java核心编程
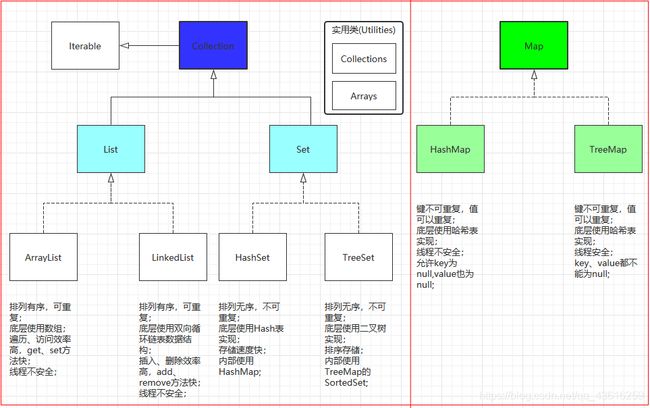
Java集合框架:
Collections binnerySearch()方法二进制检索,replaceAll()替换
Collections sort()方法的应用:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.kaoshi;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Sort implements Comparable {
private String school;
private String area;
private double score;
private int xingji;
public Sort(String school, String area, double score, int xingji) {
this.school = school;
this.area = area;
this.score = score;
this.xingji = xingji;
}
public String getSchool() {
return school;
}
public void setSchool(String school) {
this.school = school;
}
public String getArea() {
return area;
}
public void setArea(String area) {
this.area = area;
}
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public int getXingji() {
return xingji;
}
public void setXingji(int xingji) {
this.xingji = xingji;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sort sort1 = new Sort("北京大学", "北京", 100, 7);
Sort sort2 = new Sort("清华大学", "北京", 98, 7);
Sort sort3 = new Sort("复旦大学", "上海", 82, 7);
Sort sort4 = new Sort("武汉大学", "湖北", 82, 6);
Sort sort5 = new Sort("浙江大学", "浙江", 82, 5);
Sort sort6 = new Sort("中国人民大学", "北京", 81.5, 5);
Sort sort7 = new Sort("上海交通大学", "上海", 81, 5);
Sort sort8 = new Sort("南京大学", "江苏", 80.9, 5);
Sort sort9 = new Sort("国防科技大学", "湖南", 80, 5);
Sort sort10 = new Sort("中山大学", "广东", 76, 4);
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add(sort1);
arrayList.add(sort2);
arrayList.add(sort3);
arrayList.add(sort4);
arrayList.add(sort5);
arrayList.add(sort6);
arrayList.add(sort7);
arrayList.add(sort8);
arrayList.add(sort9);
arrayList.add(sort10);
Collections.sort(arrayList);
System.out.println(" " + "学校名称\t 所在地区\t 总分\t 星级排名");
for (Sort s : arrayList) {
if (s.getSchool().toCharArray().length > 4) {
System.out.println(s.getSchool() + "\t\t" + s.getArea() + "\t\t" + s.getScore() + "\t\t" + s.getXingji());
} else {
System.out.println(" " + s.getSchool() + "\t\t" + s.getArea() + "\t\t" + s.getScore() + "\t\t" + s.getXingji());
}
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Sort o) {
Double score1 = this.getScore();
Double score2 = o.getScore();
Integer xingji1 = this.getXingji();
Integer xingji2 = o.getXingji();
// if (score1.compareTo(score2) != 0) {
// return -score1.compareTo(score2);
// } else
// return -xingji1.compareTo(xingji2);
/*三目运算:*/
return score1.compareTo(score2) != 0 ? -score1.compareTo(score2) : -xingji1.compareTo(xingji2);
}
}
/* 学校名称 所在地区 总分 星级排名
北京大学 北京 100.0 7
清华大学 北京 98.0 7
复旦大学 上海 82.0 7
武汉大学 湖北 82.0 6
浙江大学 浙江 82.0 5
中国人民大学 北京 81.5 5
上海交通大学 上海 81.0 5
南京大学 江苏 80.9 5
国防科技大学 湖南 80.0 5
中山大学 广东 76.0 4*/
泛型:
指定集合中存入的数据类型,便于遍历集合时不需要再强转数据类型
ArrayList应用:
size(): 返回集合长度
get(index): 返回指定索引位置的元素
indexOf : 查找元素对应索引 返回第一个出现的索引
lastindexOf: 返回最后一个出现的索引的位置
remove(集合元素): 删除的是第一个出现的集合元素
remove(int index): 根据索引删除元素
toArray():将集合转成数组
clear(): 清空集合
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class DogArrayList {
private String name;
private String type;
public DogArrayList(String name, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DogArrayList dog0=new DogArrayList("欧欧","雪娜瑞");
DogArrayList dog1=new DogArrayList("亚亚","拉布拉多");
DogArrayList dog2=new DogArrayList("菲菲","拉布拉多");
DogArrayList dog3=new DogArrayList("美美","雪娜瑞");
List list= new ArrayList();
list.add(dog0);
list.add(dog1);
list.add(dog2);
list.add(dog3);
System.out.println("共计有"+list.size()+"条狗狗。\n分别是");
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();//迭代集合
while (iterator.hasNext()){//next向下迭代hasNext没有值返回false
DogArrayList dog=(DogArrayList)iterator.next();
System.out.println(dog.getName()+"\t"+dog.getType());
}
System.out.println("删除之前共计有"+list.size()+"条狗狗。\n");
list.remove(0);
list.remove(dog2);
System.out.println("删除之后还有"+list.size()+"条狗狗。\n分别是:");
Iterator iterator1 = list.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()){
DogArrayList dog=(DogArrayList)iterator1.next();
System.out.println(dog.getName()+"\t"+dog.getType());
}
Iterator iterator2 = list.iterator();
boolean flag=true;
String name="美美";
while (iterator2.hasNext()){
DogArrayList dog=(DogArrayList)iterator2.next();
if (dog.getName().equals(name)){
flag=false;
System.out.println("\n集合中包含"+name+"的信息");
}
}
if(flag){
System.out.println("\n集合中不包含"+name+"的信息");
}
}
}
LinkedList应用:
LinkedList采用双向循环链表存储方式,插入、删除元素时效率高
常用方法:
getLast(): 获取最后一个元素
getFirst(): 获取第一个元素
element(): 返回第一个元素
poll(): 返回并移除 第一个列表元素
removeFirst()
移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。
removeLast()
移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class DogLinkedList {
private String name;
private String type;
public DogLinkedList(String name, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DogLinkedList dog0 = new DogLinkedList("欧欧", "雪娜瑞");
DogLinkedList dog1 = new DogLinkedList("亚亚", "拉布拉多");
DogLinkedList dog2 = new DogLinkedList("菲菲", "拉布拉多");
DogLinkedList dog3 = new DogLinkedList("美美", "雪娜瑞");
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(dog0);
linkedList.add(dog1);
linkedList.addFirst(dog2);
linkedList.addLast(dog3);
