FFmpeg开发笔记(四):ffmpeg解码的基本流程详解
若该文为原创文章,未经允许不得转载
原博主博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936
原博主博客导航:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/article/details/102478062
本文章博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/article/details/108573195
各位读者,知识无穷而人力有穷,要么改需求,要么找专业人士,要么自己研究
红胖子(红模仿)的博文大全:开发技术集合(包含Qt实用技术、树莓派、三维、OpenCV、OpenGL、ffmpeg、OSG、单片机、软硬结合等等)持续更新中…(点击传送门)
FFmpeg开发专栏(点击传送门)
上一篇:《FFmpeg开发笔记(三):ffmpeg介绍、windows编译以及开发环境搭建》
下一篇:敬请期待
前言
ffmpeg涉及了很多,循序渐进,本篇描述基本的解码流程。
Demo
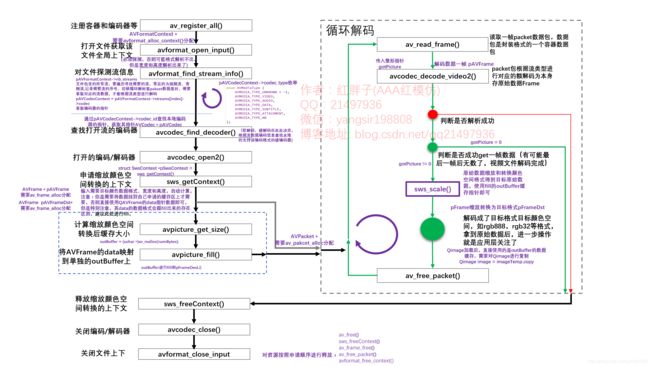
ffmpeg解码流程
ffmpeg的解码和编码都遵循其基本的执行流程。
基本流程如下:

步骤一:注册:
使用ffmpeg对应的库,都需要进行注册,可以注册子项也可以注册全部。
步骤二:打开文件:
打开文件,根据文件名信息获取对应的ffmpeg全局上下文。
步骤三:探测流信息:
一定要探测流信息,拿到流编码的编码格式,不探测流信息则其流编码器拿到的编码类型可能为空,后续进行数据转换的时候就无法知晓原始格式,导致错误。
步骤四:查找对应的解码器
依据流的格式查找解码器,软解码还是硬解码是在此处决定的,但是特别注意是否支持硬件,需要自己查找本地的硬件解码器对应的标识,并查询其是否支持。普遍操作是,枚举支持文件后缀解码的所有解码器进行查找,查找到了就是可以硬解了(此处,不做过多的讨论,对应硬解码后续会有文章进行进一步研究)。
(注意:解码时查找解码器,编码时查找编码器,两者函数不同,不要弄错了,否则后续能打开但是数据是错的)
步骤五:打开解码器
打开获取到的解码器。
步骤六:申请缩放数据格式转换结构体
此处特别注意,基本上解码的数据都是yuv系列格式,但是我们显示的数据是rgb等相关颜色空间的数据,所以此处转换结构体就是进行转换前到转换后的描述,给后续转换函数提供转码依据,是很关键并且非常常用的结构体。
步骤七:申请缓存区
申请一个缓存区outBuffer,fill到我们目标帧数据的data上,比如rgb数据,QAVFrame的data上存是有指定格式的数据,且存储有规则,而fill到outBuffer(自己申请的目标格式一帧缓存区),则是我们需要的数据格式存储顺序。
举个例子,解码转换后的数据为rgb888,实际直接用data数据是错误的,但是用outBuffer就是对的,所以此处应该是ffmpeg的fill函数做了一些转换。
进入循环解码:
步骤八:获取一帧packet
拿取封装的一个packet,判断packet数据的类型进行解码拿到存储的编码数据
步骤九:数据转换
使用转换函数结合转换结构体对编码的数据进行转换,那拿到需要的目标宽度、高度和指定存储格式的原始数据。
步骤十:自行处理
拿到了原始数据自行处理。
不断循环,直到拿取pakcet函数成功,但是无法got一帧数据,则代表文件解码已经完成。
帧率需要自己控制循环,此处只是循环拿取,可加延迟等。
步骤十一:释放QAVPacket
此处要单独列出是因为,其实很多网上和开发者的代码:
在进入循环解码前进行了av_new_packet,循环中未av_free_packet,造成内存溢出;
在进入循环解码前进行了av_new_packet,循环中进行av_free_pakcet,那么一次new对应无数次free,在编码器上是不符合前后一一对应规范的。
查看源代码,其实可以发现av_read_frame时,自动进行了av_new_packet(),那么其实对于packet,只需要进行一次av_packet_alloc()即可,解码完后av_free_packet。
执行完后,返回执行“步骤八:获取一帧packet”,一次循环结束。
步骤十二:释放转换结构体
全部解码完成后,安装申请顺序,进行对应资源的释放。
步骤十三:关闭解码/编码器
关闭之前打开的解码/编码器。
步骤十四:关闭上下文
关闭文件上下文后,要对之前申请的变量按照申请的顺序,依次释放。
另附上完成的详细解码流程图:
本文章博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/article/details/108573195
ffmpeg解码相关变量
AVFormatContext
AVFormatContext描述了一个媒体文件或媒体流的构成和基本信息,位于avformat.h文件中。
AVInputFormat
AVInputFormat 是类似COM 接口的数据结构,表示输入文件容器格式,着重于功能函数,一种文件容器格式对应一个AVInputFormat 结构,在程序运行时有多个实例,位于avoformat.h文件中。
AVDictionary
AVDictionary 是一个字典集合,键值对,用于配置相关信息。
AVCodecContext
AVCodecContext是一个描述编解码器上下文的数据结构,包含了众多编解码器需要的参数信息,位于avcodec.h文件中。
AVPacket
