HTTP 缓存机制详解
文章目录
- HTTP Cache
- 什么是 HTTP Cache
- 关键字
- 简单流程图
- 代码准备
- 不设置
- 明确禁止缓存
- private与public
- 缓存过期策略
- 1、三种方式设置服务器告知浏览器缓存过期时间
- 2、两种方式校验资源过期
- 强制校验缓存
- 性能优化
- 期中总结:HTTP 缓存性能检查清单
- 前端工程化
- 参考
- 附代码
HTTP Cache
什么是 HTTP Cache
- 我们知道通过网络获取资源缓慢且耗时,需要三次握手等协议与远程服务器建立通信,对于大点的数据需要多次往返通信大大增加了时间开销,并且当今流量依旧没有理想的快速与便宜。对于开发者来说,长久缓存复用重复不变的资源是性能优化的重要组成部分。
- HTTP 缓存机制就是,配置服务器响应头来告诉浏览器是否应该缓存资源、是否强制校验缓存、缓存多长时间;浏览器非首次请求根据响应头是否应该取缓存、缓存过期发送请求头验证缓存是否可用还是重新获取资源的过程。下面我们就来结合简单的 node 服务器代码(文末)来介绍其中原理。
关键字
| 响应头 | (常用)值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Cache-Control | no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate, max-age, public, private | 控制浏览器是否可以缓存资源、强制缓存校验、缓存时间 |
| ETag | 文件指纹(hash码、时间戳等可以标识文件是否更新) | 强校验,根据文件内容生成精确 |
| Last-Modified | 请求的资源最近更新时间 | 弱校验, 根据文件修改时间,可能内容未变,不精确 |
| Expires | 资源缓存过期时间 | 与响应头中的 Date 对比 |
| 请求头 | 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| If-None-Match | 缓存响应头中的 ETag 值 | 发送给服务器比对文件是否更新(精确) |
| If-Modified-Since | 缓存响应头中的 Last-Modified 值 | 发送给服务器比对文件是否更新(不精确) |
简单流程图
代码准备
-
index.html
-
img.png
-
server.js
为了不影响阅读代码贴在页尾,注意需要自行安装
mimenpm包。
不设置
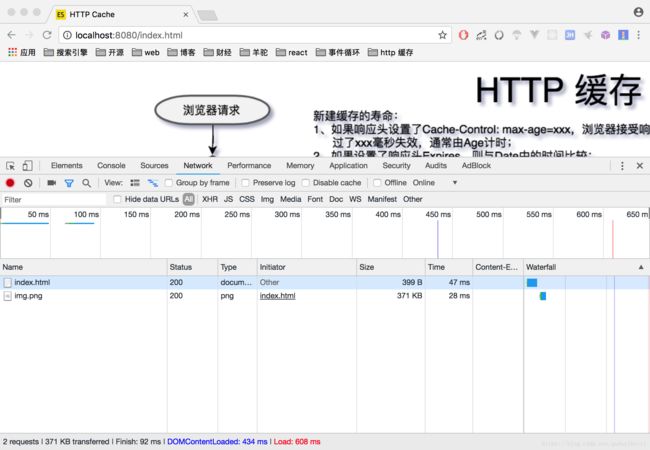
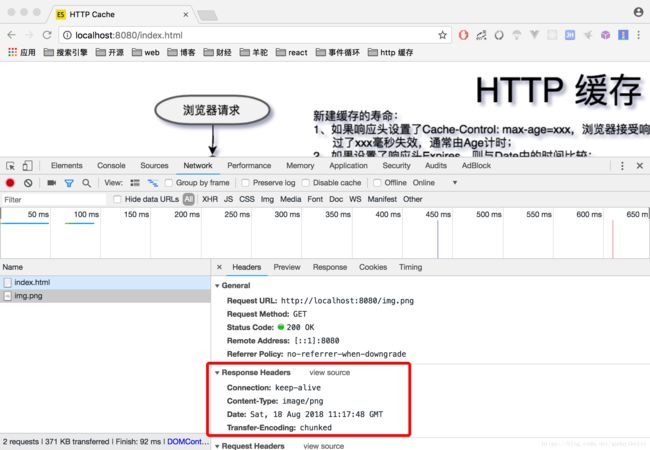
- 不设置响应头,则浏览器并不能知道是否应该缓存资源,而是每次都发送新的请求,接受新的资源。
// strategy['no-cache'](req, res, filePath, stat);
// strategy['no-store'](req, res, filePath, stat);
// strategy['cache'](req, res, filePath, stat);
strategy['nothing'](req, res, filePath, stat);
$ node server.js
浏览器里输入:localhost:8080/index.html
明确禁止缓存
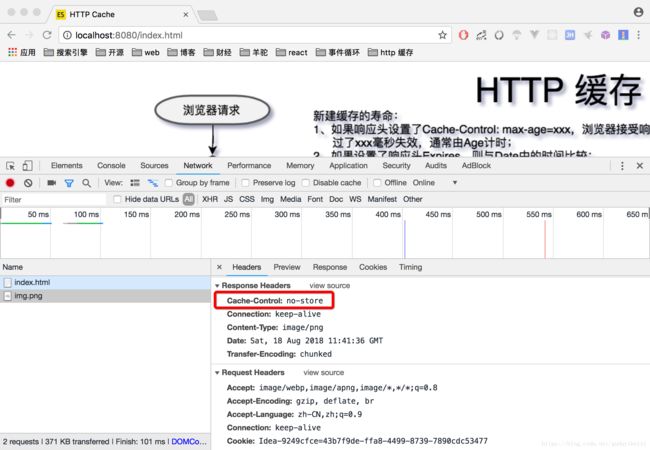
- 设置响应头
Cache-Control: no-store
或
