第一步,首先写一个Spring的demo。
public class App { public void say(){ System.out.println("cn.com.hxq.App.app()"); } }
`public class AppTest { public static void main(String[] args) { @SuppressWarnings("resource") ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicaction.xml"); App app = (App)applicationContext.getBean("app"); app.say(); }
}`
`
`
第二步,断点进入ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
`public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}`
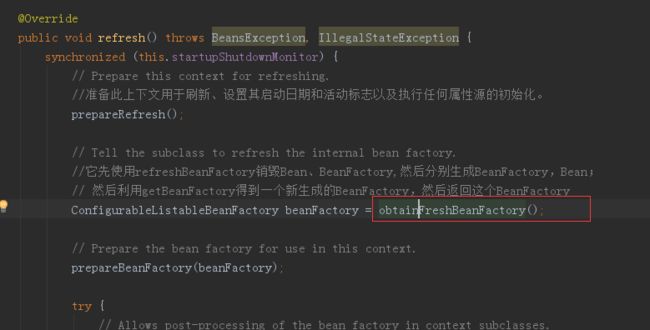
这里的setConfigLocations(configLocations)主要是加载Spring配置文件的位置。 然后看refresh()方法: 首先进入到AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法:
`@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}`
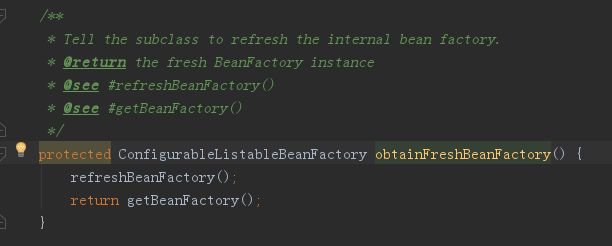
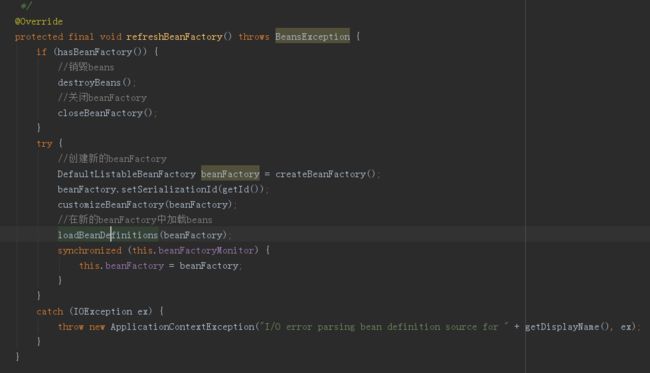
obtainFreshBeanFactory方法如下:它先使用refreshBeanFactory销毁Bean、BeanFactory,然后分别生成BeanFactory,Bean; 然后利用getBeanFactory得到一个新生成的BeanFactory,然后返回这个BeanFactory:
loadBeanDefinitions进行Beans的读取和载入,下面可以看到找到了Spring的配置文件,并且遍历对其(这里只有一个配置文件)进行了分析:
同时可以看到是,loadBeanDefinitions支持三种类型的参数,Properties说明Spring的配置支持properties文件,而Groovy可能与Groovy语言有关;
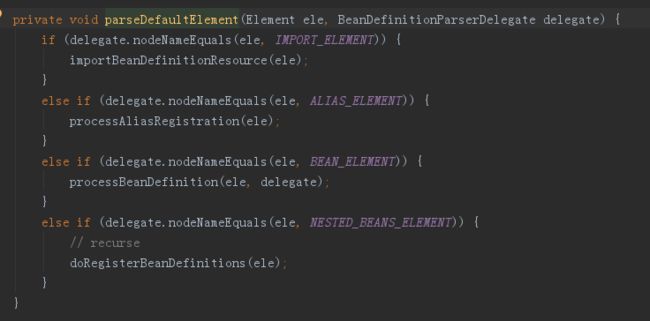
最后就是Bean的分析,可以看到分别调用的下面的方法: loadBeanDefinitions -> doLoadBeanDefinitions(加载Bean) -> registerBeanDefinitions -> doRegisterBeanDefinitions(注册Bean) -> parseBeanDefinitions(分析所有Beans) ->parseDefaultElement(分析每一个Bean元素) 我们测试时只有一个Bean,标签为
这样就对Spring中的所有节点
总的来说ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 这种形式的Spring配置文件的加载主要是下面的过程: A:加载配置文件名到系统配置 B:销毁已有的Beans和BeanFactory C:创建新的BeanFactory D:加载Beans,分析Bean中的节点,然后加载到BeanFactory,BeanFactory生效。