DogLinkedList dogLinkedList0 = (DogLinkedList) linkedList.getFirst();
DogLinkedList dogLinkedList1 = (DogLinkedList) linkedList.getLast();
System.out.println("第一条狗狗的昵称是" + dogLinkedList0.getName() + "。");
System.out.println("最后一条狗狗的昵称是" + dogLinkedList1.getName() + "。");
linkedList.remove(3);
// linkedList.pollFirst();//弹出——获取并删除列表第一个元素
linkedList.poll();//弹出获取并删除列表第一个元素
System.out.println("\n删除部分狗狗后还有" + linkedList.size() + "条狗狗。\n分别是:");
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
DogLinkedList dogLinkedList = (DogLinkedList) iterator.next();
System.out.println(dogLinkedList.getName() + "\t\t" + dogLinkedList.getType());
}
}
}
TreeSet集合的应用:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.zuoye09;
import net.sourceforge.pinyin4j.PinyinHelper;
import java.util.*;
public class DogListTreeSet implements Comparable {//利用泛型指定比较的对象,以便不再进行向下转型
private String name;
private String strain;
private int age;
public DogListTreeSet(String name, String strain, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.strain = strain;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getStrain() {
return strain;
}
public void setStrain(String strain) {
this.strain = strain;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一题:
DogListTreeSet dogList1 = new DogListTreeSet("欧欧", "田园犬", 5);
DogListTreeSet dogList2 = new DogListTreeSet("花花", "二哈", 2);
DogListTreeSet dogList3 = new DogListTreeSet("豆豆", "田园犬", 3);
DogListTreeSet dogList4 = new DogListTreeSet("豆豆", "泰迪", 1);
DogListTreeSet dogList5 = new DogListTreeSet("哪吒", "金毛", 3);
/* List lists=new ArrayList<>();
lists.add(dogList1);
lists.add(dogList2);
lists.add(dogList3);
lists.add(dogList4);
lists.add(dogList5);
Iterator iterator = lists.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
DogListTreeSet next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next.getName()+"\t"+next.getStrain()+"\t"+next.getAge());
}*/
//第二题:
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
treeMap.put(dogList1, dogList1.name);
treeMap.put(dogList2, dogList2.name);
treeMap.put(dogList3, dogList3.name);
treeMap.put(dogList4, dogList4.name);
treeMap.put(dogList5, dogList5.name);
Set dogListTreeSets = treeMap.keySet();//将狗狗对象键的集合列表通过keySet()方法
for (DogListTreeSet dogListTreeSet : dogListTreeSets) {
System.out.println(treeMap.get(dogListTreeSet) + "\t\t" + dogListTreeSet.getStrain() + "\t\t" + dogListTreeSet.getAge());
}
// Iterator iterator = dogListTreeSets.iterator();
// while (iterator.hasNext()){
// DogListTreeSet next = iterator.next();
// System.out.println(treeMap.get(next)+"\t\t"+next.getStrain()+"\t\t"+next.getAge());
// }
}
@Override
public int compareTo(DogListTreeSet o) {
String name1 = transformPinyin(this.getName());
String name2 = transformPinyin(o.getName());
// if (!name1.equals(name2)) {//注意:此处只能为name1.compareTo(name2)!=0或!name1.equals(name2),TreeMap存取对象,
// // 重写compareTo方法,对于对象中要对比的String类型属性,相等的情况TreeMap会看作是一个对象而被覆盖掉,因此需要考虑相等情况下的再次判断
// return -name1.compareTo(name2);
// } else {
// Integer age1 = this.getAge();
// Integer age2 = o.getAge();
// return age1.compareTo(age2);
// }
/*三目运算:*/
Integer age1 = this.getAge();
Integer age2 = o.getAge();
return name1.compareTo(name2) != 0 ? -name1.compareTo(name2) : age1.compareTo(age2);
}
public String transformPinyin(String name0) {
String name1 = "";
char[] chars = name0.toCharArray();
for (char c : chars) {
String[] strings = PinyinHelper.toHanyuPinyinStringArray(c);//引入PinyinHelper jar包,将汉字转成拼音
name1 += strings[0];
}
return name1;
}
}
/*参考输出:
* 欧欧 田园犬 5
哪吒 金毛 3
花花 二哈 2
豆豆 泰迪 1
豆豆 田园犬 3*/ TreeSet :唯一,排列无序(先存入,不一定先取出),存储有序 可以根据自己的规则去排序
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng;
import net.sourceforge.pinyin4j.PinyinHelper;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TeacherTreeSet implements Comparable {
private String name;
private int age;
private String clas;
public TeacherTreeSet(String name, int age, String clas) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.clas = clas;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getClas() {
return clas;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
//-1 0 1
String name = this.getName();//本对象名
char[] chars = name.toCharArray();//转换为char数组
String name1 = "";
for (char ch : chars) {
String[] strings = PinyinHelper.toHanyuPinyinStringArray(ch);//遍历数组
name1 = name1 + strings[0];
}
TeacherTreeSet teacher = (TeacherTreeSet) o;
char[] chars1 = teacher.getName().toCharArray();
String name2 = "";
for (char ch : chars1) {
String[] strings = PinyinHelper.toHanyuPinyinStringArray(ch);
name2 = name2 + strings[0];
}
// if(name1.compareTo(name2)!=0){
// return name1.compareTo(name2);
// }else {
// Integer age1=this.getAge();
// Integer age2=teacher.getAge();
// return age1.compareTo(age2);//大于0升序,小于0降序 age2>age1返回1
// }
/*三目运算*/
Integer age1 = this.getAge();
Integer age2 = teacher.getAge();
return name1.compareTo(name2) != 0 ? name1.compareTo(name2) : age1.compareTo(age2);//三目运算,return关键字必须放在前边
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TeacherTreeSet teacher1 = new TeacherTreeSet("阿里", 30, "一班");
