C++的速度优化
C++各种优化
- 1.快速结束程序
- 2.register
- 3.inline
- 4.位运算
- 5.少用或不用STL
- 6.快读快写
- 准备工作
- 计算时间
- 随机数
- 超慢cin cout
- 输出
- 原始输出
- 初级快写
- 高级快写
- 输入
- 原始输入
- 初级快读
- 中级快读
- 高级快读
- 神一般的快读快写
- 对比
- 输入速度
- 输出速度
- 7.小技巧
- 8.const
- 9.宏定义
- 其他(48行优化代码)
博客园的博客
注 : ⨁ : \ \bigoplus : ⨁是异或的意思 ( ( (^ ) ) ), ≪ n \ll n ≪n为二进制左移 n n n位, ≫ n \gg n ≫n为二进制右移 n n n位。
起因——————
中国近现代史上伟大的爱国者、伟大的革命家与改革家、伟大的民主主义者、伟大的启蒙思想家陈独秀曾经说过:
“只有两位先生才能拯救我们。”
一位叫 T T T先生 ( T L E [ T i m e L i m i t E x c e e d e d ] ) (TLE [Time \ Limit \ Exceeded]) (TLE[Time Limit Exceeded]),另一位叫 W W W先生 ( W A [ W r o n g A n s w e r ] ) (WA[Wrong \ Answer]) (WA[Wrong Answer])。
在现实中, W A WA WA可以很快改正,而 T L E TLE TLE——



呵呵
那让我们谈谈代码中的优化
1.快速结束程序
#include免得退出导致超时
例如 — — —— ——
#include可以退出其他递归,保证不会陷入 w h i l e ( 1 ) while(1) while(1)里面。
2.register
r e g i s t e r register register修饰符暗示编译程序相应的变量将被频繁地使用,如果可能的话,应将其保存在 C P U CPU CPU的寄存器中,以加快其存储速度。
3.inline
i n l i n e inline inline定义的类的内联函数,函数的代码被放入符号表中,在使用时直接进行替换,(像宏一样展开),没有了调用的开销,效率也很高。
4.位运算
因为电脑是二进制,所以用二进制的位运算会比十进制的加减乘除快得多
x × 10 → ( x ≪ 3 ) + ( x ≪ 1 ) x\times10 \rightarrow (x\ll3)+(x\ll1) x×10→(x≪3)+(x≪1)
x ≠ y x\neq y x̸=y → b o o l ( x ⨁ y ) \rightarrow bool(x\bigoplus y) →bool(x⨁y)
x ≠ − 1 → b o o l ( ∼ x ) x\neq -1 \rightarrow bool(\sim x) x̸=−1→bool(∼x)
x × 2 → x ≪ 1 x\times2 \rightarrow x\ll1 x×2→x≪1
x × 2 + 1 → x ≪ 1 ∣ 1 x\times2+1 \rightarrow x\ll1|1 x×2+1→x≪1∣1
x ÷ 2 → x ≫ 1 x\div2 \rightarrow x\gg1 x÷2→x≫1
( x + 1 ) % 2 → b o o l ( x ⨁ 1 ) (x+1)\%2 \rightarrow bool(x\bigoplus1) (x+1)%2→bool(x⨁1)
x % 2 → x\%2\rightarrow x%2→ x & 1 x\&1 x&1
为什么要加 b o o l bool bool呢?
