Spring BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别、模拟BeanFactory实例化对象的过程
了解应用:https://blog.csdn.net/mashaokang1314/article/details/87365074
BeanFactory
从应用中我们可以了解到,使用Spring的好处就是,程序员不用再关心对象的创建过程与对象之间依赖关系,这些都交给Spring去管理了。spring通过BeanFactory来管理这些对象,我们只需做到以下几点:
- 告诉spring哪些类是需要交给它去管理的;
- 怎么告诉spring这些类;
- 怎样维护依赖关系(setter或contructor);
- 怎样体现setter、contructor;
基于xml方式模拟一个简单的具有基本功能的BeanFactory
在service中调用dao方法
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
public void query() {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
UserDao userDao;
public void find() {
System.out.println("service");
userDao.query();
}
public UserDao getUserDao() {
return userDao;
}
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}
运行:
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
userService.find();
}
由于我们的service中dao是空,所以会报空指针异常。
创建spring.xml配置文件,并声明我们要创建的对象以及对象之间的依赖关系;
<beans>
<bean id="dao" class="com.luban.dao.UserDaoImpl">bean>
<bean id="service" class="com.luban.service.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="dao">property>
bean>
beans>
然后创建BeanFactory类,使用dom4j解析xml文件并创建对象
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4jgroupId>
<artifactId>dom4jartifactId>
<version>1.6.1version>
dependency>
public class BeanFactory {
private HashMap hashMap=new HashMap<String,Object>();
public BeanFactory(String xmlPath){
parseXml(xmlPath);
}
/**
* 解析xml文件
* @param xml
*/
public void parseXml(String xml){
//拿到xml文件对象
File file = new File(this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath()+"//"+xml);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
try {
//解析为document对象
Document document = reader.read(file);
//获取第一个root节点
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
for(Iterator<Element> it = rootElement.elementIterator(); it.hasNext();){
Element element= it.next();
//根据id获取bean名
Attribute attributeId = element.attribute("id");
String beanName = attributeId.getValue();
//根据class获取类名
Attribute attributeClass = element.attribute("class");
String beanClass = attributeClass.getValue();
//根据类名得到类对象
Class aClass = Class.forName(beanClass);
Object beanObject = aClass.newInstance();
//解析第二层标签
for(Iterator<Element> iterator = element.elementIterator();iterator.hasNext();){
Element secendElement = iterator.next();
//解析property标签,体现出setter方法
if (secendElement.getName().equals("property")){
Attribute name = secendElement.attribute("name");
String nameValue = name.getValue();
Attribute ref = secendElement.attribute("ref");
String refValue = ref.getValue();
//根据ref内容,获取要注入的对象
Object injectObj = hashMap.get(refValue);
Field field = aClass.getDeclaredField(nameValue);
field.setAccessible(true);
//给Service的userDao属性赋值对象
field.set(beanObject,injectObj);
}
}
//将对象放入hashmap
hashMap.put(beanName,beanObject);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Object getBean(String name){
return hashMap.get(name);
}
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
//以来UserDao
private UserDao userDao;
public void find() {
System.out.println("service");
userDao.query();
}
//提供get、set方法
public UserDao getUserDao() {
return userDao;
}
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanFactory bf = new BeanFactory("spring.xml");
UserDao userDao = (UserDao) bf.getBean("dao");
System.out.println(userDao);
UserService service = (UserService) bf.getBean("service");
System.out.println(service);
service.find();
}
基于构造方法的注入
删除set方法,提供构造方法
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public UserServiceImpl(UserDao userDao){
this.userDao=userDao;
}
public void find() {
System.out.println("service");
userDao.query();
}
}
public class BeanFactory {
private HashMap hashMap=new HashMap<String,Object>();
public BeanFactory(String xmlPath){
parseXml(xmlPath);
}
/**
* 解析xml文件
* @param xml