Cache-Control: no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate
strategy['no-store'](req, res, filePath, stat);
private与public
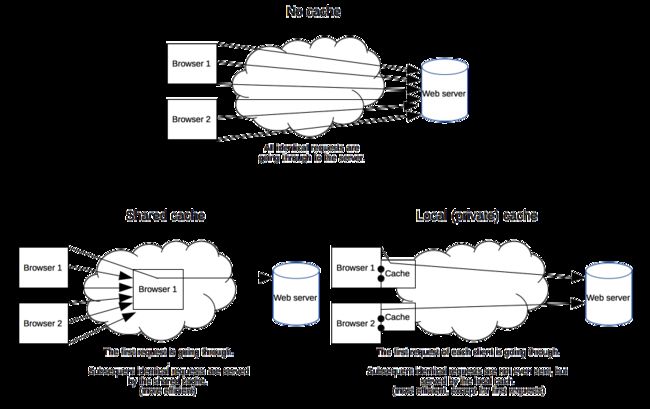
Cache-Control: public表示一些中间代理、CDN等可以缓存资源,即便是带有一些敏感 HTTP 验证身份信息甚至响应状态代码通常无法缓存的也可以缓存。通常 public 是非必须的,因为响应头 max-age 信息已经明确告知可以缓存了。Cache-Control: private明确告知此资源只能单个用户可以缓存,其他中间代理不能缓存。原始发起的浏览器可以缓存,中间代理不能缓存。例如:百度搜索时,特定搜索信息只能被发起请求的浏览器缓存。

缓存过期策略
一般缓存机制只作用于 get 请求
1、三种方式设置服务器告知浏览器缓存过期时间
设置响应头(注意浏览器有自己的缓存替换策略,即便资源过期,不一定被浏览器删除。同样资源未过期,可能由于缓存空间不足而被其他网页新的缓存资源所替换而被删除。):
- 1、设置
Cache-Control: max-age=1000//响应头中的Date经过1000s过期 - 2、设置
Expires//此时间与本地时间(响应头中的 Date )对比,小于本地时间表示过期,由于本地时钟与服务器时钟无法保持一致,导致比较不精确 - 3、如果以上均未设置,却设置了
Last-Modified,浏览器隐式的设置资源过期时间为(Date - Last-Modified) * 10%缓存过期时间。
2、两种方式校验资源过期
设置请求头:
- 1、
If-None-Match如果缓存资源过期,浏览器发起请求会自动把原来缓存响应头里的ETag值设置为请求头If-None-Match的值发送给服务器用于比较。一般设置为文件的 hash 码或其他标识能够精确判断文件是否被更新,为强校验。 - 2、
If-Modified-Since同样对应缓存响应头里的Last-Modified的值。此值可能取得 ctime 的值,该值可能被修改但文件内容未变,导致对比不准确,为弱校验。
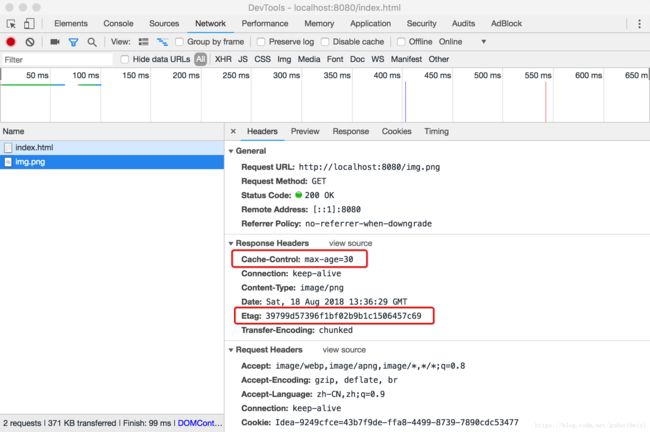
下面以常用设置了 Cache-Control: max-age=100 和 If-None-Match 的图示说明:

浏览器缓存此响应,缓存寿命为接收到此响应开始计时 100s 。
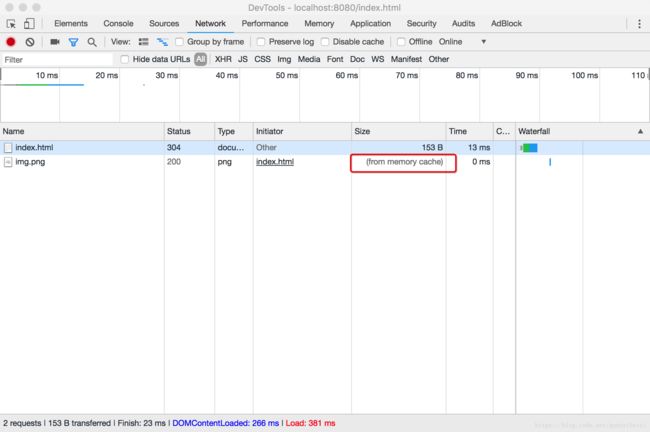
- 2、10s 过后,浏览器再次发起请求,检测缓存未过期,浏览器计算 Age: 10 ,然后直接使用缓存,这里是直接去内存中的缓存,from disk 是取磁盘上的缓存。(
这里不清楚为什么,同样的配置,index.html 文件即便有缓存也 304。)
- 3、100s 过后,浏览器再次发起请求,检测缓存过期,向服务器发起验证缓存请求。如果服务器对比文件已发生改变,则如 1;否则不返回文件数据报文,直接返回 304。
返回 304 时设置 Age: 0 与不设置效果一样, 猜测是浏览器会自动维护。

强制校验缓存
有时我们既想享受缓存带来的性能优势,可有时又不确认资源内容的更新频度或是其他资源的入口,我们想此服务器资源一旦更新能立马更新浏览器的缓存,这时我们可以设置
Cache-Control: no-cache
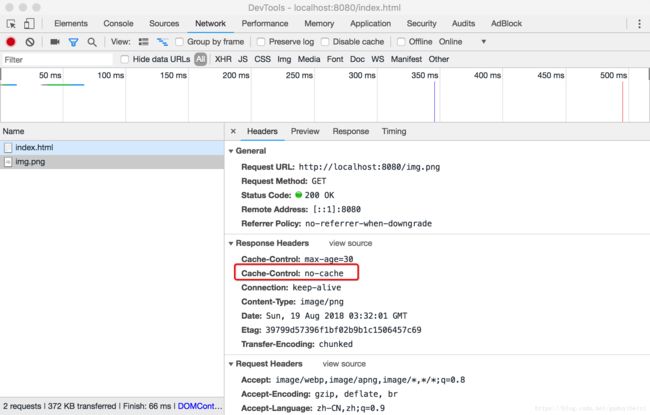
