dubbo学习笔记(二)
1. dubbo xml配置方式的标签
- dubbo:protocol标签
<dubbo:protocol name="jms">
<dubbo:parameter key="queue" value="you_queue" />
dubbo:protocol>
或者:
<dubbo:protocol name="jms" p:queue="your_queue" />
- 配置之间的关系
![]()
- 各种标签
| 标签 | 用途 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| 服务配置 | 用于暴露一个服务,定义服务的元信息,一个服务可以用多个协议暴露,一个服务也可以注册到多个注册中心 | |
| 引用服务 | 用于创建一个远程服务代理,一个引用可以指向多个注册中心 | |
| 应用配置 | 用于配置当前应用信息,不管该应用是提供者还是消费者 | |
| 协议配置 | 用于提供服务的协议信息,协议由提供方指定,消费方被动接受 | |
| 模块配置 | 用于配置当前模块信息,可选 | |
| 注册中心配置 | 用于配置连接注册中心相关信息 | |
| 监控中心配置 | 用于配置连接监控中心相关信息,可选 | |
| 提供方配置 | 当ProtocolConfig和ServiceConfig某属性没有配置时,采用此缺省值,可选 | |
| 消费方配置 | 当ReferenceConfig某属性没有配置时,采用此缺省值,可选 | |
| 方法配置 | 用于ServiceConfig和ReferenceConfig指定方法级的配置信息 | |
| 参数配置 | 用于执行方法参数配置 |
- 建议由服务提供方设置超时,因为一个方法需要执行多长时间,服务提供方更清楚,如果一个消费方同时引用多个服务,就不需要关心每个服务的超时设置。
- 理论上 ReferenceConfig 中除了
interface这一项,其他所有配置项都可以缺省不配置,框架会自动使用ConsumerConfig,ServiceConfig, ProviderConfig等提供的缺省配置。
2. 属性配置
- 如果应用够简单,不需要多注册中心或多协议,并且需要在spring容器中共享配置,那么,我们可以直接使用dubbo.properties作为默认配置。
- dubbo可以自动加载classpath根目录下的dubbo.properties,但是你同样可以使用JVM参数来指定路径:-Ddubbo.properties.file=xxx.properties 。
3. 映射规则
-
可以将xml的tag名和属性名组合起来,用**“.”**来分隔。每行一个属性。
- dubbo.application.name=foo相当与
- dubbo.registry.address=10.20.30.152:9080 相当于
- dubbo.application.name=foo相当与
-
如果在xml配置中有超过一个的tag,那么你可以使用**“id”**进行区分。如果你不指定id,它将作用于所有tag。
- dubbo.protocol.rmi.port=1099 相对与
- dubbo.registry.china.address=10.20.30.152:9090 相当于
dubbo.application.name=foo dubbo.application.owner=bar dubbo.registry.address=10.20.153.10:9090 - dubbo.protocol.rmi.port=1099 相对与
4. 重写与优先级
-
优先级从高到低:
- JVM -D参数,当你部署或者启动应用时,它可以轻易地重写配置,比如,改变dubbo协议的端口;
- XML,XML中的当前配置会重写dubbo.properties中的;
- Properties,默认配置,仅仅作用于以上两者没有配置时。
注意:
1. 如果在classpath下有超过一个dubbo.properties文件,比如,两个jar包都各自包含了dubbo.properties,dubbo将随机选择一个加载,并且打印错误日志。 2. 如果id没有在 protocol 中配置,将使用 name 作为默认属性。
5. API配置
-
服务提供者
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.config.ApplicationConfig; import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.config.RegistryConfig; import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.config.ProviderConfig; import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.config.ServiceConfig; import com.xxx.XxxService; import com.xxx.XxxServiceImpl; // 服务实现 XxxService xxxService = new XxxServiceImpl(); // 当前应用配置 ApplicationConfig application = new ApplicationConfig(); application.setName("xxx"); // 连接注册中心配置 RegistryConfig registry = new RegistryConfig(); registry.setAddress("10.20.130.230:9090"); registry.setUsername("aaa"); registry.setPassword("bbb"); // 