*/
public void parseXml(String xml){
//拿到xml文件对象
File file = new File(this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath()+"//"+xml);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
try {
//解析为document对象
Document document = reader.read(file);
//获取第一个root节点
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
for(Iterator<Element> it = rootElement.elementIterator(); it.hasNext();){
Element element= it.next();
//根据id获取bean名
Attribute attributeId = element.attribute("id");
String beanName = attributeId.getValue();
//根据class获取类名
Attribute attributeClass = element.attribute("class");
String beanClass = attributeClass.getValue();
//根据类名得到类对象
Class aClass = Class.forName(beanClass);
Object beanObject=null;
//解析第二层标签
for(Iterator<Element> iterator = element.elementIterator();iterator.hasNext();){
Element secendElement = iterator.next();
//解析property标签,体现出setter方法
if (secendElement.getName().equals("property")){
beanObject = aClass.newInstance();
Attribute name = secendElement.attribute("name");
String nameValue = name.getValue();
Attribute ref = secendElement.attribute("ref");
String refValue = ref.getValue();
//根据ref内容,获取要注入的对象
Object injectObj = hashMap.get(refValue);
Field field = aClass.getDeclaredField(nameValue);
field.setAccessible(true);
//给Service的userDao属性赋值对象
field.set(beanObject,injectObj);
}else if (secendElement.getName().equals("constructor-arg")){
String ref= secendElement.attribute("ref").getValue();
Object injectObject = hashMap.get(ref);
Class aClass1 = injectObject.getClass();
beanObject = aClass.getConstructor(aClass1.getInterfaces()[0]).newInstance(injectObject);
}
}
//没有子标签
if (beanObject==null){
beanObject= aClass.newInstance();
}
//将对象放入hashmap
hashMap.put(beanName,beanObject);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Object getBean(String name){
return hashMap.get(name);
}
}
实现byType自动注入
package com.luban.util;
public class BeanFactory {
private HashMap<String,Object> hashMap=new HashMap<String, Object>();
public BeanFactory(String xmlPath){
parseXml(xmlPath);
}
/**
* 解析xml文件
* @param xml
*/
public void parseXml(String xml){
//拿到xml文件对象
File file = new File(this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath()+"//"+xml);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
try {
//解析为document对象
Document document = reader.read(file);
//获取第一个root节点
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
for(Iterator<Element> it = rootElement.elementIterator(); it.hasNext();){
Element element= it.next();
//根据id获取bean名
Attribute attributeId = element.attribute("id");
String beanName = attributeId.getValue();
//根据class获取类名
Attribute attributeClass = element.attribute("class");
String beanClass = attributeClass.getValue();
//根据类名得到类对象
Class aClass = Class.forName(beanClass);
Object beanObject=null;
boolean flag=false;
if (rootElement.attribute("default-autowire")!=null){
flag=true;
}
//解析第二层标签
for(Iterator<Element> iterator = element.elementIterator();iterator.hasNext();){
Element secendElement = iterator.next();
//解析property标签,体现出setter方法
if (secendElement.getName().equals("property")){
beanObject = aClass.newInstance();
Attribute name = secendElement.attribute("name");
String nameValue = name.getValue();
Attribute ref = secendElement.attribute("ref");
String refValue = ref.getValue();
//根据ref内容,获取要注入的对象
Object injectObj = hashMap.get(refValue);
Field field = aClass.getDeclaredField(nameValue);
field.setAccessible(true);
//给Service的userDao属性赋值对象
field.set(beanObject,injectObj);
}else if (secendElement.getName().equals("constructor-arg")){
String ref= secendElement.attribute("ref").getValue();
Object injectObject = hashMap.get(ref);
Class aClass1 = injectObject.getClass();
beanObject = aClass.getConstructor(aClass1.getInterfaces()[0]).newInstance(injectObject);
