private final ArrayList list;
private int index; // 当前的index,在advance或split时改变
private int fence; // -1 直到被使用; 之后是最后一个能到达的index+1 (size)
private int expectedModCount; // 当fence设置时,初始化
/** 创建一个新的spliterator,覆盖给定的范围 return new ArrayListSpliterator<>(this, 0, -1, 0);*/
ArrayListSpliterator(ArrayList list, int origin, int fence,
int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list; // OK if null unless traversed
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
private int getFence() { // 第一次使用时,初始化fence=size
int hi; // (forEach 方法出现的专门的变量)
ArrayList lst;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) { // 如果fence>=0,直接返回fence
if ((lst = list) == null)
hi = fence = 0; // 如果list为null
else {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount; //否则,此时设置modCount和size给expectedModCount,fence
hi = fence = lst.size;
}
}
return hi;
}
public ArrayListSpliterator trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null : // 分割一半,除非太少了,只剩0-3个元素
// 自身:[mid,fence) 给出去的:[index,mid)
new ArrayListSpliterator(list, lo, index = mid,
expectedModCount);
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hi = getFence(), i = index;
if (i < hi) { // 如果index action) {
// i为index,hi为fence,mc为modCount
int i, hi, mc; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
ArrayList lst; Object[] a;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((lst = list) != null && (a = lst.elementData) != null) {// 如果list和里面的数组不为null
if ((hi = fence) < 0) { // 如果fence没有被初始化
mc = lst.modCount; // 初始化modCount
hi = lst.size; // 初始化 hi
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if ((i = index) >= 0 && (index = hi) <= a.length) { //设置index为fence
for (; i < hi; ++i) {
//从index循环到fence
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) a[i];
action.accept(e);
}
//循环结束后,检验modCount
if (lst.modCount == mc)
return;
}
}
// 检验不通过,到这里,抛出异常
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public long estimateSize() {
// 返回fence-index
return (long) (getFence() - index);
}
public int characteristics() {
// ORDERED,SIZED,SUBSIZED
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
其余的批量方法 forEach,removeIf,replaceAll,sort
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData;
final int size = this.size;
//不使用Iterator而是直接对数组元素进行遍历
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
action.accept(elementData[i]);
}
//在所有元素遍历中,遍历前和遍历完,之间,如果出现modCount不一致,就报错
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} @Override
public boolean removeIf(Predicate filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
// 校验哪个元素会被移除
// filter进行predicate时,抛出的任何异常,会让集合不被修改
int removeCount = 0; // 被移除的元素个数
final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size); // 哪位被set为true,哪位就被移除
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final int size = this.size;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//i到size,进行循环
final E element = (E) elementData[i];
if (filter.test(element)) {
//如果返回true记录这个被移除的元素,和被移除的元素的个数
removeSet.set(i);
removeCount++;
}
}
//如果在检验过程中,有modCount != expectedModCount ,抛出异常
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
// 将剩余元素向左移动,覆盖被移除的元素
final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0;
if (anyToRemove) {
// 如果 removeCount>0