TeacherTreeSet teacher2 = new TeacherTreeSet("巴巴", 55, "二班");
TeacherTreeSet teacher3 = new TeacherTreeSet("嫦娥", 26, "六班班");
TeacherTreeSet teacher4 = new TeacherTreeSet("芳芳", 34, "五班");
TeacherTreeSet teacher5 = new TeacherTreeSet("芳芳", 27, "三班");
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(teacher1);
treeSet.add(teacher2);
treeSet.add(teacher3);
treeSet.add(teacher4);
treeSet.add(teacher5);
for (Object obj : treeSet) {
TeacherTreeSet teacher = (TeacherTreeSet) obj;
System.out.println(teacher.getName() + "\t\t" + teacher.getAge() + "\t\t" + teacher.getClas() + "\t\t");
}
}
}
jar包放在lib鼠标右击add as lib
Enum枚举是一组常量
file-setting-general-show quick documentation on mouse move设置提醒可能出现的异常
枚举类小练习:
public enum U1 {
第一单元,
}public enum U2 {
第二单元
}
public enum U3 {
第三单元
}public enum Unit {
U1,U2,U3
}package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.unit;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class UnitS {
private U1 u1;//定义枚举类型变量
private U2 u2;
private U3 u3;
public U1 getU1() {
return u1;
}
public U2 getU2() {
return u2;
}
public U3 getU3() {
return u3;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println(getU1() + "打基础");
System.out.println(getU2() + "可以胜任Java程序开发");
System.out.println(getU3() + "可以胜任企业级Java开发");
}
public void setU1(U1 u1) {
this.u1 = u1;
}
public void setU2(U2 u2) {
this.u2 = u2;
}
public void setU3(U3 u3) {
this.u3 = u3;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
UnitS unitS = new UnitS();
unitS.setU1(U1.第一单元);//通过枚举类调用其变量
unitS.setU2(U2.第二单元);
unitS.setU3(U3.第三单元);
unitS.show();
try {
String a = "第二单元";
U1 u1 = U1.valueOf(a);
System.out.println(u1);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {//ctrl+alt+t添加异常处理try-catch
System.out.println("\n参数输入有误!");
}
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入对应单元!U1/U2/U3");
String next = s.next();
//file-setting-general-show quick documentation on mouse move设置提醒可能出现的异常
try {
Unit unit = Unit.valueOf(next);//将输入的字符通过枚举类型的.valueOf方法转换为枚举类型
//通过switch表达式变量对其内容进行选择
switch (unit) {//表达式类型:byte short int char Enum String,但不能为double类型!
case U1:
System.out.println("第一单元打基础");
break;
case U2:
System.out.println("第二单元可以胜任Java程序开发");
break;
case U3:
System.out.println("第三单元可以胜任企业级Java开发");
break;
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Map集合应用:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class StudTestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StudTreeMap stud1 = new StudTreeMap("JACK", "杰克", "男");
StudTreeMap stud2 = new StudTreeMap("Rose", "玫瑰", "女");
StudTreeMap stud3 = new StudTreeMap("MiLi", "米莉", "女");
TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
treeMap.put(stud1, stud1.getEnglishName());
treeMap.put(stud2, stud2.getEnglishName());
treeMap.put(stud3, stud3.getEnglishName());//遍历TreeMap对象要求其键必须实现Comparable接口
Set set = treeMap.keySet();//利用TreeMap对象的keySet方法获取其键的set集合
/*Iterator iterator = set.iterator();//将迭代器指定类型
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
StudTreeMap next = iterator.next();//注意itrator.next每次循环只能调用一次
System.out.println(treeMap.get(next) + "对应的学员姓名是:" + next.getName() + ";性别是:" + next.getSex());
}*/
for (StudTreeMap studTreeMap : set) {
System.out.println(treeMap.get(studTreeMap) + "对应的学员姓名是:" + studTreeMap.getName() + ";性别是:" + studTreeMap.getSex());
}
/*HashMap map=new HashMap<>();
map.put(stud1,stud1.getEnglishName());
map.put(stud2,stud2.getEnglishName());
map.put(stud3,stud3.getEnglishName());
Set studTreeMaps = map.keySet();//获取key的set集合
//遍历set集合
for(StudTreeMap studTreeMap:studTreeMaps){
System.out.println(map.get(studTreeMap)+studTreeMap.getName()+studTreeMap.getSex());
}*/
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng;
public class StudTreeMap implements Comparable {//利用泛型解决类型强制转换问题
private String englishName;
private String name;
private String sex;
public StudTreeMap(String englishName, String name, String sex) {
this.englishName = englishName;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getEnglishName() {
return englishName;
}
public void setEnglishName(String englishName) {
this.englishName = englishName;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(StudTreeMap studTreeMap) {//实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo方法,
return this.englishName.compareTo(studTreeMap.getEnglishName());//通过String重写的compareTo方法实现排序
}
}
注意:因Scanner对象不能将空格赋值给next,因此控制台输入空格时,仅仅将空格之前的字符赋值给next
package com.ibeifeng.javase.kaoshi;
import java.util.*;
public class Cishu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一段字符!");//任意输入一段字符,输出字符及其个数
String next = s.next();
System.out.println(next);
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
char[] chars = next.toCharArray();
int num = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (hashMap.get(chars[i]) == null) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < chars.length; j++) {
if (chars[i] == chars[j]) {
num++;
}
}
hashMap.put(chars[i], num);
num = 1;
}
}
Set set = hashMap.keySet();
for (Object o : set) {
System.out.println(o + "\t\t" + hashMap.get(o));
}
}
}
/*参考输出:
*请输入一段字符!
