JDK8之前的日期和日期API的测试、JDK8中新的日期和日期的API
JDK 8之前日期和时间的API测试
java.util.Date类
|—java.sql.Date类
1.两个构造器的使用
>构造器一:Date():创建一个对应当前时间的Date对象
>构造器二:创建指定毫秒数的Date对象
2.两个方法的使用
>toString():显示当前的年、月、日、时、分、秒
>getTime():获取当前Date对象对应的毫秒数。(时间戳)
3. java.sql.Date对应着数据库中的日期类型的变量
如何实例化
如何将java.util.Date对象转换为java.sql.Date对象
//1.System类中的currentTimeMillis()
@Test
public void test1(){
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
//返回当前时间与1970年1月1日0时0分0秒之间以毫秒为单位的时间差。
//称为时间戳
System.out.println(time);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
//构造器一:Date():创建一个对应当前时间的Date对象
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(date1.toString());//Sat Feb 16 16:35:31 GMT+08:00 2019
System.out.println(date1.getTime());//1550306204104
//构造器二:创建指定毫秒数的Date对象
Date date2 = new Date(155030620410L);
System.out.println(date2.toString());
//创建java.sql.Date对象
java.sql.Date date3 = new java.sql.Date(35235325345L);
System.out.println(date3);//1971-02-13
//如何将java.util.Date对象转换为java.sql.Date对象
//情况一:
// Date date4 = new java.sql.Date(2343243242323L);
// java.sql.Date date5 = (java.sql.Date) date4;
//情况二:
Date date6 = new Date();
java.sql.Date date7 = new java.sql.Date(date6.getTime());
}
SimpleDateFormat的使用
Date类的API不易于国际化,大部分被废弃了,java.text.SimpleDateFormat类是一个不与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的具体类。
它允许进行 格式化:日期-> 文本、 解析:文本 -> 日期
格式化:
- SimpleDateFormat() :默认的模式和语言环境创建对象
- public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) :该构造方法可以用参数pattern
指定的格式创建一个对象,该对象调用: - public String format(Date date) :方法格式化时间对象date
解析:
- public Date parse(String source): :从给定字符串的开始解析文本,以生成 一个日期。
代码:
@Test
public void testSimpleDateFormat() throws ParseException {
//实例化SimpleDateFormat:使用默认的构造器
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
//格式化:日期 --->字符串
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
String format = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
//解析:格式化的逆过程,字符串 ---> 日期
String str = "20-9-7 下午4:43";
Date date1 = sdf.parse(str);
System.out.println(date1);
//*************按照指定的方式格式化和解析:调用带参的构造器*****************
// SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyy.MMMMM.dd GGG hh:mm aaa");
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
//格式化
String format1 = sdf1.format(date);
System.out.println(format1);//2020-09-07 04:23:44
//解析:要求字符串必须是符合SimpleDateFormat识别的格式(通过构造器参数体现),
//否则,抛异常
Date date2 = sdf1.parse("2020-09-7 11:48:27");
System.out.println(date2);
}
java.util.Calendar( 日历)类 类
Calendar是一个抽象基类,主用用于完成日期字段之间相互操作的功能。
获取Calendar实例的方法
- 使用Calendar.getInstance()方法
- 调用它的子类GregorianCalendar的构造器。
一个Calendar的实例是系统时间的抽象表示,通过get(int field)方法来取得想
要的时间信息。比如YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_WEEK、HOUR_OF_DAY 、
MINUTE、SECOND
- public void set(int field,int value)
- public void add(int field,int amount)
- public final Date getTime()
- public final void setTime(Date date)
注意:
-
获取月份时:一月是0,二月是1,以此类推,12月是11
-
获取星期时:周日是1,周二是2 , 。。。。周六是7
@Test
public void testCalendar(){
//1.实例化
//方式一:创建其子类(GregorianCalendar)的对象