再次发起请求,无论缓存资源有没有过期都发起验证请求,未更新返回 304,否则返回新资源。
性能优化
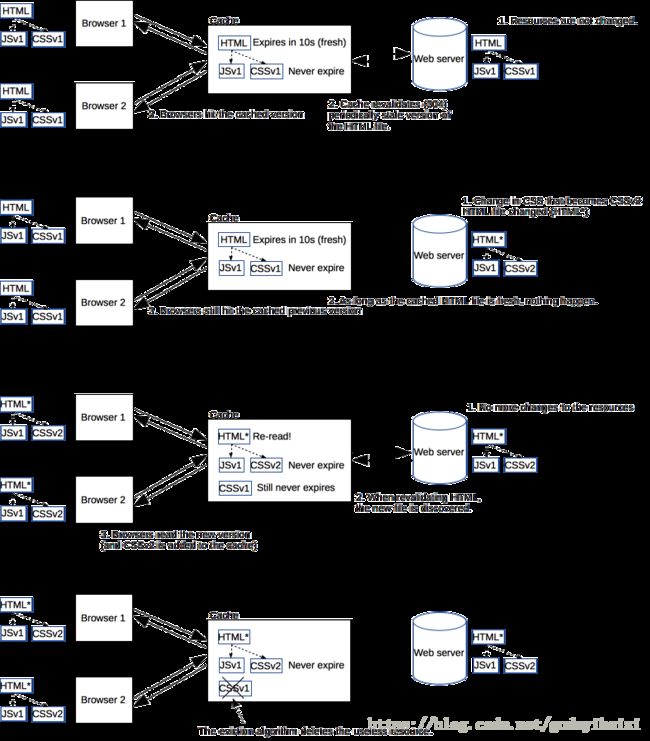
现在一些单页面技术,构建工具十分流行。一般一个 html 文件,每次打包构建工具都会动态默认把众多脚本样式文件打包成一个 bundle.hashxxx.js 。虽然一个 js 文件看似减少了 HTTP 请求数量,但对于有些三方库资源等长期不变的资源可以拆分出来,并设置长期缓存,充分利用缓存性能优势。这时我们完全可以对经常变动的 html 设置 Cache-Control: no-cahce 实时验证是否更新。而对于链接在 html 文件的资源名称均带上唯一的文件指纹(时间戳、版本号、文件hash等),设置 max-age 足够大。资源一旦变动即标识码也会变动,作为入口的 html 文件外链改变,html 变动验证返回全新的资源,拉取最新的外链资源,达到及时更新的效果。老的资源会被浏览器缓存替换机制清除。流程如下:
期中总结:HTTP 缓存性能检查清单
- 确保网址唯一:一般浏览器以
Request URL为键值(区分大小写)缓存资源,不同的网址提供相同的内容会导致多次获取缓存相同的资源。ps:常见的更新缓存的方式:在网址后面来加个 v=1,例如 https://xxx.com?v=1 来更新新的资源,但是这样的更新方式有极大的弊端。 - 确保服务器提供了验证令牌
ETag:提供资源对比机制。ps:服务器每次验证文件的话,太耗性能,现代前端构建工具都能自动更新文件hash,不需要设置Tag了,直接设置长缓存时间。 - 确定中间代理可以缓存哪些资源:对于个人隐私信息可以设置
private,对于公共资源例如 CDN 资源可以设置public。 - 为每个资源设置最佳的缓存寿命:
max-age 或 Expires,对于不经常变动或不变的资源设置尽可能大的缓存时间,充分利用缓存性能。 - 确认网站的层次机构:例如单页面技术,对于频繁更新的主入口 index.html 文件设置较短的缓存周期或
no-cache强制缓存验证,以确保外链资源的及时更新。 - 最大限度减少文件搅动:对于要打包合并的文件,应该尽量区分频繁、不频繁变动的文件,避免频繁变动的内容导致大文件的文件指纹变动(后台服务器计算文件 hash 很耗性能),尽量频繁变动的文件小而美,不经常变动例如第三方库资源可以合并减少HTTP请求数量。
前端工程化
![]()
相当,前端的概念只是编写一些页面、样式、简单脚本,然后丢给服务器就可以了,真是简单有趣…
![]()
进步青年想,对于不变的资源能不能利用缓存呢,于是有:
![]()
304有时也觉得浪费,这个请求我也想省了,未过期就不发请求:
![]()
完美!那么问题来了,有新资源我如何实时发布更新呢?
方案一:查询字符加版本号
![]()
更新资源只要更新版本号
问题来了:我可能每次只有一两个文件修改了,我得更新多有文件版本号?!
![]()
弊端:更新若干资源必须全部文件版本升级,未变动资源缓存也不能利用了。
方案二:查询字符加文件哈希
![]()
大点的公司服务器肯定不止一个,静态资源需要做集群部署、CDN等。
![]()
问题来了:我是先发动态页面,还是先发静态资源?
![]()
答案是:都不行!
弊端:
1、先发页面,这时用户正好打开了新页面,此时新资源未更新,拉取老的静态资源,并缓存,导致错误。
2、先发资源,这时新用户正好打开老的页面,拉取新资源,导致出错。
(熟悉的声音:是你缓存有问题吧,清下缓存…)。
这就是为什么要等到三更半夜,等用户休息了,先发静态资源,再发动态页面。
方案三:根据文件内容生成文件名,这就完美解决了文件更新的问题:
![]()
非覆盖式更新,改变某文件,生成新的文件并更新页面引用链接一并上传服务新文件,不影响以前用户,又能实时更新文件,完美!
问题来了,那我怎么写代码,图片、CSS、JS等静态资源怎么去维护,修改了生成新的文件,更新新的外链。。。这就不是人力所能为了。
前端工程化议题应运而生,欢迎补玉。
参考
mozilla:HTTP 缓存
谷歌有关性能的文字:HTTP 缓存
node中的缓存机制
w3c Header定义
彻底弄懂 Http 缓存机制 - 基于缓存策略三要素分解法
听说你用webpack处理文件名的hash?那么建议你看看你生成的hash对不对
附代码
index.html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>HTTP Cachetitle>
head>
<body>
<img src="img.png" alt="流程图">
body>
html>
server.js
let http = require('http');
let url = require('url');
let path = require('path');
let fs = require('fs');
let mime = require('mime');// 非 node 内核包,需 npm install
let crypto = require('crypto');
// 缓存策略
const strategy = {
'nothing': (req, res, filePath) => {
fs.createReadStream(filePath).pipe(res);
},
'no-store': (req, res, filePath, stat) => {
// 禁止缓存
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'no-store');
// res.setHeader('Cache-Control', ['no-cache', 'no-store', 'must-revalidate']);
// res.setHeader('Expires', new Date(Date.now() + 30 * 1000).toUTCString());
// res.setHeader('Last-Modified', stat.ctime.toGMTString());
fs.createReadStream(filePath).pipe(res);
},
'no-cache': (req, res, filePath, stat) => {
// 强制确认缓存
// res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'no-cache');
strategy['cache'](req, res, filePath, stat, true);
// fs.createReadStream(filePath).pipe(res);
},
'cache': async (req, res, filePath, stat, revalidate) => {
let ifNoneMatch = req.headers['if-none-match'];
let ifModifiedSince = req.headers['if-modified-since'];
let LastModified = stat.ctime.toGMTString();
let maxAge = 30;
