android RILJ运行机制
如我们所知,和phone相关的framwork层命令,最后都都会传送到RIL,最终完成语音通话,服务网络状态和手机数据连接的控制和管理。
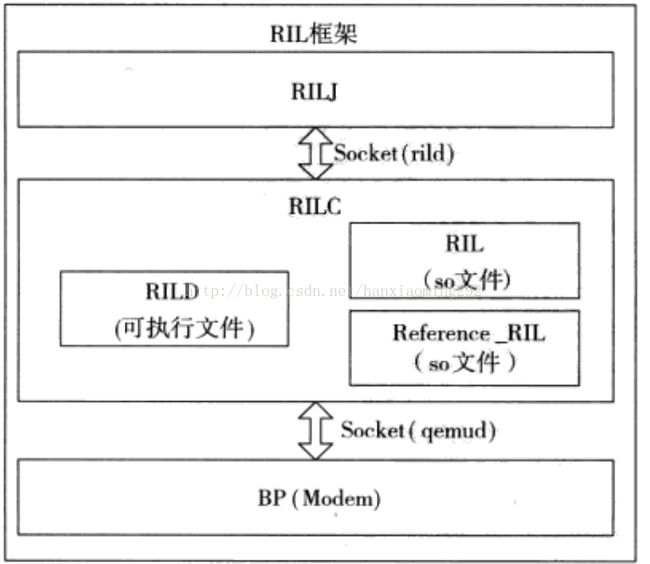
在讲解RILJ之前,我们先梳理下android的RIL框架。RIL的全名为Radio Interface Layer,android RIL代码框架可以分为两部分:
(1)Framework层的代码,是用java语言实现的,简称RILJ。
(2)HAL层中代码,是用C和C++语言来实现的,简称RILC。
上图为RILJ,RILC,RILD和modem之间的关系,在本篇文章我们只讲解RILJ,至于RILD,RILJ,RILC这三者之间的关系和交互流程,我们在后续的章节中再讲解,再本篇文章中,我们先只需要知道RILJ和RILC是通过socket进行通信的。
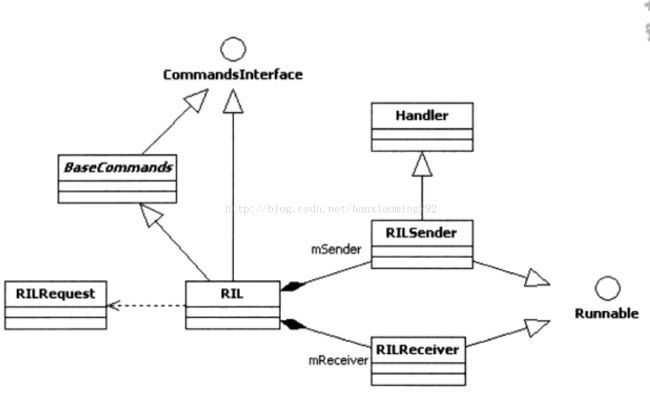
RILJ最核心的的代码主要有三个,分别是CommandsInterface.java,BaseCommands.java和RIL.java.这个三个类的关系如下图:
我们先关注RIL.java的一些关键属性:
LocalSocket mSocket;
HandlerThread mSenderThread;
RILSender mSender;//给RILC发送请求消息
Thread mReceiverThread;
RILReceiver mReceiver;//接受RILC发来的消息
Display mDefaultDisplay;
int mDefaultDisplayState = Display.STATE_UNKNOWN;
WakeLock mWakeLock;
final int mWakeLockTimeout;
// The number of wakelock requests currently active. Don't release the lock
// until dec'd to 0
int mWakeLockCount;
SparseArray mRequestList = new SparseArray();//保存solicited类型的RILrequest对象
查看ril.java文件,我们可以看出RIL.java中定义了三个内部类RILRequest,RILSender,RILReceiver。
RILRequest:每个从framework层传下的命令都会被封装成为一个RILRequest对象。
RILSender:发送从framework层传下的命令到RILC。
RILRecever:接受从RILC上报的消息。
如我们所知,java中的类在代码运行的时候,都会被new一个对象来执行代码,那么Ril.java在什么时候被new成一个对象呢,答案就是在phone模块加载的过程中,在PhoneFactory.java的makeDefaultPhone函数中会根据选网方式来创建GSMphone或者CDMAphone,在创建phone对象的时候会同时new一个RIL对象,每个phone对象会绑定一个RIL.java对象。
int numPhones = TelephonyManager.getDefault().getPhoneCount();
int[] networkModes = new int[numPhones];
sProxyPhones = new PhoneProxy[numPhones];
sCommandsInterfaces = new RIL[numPhones];
for (int i = 0; i < numPhones; i++) {
PhoneBase phone = null;
int phoneType = TelephonyManager.getPhoneType(networkModes[i]);
if (phoneType == PhoneConstants.PHONE_TYPE_GSM) {
phone = new GSMPhone(context,
sCommandsInterfaces[i], sPhoneNotifier, i);
} else if (phoneType == PhoneConstants.PHONE_TYPE_CDMA) {
phone = new CDMALTEPhone(context,
sCommandsInterfaces[i], sPhoneNotifier, i);
}
Rlog.i(LOG_TAG, "Creating Phone with type = " + phoneType + " sub = " + i);
sProxyPhones[i] = new PhoneProxy(phone);
}
接下来我们再详解看RILRequest这个类,获取这个类的对象java中工厂设计模式,RILRequest关键属性如下:
static Random sRandom = new Random();
static AtomicInteger sNextSerial = new AtomicInteger(0);//下一个RIlRequest对象编号
private static Object sPoolSync = new Object();//同步访问枷锁对象
private static RILRequest sPool = null;//保存下一个要处理的RILRequest对象
private static int sPoolSize = 0;
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 4;
