java进阶之IO流(字节流、字符流)
文章目录
- 一、IO流
- 二、字节流
-
- 1.一个一个字节读取文本
- 2.按字节数组读取复制文本
- 3.字符缓冲流一个一个读取文本
- 4.字符缓冲流按数组读取文本
- 三、字符流
-
- 1.一个一个字符读取复制文本
- 2.用字符数组读取
- 3.用缓冲流一个一个字符读取
- 4.用缓冲流按数组读取
- 5.用缓冲流按行读取
- 四、字节流字符流总结
-
- 案例:先注册,再登录系统玩猜数字游戏
- 五、对象流(序列化流)
- 六、其它流
一、IO流
(1)IO用于在设备间进行数据传输的操作 (2)分类: A:流向 输入流 读取数据 输出流 写出数据 B:数据类型 字节流 字节输入流 字节输出流 字符流 字符输入流 字符输出流 注意: a:如果我们没有明确说明按照什么分,默认按照数据类型分。 b:除非文件用windows自带的记事本打开我们能够读懂,才采用字符流,否则建议使用字节流。
二、字节流
(1)FileOutputStream写出数据
A:操作步骤
a:创建字节输出流对象
b:调用write()方法
c:释放资源
B:代码体现:
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt");
fos.write("hello".getBytes());
fos.close();
C:要注意的问题?
a:创建字节输出流对象做了几件事情?
b:为什么要close()?
c:如何实现数据的换行?
d:如何实现数据的追加写入?
(2)FileInputStream读取数据
A:操作步骤
a:创建字节输入流对象
b:调用read()方法
c:释放资源
B:代码体现:
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("fos.txt");
//方式1
int by = 0;
while((by=fis.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)by);
}
//方式2
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len=fis.read(bys))!=-1) {
System.out.print(new String(bys,0,len));
}
fis.close();
1.一个一个字节读取文本
public class Byteiotest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt");
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt");
int a=0;
while ((a=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write((char)a);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
2.按字节数组读取复制文本
public class ByteiolineTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt");
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt");
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
3.字符缓冲流一个一个读取文本
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedInputStream bfs=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt"));
int a;
while((a=bfs.read())!=-1){
bos.write((char)a);
}
bfs.close();
bos.close();
}
}
4.字符缓冲流按数组读取文本
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedInputStream bfs=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt"));
int len;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
while((len=bfs.read(bytes))!=-1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
bfs.close();
bos.close();
}
}
三、字符流
(1)字节流操作中文数据不是特别的方便,所以就出现了转换流。 转换流的作用就是把字节流转换字符流来使用。 (2)转换流其实是一个字符流 字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表 (3)编码表 A:就是由字符和对应的数值组成的一张表 B:常见的编码表 ASCII ISO-8859-1 GB2312 GBK GB18030 UTF-8 C:字符串中的编码问题 编码 String -- byte[] 解码 byte[] -- String (4)IO流中的编码问题 A:OutputStreamWriter OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream os):默认编码,GBK OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream os,String charsetName):指定编码。 B:InputStreamReader InputStreamReader(InputStream is):默认编码,GBK InputStreamReader(InputStream is,String charsetName):指定编码 C:编码问题其实很简单 编码只要一致即可 (5)字符流 Reader |--InputStreamReader |--FileReader |--BufferedReader Writer |--OutputStreamWriter |--FileWriter |--BufferedWriter (6)复制文本文件(5种方式)
1.一个一个字符读取复制文本
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
FileReader fr=new FileReader("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt");
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt");
int a;
while ((a=fr.read())!=-1){
fw.write(a);
}
fr.close();
fw.close();
}
}
2.用字符数组读取
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
FileReader fd=new FileReader("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt");
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt");
int len;
char[] chars=new char[1024];
while ((len=fd.read(chars))!=-1){
fw.write(chars,0,len);
}
fd.close();
fw.close();
}
}
3.用缓冲流一个一个字符读取
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt"));
int a;
while ((a=br.read())!=-1){
bw.write(a);
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
