Android事件分发07——TouchDelegate的使用与解析
- Android事件分发07TouchDelegate的使用与解析
- 一TouchDelegate的简单使用
- 1 图示
- 2 activity_touch_delegate_demoxml
- 2 TouchDelegateDemoActivity
- 二TouchDelegate源码
- 三主要的小小分析
- 1 构造函数
- 2 MotionEventACTION_DOWN
- 3 MotionEventACTION_MOVE和MotionEventACTION_UP
- 4 MotionEventACTION_CANCEL
- 5 余下的处理
- 四流程图
- 一TouchDelegate的简单使用
Android事件分发07——TouchDelegate的使用与解析
TouchDelegate 这个类的作用就是增大我们控件的触摸区域。前面文章(Android事件分发05——View的onTouchEvent)中,我们在分析 onTouchEvent的时候,有个步骤是这样的:
判断有没有添加TouchDelegate代理,如果添加了代理,那么调用代理的onTouchEvent方法处理,如果这个方法返回true,那么就返回true,代表消费了事件,如果没有返回true,那么继续其他处理。
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
...
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
...
}一、TouchDelegate的简单使用
我们通过下面的小小例子来演示了TouchDelegate的简单使用。
1.1 图示
1.2 activity_touch_delegate_demo.xml
activity_touch_delegate_demo.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<android.support.v7.widget.AppCompatButton
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:id="@+id/test_btn"
android:text="TouchDelegate测试"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="60dp" />
RelativeLayout>
1.2 TouchDelegateDemoActivity
TouchDelegateDemoActivity
public class TouchDelegateDemoActivity extends BaseActivity {
private AppCompatButton testBtn;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_touch_delegate_demo);
testBtn = (AppCompatButton)findViewById(R.id.test_btn);
testBtn.setOnClickListener(mOnClickListener);
View parent = (View) testBtn.getParent();
parent.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int offset = 200;
Rect rect = new Rect();
testBtn.getHitRect(rect);
rect.set(rect.left-offset, rect.top-offset, rect.right+offset, rect.bottom+offset);
TouchDelegate delegate = new TouchDelegate(rect,testBtn);
((View)testBtn.getParent()).setTouchDelegate(delegate);
}
});
}
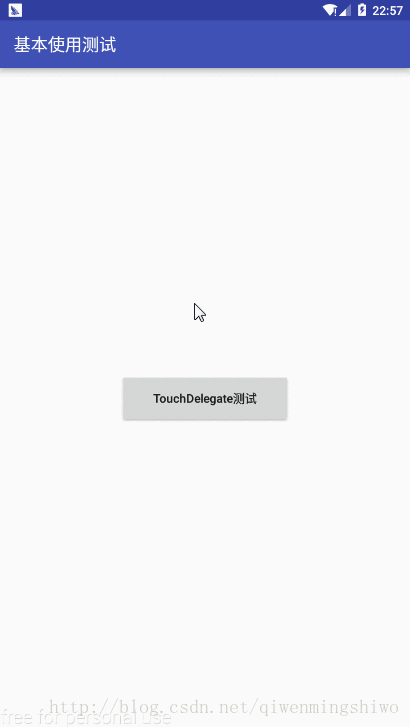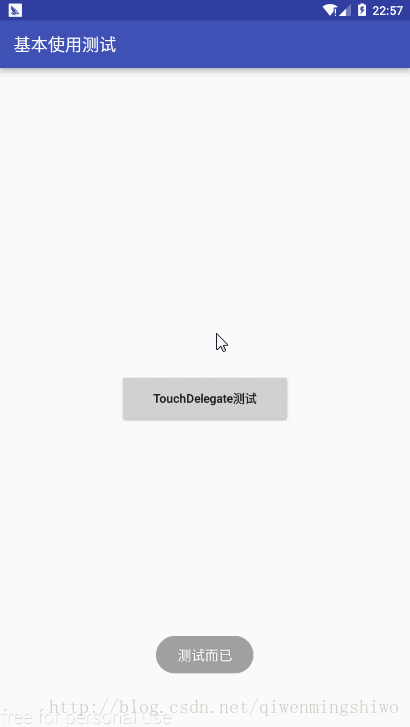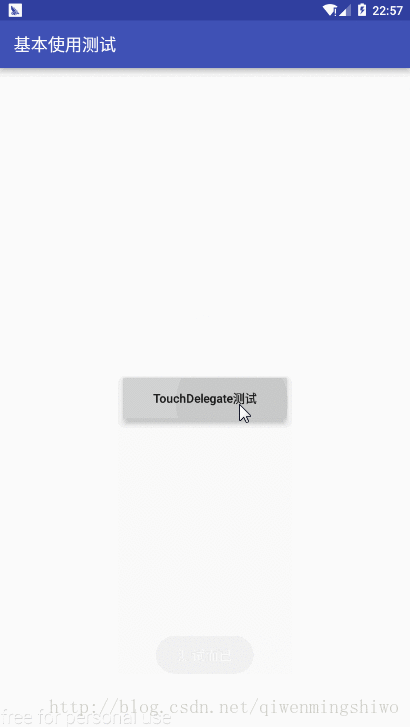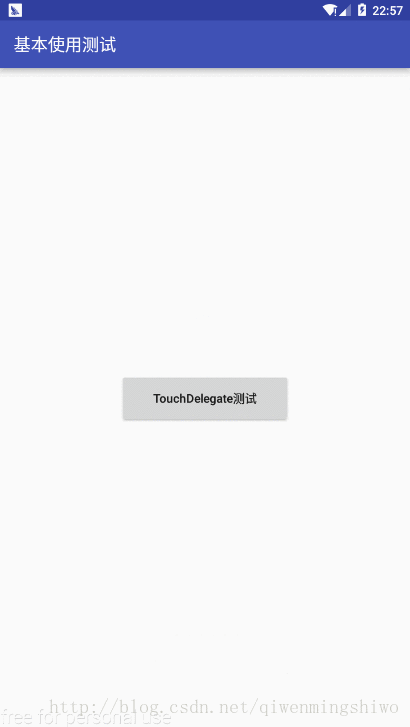