//方式二:调用其静态方法getInstance()
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
// System.out.println(calendar.getClass());
//2.常用方法
//get()
int days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(days);
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));
//set()
//calendar可变性
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,22);
days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(days);
//add()
calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,-3);
days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(days);
//getTime():日历类---> Date
Date date = calendar.getTime();
System.out.println(date);
//setTime():Date ---> 日历类
Date date1 = new Date();
calendar.setTime(date1);
days = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(days);
}
JDK8中新的日期和日期的API
新日期间 时间API 出现的背景
如果我们可以跟别人说:“我们在1502643933071见面,别晚了!”那么就再简单不过了。但是我们希望时间与昼夜和四季有关,于是事情就变复杂了。JDK 1.0中包含了一个java.util.Date类,但是它的大多数方法已经在JDK 1.1引入Calendar类之后被弃用了。而Calendar并不比Date好多少。它们面临的问题是:
- 可变性:像日期和时间这样的类应该是不可变的。
- 偏移性:Date中的年份是从1900开始的,而月份都从0开始。
- 格式化:格式化只对Date有用,Calendar则不行。
- 此外,它们也不是线程安全的;不能处理闰秒等。
总结:对日期和时间的操作一直是Java程序员最痛苦的地方之一。
新时间日期API
- 第三次引入的API是成功的,并且Java 8中引入的java.time API 已经纠正了过去的缺陷,将来很长一段时间内它都会为我们服务。
- Java 8 吸收了 Joda-Time 的精华,以一个新的开始为 Java 创建优秀的 API。 新的 java.time中包含了所有关于本地日期(LocalDate)、本地时间(LocalTime)、本地日期时间(LocalDateTime)、时区(ZonedDateTime)和持续时间(Duration)的类。历史悠久的 Date 类新增了 toInstant() 方法, 用于把 Date转换成新的表示形式。这些新增的本地化时间日期 API 大大简 化了日期时间和本地化的管理。

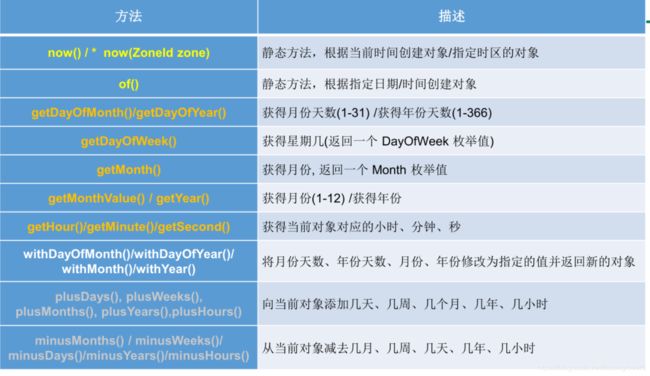
LocalDate 、LocalTime 、LocalDateTime
LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime 类是其中较重要的几个类,它们的实例是不可变的对象,分别表示使用 ISO-8601日历系统的日期、时间、日期和时间。
它们提供了简单的本地日期或时间,并不包含当前的时间信息,也不包含与时区相关的信息。
- LocalDate代表IOS格式(yyyy-MM-dd)的日期,可以存储 生日、纪念日等日期。
- LocalTime表示一个时间,而不是日期。
- LocalDateTime是用来表示日期和时间的,这是一个最常用的类之一。
注:ISO-8601日历系统是国际标准化组织制定的现代公民的日期和时间的表示 法,也就是公历。
/*
LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime 的使用
说明:
1.LocalDateTime相较于LocalDate、LocalTime,使用频率要高
2.类似于Calendar
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
//now():获取当前的日期、时间、日期+时间
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(localDate);
System.out.println(localTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
//of():设置指定的年、月、日、时、分、秒。没有偏移量
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 10, 6, 13, 23, 43);
System.out.println(localDateTime1);
//getXxx():获取相关的属性
System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfWeek());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getMonth());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getMonthValue());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getMinute());
//体现不可变性
//withXxx():设置相关的属性
LocalDate localDate1 = localDate.withDayOfMonth(22);
System.out.println(localDate);
System.out.println(localDate1);
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.withHour(4);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime2);
//不可变性