final int newSize = size - removeCount;
for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) {
// i为读指针,j为写指针
// i为在指定的起始索引上或之后发生的第一个位的索引,该位的索引被设置为false。
// 即跳过设置为true的索引,即被删除的元素
i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i);
elementData[j] = elementData[i];
}
for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) {
// 剩余的空间设置为null
elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
this.size = newSize;
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
return anyToRemove;
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
final int size = this.size;
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
//元素变为operator.apply的结果
elementData[i] = operator.apply((E) elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void sort(Comparator c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
//使用Arrays.sort直接排序数组,从0到size
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, size, c);
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
} 基本性质
1、底层使用原生数组实现,实现RandomAccess接口,可以随机访问。
随机访问指的是下标索引操作index(i)的时间复杂度是O(1)。size、isEmpty、get、set、iterator和listIterator操作在O(1)内完成,add(e)操作平均在O(1)内完成,即添加n个元素需要O(n)时间(这个是Collection.add,是在尾部添加注意区分下List.add(index, e))。其他操作基本都是O(n)内完成。ArrayList与LinkedList实现相比,O(n)的各个方法的时间复杂度的常数因子更小。
2、因为底层数组 elementData 的容量是不能改变的,所以容量不够时,需要把 elementData 换成一个更大的数组,这个过程叫作扩容。实际的元素的数量size,总是不会超过底层数组的容量 elementData.length,因为扩容需要申请更大的内存,并且需要原来数组的进行一次复制,所以扩容是个耗时的操作。在添加大量元素之前,使用者最好是预估一个大致的数量,手动调用ensureCapacity进行一次扩容操作,避免一个个添加导致频繁扩容影响性能。
3、ArrayList是未同步的,多线程并发读写时需要外部同步,如果不外部同步,那么可以使用Collections.synchronizedList方法对ArrayList的实例进行一次封装,或者使用Vector。
4、对存储的元素无限制,允许null元素。
5、ArrayList的iterator和listIterator方法返回的迭代器是快速失败的,也就是如果在创建迭代器之后的任何时间被结构性修改,除了通过迭代器自己的remove或add方法之外,迭代器将直接抛出一个ConcurrentModificationException,从而达到快速失败fail-fast的目的,尽量避免不确定的行为。
ArrayList的迭代器的快速失败行为不能被严格保证,并发修改时它会尽量但不100%保证抛出ConcurrentModificationException。因此,依赖于此异常的代码的正确性是没有保障的,迭代器的快速失败行为应该仅用于检测bug。
6、实现clone接口,可以调用其clone方法(虽然clone()是Object中的方法,但是它是protected,使用子类的clone()必须在子类中覆盖此方法)。clone方法复制一个ArrayList,底层数组elementData不共享,但是实际的元素还是共享的。
不过clone是ArrayList中覆盖的,不属于List中的方法,因此常见的声明形式
List
声明出来的变量不能直接使用clone方法,本身也用得极少。
7、实现Serializable接口,可以被序列化。ArrayList"实现"了自定义序列化方法,这么做主要是为了节省空间 。对于占用空间的大头——元素list,仅仅序列化实际size大小的元素,同时不序列化对于新对象无用属性的——来自父类AbstractList的modCount。ArrayList的实际size不会超过底层数组的length,大多数情况下比底层数组length小,使用默认序列化的话,会直接序列化整个底层数组,序列化后字节流会变大,浪费空间。
jdk1.6/1.7/1.8之间ArrayList的区别
默认构造方法,ArrayList()
关于默认构造方法,你可能在别的地方看见过这种话:
无参构造方法(默认构造方法)构造的ArrayList的底层数组elementData大小(容量)默认为10。这里告诉你,这不一定是对的。这句话在1.6版本中是对的(更之前的版本我没看),从1.7开始这句话就有问题了。下面我贴出了三个版本的代码:
jdk1.6的,初始化成10个容量。
// jdk1.6的
/** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}jdk1.7的,相对1.6版本,引入了一个新的常量EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,它是一个空数组,因此容量为0。
// jdk1.7的
/** Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. */
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
...
/** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */
public ArrayList() {
super();
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}jdk1.8的,相对1.7版本,又引入了一个新的常量DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA ,它也是一个空数组,因此容量也为0。至于两个空数组有什么区别,看下面一点说的。
/** Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. */
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
...
/** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}对比下可以看出:jdk1.6的无参构造方法(默认构造方法)构造的ArrayList的底层数组elementData大小(容量)默认为10;从1.7开始,无参构造方法构造的ArrayList的底层数组elementData大小默认为0。
java集合类在jdk1.7版本基本上都有一种改动:懒初始化。懒初始化指的是默认构造方法构造的集合类,占据尽可能少的内存空间(对于ArrayList来说,使用空数组来占据尽量少的空间,不使用null是为了避免null判断),在第一次进行包含有添加语义的操作时,才进行真正的初始化工作。
1.7开始的ArrayList,默认构造方法构造的实例,底层数组是空数组,容量为0,在进行第一次add/addAll等操作时才会真正给底层数组赋非empty的值。如果add/addAll添加的元素小于10,则把elementData数组扩容为10个元素大小,否则使用刚好合适的大小(例如,第一次addAll添加6个,那么扩容为10个,第一次添加大于10个的,比如24个,扩容为24个,刚好合适);1.8版本,默认构造的实例这个行为没有改变,只是用的数组名字变了。
带初始容量的构造方法,public ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
// 1.6
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
// 1.7 跟1.6的一样
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
// 1.8
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // 重用空数组,一个小小的优化
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity);
}
}678三个版本的这个构造方法的实际行为基本一致:如果initialCapacity >= 0,把底层数组elementData赋值为一个大小为initialCapacity的数组,数组的所有元素都是默认值null。1.8稍微进行了一点优化,也是赋值为空数组,但是重用了常量对象。
下面写个简单的例子看一个细微的区别。
// jdk1.6,两个构造的区别很明显
public class TestArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List la = new ArrayList(0); // la.elementData = new Object[0], la.elementData.length = 0
la.add("111"); // la.elementDate.length = 1,这里一次性扩容了1个,后续再按照通用扩容策略执行扩容操作
List lb = new ArrayList(); // lb.elementData = new Object[10], lb.elementData.length = 10
lb.add("111"); // lb.elementDate.length = 10,这里没有进行扩容,后续再按照通用扩容策略执行扩容操作
}
}
// jdk1.7,两个构造在第一次进行添加时才看得出区别
public class TestArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List la = new ArrayList<>(0); // la.elementData = new Object[0], la.elementData.length = 0
la.add("111"); // la.elementDate.length = 1,这里一次性扩容了1个,后续再按照通用扩容策略执行扩容操作
List lb = new ArrayList<>(); // lb.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA, lb.elementData.length = 0
lb.add("111"); // lb.elementDate.length = 10,这里一次性扩容了10个,后续再按照通用扩容策略执行扩容操作
}
}
// jdk1.8,同1.7
public class TestArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List la = new ArrayList<>(0); // la.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA, la.elementData.length = 0
la.add("111"); // la.elementDate.length = 1,这里一次性扩容了1个,后续再按照通用扩容策略执行扩容操作
List lb = new ArrayList<>(); // lb.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA, lb.elementData.length = 0
lb.add("111"); // lb.elementDate.length = 10,这里一次性扩容了10个,后续再按照通用扩容策略执行扩容操作
}
} jdk1.6中new ArrayList()跟new ArrayList(10)的行为是一模一样的,所以跟new ArrayList(0)有很明显区别,这个好理解 。从1.7版本开始,new ArrayList<>()和new ArrayList<>(0),虽然创建后底层内容和容量都一样,但是实际的行为有些细小的差别,那就是这两个在第一次自动扩容时策略不一样。不过这一点影响比较小,基本不影响使用。
1.8中使用两个空数组,正如注释所说的,是在优化(避免创建无用的空数组)的同时,保留其扩容初始策略区别。只用一个空数组就不能再优化的同时,继续保持这个小区别了。
Collection拷贝构造方法,public ArrayList(Collection c)
678三个版本的关系和第2点一样。
// jdk 1.6
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
// jdk 1.7
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
// jdk 1.8
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}关于中间这行注释,可以看下这篇博文:http://blog.csdn.net/aitangyong/article/details/30274749
此构造方法会有和Array.copyOf/System.arraycopy一样的问题,那就是它只是新建一个elementData数组,数组的内容对应相等,但是不拷贝实际的元素,实际的元素占据的内存空间还是共享的。
确保容量方法(扩容方法):ensureCapacity/ensureCapacityInternal
提前声明下:这两个方法只是确保容量,不一定会扩容,但是为了好理解,下面的文字中所说的"扩容"指的就是这两个方法。
因为原生的数组的容量不能改变,要改变数组的容量,只能是新建一个数组,并把原来数组的内容复制到新数组对应位置上去。数组拷贝使用的是Arrays.copyOf,底层用的是System.arraycopy,比循环赋值效率高。扩容示意图如下。
![]()
扩容方法四个位置用到:两个add方法,两个addAll方法,一个反序列化方法,还有就是手动扩容方法ensureCapacity(称之为手动,是因为此方法是public的,可以外部手动调用)。在1.6版本是只有这个手动的方法,内部自动操作也是调用这个方法,1.7开始进行了区分,并且进一步改进了扩容操作。
下面的是jdk1.8的代码,1.7的和1.8的基本相同,唯一的一点区别就是1.8用两个空数组,导致这里的空数组的名字不一样,两个版本的代码可以看作是一样的。
// 手动扩容方法(可以外部调用,不过大多数情况都是List = new ArrayList<>(),这样是调用不到这个方法的)// 这个方法只是简单区别下list是不是通过 new ArrayList() 来创建的,这一点前面说了
// 如果是,则尝试最小扩容10个,不是则尝试扩容指定个,具体也是通过内部扩容方法完成容量确保
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
// any size if not default element table
? 0
// larger than default for default empty table. It's already
// supposed to be at default size.
