一、思想
1.1 基本概念
- 加权无向图的生成树:一棵含有其所有顶点的无环连通子图。
- 最小生成树(MST):一棵权值最小(树中所有边的权值之和)的生成树。
1.2 算法原理
1.2.1 切分定理
- 切分定义:图的一种切分是将图的所有顶点分为两个非空且不重合的两个集合。横切边是一条连接两个属于不同集合的顶点的边。
- 切分定理:在一幅加权图中,给定任意的切分,它的横切边中的权重最小者必然属于图的最小生成树。
1.2.2 算法原理
切分定理是解决最小生成树问题的所有算法的基础。切分定理再结合贪心算法思想,就可以最终落地实现最小生成树。
Prim算法原理:
一开始树中只有一个顶点,向它添加v-1条边,每次总是将下一条连接 “树中的顶点” 与 “不在树中的顶点” 且权重最小的边,加入树中。如下图,当我们将顶点v添加到树中时,可能使得w到最小生成树的距离更近了(然后遍历顶点v的领接链表即可)。
核心:
使用一个索引优先队列,保存每个非树顶点w的一条边(将它与树中顶点连接起来的权重最小的边)。优先队列(小顶堆)的最小键即是权重最小的横切边的权重,而和它相关联的顶点V就是下一个将被添加到树中的顶点。
二、实现
2.1 无向边
1 package study.algorithm.graph; 2 3 import study.algorithm.base.StdOut; 4 5 /*** 6 * @Description 无向边 7 * @author denny.zhang 8 * @date 2020/5/25 10:34 上午 9 */ 10 public class Edge implements Comparable{ 11 12 /** 13 * 一个顶点 14 */ 15 private final int v; 16 /** 17 * 另一个顶点 18 */ 19 private final int w; 20 /** 21 * 权重 22 */ 23 private final double weight; 24 25 /** 26 * Initializes an edge between vertices { @code v} and { @code w} of 27 * the given { @code weight}. 28 * 29 * @param v one vertex 30 * @param w the other vertex 31 * @param weight the weight of this edge 32 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if either { @code v} or { @code w} 33 * is a negative integer 34 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if { @code weight} is { @code NaN} 35 */ 36 public Edge(int v, int w, double weight) { 37 if (v < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a nonnegative integer"); 38 if (w < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a nonnegative integer"); 39 if (Double.isNaN(weight)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Weight is NaN"); 40 this.v = v; 41 this.w = w; 42 this.weight = weight; 43 } 44 45 /** 46 * Returns the weight of this edge. 47 * 48 * @return the weight of this edge 49 */ 50 public double weight() { 51 return weight; 52 } 53 54 /** 55 * 返回边的任意一个顶点 56 * 57 * @return either endpoint of this edge 58 */ 59 public int either() { 60 return v; 61 } 62 63 /** 64 * 返回边的另一个顶点 65 * 66 * @param vertex one endpoint of this edge 67 * @return the other endpoint of this edge 68 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the vertex is not one of the 69 * endpoints of this edge 70 */ 71 public int other(int vertex) { 72 if (vertex == v) return w; 73 else if (vertex == w) return v; 74 else throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal endpoint"); 75 } 76 77 /** 78 * Compares two edges by weight. 79 * Note that { @code compareTo()} is not consistent with { @code equals()}, 80 * which uses the reference equality implementation inherited from { @code Object}. 81 * 82 * @param that the other edge 83 * @return a negative integer, zero, or positive integer depending on whether 84 * the weight of this is less than, equal to, or greater than the 85 * argument edge 86 */ 87 @Override 88 public int compareTo(Edge that) { 89 return Double.compare(this.weight, that.weight); 90 } 91 92 /** 93 * Returns a string representation of this edge. 94 * 95 * @return a string representation of this edge 96 */ 97 public String toString() { 98 return String.format("%d-%d %.5f", v, w, weight); 99 } 100 101 /** 102 * Unit tests the { @code Edge} data type. 103 * 104 * @param args the command-line arguments 105 */ 106 public static void main(String[] args) { 107 Edge e = new Edge(12, 34, 5.67); 108 StdOut.println(e); 109 StdOut.println("任意一个顶点="+e.either()); 110 StdOut.println("另一个顶点="+e.other(12)); 111 } 112 }
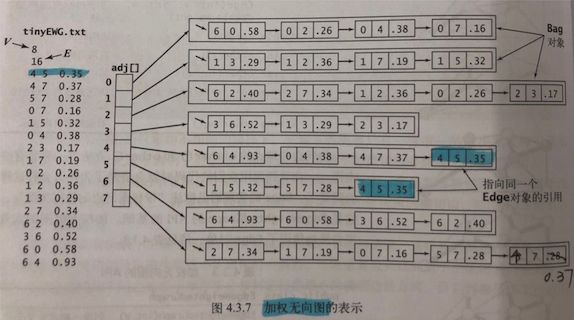
如上图,初始化时构造了一个邻接表。Bag
2.2.边加权无向图
1 package study.algorithm.graph;
2
3 import study.algorithm.base.*;
4
5 import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
6
7 /***
8 * @Description 边权重无向图
9 * @author denny.zhang
10 * @date 2020/5/25 10:50 上午
11 */
12 public class EdgeWeightedGraph {
13 private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator");
14
15 /**
16 * 顶点数
17 */
18 private final int V;
19 /**
20 * 边数
21 */
22 private int E;
23 /**
24 * 顶点邻接表,每个元素Bag代表:由某个顶点关联的边数组,按顶点顺序排列
25 */
26 private Bag[] adj;
27
28 /**
29 * Initializes an empty edge-weighted graph with {
@code V} vertices and 0 edges.
