@StreamListener注解的工作原理
一直被@StreamListener注解带来的恐惧所支配。今天来揭开它的面纱。
MAVEN引入相关jar包(版本2.0.1)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafkaartifactId>
dependency>
@StreamListener注解使用
@StreamListener
public void test(){
}
相关源码分析
先点开@StreamListener注解源码:
@Target({
ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@MessageMapping
@Documented
public @interface StreamListener {
/**
* The name of the binding target (e.g. channel) that the method subscribes to.
* @return the name of the binding target.
*/
@AliasFor("target")
String value() default "";
/**
* The name of the binding target (e.g. channel) that the method subscribes to.
* @return the name of the binding target.
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String target() default "";
/**
* A condition that must be met by all items that are dispatched to this method.
* @return a SpEL expression that must evaluate to a {@code boolean} value.
*/
String condition() default "";
/**
* When "true" (default), and a {@code @SendTo} annotation is present, copy the
* inbound headers to the outbound message (if the header is absent on the outbound
* message). Can be an expression ({@code #{...}}) or property placeholder. Must
* resolve to a boolean or a string that is parsed by {@code Boolean.parseBoolean()}.
* An expression that resolves to {@code null} is interpreted to mean {@code false}.
*
* The expression is evaluated during application initialization, and not for each
* individual message.
*
* Prior to version 1.3.0, the default value used to be "false" and headers were
* not propagated by default.
*
* Starting with version 1.3.0, the default value is "true".
*
* @since 1.2.3
*/
String copyHeaders() default "true";
}
这是它所在的包结构:
选中@StreamListener注解value()方法看谁调用了它:

可以看到下面的方法又调用了上面的方法,所以只需要展开下面的方法即可:
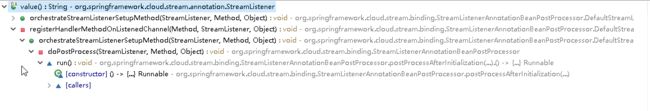
直接点击run()方法,就到了处理@StreamListener注解的代码入口(部分代码):
public class StreamListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware, SmartInitializingSingleton {
@Override
public final Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, final String beanName) throws BeansException {
Class<?> targetClass = AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean) ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean) : bean.getClass(); //找到bean对象的真实类型
Method[] uniqueDeclaredMethods = ReflectionUtils.getUniqueDeclaredMethods(targetClass); //找到bean对象的方法
//逐个遍历并处理声明了@StreamListener注解的方法
for (Method method : uniqueDeclaredMethods) {
//找声明了@StreamListener注解的方法
StreamListener streamListener = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, StreamListener.class);
if (streamListener != null && !method.isBridge()) {
streamListenerCallbacks.add(() -> {
Assert.isTrue(method.getAnnotation(Input.class) == null, StreamListenerErrorMessages.INPUT_AT_STREAM_LISTENER); //被@StreamListener注解声明的方法上不允许再声明@Input注解
this.doPostProcess(streamListener, method, bean);
});
}
}
return bean;
}
}
我们看看doPostProcess()方法中做了啥
private void doPostProcess(StreamListener streamListener, Method method, Object bean) {
streamListener = postProcessAnnotation(streamListener, method);
Optional<StreamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator> streamListenerSetupMethodOrchestratorAvailable =
streamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrators.stream()
.filter(t -> t.supports(method))
.findFirst();
Assert.isTrue(streamListenerSetupMethodOrchestratorAvailable.isPresent(),
"A matching StreamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator must be present");
StreamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator streamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator = streamListenerSetupMethodOrchestratorAvailable.get();
streamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator.orchestrateStreamListenerSetupMethod(streamListener, method, bean);
}
//啥也没干的一个方法,其实是一个扩展点
protected StreamListener postProcessAnnotation(StreamListener originalAnnotation, Method annotatedMethod) {
return originalAnnotation;
}
StreamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator类是个接口,它的实现在StreamListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类的内部类DefaultStreamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator中:
private class DefaultStreamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator implements StreamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator
@Override
public void orchestrateStreamListenerSetupMethod(StreamListener streamListener, Method method, Object bean) {
String methodAnnotatedInboundName = streamListener.value(); //处理@StreamListener注解的value值
String methodAnnotatedOutboundName = StreamListenerMethodUtils.getOutboundBindingTargetName(method); //解析输出通道
int inputAnnotationCount = StreamListenerMethodUtils.inputAnnotationCount(method);
int outputAnnotationCount = StreamListenerMethodUtils.outputAnnotationCount(method);
boolean isDeclarative = checkDeclarativeMethod(method, methodAnnotatedInboundName, methodAnnotatedOutboundName);
StreamListenerMethodUtils.validateStreamListenerMethod(method,
inputAnnotationCount, outputAnnotationCount,
methodAnnotatedInboundName, methodAnnotatedOutboundName,
isDeclarative, streamListener.condition());
if (isDeclarative) {
StreamListenerParameterAdapter[] toSlpaArray = new StreamListenerParameterAdapter[this.streamListenerParameterAdapters.size()];
Object[] adaptedInboundArguments = adaptAndRetrieveInboundArguments(method, methodAnnotatedInboundName,
this.applicationContext,