yyyjjj****&&
yyyjjj****&&
& 2
y 3
j 3
* 4 */map集合中添加数据若key 重复将进行覆盖操作
Random类的应用:
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int b = random.nextInt(100);//[0,100)
System.out.println(b);
}
}String类的应用:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.string;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class String01 {
/*通过String.length方法校验字符输入长度,如密码
*.equals方法源码:1.判断==地址相同,一定相等2.判断是否为String类型
*3.传进来的对象向下转型String,利用char[]获取长度(本类对象)与传进来对象长度比较
*相等的话,利用char[]循环判断每个元素内容
*
* */
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "f";
String t = "F";
if (s.equalsIgnoreCase(t))//忽略大小写
System.out.println(true);
boolean flag = true;
while (flag) {
System.out.println("******欢迎进入注册系统******");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入姓名:");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入密码:");
String password0 = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请再次输入密码:");
String password1 = scanner.next();
if (password0.length() < 6 || name.length() < 3) {
System.out.println("用户名长度不能小于3,密码长度不能小于6!");
} else if (!password0.equals(password1)) {
System.out.println("两次输入密码不相同!");
} else
System.out.println("注册成功!请牢记用户名和密码。");
System.out.println("是否继续n/y");
String next = scanner.next();
if (!next.equals("n") && !next.equals("y")) {
System.out.println("请重新输入n/y!");
next = scanner.next();
} else if (next.equals("n")) {
flag = false;
}
}
}
}
StringBuffer与StringBuilder:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.string;
public class String02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = " Hello World ";
String str2 = "chenchen";
System.out.println(Integer.valueOf("5555") + 6);
int ii = 10;
Integer x = new Integer(ii);//手动装箱 将基本数据类型转换成包装类
Integer y = ii;//自动装箱
Integer j = new Integer(8);//定义一个Integer包装类对象,值为8
int m = j.intValue();//手动拆箱 将包装类转换成基本数据类型
int n = j;//自动拆箱
//将基本数据类型转换为字符串
int c = 10;
String STR88 = Integer.toString(c);//利用包装类toString方法
String STR80 = String.valueOf(c);//利用String的valueOf方法
String STR90 = c + "";//三种方法
/*将字符串转换成基本类型
* 1.调用包装类pareseXxx(解析)方法
* 2.调用包装类的valueOf方法转换为基本类型的包装类,自动拆箱*/
String STR99 = "8";
int d = Integer.parseInt(STR99);//自动拆箱
int e = Integer.valueOf(STR99);//方法二
System.out.println(str1.substring(2, 4));//截取半闭半开区间:[)
System.out.println(str1.trim());//去掉头尾空格
System.out.println(str1.substring(3));//截取从第三个元素开始向后
System.out.println(str1.concat(str2));//多个字符拼接也可以用+
System.out.println(str1.contains("el"));//判断是否包含某个字符
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("ld"));//从左到右返回第一个匹配到的索引位置
System.out.println(str1.indexOf(72));//若为int类型则匹配ascii码
System.out.println(str1.lastIndexOf("o"));//取最后一个o的索引位置
String[] splits = str1.split("o");//根据正则或字符拆分字符串
for (String i : splits) {
System.out.print(" " + i);
}
System.out.println("\n*****************");
//根据索引indexOf方法只返回第一个值,若没有返回-1,配合截取substring[)方法将索引位置及之前的截掉,
// 重新赋值给变量,再次索引,用计数变量进行索引次数计数,直到返回-1,结束循环
String a = "爱我爱祖国,我爱祖国,我爱祖国爱";
int index = a.indexOf("爱");
int count1 = 0;
while (index >= 0) {
count1++;
a = a.substring(index + 1);
index = a.indexOf("爱");
}
System.out.println(count1);
System.out.println(a);
//利用分割split方法值为"" 将字符串分割为单个字符,存入String数组,遍历数组获取字符出现次数
String b = "爱我爱祖国,我爱祖国,我爱祖国爱";
String[] split = b.split("");
int count = 0;
for (String s : split) {
if (s.equals("爱")) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
/*5561
el
Hello World
llo World
Hello World chenchen
true
10
1
8
Hell W rld
*****************
5
5
*/装箱:
将基本数据类型转换成包装类
拆箱:
将包装类转换成基本数据类型
除了Character 包装类外其他的包装类都可以将一个字符串作为参数构造他们的实例,原因在于:其他的包装类中都含有带一个String 类型的参数的构造方法而Character 没有
split() 拆分字符串
getBytes: 生成的是字节数组
endsWith(): 测试字符串是否以指定的后缀结尾
Date类的应用:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.string;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Date01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
//创建当前时间Date对象
Date date = new Date();
// System.out.println(date);
// System.out.println(date.toString());
//SimpleDateFormat自定义日期格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 a hh时:mm分:ss秒 E w周");
String format = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
String date2 = "2018年09月19日 下午 04时:18分:14秒 星期四 38周";
try {
//类比字符转换成基本类型
Date date3 = sdf.parse(date2);//利用parse方法实现字符转日期,checkd解析异常
System.out.println(date3);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*2019年09月19日 下午 04时:23分:56秒 星期四 38周
Thu Sep 20 16:18:14 CST 2018*/Calendar类的应用:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.string;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class CalendarTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//抽象类Calendar调用静态方法getInstance
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
// System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
// System.out.println(calendar.get(1));
// System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));//一个月中多少天
// System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1);//存的月份是0-11
// System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH));
//修改calendar对象信息
calendar.set(2018, 10, 19, 8, 10, 20);//注意set()方法设置时间多一个月,getTime()方法多一天
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK));
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.WEEK_OF_MONTH));
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.zuoye10;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class StrStrBStrF {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*第一题:字符拼接*/
String str1 = "hello";
StringBuffer sf = new StringBuffer("hello");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("hello");
//String用时:466765
long s1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
str1 += "t";
}
long e1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(e1 - s1);
//StringBuffer用时:31
long s2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
sf.append("t");
}
long e2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(e2 - s2);
//StringBiulder用时:16
long s3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
sb.append("t");
}
long e3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(e3 - s3);
/*第三题:字符转日期*/
String str = "2018年10月19号 20点40分30秒";
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd号 HH点mm分ss秒");