private View.OnClickListener mOnClickListener = new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(TouchDelegateDemoActivity.this, "测试而已", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
};
}二、TouchDelegate源码
public class TouchDelegate {
/**
* View that should receive forwarded touch events
* 代理的view
*/
private View mDelegateView;
/**
* Bounds in local coordinates of the containing view that should be mapped to the delegate
* view. This rect is used for initial hit testing.
* 触摸区域
*/
private Rect mBounds;
/**
* mBounds inflated to include some slop. This rect is to track whether the motion events
* should be considered to be be within the delegate view.
* 移动时候触摸区域,包含了误差
*/
private Rect mSlopBounds;
/**
* True if the delegate had been targeted on a down event (intersected mBounds).
* 标记 down 事件,是否落在了触摸区域内
*/
private boolean mDelegateTargeted;
/**
* The touchable region of the View extends above its actual extent.
*/
public static final int ABOVE = 1;
/**
* The touchable region of the View extends below its actual extent.
*/
public static final int BELOW = 2;
/**
* The touchable region of the View extends to the left of its
* actual extent.
*/
public static final int TO_LEFT = 4;
/**
* The touchable region of the View extends to the right of its
* actual extent.
*/
public static final int TO_RIGHT = 8;
private int mSlop;
/**
* Constructor
*
* @param bounds Bounds in local coordinates of the containing view that should be mapped to
* the delegate view
* @param delegateView The view that should receive motion events
*/
public TouchDelegate(Rect bounds, View delegateView) {
mBounds = bounds;
//获取相对的触摸区域的误差值(就是在这个超过原来的触摸区域,只要超出值小于等于这个值,都算在触摸区域内)
mSlop = ViewConfiguration.get(delegateView.getContext()).getScaledTouchSlop();
mSlopBounds = new Rect(bounds);
mSlopBounds.inset(-mSlop, -mSlop);
mDelegateView = delegateView;
}
/**
* Will forward touch events to the delegate view if the event is within the bounds
* specified in the constructor.