this.streamListenerParameterAdapters.toArray(toSlpaArray));
invokeStreamListenerResultAdapter(method, bean, methodAnnotatedOutboundName, adaptedInboundArguments);
} else {
registerHandlerMethodOnListenedChannel(method, streamListener, bean);
}
}
}
可以看到,这段代码中完成了对@StreamListener注解的解析,并在最后调用了registerHandlerMethodOnListenedChannel()方法完成了注册,看一下具体实现:
private void registerHandlerMethodOnListenedChannel(Method method, StreamListener streamListener, Object bean) {
Assert.hasText(streamListener.value(), "The binding name cannot be null");
if (!StringUtils.hasText(streamListener.value())) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("A bound component name must be specified");
}
final String defaultOutputChannel = StreamListenerMethodUtils.getOutboundBindingTargetName(method);
if (Void.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
Assert.isTrue(StringUtils.isEmpty(defaultOutputChannel),
"An output channel cannot be specified for a method that does not return a value");
}
else {
Assert.isTrue(!StringUtils.isEmpty(defaultOutputChannel),
"An output channel must be specified for a method that can return a value");
}
StreamListenerMethodUtils.validateStreamListenerMessageHandler(method);
mappedListenerMethods.add(streamListener.value(),
new StreamListenerHandlerMethodMapping(bean, method, streamListener.condition(), defaultOutputChannel,
streamListener.copyHeaders()));
}
所以呢,最后的结果是,@StreamListener注解标注的方法会在系统启动时由StreamListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类发起解析,然后被StreamListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类的内部类DefaultStreamListenerSetupMethodOrchestrator解析并注册到mappedListenerMethods中,看一下mappedListenerMethods是个啥:
private final MultiValueMap<String, StreamListenerHandlerMethodMapping> mappedListenerMethods = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
额…一个map而已。name问题来了,注册完了,它是怎么工作的?在StreamListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类全局搜mappedListenerMethods,可以看到它出现在了这段代码里:
@Override
public final void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
this.injectAndPostProcessDependencies();
EvaluationContext evaluationContext = IntegrationContextUtils.getEvaluationContext(this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
for (Map.Entry<String, List<StreamListenerHandlerMethodMapping>> mappedBindingEntry : mappedListenerMethods
.entrySet()) {
ArrayList<DispatchingStreamListenerMessageHandler.ConditionalStreamListenerMessageHandlerWrapper> handlers = new ArrayList<>();
for (StreamListenerHandlerMethodMapping mapping : mappedBindingEntry.getValue()) {
final InvocableHandlerMethod invocableHandlerMethod = this.messageHandlerMethodFactory
.createInvocableHandlerMethod(mapping.getTargetBean(),
checkProxy(mapping.getMethod(), mapping.getTargetBean()));
StreamListenerMessageHandler streamListenerMessageHandler = new StreamListenerMessageHandler(
invocableHandlerMethod, resolveExpressionAsBoolean(mapping.getCopyHeaders(), "copyHeaders"),
springIntegrationProperties.getMessageHandlerNotPropagatedHeaders());
streamListenerMessageHandler.setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
streamListenerMessageHandler.setBeanFactory(this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
if (StringUtils.hasText(mapping.getDefaultOutputChannel())) {
streamListenerMessageHandler.setOutputChannelName(mapping.getDefaultOutputChannel());
}
streamListenerMessageHandler.afterPropertiesSet();
if (StringUtils.hasText(mapping.getCondition())) {
String conditionAsString = resolveExpressionAsString(mapping.getCondition(), "condition");
Expression condition = SPEL_EXPRESSION_PARSER.parseExpression(conditionAsString);
handlers.add(
new DispatchingStreamListenerMessageHandler.ConditionalStreamListenerMessageHandlerWrapper(
condition, streamListenerMessageHandler));
}
else {
handlers.add(
new DispatchingStreamListenerMessageHandler.ConditionalStreamListenerMessageHandlerWrapper(
null, streamListenerMessageHandler));
}
}
if (handlers.size() > 1) {
for (DispatchingStreamListenerMessageHandler.ConditionalStreamListenerMessageHandlerWrapper handler : handlers) {
Assert.isTrue(handler.isVoid(), StreamListenerErrorMessages.MULTIPLE_VALUE_RETURNING_METHODS);
}
}
AbstractReplyProducingMessageHandler handler;
if (handlers.size() > 1 || handlers.get(0).getCondition() != null) {
handler = new DispatchingStreamListenerMessageHandler(handlers, evaluationContext);
}
else {
handler = handlers.get(0).getStreamListenerMessageHandler();
}
handler.setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
handler.setChannelResolver(this.binderAwareChannelResolver);
handler.afterPropertiesSet();
this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(handler.getClass().getSimpleName() + handler.hashCode(), handler);
applicationContext.getBean(mappedBindingEntry.getKey(), SubscribableChannel.class).subscribe(handler);
}
this.mappedListenerMethods.clear();
}
真是好头疼的一大段代码啊,完全不想看干嘛的。所以,偷个懒?简化下它:
@Override
public final void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
for (Map.Entry<String, List<StreamListenerHandlerMethodMapping>> mappedBindingEntry : mappedListenerMethods
.entrySet()) {
applicationContext.getBean(mappedBindingEntry.getKey(), SubscribableChannel.class).subscribe(handler);
}
this.mappedListenerMethods.clear();
}
是不是舒服多了?做了什么一目了然啊!遍历整个mappedListenerMethods,按个取出元素,一同猛如虎的操作,然后取出了bean名称为mappedBindingEntry.getKey(),类型为SubscribableChannel的bean对象执行了下subscribe()方法。然后,就订阅了MQ消息???
嗯,终于看完了。就这样吧。