30 *
31 * @param V the number of vertices
32 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {
@code V < 0}
33 */
34 public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V) {
35 if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices must be nonnegative");
36 this.V = V;
37 this.E = 0;
38 adj = (Bag[]) new Bag[V];
39 for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
40 adj[v] = new Bag();
41 }
42 }
43
44 /**
45 * Initializes a random edge-weighted graph with {
@code V} vertices and E edges.
46 *
47 * @param V the number of vertices
48 * @param E the number of edges
49 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {
@code V < 0}
50 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {
@code E < 0}
51 */
52 public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V, int E) {
53 this(V);
54 if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
55 for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
56 int v = StdRandom.uniform(V);
57 int w = StdRandom.uniform(V);
58 double weight = Math.round(100 * StdRandom.uniform()) / 100.0;
59 Edge e = new Edge(v, w, weight);
60 addEdge(e);
61 }
62 }
63
64 /**
65 * Initializes an edge-weighted graph from an input stream.
66 * The format is the number of vertices V,
67 * followed by the number of edges E,
68 * followed by E pairs of vertices and edge weights,
69 * with each entry separated by whitespace.
70 *
71 * @param in the input stream
72 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {
@code in} is {
@code null}
73 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the endpoints of any edge are not in prescribed range
74 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the number of vertices or edges is negative
75 */
76 public EdgeWeightedGraph(In in) {
77 if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null");
78
79 try {
80 // 顶点数
81 V = in.readInt();
82 // 邻接表
83 adj = (Bag[]) new Bag[V];
84 // 初始化邻接表,一个顶点对应一条链表
85 for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
86 adj[v] = new Bag();
87 }
88 // 边数
89 int E = in.readInt();
90 if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
91 // 遍历每一条边
92 for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
93 // 一个顶点
94 int v = in.readInt();
95 // 另一个顶点
96 int w = in.readInt();
97 validateVertex(v);
98 validateVertex(w);
99 // 权重
100 double weight = in.readDouble();
101 // 构造边
102 Edge e = new Edge(v, w, weight);
103 // 添加边
104 addEdge(e);
105 }
106 }
107 catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
108 throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in EdgeWeightedGraph constructor", e);
109 }
110
111 }
112
113 /**
114 * Initializes a new edge-weighted graph that is a deep copy of {
@code G}.
115 *
116 * @param G the edge-weighted graph to copy
117 */
118 public EdgeWeightedGraph(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
119 this(G.V());
120 this.E = G.E();
121 for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
122 // reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original
123 Stack reverse = new Stack();
124 for (Edge e : G.adj[v]) {
125 reverse.push(e);
126 }
127 for (Edge e : reverse) {
128 adj[v].add(e);
129 }
130 }
131 }
132
133
134 /**
135 * Returns the number of vertices in this edge-weighted graph.
136 *
137 * @return the number of vertices in this edge-weighted graph
138 */
139 public int V() {
140 return V;
141 }
142
143 /**
144 * Returns the number of edges in this edge-weighted graph.
145 *
146 * @return the number of edges in this edge-weighted graph
147 */
148 public int E() {
149 return E;
150 }
151
152 // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
153 private void validateVertex(int v) {
154 if (v < 0 || v >= V)
155 throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
156 }
157
158 /**
159 * Adds the undirected edge {
@code e} to this edge-weighted graph.