let etag = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 生成文件 hash
let out = fs.createReadStream(filePath);
let md5 = crypto.createHash('md5');
out.on('data', function (data) {
md5.update(data)
});
out.on('end', function () {
resolve( md5.digest('hex') );
});
});
console.log(etag);
if (ifNoneMatch) {
if (ifNoneMatch == etag) {
console.log('304');
// res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'max-age=' + maxAge);
// res.setHeader('Age', 0);
res.writeHead('304');
res.end();
} else {
// 设置缓存寿命
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'max-age=' + maxAge);
res.setHeader('Etag', etag);
fs.createReadStream(filePath).pipe(res);
}
}
/*else if ( ifModifiedSince ) {
if (ifModifiedSince == LastModified) {
res.writeHead('304');
res.end();
} else {
res.setHeader('Last-Modified', stat.ctime.toGMTString());
fs.createReadStream(filePath).pipe(res);
}
}*/
else {
// 设置缓存寿命
// console.log('首次响应!');
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'max-age=' + maxAge);
res.setHeader('Etag', etag);
// res.setHeader('Last-Modified', stat.ctime.toGMTString());
revalidate && res.setHeader('Cache-Control', [
'max-age=' + maxAge,
'no-cache'
]);
fs.createReadStream(filePath).pipe(res);
}
}
};
http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log( new Date().toLocaleTimeString() + ':收到请求')
let { pathname } = url.parse(req.url, true);
let filePath = path.join(__dirname, pathname);
// console.log(filePath);
fs.stat(filePath, (err, stat) => {
if (err) {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html');
res.setHeader('404', 'Not Found');