*
* @param event The touch event to forward
* @return True if the event was forwarded to the delegate, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int x = (int)event.getX();
int y = (int)event.getY();
boolean sendToDelegate = false;
boolean hit = true;
boolean handled = false;
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Rect bounds = mBounds;
//判断这个区域包含不包含这个点
if (bounds.contains(x, y)) {
mDelegateTargeted = true;
sendToDelegate = true;
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted;
if (sendToDelegate) {
Rect slopBounds = mSlopBounds;
//判断移动的点是否超出了范围
if (!slopBounds.contains(x, y)) {
hit = false;
}
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted;
mDelegateTargeted = false;
break;
}
if (sendToDelegate) {
final View delegateView = mDelegateView;
//判断移动的点是否没有超出了我们的范围
if (hit) {
// Offset event coordinates to be inside the target view
//没有超出,重新设置触摸的点,以确保我们下面调用代理的view的分发方法时,控件能够判断点是落在它上面的
event.setLocation(delegateView.getWidth() / 2, delegateView.getHeight() / 2);
} else {
// Offset event coordinates to be outside the target view (in case it does
// something like tracking pressed state)
int slop = mSlop;
//超出了,重新设置触摸的点,保证控件能判断点不是落在它上面
event.setLocation(-(slop * 2), -(slop * 2));
}
handled = delegateView.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
return handled;
}
}三、主要的小小分析
主要说明一下,TouchDelegate的原理,其实很简单,就是:事件传递到我们的代理中来的时候,我们的判断点有木有落在我们指定的区域内,如果落在区域内,那么我们把点修改为控件中间的点(这样可以确保此控件为最合适的view),如果点不在区域内,那么我们修改点击的点(这样可以确保此控件不是最合适的view),通过判断要不要分发动作,如果需要那么我们就用代理的view来分发事件。
3.1 构造函数
首先来看看 60–67行:这里面是构造函数初始化部分
public TouchDelegate(Rect bounds, View delegateView) {
mBounds = bounds;
//获取相对的触摸区域的误差值(就是在这个超过原来的触摸区域,只要超出值小于等于这个值,都算在触摸区域内)
mSlop = ViewConfiguration.get(delegateView.getContext()).getScaledTouchSlop();
mSlopBounds = new Rect(bounds);
mSlopBounds.inset(-mSlop, -mSlop);
mDelegateView = delegateView;
}mBounds这个使我们按下时候判断的区域
mSlopBounds这个是我们移动时候判断的区域
3.2 MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Rect bounds = mBounds;
//判断这个区域包含不包含这个点
if (bounds.contains(x, y)) {
//如果点在区域内,那么标记我们有代理
mDelegateTargeted = true;
//标记需要发送处理到代理
sendToDelegate = true;
}
break;按下的时候,判断当前的点是不是落在我们的区域内,如果是,那么我们标记我们的初始值。
3.3 MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE和MotionEvent.ACTION_UP
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted;
if (sendToDelegate) {//有代理
Rect slopBounds = mSlopBounds;
//判断移动的点是否超出了范围
if (!slopBounds.contains(x, y)) {
hit = false;
}
}
break;判断有没有代理,有代理,点超出了范围,那么设置hit = false;。
3.4 MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
//修改状态
sendToDelegate = mDelegateTargeted;
mDelegateTargeted = false;3.5 余下的处理
if (sendToDelegate) {
final View delegateView = mDelegateView;
//判断移动的点是否没有超出了我们的范围
if (hit) {
// Offset event coordinates to be inside the target view
//没有超出,重新设置触摸的点,以确保我们下面调用代理的view的分发方法时,控件能够判断点是落在它上面的
event.setLocation(delegateView.getWidth() / 2, delegateView.getHeight() / 2);
} else {
// Offset event coordinates to be outside the target view (in case it does
// something like tracking pressed state)
int slop = mSlop;
//超出了,重新设置触摸的点,保证控件能判断点不是落在它上面
event.setLocation(-(slop * 2), -(slop * 2));
}
handled = delegateView.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}根据前面的动作处理以后的标记判断,时候需要代理来处理消息,如果需要返回false,,如果需要我们判断,点是否已经超出了触摸范围,更改点的位置,调用代理view的事件分发。