160 *
161 * @param e the edge
162 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless both endpoints are between {
@code 0} and {
@code V-1}
163 */
164 public void addEdge(Edge e) {
165 // 一个顶点
166 int v = e.either();
167 // 另一个顶点
168 int w = e.other(v);
169 validateVertex(v);
170 validateVertex(w);
171 // 追加进顶点v的邻接链表
172 adj[v].add(e);
173 // 追加进顶点w的领接链表
174 adj[w].add(e);
175 // 边数++
176 E++;
177 }
178
179 /**
180 * 顶点V关联的全部边
181 *
182 * @param v the vertex
183 * @return the edges incident on vertex {
@code v} as an Iterable
184 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {
@code 0 <= v < V}
185 */
186 public Iterable adj(int v) {
187 validateVertex(v);
188 return adj[v];
189 }
190
191 /**
192 * Returns the degree of vertex {
@code v}.
193 *
194 * @param v the vertex
195 * @return the degree of vertex {
@code v}
196 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless {
@code 0 <= v < V}
197 */
198 public int degree(int v) {
199 validateVertex(v);
200 return adj[v].size();
201 }
202
203 /**
204 * Returns all edges in this edge-weighted graph.
205 * To iterate over the edges in this edge-weighted graph, use foreach notation:
206 * {
@code for (Edge e : G.edges())}.
207 *
208 * @return all edges in this edge-weighted graph, as an iterable
209 */
210 public Iterable edges() {
211 Bag list = new Bag();
212 for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
213 int selfLoops = 0;
214 for (Edge e : adj(v)) {
215 if (e.other(v) > v) {
216 list.add(e);
217 }
218 // add only one copy of each self loop (self loops will be consecutive)
219 else if (e.other(v) == v) {
220 if (selfLoops % 2 == 0) list.add(e);
221 selfLoops++;
222 }
223 }
224 }
225 return list;
226 }
227
228 /**
229 * Returns a string representation of the edge-weighted graph.
230 * This method takes time proportional to E + V.
231 *
232 * @return the number of vertices V, followed by the number of edges E,
233 * followed by the V adjacency lists of edges
234 */
235 public String toString() {
236 StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
237 s.append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE);
238 for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
239 s.append(v + ": ");
240 for (Edge e : adj[v]) {
241 s.append(e + " ");
242 }
243 s.append(NEWLINE);
244 }
245 return s.toString();
246 }
247
248 /**
249 * Unit tests the {
@code EdgeWeightedGraph} data type.
250 *
251 * @param args the command-line arguments
252 */
253 public static void main(String[] args) {
254 In in = new In(args[0]);
255 EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
256 StdOut.println(G);
257 }
258
259 }
2.3 索引小值优先队列
1 package study.algorithm.base; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 5 6 /** 7 * 索引(顶点)最小优先级队列 8 * 9 * @param10 */ 11 public class IndexMinPQ > implements Iterable { 12 /** 13 * 元素数量上限 14 */ 15 private int maxN; 16 /** 17 * 元素数量 18 */ 19 private int n; 20 /** 21 * 索引二叉堆(数组中每个元素都是顶点,顶点v,对应keys[v]):数组从pq[0]代表原点其它顶点从pq[1]开始插入 22 */ 23 private int[] pq; 24 /** 25 * 标记索引为i的元素在二叉堆中的位置。pq的反转数组(qp[index]=i):qp[pq[i]] = pq[qp[i]] = i 26 */ 27 private int[] qp; 28 29 /** 30 * 元素有序数组(按照pq的索引赋值) 31 */ 32 public Key[] keys; 33 34 /** 35 * 初始化一个空索引优先队列,索引范围:0 ~ maxN-1 36 * 37 * @param maxN the keys on this priority queue are index from { @code 0} 38 * { @code maxN - 1} 39 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if { @code maxN < 0} 40 */ 41 public IndexMinPQ(int maxN) { 42 if (maxN < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 43 this.maxN = maxN; 44 // 初始有0个元素 45 n = 0; 46 // 初始化键数组长度为maxN + 1 47 keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[maxN + 1]; 48 // 初始化"键值对"数组长度为maxN + 1 49 pq = new int[maxN + 1]; 50 // 初始化"值键对"数组长度为maxN + 1 51 qp = new int[maxN + 1]; 52 // 遍历给"值键对"数组赋值-1,后续只要!=-1,即包含i 53 for (int i = 0; i <= maxN; i++) 54 qp[i] = -1; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Returns true if this priority queue is empty. 59 * 60 * @return { @code true} if this priority queue is empty; 61 * { @code false} otherwise 62 */ 63 public boolean isEmpty() { 64 return n == 0; 65 } 66 67 /** 68 * Is { @code i} an index on this priority queue? 69 * 70 * @param i an index 71 * @return { @code true} if { @code i} is an index on this priority queue; 72 * { @code false} otherwise 73 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless { @code 0 <= i < maxN} 74 */ 75 public boolean contains(int i) { 76 validateIndex(i); 77 return qp[i] != -1; 78 } 79 80 /** 81 * Returns the number of keys on this priority queue. 