try {
// simpleDateFormat.format();
Date parse = simpleDateFormat.parse(str);
System.out.println(parse);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*第四题:*/
String str4 = "2018年10月19号 20点40分30秒";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd号 HH点mm分ss秒");
try {
Date parse = sdf.parse(str4);
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.setTime(parse);//注意,此处若用set()进行时间设置,系统会多一个月
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.WEEK_OF_YEAR));//获取它是一年中的第几个星期
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR));//一年中的第几天
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK));//一个星期中的第几天
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1);//一年中的第几个月
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.WEEK_OF_MONTH));//一个月中的第几个星期
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件:在java 中文件夹和文件都属于文件
操作文件的类是: java.io
创建一个File 对象
File file = new File(String filename)
mkdir : 创建单层文件夹
mkdirs : 创建文件夹 如果文件夹中多层会继续创建多层文件夹
createNewFile()
isFile()
isDirectory()
exists()
delete()
getName()
getAbsolutePath()
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.zuoye11;
import java.io.File;
public class DiguiSearch {
/*第一题:查找文件夹upload 中 a.txt 所有文件的位置*/
public void getPath(String searchname, String dir) {
File f = new File(dir);//根据路径创建文件对象
File[] files = f.listFiles();//列出文件中所有对象
for (File i : files) {//遍历文件对象进行判断
if (i.isFile() && i.getName().equals(searchname)) {
System.out.println(i.getAbsolutePath());
} else
getPath(searchname, i.getAbsolutePath());//递归方法,对新的目录进行遍历寻找
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File F = new File("e:/upload");
String searchname = "a.txt";
String dir = "E:/upload";
DiguiSearch diguiSearch = new DiguiSearch();
if (F.isDirectory()) {
diguiSearch.getPath(searchname, dir);
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class FileIo {
private static int count;
public int getFile(String name, String directory) {
File file = new File(directory);//根据传进来的路径创建一个新的文件对象
File[] files = file.listFiles();//获取file下所有对象
for (File f : files) {
if (f.isFile() && f.getName().equals(name)) {//判断是否是想找的文件名
count++;
} else {
getFile(name, f.getAbsolutePath());//通过递归对新的文件创建新的对象
}
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* //文件、文件夹在Java中都为文件
File file=new File("");//\表示转义字符,\\表示它本身,通常用/表示
//mkdir:创建单层文件夹 mkdirs创建的是多层文件夹
if (!file.isDirectory()){//判断是否为目录
file.mkdir();//创建单层目录
try {
file.createNewFile();//创建文件
file.mkdirs();//创建不存在的多层目录
String[] list = file.list();//获取file对象下所有文件名存入到集合
System.out.println(list);
file.listFiles();//获取file下所有文件对象
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}*/
/*
FileIo fileIo=new FileIo();
String a="a.txt";
String b="e:/A";
System.out.println( fileIo.getFile(a, b));*/
/*相对于内存来说:
*按流向区分:以数据的传输方向为单位(程序)
*输入流:外部数据写入程序 IntputStream Reader为基类
* 输出流:程序内的数据写入外部 OutputStream Writer 为基类
*按处理数据的单元区分:
*字符流:以16位的unicode码作为传输单元
* 输入流:以Readr为基类
* 输出流:以Writer为基类
*字节流:以8位的byte字节作为传输单元
* 输入流:以InputStream为基类
* 输出流:是以OutStream为基类
*/
//小测试:字节输入流InputStream
try {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\\A\\b\\bbb\\a.txt");//可以传一个File或String类型路径
System.out.println(inputStream.available());//求字节数
System.out.println(inputStream.read());//求第一个字节对应ascii码
System.out.println(inputStream.read());//第二个ascii码
int read = inputStream.read();//read区别于迭代器的next,读后的数据随之消失
byte[] b = {(byte) read};//当read方法读到文尾不在有数据时返回-1
String str = new String(b);//利用String的构造方法将ascii转为字符
System.out.println(str);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
IO流
分类
-1 以数据的传输方向为单位(程序)
输入流:外部数据写入程序 以 InputStream Reader为基类
输出流:程序内的数据写入外部 以 OutputStream Writer 为基类
-2 字符流: 是以16位 的unicode 码作为传输单元
输入流:
Reader为基类
输出流:
Writer类 为基类
-3 字节流: 是以8位的byte 字节作为传输单元
输入流: InputStream 为基类
输出流: 是以OutputStream为基类
InputStream :
read(): 每次调用读取一个字节
read(byte[] bytes): 当从输入流中读取出数据,返回的是读取字节的字节数,当从输入流中没有读取字节数时则返回-1
创建文件 a.txt
写入数据:
利用InputStream 读取a.txt文件输出到控制台中
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class IoStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream in = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream("E:\\A\\b\\bbb\\a.txt");//读到内存
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//定义一个缓冲区
// int length = in.read(bytes);//从此输入流中将最多 b.length 个字节的数据读入一个字节数组中。
// System.out.println(length);
// String s = new String(bytes,0,length);//构造一个新的 String,方法是使用指定的字符集解码字节的指定子数组,定义数组长度为read返回长度
// System.out.println(s);
//
// String str1=new String(bytes);//构造一个新的 String,方法是使用平台的默认字符集解码字节的指定数组。
// System.out.println(str1.length());//长度为数组长度,read已将数据导入数组中
// System.out.println(str1);
int len;
while ((len = in.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.zuoye11;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class PictureIn {
public void input(String dir) {
FileInputStream picturein = null;
try {
picturein = new FileInputStream(dir);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = picturein.read(b)) != -1) {//字节流类读取数据放在缓冲区,直到长度等于-1,
// 到字节尾部,缓冲区仍会留存部分未被覆盖的数据,通过finally 执行字节流类的close方法,释放全部内存。
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (picturein != null) {
try {
picturein.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PictureIn pictureIn = new PictureIn();
pictureIn.input("任意图片地址!!");
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class IoStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream in = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream("E:\\A\\b\\bbb\\a.txt");//读到内存
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//定义一个缓冲区
// int length = in.read(bytes);//从此输入流中将最多 b.length 个字节的数据读入一个字节数组中。
// System.out.println(length);
// String s = new String(bytes,0,length);//构造一个新的 String,方法是使用指定的字符集解码字节的指定子数组,定义数组长度为read返回长度
// System.out.println(s);
//
// String str1=new String(bytes);//构造一个新的 String,方法是使用平台的默认字符集解码字节的指定数组。
// System.out.println(str1.length());//长度为数组长度,read已将数据导入数组中
// System.out.println(str1);
int len;
while ((len = in.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferReaderTest {//增强型字符流
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt"), "utf-8");
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(reader);
// StringBuffer str=new StringBuffer("");//新增元素效率高