res.end('404 Not Found');
} else {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', mime.getType(filePath));
// strategy['no-cache'](req, res, filePath, stat);
// strategy['no-store'](req, res, filePath, stat);
strategy['cache'](req, res, filePath, stat);
// strategy['nothing'](req, res, filePath, stat);
}
});
})
.on('clientError', (err, socket) => {
socket.end('HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request\r\n\r\n');
})
.listen(8080);
标准配置
'use strict';
/** deps */
var path = require('path'),
express = require('express'),
mime = require('express/lib/express').mime,
/** cache values */
ONE_HOUR = 60 * 60,
ONE_WEEK = ONE_HOUR * 24 * 7,
ONE_MONTH = ONE_WEEK * 4,
ONE_YEAR = ONE_MONTH * 12,
/** mime type regexps */
RE_MIME_IMAGE = /^image/,
RE_MIME_FONT = /^(?:application\/(?:font-woff|x-font-ttf|vnd\.ms-fontobject)|font\/opentype)$/,
RE_MIME_DATA = /^(?:text\/(?:cache-manifest|html|xml)|application\/(?:(?:rdf\+)?xml|json))/,
RE_MIME_FEED = /^application\/(?:rss|atom)\+xml$/,
RE_MIME_FAVICON = /^image\/x-icon$/,
RE_MIME_MEDIA = /(image|video|audio|text\/x-component|application\/(?:font-woff|x-font-ttf|vnd\.ms-fontobject)|font\/opentype)/,
RE_MIME_CSSJS = /^(?:text\/(?:css|x-component)|application\/javascript)/,
/** misc regexps */
RE_WWW = /^www\./,
RE_MSIE = /MSIE/,
RE_HIDDEN = /(^|\/)\./,
RE_SRCBAK = /\.(?:bak|config|sql|fla|psd|ini|log|sh|inc|swp|dist)|~/;
// load additional node mime types
mime.load(path.join(__dirname, 'node.types'));
// apply `ServerResponse` patch
require('../patch');
/**
* Configures headers layer.