4.用缓冲流按数组读取
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt"));
char[] chars=new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len=br.read(chars))!=-1){
bw.write(chars,0,len);
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
5.用缓冲流按行读取
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text1.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\text2.txt"));
String string;
while((string=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(string);
bw.newLine();
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
四、字节流字符流总结
IO流 |--字节流 |--字节输入流 InputStream int read():一次读取一个字节 int read(byte[] bys):一次读取一个字节数组 |--FileInputStream |--BufferedInputStream |--字节输出流 OutputStream void write(int by):一次写一个字节 void write(byte[] bys,int index,int len):一次写一个字节数组的一部分 |--FileOutputStream |--BufferedOutputStream |--字符流 |--字符输入流 Reader int read():一次读取一个字符 int read(char[] chs):一次读取一个字符数组 |--InputStreamReader |--FileReader |--BufferedReader String readLine():一次读取一个字符串 |--字符输出流 Writer void write(int ch):一次写一个字符 void write(char[] chs,int index,int len):一次写一个字符数组的一部分 |--OutputStreamWriter |--FileWriter |--BufferedWriter void newLine():写一个换行符 void write(String line):一次写一个字符串
案例:先注册,再登录系统玩猜数字游戏
User
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public User(){
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
UserDao
public interface UserDao {
public abstract boolean isLogin(String username,String password);
public abstract void regist(User user);
}
UserDaoImpl
import java.io.*;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
private static File file=new File("user.txt");
static {
try{
file.createNewFile();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("创建文件失败");
}
}
@Override
public boolean isLogin(String username, String password) {
boolean flag=false;
BufferedReader br=null;
try{
br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line=null;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
String[] datas=line.split("=");
if(datas[0].equals(username)&&datas[1].equals(password)){
flag=true;
break;
}
}
}catch (FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println("用户登录找不到信息所在的文件");
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("用户登录失败");
}finally {
if(br!=null){
try{
br.close();
}
catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("用户登录释放资源失败");
}
}
}
return flag;
}
@Override
public void regist(User user) {
BufferedWriter bw=null;
try{
bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file,true));
bw.write(user.getUsername()+"="+user.getPassword());
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("用户注册失败");
}finally {
if(bw!=null){
try{
bw.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("用户注册释放资源失败");
}
}
}
}
}
GuessNumber
public class GuessNumber {
private GuessNumber(){
}
public static void start(){
int number=(int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
int count=0;
while (true){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入数据(1-100):");
int guessNumber=sc.nextInt();
count++;
if(guessNumber>number) {
System.out.println("你猜的数据" + guessNumber + "大了");
}else if(guessNumber<number){
System.out.println("你猜的数据"+guessNumber+"小了");
}else {
System.out.println("恭喜你,"+count+"次就猜中了");
break;
}
}
}
}
UserTest
public class UserTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true){
System.out.println("----------欢迎光临---------");
System.out.println("1.登录");
System.out.println("2.注册");
System.out.println("3.退出");
System.out.println("请输入你的选择:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String choice=sc.nextLine();
UserDao ud=new UserDaoImpl();