服务提供者协议配置 ProtocolConfig protocol = new ProtocolConfig(); protocol.setName("dubbo"); protocol.setPort(12345); protocol.setThreads(200); // 注意:ServiceConfig为重对象,内部封装了与注册中心的连接,以及开启服务端口 // 服务提供者暴露服务配置 ServiceConfig<XxxService> service = new ServiceConfig<XxxService>(); // 此实例很重,封装了与注册中心的连接,请自行缓存,否则可能造成内存和连接泄漏 service.setApplication(application); service.setRegistry(registry); // 多个注册中心可以用setRegistries() service.setProtocol(protocol); // 多个协议可以用setProtocols() service.setInterface(XxxService.class); service.setRef(xxxService); service.setVersion("1.0.0"); // 暴露及注册服务 service.export(); -
服务消费者
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.config.ApplicationConfig; import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.config.RegistryConfig; import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.config.ConsumerConfig; import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.config.ReferenceConfig; import com.xxx.XxxService; // 当前应用配置 ApplicationConfig application = new ApplicationConfig(); application.setName("yyy"); // 连接注册中心配置 RegistryConfig registry = new RegistryConfig(); registry.setAddress("10.20.130.230:9090"); registry.setUsername("aaa"); registry.setPassword("bbb"); // 注意:ReferenceConfig为重对象,内部封装了与注册中心的连接,以及与服务提供方的连接 // 引用远程服务 ReferenceConfig<XxxService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<XxxService>(); // 此实例很重,封装了与注册中心的连接以及与提供者的连接,请自行缓存,否则可能造成内存和连接泄漏 reference.setApplication(application); reference.setRegistry(registry); // 多个注册中心可以用setRegistries() reference.setInterface(XxxService.class); reference.setVersion("1.0.0"); // 和本地bean一样使用xxxService XxxService xxxService = reference.get(); // 注意:此代理对象内部封装了所有通讯细节,对象较重,请缓存复用 -
特殊场景
-
方法级设置
... // 方法级配置 List<MethodConfig> methods = new ArrayList<MethodConfig>(); MethodConfig method = new MethodConfig(); method.setName("createXxx"); method.setTimeout(10000); method.setRetries(0); methods.add(method); // 引用远程服务 ReferenceConfig<XxxService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<XxxService>(); // 此实例很重,封装了与注册中心的连接以及与提供者的连接,请自行缓存,否则可能造成内存和连接泄漏 ... reference.setMethods(methods); // 设置方法级配置 ... -
点对点直连
... ReferenceConfig<XxxService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<XxxService>(); // 此实例很重,封装了与注册中心的连接以及与提供者的连接,请自行缓存,否则可能造成内存和连接泄漏 // 如果点对点直连,可以用reference.setUrl()指定目标地址,设置url后将绕过注册中心, // 其中,协议对应provider.setProtocol()的值,端口对应provider.setPort()的值, // 路径对应service.setPath()的值,如果未设置path,缺省path为接口名 reference.setUrl("dubbo://10.20.130.230:20880/com.xxx.XxxService"); ...