* @type {Function}
*/
module.exports = function(options) {
/**
* The actual headers layer, invoked for each request hit.
* Applies all h5bp goodness relative to response headers.
*/
return function headersLayer(req, res, next) {
var url = req.url,
pathname = req.path || '/',
host = req.headers.host,
ua = req.headers['user-agent'],
cc = '',
type;
// Block access to "hidden" directories or files whose names begin with a
// period. This includes directories used by version control systems such as
// Subversion or Git.
// 隐藏文件,403拒绝访问
if (!options.dotfiles && RE_HIDDEN.test(pathname)) {
next(403);
return;
}
// Block access to backup and source files. These files may be left by some
// text/html editors and pose a great security danger, when anyone can access
// them.
// 备份、源文件,403拒绝访问
if (RE_SRCBAK.test(pathname)) {
next(403);
return;
}
/**
* Suppress or force the "www." at the beginning of URLs
*/
// The same content should never be available under two different URLs -
// especially not with and without "www." at the beginning, since this can cause
// SEO problems (duplicate content). That's why you should choose one of the
// alternatives and redirect the other one.
// By default option 1 (no "www.") is activated.
// no-www.org/faq.php?q=class_b
// If you'd prefer to use option 2, just comment out all option 1 lines
// and uncomment option 2.
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Option 1:
// Rewrite "www.example.com -> example.com".
// 重定向
if (false === options.www && RE_WWW.test(host)) {
res.setHeader('Location', '//' + host.replace(RE_WWW, '') + url);
next(301);
return;
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Option 2:
// Rewrite "example.com -> www.example.com".
// Be aware that the following rule might not be a good idea if you use "real"
// subdomains for certain parts of your website.
if (true === options.www && !RE_WWW.test(host)) {
res.setHeader('Location', '//www.' + host.replace(RE_WWW, '') + url);
next(301);
return;
}
/**
* Built-in filename-based cache busting
*/
// If you're not using the build script to manage your filename version revving,
// you might want to consider enabling this, which will route requests for
// /css/style.20110203.css to /css/style.css
// To understand why this is important and a better idea than all.css?v1231,
// read: github.com/h5bp/html5-boilerplate/wiki/cachebusting
req.baseUrl = req.url;
req.url = req.url.replace(/^(.+)\.(\d+)\.(js|css|png|jpg|gif)$/, '$1.$3');
// Headers stuff!!
// Subscribes to the `header` event in order to:
// - let content generator middlewares set the appropriate content-type.
// - "ensures" that `h5bp` is the last to write headers.
res.on('header', function() {
/**
* Proper MIME type for all files
*/
// Here we delegate it to `node-mime` which already does that for us and maintain a list of fresh
// content types.
// https://github.com/broofa/node-mime
type = res.getHeader('Content-Type');
// normalize unknown types to empty string
if (!type || !mime.extension(type.split(';')[0])) {
type = '';
}
/**
* Better website experience for IE users
*/
// Force the latest IE version, in various cases when it may fall back to IE7 mode
// github.com/rails/rails/commit/123eb25#commitcomment-118920
// https://www.cnblogs.com/menyiin/p/6527339.html
// chrome IE壳
if (RE_MSIE.test(ua) && ~type.indexOf('text/html')) {
res.setHeader('X-UA-Compatible', 'IE=Edge,chrome=1');
}
/**
* Cross-domain AJAX requests
*/
// Serve cross-domain Ajax requests, disabled by default.