82 * 83 * @return the number of keys on this priority queue 84 */ 85 public int size() { 86 return n; 87 } 88 89 /** 90 * 插入一个元素,将元素key关联索引i 91 * 92 * @param i an index 93 * @param key the key to associate with index { @code i} 94 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless { @code 0 <= i < maxN} 95 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if there already is an item associated 96 * with index { @code i} 97 */ 98 public void insert(int i, Key key) { 99 validateIndex(i); 100 if (contains(i)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is already in the priority queue"); 101 // 元素个数+1 102 n++; 103 // 索引为i的二叉堆位置为n 104 qp[i] = n; 105 // 二叉堆底部插入新元素,值=i 106 pq[n] = i; 107 // 索引i对应的元素赋值 108 keys[i] = key; 109 // 二叉堆中,上浮最后一个元素(小值上浮) 110 swim(n); 111 } 112 113 /** 114 * 返回最小元素的索引 115 * 116 * @return an index associated with a minimum key 117 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty 118 */ 119 public int minIndex() { 120 if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 121 return pq[1]; 122 } 123 124 /** 125 * 返回最小元素(key) 126 * 127 * @return a minimum key 128 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty 129 */ 130 public Key minKey() { 131 if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 132 return keys[pq[1]]; 133 } 134 135 /** 136 * 删除最小值key,并返回最小值(优先队列索引) 137 * 138 * @return an index associated with a minimum key 139 * @throws NoSuchElementException if this priority queue is empty 140 */ 141 public int delMin() { 142 if (n == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow"); 143 // pq[1]即为索引最小值 144 int min = pq[1]; 145 // 交换第一个元素和最后一个元素 146 exch(1, n--); 147 // 把新换来的第一个元素下沉 148 sink(1); 149 // 校验下沉后,最后一个元素是最小值 150 assert min == pq[n+1]; 151 // 恢复初始值,-1即代表该元素已删除 152 qp[min] = -1; // delete 153 // 方便垃圾回收 154 keys[min] = null; 155 // 最后一个元素(索引)赋值-1 156 pq[n+1] = -1; // not needed 157 return min; 158 } 159 160 /** 161 * Returns the key associated with index { @code i}. 162 * 163 * @param i the index of the key to return 164 * @return the key associated with index { @code i} 165 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless { @code 0 <= i < maxN} 166 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index { @code i} 167 */ 168 public Key keyOf(int i) { 169 validateIndex(i); 170 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 171 else return keys[i]; 172 } 173 174 /** 175 * Change the key associated with index { @code i} to the specified value. 176 * 177 * @param i the index of the key to change 178 * @param key change the key associated with index { @code i} to this key 179 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless { @code 0 <= i < maxN} 180 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index { @code i} 181 */ 182 public void changeKey(int i, Key key) { 183 validateIndex(i); 184 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 185 keys[i] = key; 186 swim(qp[i]); 187 sink(qp[i]); 188 } 189 190 /** 191 * Change the key associated with index { @code i} to the specified value. 192 * 193 * @param i the index of the key to change 194 * @param key change the key associated with index { @code i} to this key 195 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless { @code 0 <= i < maxN} 196 * @deprecated Replaced by { @code changeKey(int, Key)}. 197 */ 198 @Deprecated 199 public void change(int i, Key key) { 200 changeKey(i, key); 201 } 202 203 /** 204 * 减小索引i对应的值为key 205 * 更新: 206 * 1.元素数组keys[] 207 * 2.小顶二叉堆pq[] 208 * 209 * @param i the index of the key to decrease 210 * @param key decrease the key associated with index { @code i} to this key 211 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless { @code 0 <= i < maxN} 212 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if { @code key >= keyOf(i)} 213 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index { @code i} 214 */ 215 public void decreaseKey(int i, Key key) { 216 validateIndex(i); 217 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 218 // key 值一样,报错 219 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) 220 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with a key equal to the key in the priority queue"); 221 // key比当前值大,报错 222 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) < 0) 223 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with a key strictly greater than the key in the priority queue"); 224 // key比当前值小,把key赋值进去 225 keys[i] = key; 226 // 小值上浮(qp[i]=索引i在二叉堆pq[]中的位置) 227 swim(qp[i]); 228 } 229 230 /** 231 * Increase the key associated with index { @code i} to the specified value. 