-
6. 注解配置
-
服务提供方
-
Service注解暴露服务
@Service public class AnnotationServiceImpl implements AnnotationService { @Override public String sayHello(String name) { return "annotation: hello, " + name; } } -
增加应用共享配置
# dubbo-provider.properties dubbo.application.name=annotation-provider dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo dubbo.protocol.port=20880 -
指定Spring扫描路径
@Configuration @EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "org.apache.dubbo.samples.simple.annotation.impl") @PropertySource("classpath:/spring/dubbo-provider.properties") static public class ProviderConfiguration { }
-
-
服务消费方
-
Reference注解引用服务
@Component("annotationAction") public class AnnotationAction { @Reference private AnnotationService annotationService; public String doSayHello(String name) { return annotationService.sayHello(name); } } -
增加应用共享配置
# dubbo-consumer.properties dubbo.application.name=annotation-consumer dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 dubbo.consumer.timeout=3000 -
指定Spring扫描路径
@Configuration @EnableDubbo(scanBasePackages = "org.apache.dubbo.samples.simple.annotation.action") @PropertySource("classpath:/spring/dubbo-consumer.properties") @ComponentScan(value = { "org.apache.dubbo.samples.simple.annotation.action"}) static public class ConsumerConfiguration { } -
服务调用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConsumerConfiguration.class); context.start(); final AnnotationAction annotationAction = (AnnotationAction) context.getBean("annotationAction"); String hello = annotationAction.doSayHello("world"); }
-
7. 动态配置中心
-
配置中心(v2.7.0)在Dubbo中承担两个职责:
-
外部化配置。启动配置的集中式存储 (简单理解为dubbo.properties的外部化存储)。
-
服务治理。服务治理规则的存储与通知。
-
启用动态配置(以zookeeper为例,可以查看动态配置配置项详解):
<dubbo:config-center address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>或者
dubbo.config-center.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181或者
ConfigCenterConfig configCenter = new ConfigCenterConfig(); configCenter.setAddress("zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181");为了兼容2.6.x版本配置,在使用Zookeeper作为注册中心,且没有显示配置配置中心的情况下,Dubbo框架会默认将此Zookeeper用作配置中心,但将只作服务治理用途。
-
-
外部化配置
-
外部化配置目的之一是实现配置的集中式管理,这部分业界已经有很多成熟的专业配置系统如Apollo, Nacos等,Dubbo所做的主要是保证能配合这些系统正常工作。