String str = "";
while ((str = bfr.readLine()) != null) {//因readling 返回为String类型,因此效率较低,readLine本身就是缓冲区,不需要创建新的缓冲区
System.out.println(str);
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class OutStreamTxt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fi = null;
FileOutputStream fo = null;
File fsource = null;
File ftarget = null;
try {
fsource = new File("d:/我的青春谁做主.txt");
ftarget = new File("c:/myFile/myPrime.txt");
fi = new FileInputStream(fsource);
fo = new FileOutputStream(ftarget, true);//追加
byte[] b = new byte[512];
int len;
while ((len = fi.read(b)) != -1) {
fo.write(b, 0, len);
fo.flush();//注意字符流必须用flush方法(字符会出现未写入的情况),字节流可以不用flush(刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节)
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fi != null || fo != null) {
try {
fi.close();
fo.close();
fsource.delete();//剪切操作在流关闭后将其删除,流未关闭相当于文件处于打开的情况
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class ZuoyeIO {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream is = null;
try {
File f = new File("e:/a.txt");
f.createNewFile();
is = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(b)) != -1) {//注意循环中,每次判断都读取一次
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {//此处用try避免throw
if (is != null)
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class CopyIoStreamReader {
public void copyFileFR(String source, String tar) {
//引入字符流因为字符进行字符读取时是按字符读取,相比按字节读取速度更快
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(source);
fw = new FileWriter(tar, true);//可追加
char[] ch = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(ch)) != -1) {
fw.write(ch, 0, len);
fw.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fr != null) fr.close();
if (fw != null) fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void copyFileISR(String source, String tar) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(source);
fos = new FileOutputStream(tar);
isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "gbk");//可转码
char[] ch = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(ch)) != -1) {
osw.write(ch, 0, len);
osw.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) fis.close();
if (fos != null) fos.close();
if (isr != null) isr.close();
if (osw != null) osw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void cpBufferString(String source, String tar) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(source);
fos = new FileOutputStream(tar);
isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
String str = "";
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {//注意此处readLine方法返回String类型,用String类型接收
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) fis.close();
if (fos != null) fos.close();
if (isr != null) isr.close();
if (osw != null) osw.close();
if (br != null) br.close();
if (bw != null) bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void cpBufferChar(String source, String tar) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(source);
fos = new FileOutputStream(tar);
isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "gbk");//可以更改字符集
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
char[] ch = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = br.read(ch)) != -1) {//注意此处readLine方法返回String类型,用String类型接收
bw.write(ch, 0, len);
bw.flush();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) fis.close();
if (fos != null) fos.close();
if (isr != null) isr.close();
if (osw != null) osw.close();
if (br != null) br.close();
if (bw != null) bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyIoStreamReader cisr = new CopyIoStreamReader();
// cisr.copyFileFR("D:\\myPrime.txt", "C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt");
// cisr.copyFileISR("D:\\myPrime.txt", "C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt");
// cisr.cpBufferString("D:\\myPrime.txt", "C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt");
cisr.cpBufferChar("D:\\myPrime.txt", "C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt");
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class JianQiePic {
public void jianQie(String source, String target) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
File file = new File(source);
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(target);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
fos.write(b, 0, len);
fos.flush();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) fis.close();
if (fos != null) fos.close();
file.delete();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JianQiePic jianQiePic = new JianQiePic();
jianQiePic.jianQie("C:\\Users\\qiqu\\Desktop\\2019-09-15_132523.png", "D:\\1.png");
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class DataInputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/myPrime.txt");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);
byte[] b = new byte[512];
int len;
while ((len = dis.read(b)) != -1) {
dos.write(b, 0, len);
dos.flush();
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class InputStreamReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
InputStreamReader irs = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt");//转成字节流
irs = new InputStreamReader(is, "utf-8");//gbk 创建使用指定字符集的 InputStreamReader。
System.out.println(irs.getEncoding());
char[] c = new char[512];
int len;
while ((len = irs.read(c)) != -1) {
for (char c1 : c) {
System.out.print(c1);
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException | UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (is != null || irs != null) {
try {
is.close();
irs.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
序列化\反序列化:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.file;
import java.io.*;
public class ObjectOutputStreamTest implements Serializable {//序列化对象必须实现序列化接口
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//序列化:内存->磁盘 反序列化:磁盘->内存
String str = "hhh哈哈哈";
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt"));
oos.writeBytes(str);
//序列化对象,必须实现序列化接口Serializable
ObjectOutputStreamTest oost = new ObjectOutputStreamTest();
oos.writeObject(oost);//序列化