因为 ≠ \neq ̸=和 % 2 \%2 %2只有 1 1 1和 0 0 0这两个返回值,就是 b o o l bool bool类型。
而 ⨁ \bigoplus ⨁有多种返回。
在 a [ x ≠ y ] a[x\neq y] a[x̸=y]中,直接转成 a [ x ⨁ y ] a[x\bigoplus y] a[x⨁y]可能会导致 R E RE RE
例如
#include如果直接转换,将会出现以下情况
#include明显当 x x x和 y y y选一些值就卡掉了 ( 1 , 2 ) (1,2) (1,2)
5.少用或不用STL
这里要提到一个万恶的头文件
#include其中有两个函数,叫 m a x max max和 m i n min min。
速度慢,是 S T L STL STL的天生一大劣势。
max \max max和 min \min min比 a > b ? a : b a>b?a:b a>b?a:b和 a < b ? a : b a<b?a:b a<b?a:b慢好几倍
除了 s o r t sort sort(快速排序)和 p r i o r i t y priority priority_ q u e u e queue queue(堆排序)这种比较难不用 S T L STL STL的这种以外尽量少用
比如
void swap(int &x,int &y){int t=x;x=y;y=t;}
swap(a,b);
再比如
inline int mymax(int x,int y){return x>y?x:y}//等于STL的max
inline int mymin(int x,int y){return x<y?x:y}//等于STL的min
x > y ? x : y x>y?x:y x>y?x:y意思是
如果 x > y x>y x>y那么着整个式子表示 x x x,不然表示 y y y。
(如果想用且想快,请见其他里的氧气)
6.快读快写
当然不能少这个啦
先给大家一个东西
准备工作
计算时间
#include用于运行计算时间,精度可以自己调 (其实是抄来的)
随机数
还有随机数
#include超慢cin cout
乌龟都比 c i n cin cin和 c o u t cout cout快,尤其是 c i n cin cin
除了万不得已千万别用
如习惯用了,就加上这个
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
之后就不要能 s c a n f scanf scanf和 p r i n t f printf printf了
#include慢的抠脚
#include输出
从输出讲起
我们来尝试输出 100 100 100万个数字
原始输出
#include初级快写
用上快写
#include高级快写
然而还可以更快
因为 0 0 0的 A S C I I ASCII ASCII码为 48 , 9 48,9 48,9为 57 57 57
转化为2进制为
110000 110000 110000
就是
32 ∗ 1 + 16 ∗ 1 + 8 ∗ 0 + 4 ∗ 0 + 2 ∗ 0 + 1 ∗ 0 = 48 32*1+16*1+8*0+4*0+2*0+1*0=48 32∗1+16∗1+8∗0+4∗0+2∗0+1∗0=48
可以用异或来加上(或消去)48,而异或比减法快得多
000000 ( 0 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 000000(0)\bigoplus110000(48) 000000(0)⨁110000(48)得到 110000 ( ′ 0 ′ ) 110000('0') 110000(′0′)
000001 ( 1 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 000001(1)\bigoplus110000(48) 000001(1)⨁110000(48)得到 110001 ( ′ 1 ′ ) 110001('1') 110001(′1′)
000010 ( 2 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 000010(2)\bigoplus110000(48) 000010(2)⨁110000(48)得到 110010 ( ′ 2 ′ ) 110010('2') 110010(′2′)
000011 ( 3 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 000011(3)\bigoplus110000(48) 000011(3)⨁110000(48)得到 110011 ( ′ 3 ′ ) 110011('3') 110011(′3′)
000100 ( 4 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 000100(4)\bigoplus110000(48) 000100(4)⨁110000(48)得到 110100 ( ′ 4 ′ ) 110100('4') 110100(′4′)
000101 ( 5 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 000101(5)\bigoplus110000(48) 000101(5)⨁110000(48)得到 110101 ( ′ 5 ′ ) 110101('5') 110101(′5′)
000110 ( 6 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 000110(6)\bigoplus110000(48) 000110(6)⨁110000(48)得到 110110 ( ′ 6 ′ ) 110110('6') 110110(′6′)
000111 ( 7 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 000111(7)\bigoplus110000(48) 000111(7)⨁110000(48)得到 110111 ( ′ 7 ′ ) 110111('7') 110111(′7′)
001000 ( 8 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 001000(8)\bigoplus110000(48) 001000(8)⨁110000(48)得到 111000 ( ′ 8 ′ ) 111000('8') 111000(′8′)
001001 ( 9 ) ⨁ 110000 ( 48 ) 001001(9)\bigoplus110000(48) 001001(9)⨁110000(48)得到 111001 ( ′ 9 ′ ) 111001('9') 111001(′9′)
#include输入
现在来看快读
原始输入
#include直接用 s c a n f scanf scanf,输入100万个数已经超时