switch (choice){
case "1":
System.out.println("----------登录界面------------");
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username=sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password=sc.nextLine();
boolean flag=ud.isLogin(username,password);
if(flag){
System.out.println("登录成功,可以开始玩游戏了");
System.out.println("你玩吗?y/n");
while (true){
String resultString=sc.nextLine();
if(resultString.equals("y")) {
GuessNumber.start();
System.out.println("你还玩吗?y/n");
}
else {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("谢谢使用,欢迎下次再来");
System.exit(0);
}else {
System.out.println("用户名和密码有误,登录失败");
}
break;
case"2":
System.out.println("----------注册界面--------");
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String newUsername=sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String newPassword=sc.nextLine();
User user=new User();
user.setPassword(newPassword);
user.setUsername(newUsername);
ud.regist(user);
System.out.println("注册成功");
break;
case"3":
default:
System.out.println("谢谢使用,欢迎下次再来");
System.exit(0);
break;
}
}
}
}
五、对象流(序列化流)
序列化流 (1)可以把对象写入文本文件或者在网络中传输 (2)如何实现序列化呢? 让被序列化的对象所属类实现序列化接口。 该接口是一个标记接口。没有功能需要实现。 (3)注意问题: 把数据写到文件后,在去修改类会产生一个问题。 如何解决该问题呢? 在类文件中,给出一个固定的序列化id值。 而且,这样也可以解决黄色警告线问题 (4)面试题: 什么时候序列化? 可以把对象以字节形式写入文本文件或者在网络中传输 如何实现序列化? 让被序列化的对象所属类实现序列化接口。 什么是反序列化? 将文本文件或者在网络中传输的字节还原为对象。
代码演示
创建一个对象,注意需要实现序列化
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
transient String sex;
public Student(){
}
public Student(String name, int age,String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex=sex;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
读取对象流
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
Student zs=new Student("张三",23,"女");
//序列化
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\test.txt"));
oos.writeObject(zs);
//反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\IdeaProjects\\HuiHui\\data\\test.txt"));
Object o=ois.readObject();
//需向下转型,调用子类方法
Student s=(Student)o;
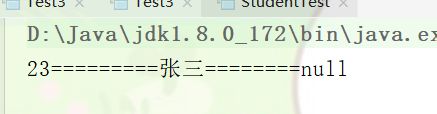
System.out.println(s.getAge()+"========="+s.getName()+"========"+s.getSex());
}
}
六、其它流
1:数据操作流(操作基本类型数据的流)
(1)可以操作基本类型的数据
(2)流对象名称
DataInputStream
DataOutputStream
2:内存操作流
(1)有些时候我们操作完毕后,未必需要产生一个文件,就可以使用内存操作流。
(2)三种
A:ByteArrayInputStream,ByteArrayOutputStream
B:CharArrayReader,CharArrayWriter
C:StringReader,StringWriter
3:打印流
(1)字节打印流,字符打印流
(2)特点:
A:只操作目的地,不操作数据源
B:可以操作任意类型的数据
C:如果启用了自动刷新,在调用println()方法的时候,能够换行并刷新
D:可以直接操作文件
问题:哪些流可以直接操作文件呢?
看API,如果其构造方法能够同时接收File和String类型的参数,一般都是可以直接操作文件的
(3)复制文本文件
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("b.txt"),true);
String line = null;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null) {
pw.println(line);
}
pw.close();
br.close();
4:标准输入输出流
(1)System类下面有这样的两个字段
in 标准输入流
out 标准输出流
(2)三种键盘录入方式
A:main方法的args接收参数
B:System.in通过BufferedReader进行包装
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
C:Scanner
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
(3)输出语句的原理和如何使用字符流输出数据
A:原理
System.out.println("helloworld");
PrintStream ps = System.out;
ps.println("helloworld");
B:把System.out用字符缓冲流包装一下使用
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
5:随机访问流
(1)可以按照文件指针的位置写数据和读数据。
(2)案例:
A:写数据
B:读数据
C:获取和改变文件指针的位置
6:合并流
(1)把多个输入流的数据写到一个输出流中。
(2)构造方法:
A:SequenceInputStream(InputStream s1, InputStream s2)
B:SequenceInputStream(Enumeration e)
java入门基础学习(一)
java入门基础学习(二)
java入门基础学习(三)
java入门基础学习(四)
java入门基础学习(五)
java入门基础学习(六)
java入门基础学习(七)
java入门基础学习(八)
java入门基础学习(九)
java入门基础学习(十)
java入门基础学习(十一)
java入门基础学习(十二)
java进阶之常见对象(一)
java进阶之常见对象(二)
java进阶之冒泡排序
java进阶之选择排序
java进阶之面向对象(封装)
java进阶之面向对象(代码块、继承)
java进阶之面向对象(多态、抽象、接口)
java进阶之匿名内部类、访问修饰符、包