oos.flush();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\myFile\\myPrime.txt"));
Object o = ois.readObject();//反序列化
oos.close();
ois.close();
}
}
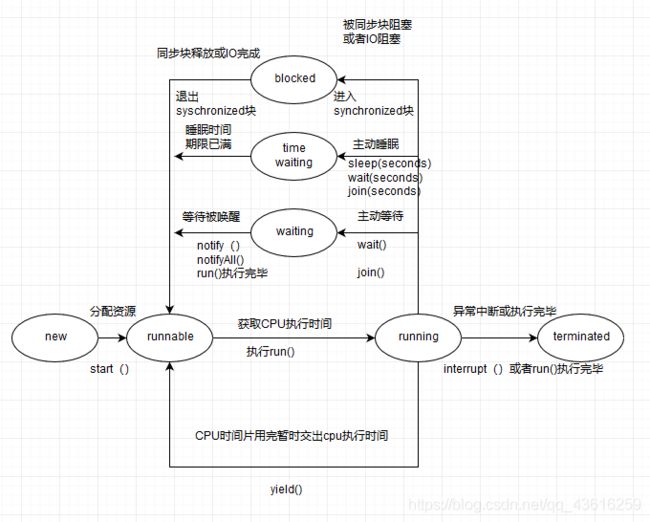
多线程:
进程:应用程序在运行的状态
内存是由cpu 分配
线程:
所有的线程资源相加不能超过进程的总资源
cpu调度和执行的最小单元
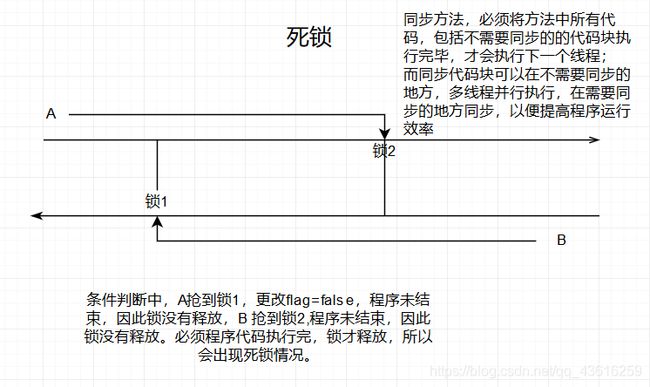
死锁:
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.synchronizedtest;
public class LockTest implements Runnable{
private String str1=new String("");
private String str2=new String("");
boolean flag=true;
@Override
public void run() {//死锁:两把锁,一个左侧,一个右侧 不要嵌套使用同步代码块
if(flag){
flag=false;
synchronized (str1){
System.out.println("111");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (str2){
System.out.println("333");
}
}
}else {
flag=true;
synchronized (str2){
System.out.println("333");
synchronized (str1){
System.out.println("111");
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LockTest lockTest1=new LockTest();
LockTest lockTest2=new LockTest();
new Thread(lockTest1,"线程1:"){
}.start();
Thread thread2=new Thread(lockTest2,"线程2:");
thread2.start();
}
}package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.synchronizedtest;
/**
* @author TongChenChen
*/
public class SynchronizedTest implements Runnable {
//volatile保证并发编程的可见性和有序性
private volatile int count;
/**
* 同步方法
*/
public synchronized void show() {//synchronized保证并发编程的原子性
count -= 50;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//一个对象一把锁,多个线程多个锁
// static修饰的方法,所有对象调用的都是同一个方法
SynchronizedTest synchronizedTest = new SynchronizedTest();
synchronizedTest.setCount(500);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(synchronizedTest, "线程一:");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(synchronizedTest, "线程二:");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
show();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + getCount());
}
}
}
class SynchronizedTest1 implements Runnable {
/**volatile保证并发编程的可见性和有序性*/
private volatile int count;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronizedTest1 synchronizedTest1 = new SynchronizedTest1();
synchronizedTest1.setCount(500);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(synchronizedTest1, "线程一:");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(synchronizedTest1, "线程二:");
thread1.start();//启动线程
thread2.start();
thread1.join();//等待该线程终止,main线程优先级最高
thread2.join();
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
/**同步代码块*/
//synchronized同步:不同线程,当前方法调用执行结束,再进行下一个线程调用;antagonized异步:不同线程方法调用即执行
synchronized (this) {
//一般用同步代码块来做
count -= 50;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + getCount());
}
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.synchronizedtest;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class ThreadTest extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("创建线程的第一种方法:继承Thread");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadTest synchroTest=new ThreadTest();
Thread thread1=new Thread(synchroTest);
thread1.start();
thread1.join();
}
}
class Thread2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"实现Runnable");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread2 synchroTest1=new Thread2();
Thread thread2=new Thread(synchroTest1,"第二种创建线程方法:");
thread2.start();
thread2.join();
}
}
class Thread3 implements Callable {//返回值类型
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第三种创建线程的方法");
return Thread.currentThread().getName();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Thread3 synchroTest2=new Thread3();
FutureTask futureTask=new FutureTask(synchroTest2);
Thread thread3=new Thread(futureTask,"第三种创建线程方法,有返回值");
thread3.start();
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
thread3.join();
}
} 生产者 消费者
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.zuoye13;
public class NaoZhong implements Runnable {
private boolean ring = false;
public boolean isRing() {
return ring;
}
public void setRing(boolean ring) {
this.ring = ring;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
synchronized (this) {
if (!isRing()) {
setRing(true);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "叮叮该起床啦!");
this.notify();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.zuoye13;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author TongChenChen
*/
public class SockerSeverTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(7777);
while (true) {
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream inputStream = accept.getInputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[512];
System.out.println("来自客户端:"+accept.getInetAddress().getHostAddress()+":\t"+new String(b, 0, inputStream.read(b)));
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.zuoye13;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SockerTest implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this) {
Socket socket = null;
try {//localhost
socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 7777);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("客户端"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+":请向服务器发送一段话!");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String next = scanner.next();
try {
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(next.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SockerTest sockerTest = new SockerTest();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(sockerTest).start();
}
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.zuoye13;
public class Ticket implements Runnable {
private volatile int count = 100;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this) {
while (true) {
if (getCount() > 0) {
this.count -= 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖掉1张票");
System.out.println("还剩" + this.count + "张票");
this.notify();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"票已卖完!");
notify();
break;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Ticket ticket = new Ticket();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(ticket, "窗口一");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(ticket, "窗口二");
Thread thread3 = new Thread(ticket, "窗口三");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
thread3.join();