232 * 233 * @param i the index of the key to increase 234 * @param key increase the key associated with index { @code i} to this key 235 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless { @code 0 <= i < maxN} 236 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if { @code key <= keyOf(i)} 237 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index { @code i} 238 */ 239 public void increaseKey(int i, Key key) { 240 validateIndex(i); 241 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 242 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) 243 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling increaseKey() with a key equal to the key in the priority queue"); 244 if (keys[i].compareTo(key) > 0) 245 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling increaseKey() with a key strictly less than the key in the priority queue"); 246 keys[i] = key; 247 sink(qp[i]); 248 } 249 250 /** 251 * Remove the key associated with index { @code i}. 252 * 253 * @param i the index of the key to remove 254 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless { @code 0 <= i < maxN} 255 * @throws NoSuchElementException no key is associated with index { @code i} 256 */ 257 public void delete(int i) { 258 validateIndex(i); 259 if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue"); 260 int index = qp[i]; 261 exch(index, n--); 262 swim(index); 263 sink(index); 264 keys[i] = null; 265 qp[i] = -1; 266 } 267 268 // throw an IllegalArgumentException if i is an invalid index 269 private void validateIndex(int i) { 270 if (i < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is negative: " + i); 271 if (i >= maxN) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index >= capacity: " + i); 272 } 273 274 /*************************************************************************** 275 * General helper functions. 276 ***************************************************************************/ 277 private boolean greater(int i, int j) { 278 return keys[pq[i]].compareTo(keys[pq[j]]) > 0; 279 } 280 281 private void exch(int i, int j) { 282 int swap = pq[i]; 283 pq[i] = pq[j]; 284 pq[j] = swap; 285 qp[pq[i]] = i; 286 qp[pq[j]] = j; 287 } 288 289 290 /*************************************************************************** 291 * Heap helper functions. 上浮 292 ***************************************************************************/ 293 private void swim(int k) { 294 // 如果父节点值比当前节点值大,交换,父节点作为当前节点,轮询。即小值上浮。 295 while (k > 1 && greater(k/2, k)) { 296 exch(k, k/2); 297 k = k/2; 298 } 299 } 300 //下沉 301 private void sink(int k) { 302 while (2*k <= n) { 303 int j = 2*k; 304 if (j < n && greater(j, j+1)) j++; 305 if (!greater(k, j)) break; 306 exch(k, j); 307 k = j; 308 } 309 } 310 311 312 /*************************************************************************** 313 * Iterators. 314 ***************************************************************************/ 315 316 /** 317 * Returns an iterator that iterates over the keys on the 318 * priority queue in ascending order. 319 * The iterator doesn't implement { @code remove()} since it's optional. 320 * 321 * @return an iterator that iterates over the keys in ascending order 322 */ 323 @Override 324 public Iterator iterator() { return new HeapIterator(); } 325 326 private class HeapIterator implements Iterator { 327 // create a new pq 328 private IndexMinPQ copy; 329 330 // add all elements to copy of heap 331 // takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move 332 public HeapIterator() { 333 copy = new IndexMinPQ (pq.length - 1); 334 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 335 copy.insert(pq[i], keys[pq[i]]); 336 } 337 338 @Override 339 public boolean hasNext() { return !copy.isEmpty(); } 340 @Override 341 public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } 342 343 @Override 344 public Integer next() { 345 if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); 346 return copy.delMin(); 347 } 348 } 349 350 351 /** 352 * Unit tests the { @code IndexMinPQ} data type. 353 * 354 * @param args the command-line arguments 355 */ 356 public static void main(String[] args) { 