2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> ![]()
源码地址: GitHub
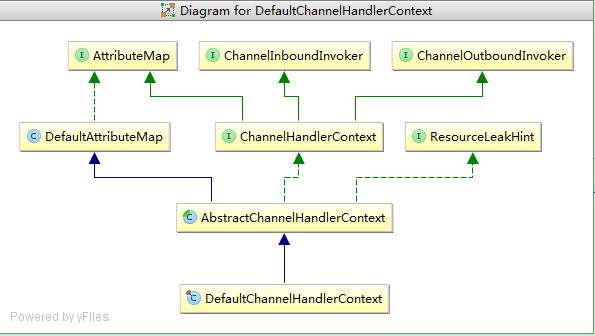
我们知道对于每个在pipeline中的ChannelHandler (入栈 或者 出栈),都对应一个ChannelHandlerContext与其绑定。细节可通 https://my.oschina.net/LucasZhu/blog/1618012
了解
我们常用ChannelHandlerContext中常用的方法有(主要分析相关数据流传递的方法):
- public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(final Object msg);
- public ChannelFuture write(Object msg);
- public ChannelPipeline pipeline().write(Object msg);
- public Channel channel().write(Object msg);
1 . public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(final Object msg);
@Override
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(final Object msg) {
invokeChannelRead(findContextInbound(), msg);
return this;
}
向后查找,如果ChannelHandlerContext 为 inbound 的类型 就返回
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (!ctx.inbound);
return ctx;
}
//调用next的 ContextRead 方法
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {
final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
//主要方法
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
} else {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
});
}
}
private void invokeChannelRead(Object msg) {
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
//获取handler对象(ChannelInboundHandler)并且执行该对象的channelRead方法......
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelRead(this, msg);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
} else {
fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
findContextInbound() 是数据流向的关键,是pipeline 后查找InboundHandler 并执行该handler的 channelRead方法。
2 . public ChannelFuture write(Object msg); 源码解析
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java
执行ChannelHandlerContext的write方法
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return write(msg, newPromise());
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(final Object msg, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (msg == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("msg");
}
try {
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, true)) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
// cancelled
return promise;
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
throw e;
}
write(msg, false, promise);
return promise;
}
private void write(Object msg, boolean flush, ChannelPromise promise) {
//从 this 在队列的位置开始,向上查找OutBound的ChannelHandlerContext对象
AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();
final Object m = pipeline.touch(msg, next);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
if (flush) {
next.invokeWriteAndFlush(m, promise);
} else {
调用获取对象的write方法
next.invokeWrite(m, promise);
}
} else {
AbstractWriteTask task;
if (flush) {
task = WriteAndFlushTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);
} else {
task = WriteTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);
}
safeExecute(executor, task, promise, m);
}
}
private void invokeWrite(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
if (invokeHandler()) {
invokeWrite0(msg, promise);
} else {
write(msg, promise);
}
}
private void invokeWrite0(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
获取OutboundHandlerContext中的handler对象,调用该对象的write方法。
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).write(this, msg, promise);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);
}
}
// 重点从对象所在队列的位置开始 ,向队列(链表)上方查找可以执行(OutboundHandler)的Handler对象
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextOutbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.prev;
} while (!ctx.outbound);
return ctx;
}
MessageToByteEncoder.java
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = null;
try {
if (acceptOutboundMessage(msg)) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I cast = (I) msg;
buf = allocateBuffer(ctx, cast, preferDirect);
try {
encode(ctx, cast, buf);
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
}
if (buf.isReadable()) {
ctx.write(buf, promise);
} else {
buf.release();
ctx.write(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER, promise);
}
buf = null;
} else {
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
} catch (EncoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new EncoderException(e);
} finally {
if (buf != null) {
buf.release();
}
}
}3.public ChannelPipeline pipeline().write(Object msg);
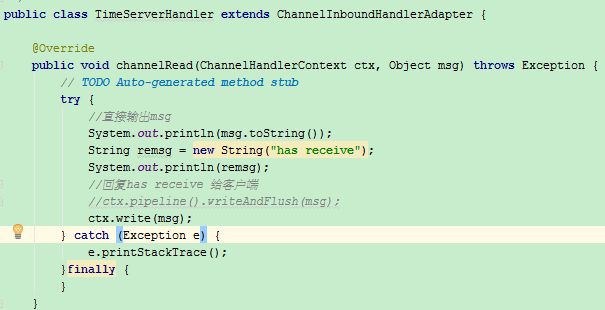
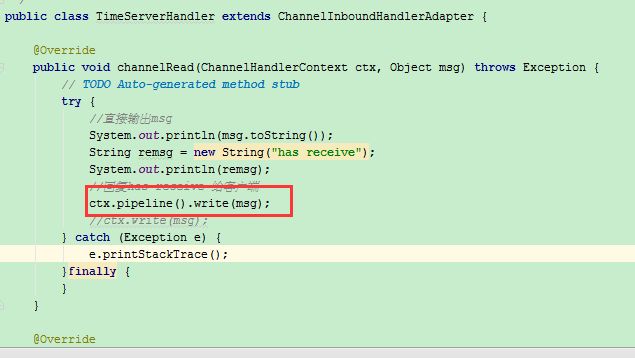
ctx.pipeline().write(msg);
DefaultChannelPipeline.java
@Override
public final ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
// 从pipeline队列最后的HandlerContext开始,向前遍历写数据到ChannelOutboundHandler中
return tail.write(msg);
}
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return write(msg, newPromise());
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(final Object msg, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (msg == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("msg");
}
try {
if (isNotValidPromise(promise, true)) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
// cancelled
return promise;
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
throw e;
}
write(msg, false, promise);
return promise;
}
private void write(Object msg, boolean flush, ChannelPromise promise) {
// 向前查找ChannelHandlerContext 为Inbound的Handler 处理数据
AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();
final Object m = pipeline.touch(msg, next);
EventExecutor executor = next.executor();
if (executor.inEventLoop()) {
if (flush) {
next.invokeWriteAndFlush(m, promise);
} else {
//调用方法
next.invokeWrite(m, promise);
}
} else {
AbstractWriteTask task;
if (flush) {
task = WriteAndFlushTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);
} else {
task = WriteTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);
}
safeExecute(executor, task, promise, m);
}
}
private void invokeWrite0(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).write(this, msg, promise);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);
}
}
// 向前查找ChannelHandlerContext 为Inbound的Handler 处理数据
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextOutbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.prev;
} while (!ctx.outbound);
return ctx;
}
public Channel channel().write(Object msg);
ctx.channel().write(msg);
AbstractChannel.java
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return pipeline.write(msg);
}
DefaultChannelPipeline.java
@Override
public final ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return tail.write(msg);
}
.... 同上