AVPacket是FFmpeg中很重要的一个数据结构,它保存了解复用(demuxer)之后,解码(decode)之前的数据(仍然是压缩后的数据)和关于这些数据的一些附加的信息,如显示时间戳(pts),解码时间戳(dts),数据时长(duration),所在流媒体的索引(stream_index)等等。
使用前,使用av_packet_alloc()分配,
AVCodec
AVCodec是存储编解码器信息的结构体,位于avcodec.h文件中。
AVFrame
AVFrame中存储的是经过解码后的原始数据。在解码中,AVFrame是解码器的输出;在编码中,AVFrame是编码器的输入。
使用前,使用av_frame_alloc()进行分配。
struct SwsContext
使用前,使用sws_getContext()进行获取,主要用于视频图像的转换。
ffmpeg解码流程相关函数原型
av_register_all
void av_register_all(void);
初始化libavformat并注册所有muxer、demuxer和协议。如果不调用此函数,则可以选择想要指定注册支持的哪种格式,通过av_register_input_format()、av_register_output_format()。
avformat_open_input
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps,
const char *url,
AVInputFormat *fmt,
AVDictionary **options);
打开输入流并读取标头。编解码器未打开。流必须使用avformat_close_input()关闭,返回0-成功,<0-失败错误码。
- 参数一:指向用户提供的AVFormatContext(由avformat_alloc_context分配)的指针。
- 参数二:要打开的流的url
- 参数三:fmt如果非空,则此参数强制使用特定的输入格式。否则将自动检测格式。
- 参数四:包含AVFormatContext和demuxer私有选项的字典。返回时,此参数将被销毁并替换为包含找不到的选项。都有效则返回为空。
avformat_find_stream_info
int avformat_find_stream_info(AVFormatContext *ic, AVDictionary **options);
读取检查媒体文件的数据包以获取具体的流信息,如媒体存入的编码格式。
- 参数一:媒体文件上下文。
- 参数二:字典,一些配置选项。
avcodec_find_decoder
AVCodec *avcodec_find_decoder(enum AVCodecID id);
查找具有匹配编解码器ID的已注册解码器,解码时,已经获取到了,注册的解码器可以通过枚举查看,枚举太多,略。
avcodec_open2
int avcodec_open2(AVCodecContext *avctx,
const AVCodec *codec,
AVDictionary **options);
初始化AVCodeContext以使用给定的AVCodec。
sws_getContext
struct SwsContext *sws_getContext(int srcW,
int srcH,
enum AVPixelFormat srcFormat,
int dstW,
int dstH,
enum AVPixelFormat dstFormat,
int flags, SwsFilter *srcFilter,
SwsFilter *dstFilter,
const double *param);
分配并返回一个SwsContext。需要它来执行sws_scale()进行缩放/转换操作。
avpicture_get_size
int avpicture_get_size(enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt, int width, int height);
返回存储具有给定参数的图像的缓存区域大小。
- 参数一:图像的像素格式
- 参数二:图像的像素宽度
- 参数三:图像的像素高度
avpicture_fill
int avpicture_fill(AVPicture *picture,
const uint8_t *ptr,
enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt,
int width,
int height);
根据指定的图像、提供的数组设置数据指针和线条大小参数。
- 参数一:输入AVFrame指针,强制转换为AVPciture即可。
- 参数二:映射到的缓存区,开发者自己申请的存放图像数据的缓存区。
- 参数三:图像数据的编码格式。
- 参数四:图像像素宽度。
- 参数五:图像像素高度。
av_read_frame
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);
返回流的下一帧。此函数返回存储在文件中的内容,不对有效的帧进行验证。获取存储在文件中的帧中,并为每个调用返回一个。不会的省略有效帧之间的无效数据,以便给解码器最大可用于解码的信息。
返回0是成功,小于0则是错误,大于0则是文件末尾,所以大于等于0是返回成功。
avcodec_decode_video2
int avcodec_decode_video2(AVCodecContext *avctx,
AVFrame *picture,
int *got_picture_ptr,
const AVPacket *avpkt);