357 // insert a bunch of strings 358 String[] strings = { "it", "was", "the", "best", "of", "times", "it", "was", "the", "worst" }; 359 360 IndexMinPQ pq = new IndexMinPQ (strings.length); 361 for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { 362 pq.insert(i, strings[i]); 363 } 364 365 // delete and print each key 366 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 367 int i = pq.delMin(); 368 StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); 369 } 370 StdOut.println(); 371 372 // reinsert the same strings 373 for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) { 374 pq.insert(i, strings[i]); 375 } 376 377 // print each key using the iterator 378 for (int i : pq) { 379 StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]); 380 } 381 while (!pq.isEmpty()) { 382 pq.delMin(); 383 } 384 385 } 386 }
2.4 Prim算法(基于二叉堆)
1 package study.algorithm.graph;
2
3 import study.algorithm.base.*;
4
5 import java.util.Arrays;
6
7 /***
8 * @Description 使用Prim算法计算一棵最小生成树 27 *
28 * @author denny.zhang
29 * @date 2020/5/26 9:50 上午
30 */
31 public class PrimMST {
32 private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12;
33
34 /**
35 * 顶点索引,树顶点到非树顶点的最短边(距离树最近的边)
36 */
37 private Edge[] edgeTo;
38 /**
39 * 顶点索引,最短边的权重
40 */
41 private double[] distTo;
42 /**
43 * 顶点索引,标记顶点是否在最小生成树中
44 */
45 private boolean[] marked;
46 /**
47 * 有效的横切边(索引最小优先队列,索引为顶点v,值pq[v]=edgeTo[v].weight()=distTo[v])
48 */
49 private IndexMinPQ pq;
50
51 /**
52 * 计算一个边加权图的最小生成树
53 * @param G the edge-weighted graph
54 */
55 public PrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
56 // 初始化3个顶点索引数组
57 edgeTo = new Edge[G.V()];
58 distTo = new double[G.V()];
59 marked = new boolean[G.V()];
60 // 初始化:顶点索引最小优先队列
61 pq = new IndexMinPQ(G.V());
62 for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
63 // 初始化为无穷大
64 distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
65 }
66 // 遍历顶点数
67 for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
68 {
69 // 如果顶点0开始能全进树,那就一次搞定
70 StdOut.println("v="+ v+",marked[v]="+marked[v]);
71 // 如果没进树
72 if (!marked[v]) {
73 StdOut.println("v="+v+",执行prim");
74 // 最小生成树
75 prim(G, v);
76 }
77 }
78
79 // 校验,可省略
80 assert check(G);
81 }
82
83
84 /**
85 * 从顶点s开始生成图G
86 * @param G
87 * @param s
88 */
89 private void prim(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int s) {
90 // 顶点s的权重=0
91 distTo[s] = 0.0;
92 // 顶点s进队列,key为索引,value为边权重
93 pq.insert(s, distTo[s]);
94 StdOut.println("顶点s进队列: s="+ s+",distTo[s]="+distTo[s]);
95 StdOut.println("pq="+ Arrays.toString(pq.keys));
96
97 // 循环
98 while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
99 // 取出最小权重边的顶点(最近的顶点)
100 int v = pq.delMin();
101 // 添加到树中
102 scan(G, v);
103 }
104 }
105
106 /**
107 * 将顶点V添加到树中,更新数据
108 * @param G
109 * @param v
110 */
111 private void scan(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) {
112 StdOut.println("v="+ v+",进树");
113 // 标记 进树
114 marked[v] = true;
115 // 遍历顶点v的邻接边
116 for (Edge e : G.adj(v)) {
117 StdOut.println("遍历顶点v的邻接边:v="+ v+",e="+e.toString());
118 // 另一个顶点
119 int w = e.other(v);
120 StdOut.println("w=" + w);
121 // 如果w已进树,跳过(至少有一个点不在树中,计算才有意义)
122 if (marked[w]) {
123 StdOut.println("已进树,跳过w=" + w);
124 continue;
125 }
126 // 如果边e的权重 < 当前到顶点w的权重
127 if (e.weight() < distTo[w]) {
128 StdOut.println("e.weight()="+e.weight()+" ,distTo[w]=" + distTo[w]);
129 // 更新最小权重
130 distTo[w] = e.weight();
131 // 连接w和树的最佳边变为e
132 edgeTo[w] = e;
133 // 顶点w在pq队列中
134 if (pq.contains(w)) {
135 StdOut.println("顶点w在pq队列中:w="+w);
136 // 减小w索引对应的权重值,小值上浮
137 pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo[w]);
138 // 顶点w不在队列中
139 } else {
140 StdOut.println("顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列前:w="+w+",pq="+ Arrays.toString(pq.keys));
141 // 插入队列
142 pq.insert(w, distTo[w]);
143 StdOut.println("顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列后:w="+w+",pq="+Arrays.toString(pq.keys));
144 }
145 }
146 }
147 }
148
149 /**
150 * Returns the edges in a minimum spanning tree (or forest).
151 * @return the edges in a minimum spanning tree (or forest) as
152 * an iterable of edges
153 */
154 public Iterable edges() {
155 Queue mst = new Queue();
156 for (int v = 0; v < edgeTo.length; v++) {
157 Edge e = edgeTo[v];
158 if (e != null) {
159 mst.enqueue(e);
160 }
161 }
162 return mst;
163 }
164
165 /**
166 * Returns the sum of the edge weights in a minimum spanning tree (or forest).