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.zuoye13;
public class XiaoMing implements Runnable {
private NaoZhong naozhong;
public NaoZhong getNaozhong() {
return naozhong;
}
public void setNaozhong(NaoZhong naozhong) {
this.naozhong = naozhong;
}
public void setNaoZhong(NaoZhong naozhong) {
this.naozhong = naozhong;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (getNaozhong()) {
if (getNaozhong().isRing() == true) {
System.out.println("好的好的我起来啦!");
getNaozhong().setRing(false);
getNaozhong().notify();
try {
getNaozhong().wait();/*1*/
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
getNaozhong().notify();
try {
getNaozhong().wait();/*2:注意此处必须为线程锁调用??*/
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NaoZhong naozhong = new NaoZhong();
XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
xiaoMing.setNaozhong(naozhong);//注意此处将生产者与消费者关联
Thread thread1 = new Thread(naozhong, "生产者闹钟:");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(xiaoMing, "消费者小明:");
thread2.setDaemon(true);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
package com.ibeifeng.javase.hexinbiancheng.synchronizedtest;
public class SynchronizedTest implements Runnable {
private volatile int count;//volatile保证并发编程的可见性和有序性
/**
* 同步方法
*/
public synchronized void show() {//synchronized保证并发编程的原子性
count -= 50;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronizedTest synchronizedTest = new SynchronizedTest();
synchronizedTest.setCount(500);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(synchronizedTest, "线程一:");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(synchronizedTest, "线程二:");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
show();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + getCount());
}
}
}
class SynchronizedTest1 implements Runnable {
private volatile int count;//volatile保证并发编程的可见性和有序性
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronizedTest1 synchronizedTest1 = new SynchronizedTest1();
synchronizedTest1.setCount(500);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(synchronizedTest1, "线程一:");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(synchronizedTest1, "线程二:");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
/**同步代码块*/
synchronized(this){
count-=50;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + getCount());
}
}
}
}
lamda函数
package com.beifeng;
import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.api.model.wsdl.WSDLOutput;
/**
* Hello world!
*/
interface Student{
int cal(int a,int b);
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Lamda表达式 一个接口中只有一个方法时可以使用匿名函数
/* Student student=new Student() {
@Override
public int cal(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
};*/
Student student1=(a,b)->(a+b);
Student student2=(a,b)->(a*b);
System.out.println(student2.cal(3,6));
System.out.println(student1.cal(1,2));
//spark:scala java python
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("线程一");
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("线程二");
}).start();
}
}
package beifeng.lamda;
public interface LamdaPiao {
void sall() throws InterruptedException;
}
class Piao implements Runnable {
private volatile int count;
LamdaPiao lamdaPiao = () -> {
synchronized (this) {
while (true) {
if (getCount() > 0) {
setCount(getCount() - 1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖掉1张票,还剩" + getCount() + "张票");
this.notifyAll();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
this.notifyAll();
System.out.println("票已卖完");
break;
}
}
}
};
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Piao piao = new Piao();
piao.setCount(100);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(piao, "窗口一");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(piao, "窗口二");
Thread thread3 = new Thread(piao, "窗口三");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread3.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
lamdaPiao.sall();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
UDP:
package beifeng.udp;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.SocketException;
public interface Receiver {
void receive() throws IOException;
}
package beifeng.udp;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.SocketException;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public interface Sender {
void send() throws IOException;
}
package beifeng.udp;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author TongChenChen
*/
public class UdpTest implements Runnable {
private int port;
UdpTest(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Receiver receiver = () -> {
while (true) {
//接收数据
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(port);
byte[] b = new byte[512];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(b, 0, b.length);
ds.receive(dp);
System.out.println("\n收到信息:\t" + new String(b, 0, dp.getLength()));
ds.close();
}
};
try {
receiver.receive();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/** 因为线程运行中,只有发送信息有输出,接收信息并无输出,因此同时运行两股线程,发送信息首先占用线程*/
//客户端A
//接收信息:只接受来自端口6666的线程信息
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new UdpTest(6666));
thread1.start();
//发送信息:只向端口7777发送信息
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new UdpTest01(7777, "localhost"));
thread2.start();
}
}
class UdpTest01 implements Runnable {
private int port;
private String host;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//客户端B
//发送信息:只向端口6666发送信息
Thread thread1=new Thread(new UdpTest01(6666, "localhost"));
thread1.start();
//接收信息:只接收来自端口7777的线程信息
Thread thread2=new Thread(new UdpTest(7777));
thread2.start();
}
UdpTest01(int port, String host) {
this.port = port;
this.host = host;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Sender sender = () -> {
while (true) {
//创造数据并发送数据
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请发送信息:");
String next = scanner.next();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(next.getBytes(), 0, next.getBytes().length, InetAddress.getByName(host), port);
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
ds.send(dp);
ds.close();
}
};
try {
sender.send();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}