private Context mContext;
//***** Instance Variables
int mSerial;//当前RIL的请求编号
int mRequest;//RIL请求类型
Message mResult;//从Framework层传下来的命令消息对象
Parcel mParcel;
RILRequest mNext;//保存下一个要处理的RILRequest对象
RILSender这个内部类集成了handler类同时实现了Runnable接口,RILSender的handleMessage的处理的一个重要消息就是EVENT_SEND,每个framework层下发的命令最后都会调用send函数,send函数会封装一个EVENT_SEND消息,最后交由RILSender的handleMessage函数来处理。
private void
send(RILRequest rr) {
Message msg;
if (mSocket == null) {
rr.onError(RADIO_NOT_AVAILABLE, null);
rr.release();
return;
}
msg = mSender.obtainMessage(EVENT_SEND, rr);
acquireWakeLock();
msg.sendToTarget();
}
RILSender的handleMessage的函数收到EVENT_SEND消息后,首先会获取跟RILC建立起来的socket客户端,然后通过java输出流把数据发送到RILC。
LocalSocket s;
s = mSocket;
if (s == null) {
rr.onError(RADIO_NOT_AVAILABLE, null);
rr.release();
decrementWakeLock();
return;
}
synchronized (mRequestList) {
mRequestList.append(rr.mSerial, rr);
}
byte[] data;
data = rr.mParcel.marshall();
rr.mParcel.recycle();
rr.mParcel = null;
if (data.length > RIL_MAX_COMMAND_BYTES) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Parcel larger than max bytes allowed! "
+ data.length);
}
// parcel length in big endian
dataLength[0] = dataLength[1] = 0;
dataLength[2] = (byte)((data.length >> 8) & 0xff);
dataLength[3] = (byte)((data.length) & 0xff);
//Rlog.v(RILJ_LOG_TAG, "writing packet: " + data.length + " bytes");
s.getOutputStream().write(dataLength);
s.getOutputStream().write(data);
那么RILJ跟RILC的socket连接什么时候建立起来的呢,那么接下我们在分析RILReceiver这个类,看完这个类你就会明白上面提到的socket是什么时候建立起来的,观看代码我们会发现RILReceiver实现了Runnable接口,它会以一个单独线程在运行,查看RILReceiver的run函数,我们会发现socket连接会在这个函数中建立,代码如下:
LocalSocket s = null;
LocalSocketAddress l;
if (mInstanceId == null || mInstanceId == 0 ) {
rilSocket = SOCKET_NAME_RIL[0];
} else {
rilSocket = SOCKET_NAME_RIL[mInstanceId];
}
try {
s = new LocalSocket();
l = new LocalSocketAddress(rilSocket,
ocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED);
s.connect(l);
RILReceiver的run函数中有一个for死循环,就是不停的接受从RILC上报的消息,代码如下:
Parcel p;
length = readRilMessage(is, buffer);
if (length < 0) {
// End-of-stream reached
break;
}
p = Parcel.obtain();
p.unmarshall(buffer, 0, length);
p.setDataPosition(0);
//Rlog.v(RILJ_LOG_TAG, "Read packet: " + length + " bytes");
processResponse(p);
p.recycle(); processResponse这个函数就是处理从RILC上报的消息,在函数processResponse中我们会发现首先会获取RILC上报的消息的类型,如果是RESPONSE_UNSOLICITED,就会调用processUnsolicited函数,如果是RESPONSE_SOLICITED就是调用processSolicited函数,processUnsolicited函数和processSolicited函数在这里就不多解析了,有兴趣的读者可以自己查看相应的代码。