初级快读
利用 g e t c h a r getchar getchar比 s c a n f scanf scanf快得多的特性
加上前面提到的异或的
#include中级快读
然而 x × 10 x\times10 x×10还可以转化为 ( x ≪ 3 ) + ( x ≪ 1 ) (x\ll3)+(x\ll1) (x≪3)+(x≪1)
#include高级快读
∣ \mid ∣和 ? : ?: ?:还是比 i f if if和 × \times ×快的
#include这就差不多了
神一般的快读快写
但还有更快的
不要以为 g e t c h a r , p u t c h a r getchar,putchar getchar,putchar是最快的,利用 f r e a d , f w r i t e fread,fwrite fread,fwrite会更快,但风险很大,很多 o j oj oj上不能用,需要 f r e o p e n freopen freopen才能使用,不会在运行是输出,全都保存在一个文件里

里面长这样

一堆乱码
不过很快
#include#include这才是快读快写的真实水平
对比
输入速度
c i n cin cin运行时间为 3.406000000000000138555833473219536245 3.406000000000000138555833473219536245 3.406000000000000138555833473219536245秒
s c a n f scanf scanf运行时间为 1.655999999999999916511228548188228160 1.655999999999999916511228548188228160 1.655999999999999916511228548188228160秒
初级快读运行时间为 0.420999999999999985345056074947933666 0.420999999999999985345056074947933666 0.420999999999999985345056074947933666秒
中级快读运行时间为 0.406000000000000027533531010703882203 0.406000000000000027533531010703882203 0.406000000000000027533531010703882203秒
高级快读运行时间为 0.406000000000000027533531010703882203 0.406000000000000027533531010703882203 0.406000000000000027533531010703882203秒
神一般的快读运行时间为 0.061999999999999999555910790149937384 0.061999999999999999555910790149937384 0.061999999999999999555910790149937384秒
输出速度
c o u t cout cout运行时间为 3.625000000000000000000000000000000000 3.625000000000000000000000000000000000 3.625000000000000000000000000000000000秒
p r i n t f printf printf运行时间为 3.406000000000000138555833473219536245 3.406000000000000138555833473219536245 3.406000000000000138555833473219536245秒
初级快写运行时间为 0.623999999999999999111821580299874768 0.623999999999999999111821580299874768 0.623999999999999999111821580299874768秒
高级快写运行时间为 0.577999999999999958255614274094114080 0.577999999999999958255614274094114080 0.577999999999999958255614274094114080秒
神一般的快写运行时间为 0.265000000000000013322676295501878485 0.265000000000000013322676295501878485 0.265000000000000013322676295501878485秒
7.小技巧
非常小的优化也不能放过
+ + i ++i ++i比 i + + i++ i++要快一些
定义数组时,大的尽量放前面
8.const
并不是所有优化都是运行时间上的优化,打代码时间减少也算优化
c o n s t const const为常量,从开始就要被赋值,之后不变。
定义同样大数组时,可以先用定义一个常量,然后将常量放到数组里
例如我们要定义一堆容量为 41000 41000 41000的数组
const int N=41000;
int a[N],b[N],c[N],d[N],e[N]/*······*/;
可节省打代码的时间。
9.宏定义
比 c o n s t const const快,可以代替冗长的东西,比如上文提到的 g e t c h a r getchar getchar我是用宏定义将 g e t c h a r getchar getchar定义成 g c gc gc。
上面提到 i n l i n e inline inline可以像宏一样展开,就是将在下面代码出现的同样的东西转化成定义的东西
格式
#define+空格+要转化的东西+空格+被转化的东西(可以中间带空格)
例如
#define LL long long
代表将出现 L L LL LL的地方转化成 l o n g l o n g long \ long long long
是全字匹配
可以这样
#define R register
#define ri R int
不会编译错误
可以里面又带权值的东西
例如上文的 m y m a x mymax mymax和 m y m i n mymin mymin可以写成
inline int mymax(int x,int y){return x>y?x:y}
inline int mymin(int x,int y){return x<y?x:y}
还可以写成
#define mymax(a,b) a>b?a:b
#define mymin(a,b) a
举个栗子
#define mymax(a,b) a>b?a:b
#define mymin(a,b) a
int x,y,a,b;
a=mymax(x,y);b=mymax(x,y);
等于
a=x>y?x:y;b=x<y?x:y;
再比如
#define rep(a,b,c) for(int a=b;a<=c;++a)
rep(i,1,n)
等于
for(int i=1,i<=n;++i)