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}
// 下面是内部扩容相关的几个方法的代码
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code 考虑int型溢出
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code 考虑int型溢出
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow int型溢出,直接报错
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}下面这是1.6的相关代码,可以对比看下:
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[] = elementData;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
区别就是:1.6的方法只是简单进行了逻辑上的操作,没有过多考虑int型溢出的问题,从1.7(上面贴的是1.8的)开始对这个进行了完善。
最主要的问题:就是minCapacity>oldCapacity的负数溢出问题,和从oldCapacity变成newCapacity的过程中,的过早溢出。
先仔细看看1.6的问题,整体来说都是int型溢出的问题。
1、没考虑入参minCapacity可能因为int溢出变为负数。这个方法可以外部手动调用,手动扩容传入负数这个肯定是应该拦截掉的。但是自动扩容会因为int溢出产生负数,碰到这种情况时应该特殊处理,而不是什么都不做,等着后面抛出一个ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。
2、就是这句代码不太好,过早溢出
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
虽然上面这行代码和1.7开始的oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1) 看上去一样,都是相当于1.5倍,但实际上是有区别的。
两个区别,第一个小区别是jdk1.6的那种乘除运算的数学结果比后面一个大1比如oldCapacity=10,1.6的算法得到16,1.7开始的算法得到15,这个影响不大;
第二个区别就是两者在数字比较大是运算结果不一样,比如oldCapacity=10^9,这个数和Integer.MAX_VALUE位数一样,用1.6的算法得到的会是错误的-647483647(因为一开始*3溢出,而*1.5不溢出),用1.7的则是正确的1500000000,这时候明明可以1.5倍扩容,但是jdk1.6却用的是按需扩容。
在计算机里面对于int型的两个不同的数a和b,有
a-b>0 不等价于 a>b
因为,a-b>0会被int溢出影响,a>b不会受int溢出影响。无符号的int型中a-b>0是一定成立的;有符号的int型,负数可以看成是正数的溢出,假设a = Integer.MAX_VALUE + 10,b = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 10,很明显a是负数,b是正数,运行一遍a>b得到false,再运行一遍a-b得到的是20,a-b>0得到true。因此对于int型,a>b和a-b>0在if判断中有不同的功能,前者是纯粹比较大小,正数一定大于负数;后者可以判断溢出,正数不一定大于负数。
所以1.7版本对上面两个问题做了修改。
1、从1.7开始将内部扩容和外部可以调用的扩容方法分开了,通过源码(上面贴的是1.8的代码,可以看出是一样的)可以看出:外部调用的手动扩容方法ensureCapacity要多一个判断条件 minCapacity > minExpand,这个判断条件拦截掉负数的minCapacity,这样调用内部扩容ensureCapacityInternal方法时,minCapacity一定是正数
内部扩容方法直接就用minCapacity - elementData.length > 0判断,此条件可以检测出int型溢出,碰到溢出最后会抛出一个OOM错误。jdk1.7用OOM,这比jdk1.6用ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException更好,因为此时数组大小超出了虚拟机对数组的限制,虚拟机无法处理这种情况了,抛出一个ERROR是合理的。
2、使用这行代码
newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
这行不仅仅是是用位运算加快执行速度,上面说了,这种做法才是对的,是真正的1.5倍。不仅仅因为那一个大小的差别,更重要的是避免过早出现int溢出的情况,保证了内部自动扩容会尽量按规定的策略执行。同时整个扩容处理流程中多增加了几处if判断,对各种情况处理更加完善。
还有数组最大长度问题
还有一个问题就是,MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8。这个是1.7开始才有的,注释说这个是因为在一些虚拟机的数组实现中,会有array header这个保留部分,所以数组最大长度并不是实际的Integer.MAX_VALUE。这个在1.8自带的HotSpot上测试(环境Win7 64位,Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.111-b14, mixed mode)),准确值应该是Integer.MAX_VALUE - 2,比这个值大就会出现OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit。此Error和hugeCapacity中抛出的OOM基本上差不多,这两个跟一般的OOM还是有区别的。抛出这个异常时,一般是程序有问题,此时虚拟机看看数组大小,就知道了它是不能完成这样的内存分配的,跟剩余的内存空间大小没关系。