167 * @return the sum of the edge weights in a minimum spanning tree (or forest)
168 */
169 public double weight() {
170 double weight = 0.0;
171 for (Edge e : edges()) {
172 weight += e.weight();
173 }
174 return weight;
175 }
176
177
178 // check optimality conditions (takes time proportional to E V lg* V)
179 private boolean check(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
180
181 // check weight
182 double totalWeight = 0.0;
183 for (Edge e : edges()) {
184 totalWeight += e.weight();
185 }
186 if (Math.abs(totalWeight - weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) {
187 System.err.printf("Weight of edges does not equal weight(): %f vs. %f\n", totalWeight, weight());
188 return false;
189 }
190
191 // check that it is acyclic
192 UF uf = new UF(G.V());
193 for (Edge e : edges()) {
194 int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v);
195 if (uf.find(v) == uf.find(w)) {
196 System.err.println("Not a forest");
197 return false;
198 }
199 uf.union(v, w);
200 }
201
202 // check that it is a spanning forest
203 for (Edge e : G.edges()) {
204 int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v);
205 if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) {
206 System.err.println("Not a spanning forest");
207 return false;
208 }
209 }
210
211 // check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions)
212 for (Edge e : edges()) {
213
214 // all edges in MST except e
215 uf = new UF(G.V());
216 for (Edge f : edges()) {
217 int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x);
218 if (f != e) {
219 uf.union(x, y);
220 }
221 }
222
223 // check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut
224 for (Edge f : G.edges()) {
225 int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x);
226 if (uf.find(x) != uf.find(y)) {
227 if (f.weight() < e.weight()) {
228 System.err.println("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions");
229 return false;
230 }
231 }
232 }
233
234 }
235
236 return true;
237 }
238
239 public static void main(String[] args) {
240 // 读取图文件
241 In in = new In(args[0]);
242 // 初始化:边加权无向图
243 EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
244 // 核心算法Prim
245 PrimMST mst = new PrimMST(G);
246 // 打印全部边
247 for (Edge e : mst.edges()) {
248 StdOut.println(e);
249 }
250 // 打印总权重
251 StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", mst.weight());
252 }
253
254
255 }
运行方法:
使用导入文件的方式,后续只需要修改文件内容,即可执行,比较方便。8个顶点,16条边的边加权无向图,内容如下:
8 16 4 5 0.35 4 7 0.37 5 7 0.28 0 7 0.16 1 5 0.32 0 4 0.38 2 3 0.17 1 7 0.19 0 2 0.26 1 2 0.36 1 3 0.29 2 7 0.34 6 2 0.40 3 6 0.52 6 0 0.58 6 4 0.93
运行配置:
运行:
结合邻接链表来看结果,其实就是遍历了一遍邻接表。
v=0,marked[v]=false----从顶点0作为原点,构建最小生成树,---begin! v=0,执行prim 顶点s进队列: s=0,distTo[s]=0.0 pq=[0.0, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null] v=0,进树---》顶点0开始 另一个顶点: 6 2 4 7 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=0,e=6-0 0.58000 w=6 e.weight()=0.58 ,distTo[w]=Infinity 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列前:w=6,pq=[null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null] 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列后:w=6,pq=[null, null, null, null, null, null, 0.58, null, null] 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=0,e=0-2 0.26000 w=2 e.weight()=0.26 ,distTo[w]=Infinity 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列前:w=2,pq=[null, null, null, null, null, null, 0.58, null, null] 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列后:w=2,pq=[null, null, 0.26, null, null, null, 0.58, null, null] 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=0,e=0-4 0.38000 w=4 e.weight()=0.38 ,distTo[w]=Infinity 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列前:w=4,pq=[null, null, 0.26, null, null, null, 0.58, null, null] 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列后:w=4,pq=[null, null, 0.26, null, 0.38, null, 0.58, null, null] 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=0,e=0-7 0.16000 w=7 e.weight()=0.16 ,distTo[w]=Infinity 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列前:w=7,pq=[null, null, 0.26, null, 0.38, null, 0.58, null, null] 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列后:w=7,pq=[null, null, 