比加了 i n l i n e inline inline的函数快,简单的东西可以代替。
不过,也要承担很大的风险
因为是直接展开,所以可能会因为运算符的优先级而导致错误
例如
#define po(n) 1<//求2的n次方
printf("%d",po(4)+1);
你希望的肯定是输出 17 , 17, 17,但是它所输出的是 32 , 32, 32,因为它展开后是
printf("%d",1<<4+1);

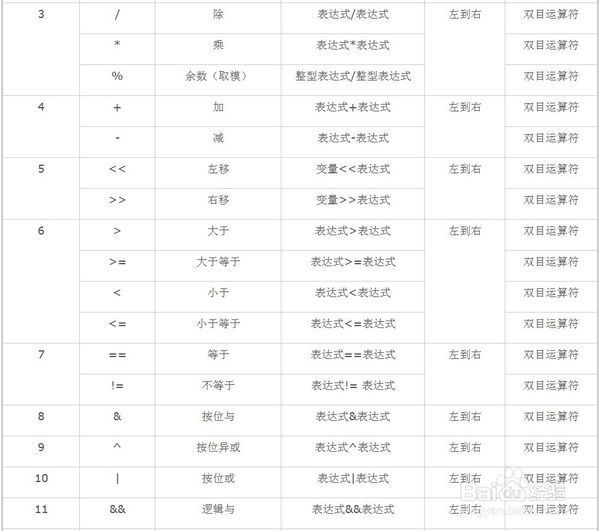

由上表得知, + + +的在 ≪ \ll ≪前运算
所以运算一次后就得
printf("%d",1<<5);
当然输出 32 32 32啦
尽量在上面加括号
#define po(n) (1<
其他(48行优化代码)
(慎用)
#pragma GCC target("avx")//AVX指令集(不懂的去问度娘)
#pragma GCC optimize(2)//吸氧气(O2)
#pragma GCC optimize(3)//吸臭氧(O3)
#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")//吸更高质量的氧(优化到破坏标准合规性的点),
#pragma GCC optimize("inline")//至于其他的我就不懂了
#pragma GCC optimize("-fgcse")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fgcse-lm")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fipa-sra")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ftree-pre")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ftree-vrp")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fpeephole2")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ffast-math")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fsched-spec")
#pragma GCC optimize("unroll-loops")
#pragma GCC optimize("-falign-jumps")
#pragma GCC optimize("-falign-loops")
#pragma GCC optimize("-falign-labels")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fdevirtualize")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fcaller-saves")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fcrossjumping")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fthread-jumps")
#pragma GCC optimize("-funroll-loops")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fwhole-program")
#pragma GCC optimize("-freorder-blocks")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fschedule-insns")
#pragma GCC optimize("inline-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ftree-tail-merge")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fschedule-insns2")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fstrict-aliasing")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fstrict-overflow")
#pragma GCC optimize("-falign-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fcse-skip-blocks")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fcse-follow-jumps")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fsched-interblock")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fpartial-inlining")
#pragma GCC optimize("no-stack-protector")
#pragma GCC optimize("-freorder-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-findirect-inlining")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fhoist-adjacent-loads")
#pragma GCC optimize("-frerun-cse-after-loop")
#pragma GCC optimize("inline-small-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-finline-small-functions")
#pragma GCC optimize("-ftree-switch-conversion")
#pragma GCC optimize("-foptimize-sibling-calls")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fexpensive-optimizations")
#pragma GCC optimize("-funsafe-loop-optimizations")
#pragma GCC optimize("inline-functions-called-once")
#pragma GCC optimize("-fdelete-null-pointer-checks")
能加速很多
但明显像NOIP这类比赛不能用