测试下实际MAX_ARRAY_SIZE(都是64bit的)
jdk1.8 Integer,MAX_VALUE - 2,超过这个值(实际上也只有两个数可选,Integer.MAX_VALUE和Integer.MAX_VALUE - 1)就抛出OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
jdk1.7 Integer.MAX_VALUE - 2
jdk1.6 Integer.MAX_VALUE,使用这个值能够成功创建数组(使用boolean数组)
在带初始容量的构造方法 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) 中,并没有判断初始容量是否大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE。个人觉得还是判断下好,不判断可能在扩容时会有点问题。下面给一组变量值大家试下,看下是不是真有问题。
初始数组长度 elementData.length = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 5 = 2147483642;
还要继续添加的长度 expand = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 2 = 2147483645;
最小容量 minCapacity = expand + elementData.length = -9;
ensureExplicitCapacity方法中 minCapacity - elementData.length = 2147483645 > 0,会继续执行grow方法;
grow方法中 newCapacity = elementData.length + (elementData.length >> 1) = -1073741833;
grow方法中的第一个if,newCapacity - minCapacity = -1073741824 < 0,执行第一个if中的 newCapacity = minCapacity,newCapacity = -9;
grow方法中的第二个if,newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = -2147483648 < 0,不执行第二个if中的语句;
执行最后的Arrays.copyOf,因为newCapacity = -9 < 0,会抛出异常NegativeArraySizeException。
grow方法中第二个if,如果newCapacity是负数,只有是-9到-1这几个负数,才会不执行hugeCapacity方法而是直接执行Arrays.copyOf抛出异常。如果构造方法中拦截判断下是否大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,一开始的数组长度就限制在Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8,应该是无法通过一个正数的expand,使得minCapacity在[-9,-1]内。严格证明暂时给不出,实际运行中由于内存限制无法演示。
jdk1.6/1.7/1.8之间小结
简单总结下,jdk1.7和1.8之间大致相同,jdk1.7版本对比1.6版本,三个改动:
1、懒初始化,因此默认构造方法创建的是空数组,不再是10个大小的数组;
2、扩容相关的完善;
3、一些方法不再直接使用父类的通用实现,改为利用数组特性的更有效率的实现。
ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList之前区别
ArrayList、Vector和LinkedList类均在java.util包下
ArrayList和Vector都是基于存储元素的Object[] array来实现的,它们会在内存中开辟一块连续的空间来存储,因为数据存储是连续的,所以它们支持用下标来访问元素,索引数据的速度比较快。
1)ArrayList和Vector都有一个初始化的容量大小,当里面存储的元素超过初始的大小时就需要动态地扩充它们的存储空间,Vector默认扩充为原来的两倍(每次扩充空间的大小可以设置),ArrayList默认扩充为原来的1.5倍(没有提供方法来设置空间扩充的方法)。
2)ArrayList和Vector最大的区别就是synchronization的使用,没有一个ArrayList的方法是同步的,而Vector的绝大多数方法(如add,insert,remove,set,equals,hashcode)都是直接或间接同步的,所以Vector是线程安全的,ArrayList不是线程安全的。正是由于Vector提供了线程安全的机制,其性能上也要稍逊于ArrayList
LinkedList是采用双向列表来实现的,内部是链表结构,对数据的索引需要从列表头开始遍历,因此用于随机访问则效率比较低,但是插入元素时不需要对数据进行移动,因此插入效率较高。同时,LinkedList是非线程安全的容器
对容器的选择:
当对数据的主要操作是索引或只在集合的末端增加、删除元素时,使用ArrayList或Vector效率比较高,
当对数据的操作主要为指定位置或删除操作时,使用LikedList效率比较高;
当在多线程中使用容器时,选用Vector较为安全