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = localDateTime.plusMonths(3);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime3);
LocalDateTime localDateTime4 = localDateTime.minusDays(6);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime4);
}
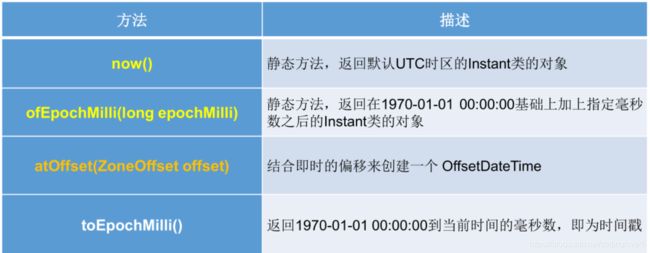
瞬时:Instant
- Instant:时间线上的一个瞬时点。 这可能被用来记录应用程序中的事件时间戳。
- 在处理时间和日期的时候,我们通常会想到年,月,日,时,分,秒。然而,这只是时间的一个模型,是面向人类的。第二种通用模型是面向机器的,或者说是连 续的。在此模型中,时间线中的一个点表示为一个很大的数,这有利于计算机处理。在UNIX中,这个数从1970年开始,以秒为的单位;同样的,在Java中, 也是从1970年开始,但以毫秒为单位。
- java.time包通过值类型Instant提供机器视图,不提供处理人类意义上的时间单位。Instant表示时间线上的一点,而不需要任何上下文信息,例如,时区。概念上讲,它只是简单的表示自1970年1月1日0时0分0秒(UTC)开始的秒数。因为java.time包是基于纳秒计算的,所以Instant的精度可以达到纳秒级。
- (1 ns = 10 -9 s) 1秒 = 1000毫秒 =106微秒=109纳秒
 代码:
代码:
/*
Instant的使用
类似于 java.util.Date类
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
//now():获取本初子午线对应的标准时间
Instant instant = Instant.now();
System.out.println(instant);//2019-02-18T07:29:41.719Z
//添加时间的偏移量
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
System.out.println(offsetDateTime);//2019-02-18T15:32:50.611+08:00
//toEpochMilli():获取自1970年1月1日0时0分0秒(UTC)开始的毫秒数 ---> Date类的getTime()
long milli = instant.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(milli);
//ofEpochMilli():通过给定的毫秒数,获取Instant实例 -->Date(long millis)
Instant instant1 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(1550475314878L);
System.out.println(instant1);
}
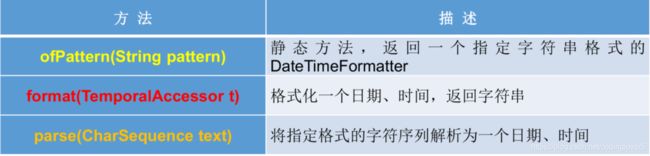
格式化与解析日期 或 时间
java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter 类:该类提供了三种格式化方法:
- 预定义的标准格式。如: ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;ISO_LOCAL_DATE;ISO_LOCAL_TIME
- 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.LONG)
- 自定义的格式。如:ofPattern(“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss”)
 代码;
代码;
@Test
public void test3(){
// 方式一:预定义的标准格式。如:ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;ISO_LOCAL_DATE;ISO_LOCAL_TIME
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;
//格式化:日期-->字符串
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
String str1 = formatter.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(str1);//2019-02-18T15:42:18.797
//解析:字符串 -->日期
TemporalAccessor parse = formatter.parse("2019-02-18T15:42:18.797");
System.out.println(parse);
// 方式二:
// 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDateTime()
// FormatStyle.LONG / FormatStyle.MEDIUM / FormatStyle.SHORT :适用于LocalDateTime
DateTimeFormatter formatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.LONG);
//格式化
String str2 = formatter1.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(str2);//2019年2月18日 下午03时47分16秒
// 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDate()
// FormatStyle.FULL / FormatStyle.LONG / FormatStyle.MEDIUM / FormatStyle.SHORT : 适用于LocalDate
DateTimeFormatter formatter2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.MEDIUM);
//格式化
String str3 = formatter2.format(LocalDate.now());
System.out.println(str3);//2019-2-18
// 重点: 方式三:自定义的格式。如:ofPattern(“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss”)