0.26, null, 0.38, null, 0.58, 0.16, null] v=7,进树---》顶点7开始 另一个顶点: 2 1 0 5 4 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=7,e=2-7 0.34000 w=2 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=7,e=1-7 0.19000 w=1 e.weight()=0.19 ,distTo[w]=Infinity 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列前:w=1,pq=[null, null, 0.26, null, 0.38, null, 0.58, null, null] 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列后:w=1,pq=[null, 0.19, 0.26, null, 0.38, null, 0.58, null, null] 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=7,e=0-7 0.16000 w=0 已进树,跳过w=0 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=7,e=5-7 0.28000 w=5 e.weight()=0.28 ,distTo[w]=Infinity 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列前:w=5,pq=[null, 0.19, 0.26, null, 0.38, null, 0.58, null, null] 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列后:w=5,pq=[null, 0.19, 0.26, null, 0.38, 0.28, 0.58, null, null] 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=7,e=4-7 0.37000 w=4 e.weight()=0.37 ,distTo[w]=0.38 顶点w在pq队列中:w=4 v=1,进树---》顶点1开始 另一个顶点: 3 2 7 5 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=1,e=1-3 0.29000 w=3 e.weight()=0.29 ,distTo[w]=Infinity 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列前:w=3,pq=[null, null, 0.26, null, 0.37, 0.28, 0.58, null, null] 顶点w不在pq队列中,插入队列后:w=3,pq=[null, null, 0.26, 0.29, 0.37, 0.28, 0.58, null, null] 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=1,e=1-2 0.36000 w=2 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=1,e=1-7 0.19000 w=7 已进树,跳过w=7 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=1,e=1-5 0.32000 w=5 v=2,进树---》顶点2开始 另一个顶点: 6 7 1 0 3 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=2,e=6-2 0.40000 w=6 e.weight()=0.4 ,distTo[w]=0.58 顶点w在pq队列中:w=6 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=2,e=2-7 0.34000 w=7 已进树,跳过w=7 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=2,e=1-2 0.36000 w=1 已进树,跳过w=1 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=2,e=0-2 0.26000 w=0 已进树,跳过w=0 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=2,e=2-3 0.17000 w=3 e.weight()=0.17 ,distTo[w]=0.29 顶点w在pq队列中:w=3 v=3,进树---》顶点3开始 另一个顶点: 6 1 2 5 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=3,e=3-6 0.52000 w=6 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=3,e=1-3 0.29000 w=1 已进树,跳过w=1 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=3,e=2-3 0.17000 w=2 已进树,跳过w=2 v=5,进树---》顶点5开始 另一个顶点: 1 7 4 w=1 已进树,跳过w=1 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=5,e=5-7 0.28000 w=7 已进树,跳过w=7 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=5,e=4-5 0.35000 w=4 e.weight()=0.35 ,distTo[w]=0.37 顶点w在pq队列中:w=4 v=4,进树---》顶点4开始 另一个顶点:6 0 7 5 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=4,e=6-4 0.93000 w=6 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=4,e=0-4 0.38000 w=0 已进树,跳过w=0 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=4,e=4-7 0.37000 w=7 已进树,跳过w=7 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=4,e=4-5 0.35000 w=5 已进树,跳过w=5 v=6,进树---》顶点6开始 另一个顶点:4 0 3 2 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=6,e=6-4 0.93000 w=4 已进树,跳过w=4 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=6,e=6-0 0.58000 w=0 已进树,跳过w=0 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=6,e=3-6 0.52000 w=3 已进树,跳过w=3 遍历顶点v的邻接边:v=6,e=6-2 0.40000 w=2 已进树,跳过w=2----从顶点0作为原点,构建最小生成树,---end! v=1,marked[v]=true----从顶点1作为原点,构建最小生成树,已经入树,跳过!后续节点都已进树,都跳过。 v=2,marked[v]=true v=3,marked[v]=true v=4,marked[v]=true v=5,marked[v]=true v=6,marked[v]=true v=7,marked[v]=true 1-7 0.19000---》打印最小生成树的边 权重 0-2 0.26000 2-3 0.17000 4-5 0.35000 5-7 0.28000 6-2 0.40000 0-7 0.16000 1.810000---》打印最小生成树的总权重
三、总结
使用二叉堆(索引小值优先队列实现)优化的Prim算法,
3.1 空间复杂度
构造了几个顶点v索引的数组,所以和顶点数v成正比。
3.2 时间复杂度
主要就在优先队列的操作上
- 1.PrimMST->prim中:共v个顶点,每次取出最小值pq.delMin() 取第一个最小值元素,并把最后一个元素填充,新上来的这个元素下沉sink()大值下沉,时间复杂度=logv, 共v个顶点,也就是vlogv。
- 2.PrimMST->prim->scan 中 :遍历顶点的邻接表(邻接边链表),不管是 更新更小值 decreaseKey()、还是 插入新值 insert() ->都要执行swim()小值上浮, 时间复杂度=logv,一共E条边,所以Elogv.
所以:O(vlgv+elgv)=ElgV
3.3. 优化
1.如果使用斐波那契堆也就是Fredman-Tarjan算法,稠密图的decreaseKey操作耗时可以降到O(1),所以总耗时=O(V*logV+E*O(1))=ElgV
2.接近线性的算法Chazelle,但算法很复杂,就不再描述。
下一节,我们分析Kruskal算法。