外部化配置和其他本地配置在内容和格式上并无区别,可以简单理解为
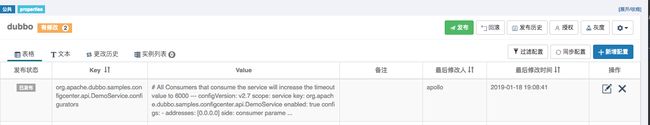
dubbo.properties的外部化存储,配置中心更适合将一些公共配置如注册中心、元数据中心配置等抽取以便做集中管理。# 将注册中心地址、元数据中心地址等配置集中管理,可以做到统一环境、减少开发侧感知。 dubbo.registry.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 dubbo.registry.simplified=true dubbo.metadata-report.address=zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 dubbo.protocol.name=dubbo dubbo.protocol.port=20880 dubbo.application.qos.port=33333-
优先级
-
外部化配置默认较本地配置有更高的优先级,因此这里配置的内容会覆盖本地配置值,关于各配置形式间的覆盖关系有单独一章说明,你也可通过以下选项调整配置中心的优先级:
-Ddubbo.config-center.highest-priority=false-
作用域
-
外部化配置有全局和应用两个级别,全局配置是所有应用共享的,应用级配置是由每个应用自己维护且只对自身可见的。
当前已支持的扩展实现有Zookeeper、Apollo。
Zookeeper
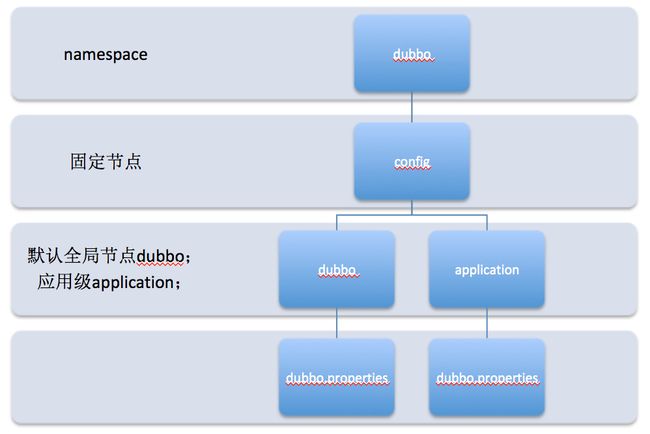
<dubbo:config-center address="zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"/>默认所有的配置都存储在/dubbo/config 节点,具体节点结构图图下:
-
namespace,用于不同配置的环境隔离。
-
config,Dubbo约定的固定节点,不可更改,所有配置和服务治理规则都存储在此节点下。
-
dubbo/application,分别用来隔离全局配置、应用级别配置:dubbo是默认group值,application对应应用名
-
dubbo.properties,此节点的node value存储具体配置内容
Apollo
<dubbo:config-center protocol="apollo" address="127.0.0.1:2181"/>Apollo中的一个核心概念是命名空间 - namespace(和上面zookeeper的namespace概念不同),在这里全局和应用级别配置就是通过命名空间来区分的。
默认情况下,Dubbo会从名叫
dubbo(由于 Apollo 不支持特殊后缀.properties)的命名空间中读取全局配置(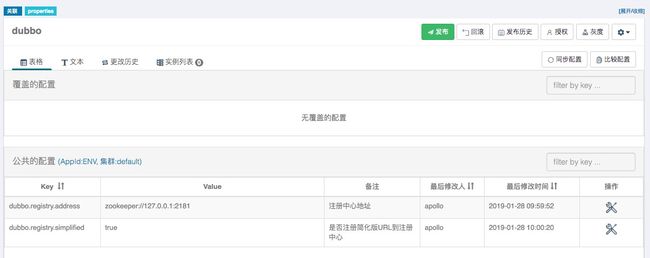
-
由于 Apollo 也默认将会在
dubbonamespace 中存储服务治理规则(如路由规则),建议通过单独配置group将服务治理和配置文件托管分离开,以 XML 配置方式为例: -
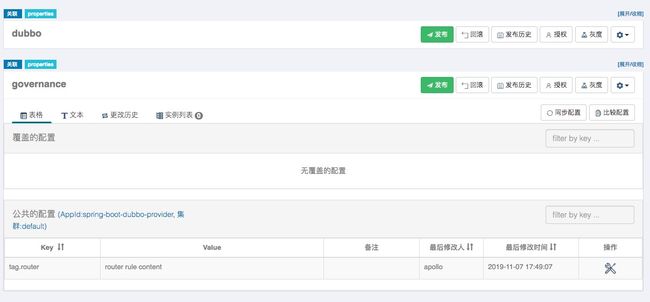
这里,服务治理规则将存储在 governance namespace,而配置文件将存储在 dubbo namespace,如下图所示:
关于文件配置托管,相当于是把
dubbo.properties配置文件的内容存储在了 Apollo 中,应用通过关联共享的dubbonamespace 继承公共配置, 应用也可以按照 Apollo 的做法来覆盖个别配置项。-
自己加载外部化配置
-
所谓Dubbo对配置中心的支持,本质上就是把
.properties从远程拉取到本地,然后和本地的配置做一次融合。理论上只要Dubbo框架能拿到需要的配置就可以正常的启动,它并不关心这些配置是自己加载到的还是应用直接塞给它的,所以Dubbo还提供了以下API,让用户将自己组织好的配置塞给Dubbo框架(配置加载的过程是用户要完成的),这样Dubbo框架就不再直接和Apollo或Zookeeper做读取配置交互。// 应用自行加载配置 Map<String, String> dubboConfigurations = new HashMap<>(); dubboConfigurations.put("dubbo.registry.address", "zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181"); dubboConfigurations.put("dubbo.registry.simplified", "true"); //将组织好的配置塞给Dubbo框架 ConfigCenterConfig configCenter = new ConfigCenterConfig(); configCenter.setExternalConfig(dubboConfigurations);
-
-
-
-
-
服务治理