// enable-cors.org
// code.google.com/p/html5security/wiki/CrossOriginRequestSecurity
// cors 跨域
if (options.cors) {
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
}
/**
* CORS-enabled images (@crossorigin)
*/
// Send CORS headers if browsers request them; enabled by default for images.
// developer.mozilla.org/en/CORS_Enabled_Image
// blog.chromium.org/2011/07/using-cross-domain-images-in-webgl-and.html
// hacks.mozilla.org/2011/11/using-cors-to-load-webgl-textures-from-cross-domain-images/
// wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Reviews/crossoriginAttribute
// 图片可跨域
if (RE_MIME_IMAGE.test(type)) {
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
}
/**
* Webfont access
*/
// Allow access from all domains for webfonts.
// Alternatively you could only whitelist your
// subdomains like "subdomain.example.com".
// 字体可跨域
if (RE_MIME_FONT.test(type) || '/font.css' == pathname) {
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
}
/**
* Expires headers (for better cache control)
*/
// These are pretty far-future expires headers.
// They assume you control versioning with filename-based cache busting
// Additionally, consider that outdated proxies may miscache
// www.stevesouders.com/blog/2008/08/23/revving-filenames-dont-use-querystring/
// If you don't use filenames to version, lower the CSS and JS to something like
// "access plus 1 week".
// note: we don't use express.static maxAge feature because it does not allow fine tune
// Perhaps better to whitelist expires rules? Perhaps.
// cache.appcache needs re-requests in FF 3.6 (thanks Remy ~Introducing HTML5)
// Your document html
// Data
if (!type || RE_MIME_DATA.test(type)) {
cc = 'public,max-age=0';
}
// Feed
else if (RE_MIME_FEED.test(type)) {
cc = 'public,max-age=' + ONE_HOUR;
}
// Favicon (cannot be renamed)
else if (RE_MIME_FAVICON.test(type)) {
cc = 'public,max-age=' + ONE_WEEK;
}
// Media: images, video, audio
// HTC files (css3pie)
// Webfonts
else if (RE_MIME_MEDIA.test(type)) {
cc = 'public,max-age=' + ONE_MONTH;
}
// CSS and JavaScript
else if (RE_MIME_CSSJS.test(type)) {
cc = 'public,max-age=' + ONE_YEAR;
}
// Misc
else {
cc = 'public,max-age=' + ONE_MONTH;
}
/**
* Prevent mobile network providers from modifying your site
*/
// The following header prevents modification of your code over 3G on some
// European providers.
// This is the official 'bypass' suggested by O2 in the UK.
//no-siteapp
// 禁止网站转码
cc += (cc ? ',' : '') + 'no-transform';
res.setHeader('Cache-Control', cc);
/**
* ETag removal
*/
// Since we're sending far-future expires, we don't need ETags for
// static content.
// developer.yahoo.com/performance/rules.html#etags
// 干掉Tag,避免浪费服务资源,良好的缓存机制既能做到实时正确更新又能尽可能利用缓存优势
res.removeHeader('ETag');
/**
* Stop screen flicker in IE on CSS rollovers
*/
// The following directives stop screen flicker in IE on CSS rollovers - in
// combination with the "ExpiresByType" rules for images (see above).
// TODO
/**
* Set Keep-Alive Header
*/
// Keep-Alive allows the server to send multiple requests through one
// TCP-expression. Be aware of possible disadvantages of this setting. Turn on
// if you serve a lot of static content.
// 保持长联,减少多回三次握手带来的性能损失,但要有可靠的超时机制
res.setHeader('Connection', 'keep-alive');
/**
* Cookie setting from iframes
*/
// Allow cookies to be set from iframes (for IE only)
// If needed, specify a path or regex in the Location directive.
// TODO
/**
* A little more security
*/
// do we want to advertise what kind of server we're running?
if ('express' == options.server) {
res.removeHeader('X-Powered-By');
}
});
next(null, req, res);
};
};