}
}
//自动注入
if (flag==true){
int count=0;
beanObject = aClass.newInstance();
Object injectObject=null;
for (Field field : aClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
//属性的类型
Class type = field.getType();
//判断在map中是否有需要注入的属性类型
for (String key:hashMap.keySet()) {
Class temp=hashMap.get(key).getClass().getInterfaces()[0];
if (temp.getName().equals(type.getName())){
injectObject=hashMap.get(key);
count++;
}
}
if (count>1){
throw new RuntimeException("只需要一个属性,你给了"+count+"个");
}else {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(beanObject,injectObject);
}
}
}
//没有子标签
if (beanObject==null){
beanObject= aClass.newInstance();
}
//将对象放入hashmap
hashMap.put(beanName,beanObject);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Object getBean(String name){
return hashMap.get(name);
}
}
BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别
BeanFactory
BeanFactory是一个spring中的一个工厂,可以产生bean,可以通过getBean获取;
FactoryBean
FactoryBean是spring中一个特殊的bean,它可以产生bean,实现了FactoryBean接口的类,可以通过getObject获取生产出来的bean。FactoryBean和它所产生出来的bean的存在形式也不一样,如果你想要直接获取FactoryBean本身则通过getBean(bean名字)获取,如果想要获取它生产出来的bean则通过getBean(&bean名字)来获取。
个人理解:使用FactoryBean的目的是解决第三方依赖过多,就像整合Mybatis不仅要使用Mybatis的依赖,Mybatis可能还有其他第三方依赖,是我们不能配置的,即使可以配置那也是相当麻烦的。所以就有了SqlSessionFactoryBean这个类,它实现了FactoryBean这个接口,我们只需要给它提供比如数据源DataSouce信息等,它在getObject中将DataSouce配置给SqlSessionFactory然后返回,就可以自动帮我们配置好,我们可以直接使用SqlSessionFactoryBean,而不用再去配置。
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
public void test() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
public class MyFactoryBean implements FactoryBean {
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return new UserDaoImpl();
}
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return UserDaoImpl.class;
}
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
<bean id="factoryBean" class="com.luban.util.MyFactoryBean">bean>
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext cpx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
MyFactoryBean factoryBean = (MyFactoryBean) cpx.getBean("factoryBean");
UserDaoImpl object = (UserDaoImpl) factoryBean.getObject();
object.test();
}
}
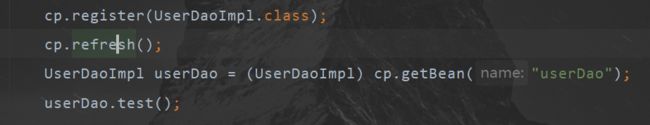
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext cpx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
UserDaoImpl factoryBean = (UserDaoImpl) cpx.getBean("factoryBean");
factoryBean.test();
}
![]()
异常原因:通过factoryBean获取到的并不是MyFactoryBean,而是它里面通过getObject返回的类型。而如果我们需要获取MyFactoryBean本身,则需要通过&factoryBean来获取;
MyFactoryBean factoryBean = (MyFactoryBean) cpx.getBean("&factoryBean");
System.out.println(factoryBean);
如果你把一个实现了FactoryBean的类交给spring去管理,会产生两个对象,一个是本身对象,一个是通过getObject返回的对象。
源码跟踪getBean,发现在doGetBean中有一个字符串转换的方法,通过传入的name获取beanName。
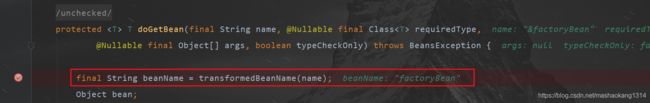
这里不直接使用name作为beanName有两个原因:
- name可能会以&开头,表明想获取FactoryBean本身,而非FactoryBean所创建的bean,在BeanFactory中,FactoryBean的实现类和其他的bean存储的方式一致,即
- 如果有类别名,则通过类别名获取beanName;
spring初始化有两种办法:
基于xml将定义bean和扫描包结合在一起,也就是说只要你在spring.xml中定义了bean,就直接交由spring去管理的;而基于JavaConfig就算你加了@service、@Compontent等注解,还要去扫描包。
模拟scan方法
public class AnnotationApplicationContext {
public void scan(String basePackage){
//获取当前所在根路径
String rootPath = this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath();
String basePackagePath = basePackage.replaceAll("\\.", "\\\\");
File file = new File(rootPath + "//" + basePackage);
//获取这个路径下的所有文件
String[] names = file.list();
for (String name : names) {
//去掉文件名后的.class就是类名
name = name.replaceAll(".class", "");
//根据包名+类名获取类对象
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(basePackage + "." + name);
//判断类上是否有指定扫描的自定义注解,如果有就new对象
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class)){
//TODO创建对象
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}