DateTimeFormatter formatter3 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
//格式化
String str4 = formatter3.format(LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println(str4);//2019-02-18 03:52:09
//解析
TemporalAccessor accessor = formatter3.parse("2019-02-18 03:52:09");
System.out.println(accessor);
}
其它API
- ZoneId :该类中包含了所有的时区信息,一个时区的ID,如 Europe/Paris
- ZonedDateTime :一个在ISO-8601日历系统时区的日期时间,如 2007-12- 03T10:15:30+01:00Europe/Paris。
- 其中每个时区都对应着ID,地区ID都为“{区域}/{城市}”的格式,例如: Asia/Shanghai等
- Clock: :使用时区提供对当前即时、日期和时间的访问的时钟。
- 持续时间:Duration,用于计算两个“时间”间隔
- 日期间隔:Period,用于计算两个“日期”间隔
- TemporalAdjuster : 时间校正器。有时我们可能需要获取例如:将日期调整 到“下一个工作日”等操作。
- TemporalAdjusters : 该类通过静态方法
(firstDayOfXxx()/lastDayOfXxx()/nextXxx())提供了大量的常用 TemporalAdjuster
的实现。
//ZoneId:类中包含了所有的时区信息
// ZoneId的getAvailableZoneIds():获取所有的ZoneId
Set<String> zoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
for (String s : zoneIds) {
System.out.println(s);
}
// ZoneId的of():获取指定时区的时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println(localDateTime);
//ZonedDateTime:带时区的日期时间
// ZonedDateTime的now():获取本时区的ZonedDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(zonedDateTime);
// ZonedDateTime的now(ZoneId id):获取指定时区的ZonedDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime1 = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println(zonedDateTime1);
//Duration:用于计算两个“时间”间隔,以秒和纳秒为基准
LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();
LocalTime localTime1 = LocalTime.of(15, 23, 32);
//between():静态方法,返回Duration对象,表示两个时间的间隔
Duration duration = Duration.between(localTime1, localTime);
System.out.println(duration);
System.out.println(duration.getSeconds());
System.out.println(duration.getNano());
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2016, 6, 12, 15, 23, 32);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2017, 6, 12, 15, 23, 32);
Duration duration1 = Duration.between(localDateTime1, localDateTime);
System.out.println(duration1.toDays());
//Period:用于计算两个“日期”间隔,以年、月、日衡量
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2028, 3, 18);
Period period = Period.between(localDate, localDate1);
System.out.println(period);
System.out.println(period.getYears());
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());
Period period1 = period.withYears(2);
System.out.println(period1);
// TemporalAdjuster:时间校正器
// 获取当前日期的下一个周日是哪天?
TemporalAdjuster temporalAdjuster = TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now().with(temporalAdjuster);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
// 获取下一个工作日是哪天?
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now().with(new TemporalAdjuster() {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
LocalDate date = (LocalDate) temporal;
if (date.getDayOfWeek().equals(DayOfWeek.FRIDAY)) {
return date.plusDays(3);
} else if (date.getDayOfWeek().equals(DayOfWeek.SATURDAY)) {
return date.plusDays(2);
} else {
return date.plusDays(1);
}
}
});
System.out.println("下一个工作日是:" + localDate);