将大小为avpkt->size from avpkt->data的视频帧解码为图片。一些解码器可以支持单个avpkg包中的多个帧,解码器将只解码第一帧。出错时返回负值,否则返回字节数,如果没有帧可以解压缩,则为0。
- 参数一:编解码器上下文。
- 参数二:将解码视频帧存储在AVFrame中。
- 参数三:输入缓冲区的AVPacket。
- 参数四:如果没有帧可以解压,那么得到的图片是0,否则,它是非零的。
sws_scale
int sws_scale(struct SwsContext *c,
const uint8_t *const srcSlice[],
const int srcStride[],
int srcSliceY,
int srcSliceH,
uint8_t *const dst[],
const int dstStride[]);
在srcSlice中缩放图像切片并将结果缩放在dst中切片图像。切片是连续的序列图像中的行。
- 参数一:以前用创建的缩放上下文*sws_getContext()。
- 参数二:包含指向源片段,就是AVFrame的data。
- 参数三:包含每个平面的跨步的数组,其实就是AVFrame的linesize。
- 参数四:切片在源图像中的位置,从开始计数0对应切片第一行的图像,所以直接填0即可。
- 参数五:源切片的像素高度。
- 参数六:目标数据地址映像,是目标AVFrame的data。
- 参数七:目标每个平面的跨步的数组,就是linesize。
av_free_packet
void av_free_packet(AVPacket *pkt);
释放一个包。
avcodec_close
int avcodec_close(AVCodecContext *avctx);
关闭给定的avcodeContext并释放与之关联的所有数据(但不是AVCodecContext本身)。
avformat_close_input
void avformat_close_input(AVFormatContext **s);
关闭打开的输入AVFormatContext。释放它和它的所有内容并将*s设置为空。
Demo源码
void FFmpegManager::testDecode()
{
// QString fileName = "test/1.avi";
QString fileName = "test/1.mp4";
// ffmpeg相关变量预先定义与分配
AVFormatContext *pAVFormatContext = 0; // ffmpeg的全局上下文,所有ffmpeg操作都需要
AVInputFormat *pAVInputFormat = 0; // ffmpeg的输入格式结构体
AVDictionary *pAVDictionary = 0; // ffmpeg的字典option,各种参数给格式编解码配置参数的
AVCodecContext *pAVCodecContext = 0; // ffmpeg编码上下文
AVCodec *pAVCodec = 0; // ffmpeg编码器
AVPacket *pAVPacket = 0; // ffmpag单帧数据包
AVFrame *pAVFrame = 0; // ffmpeg单帧缓存
AVFrame *pAVFrameRGB32 = 0; // ffmpeg单帧缓存转换颜色空间后的缓存
struct SwsContext *pSwsContext = 0; // ffmpag编码数据格式转换
int ret = 0; // 函数执行结果
int videoIndex = -1; // 音频流所在的序号
int gotPicture = 0; // 解码时数据是否解码成功
int numBytes = 0; // 解码后的数据长度
uchar *outBuffer = 0; // 解码后的数据存放缓存区
pAVFormatContext = avformat_alloc_context(); // 分配
pAVPacket = av_packet_alloc(); // 分配
pAVFrame = av_frame_alloc(); // 分配
pAVFrameRGB32 = av_frame_alloc(); // 分配
if(!pAVFormatContext || !pAVPacket || !pAVFrame || !pAVFrameRGB32)
{
LOG << "Failed to alloc";
goto END;
}
// 步骤一:注册所有容器和编解码器(也可以只注册一类,如注册容器、注册编码器等)
av_register_all();
// 步骤二:打开文件(ffmpeg成功则返回0)
LOG << "文件:" << fileName << ",是否存在:" << QFile::exists(fileName);
ret = avformat_open_input(&pAVFormatContext, fileName.toUtf8().data(), pAVInputFormat, 0);
if(ret)
{
LOG << "Failed";
goto END;
}
// 步骤三:探测流媒体信息
// Assertion desc failed at libswscale/swscale_internal.h:668
// 入坑:因为pix_fmt为空,需要对编码器上下文进一步探测
ret = avformat_find_stream_info(pAVFormatContext, 0);
if(ret < 0)
{
LOG << "Failed to avformat_find_stream_info(pAVCodecContext, 0)";
goto END;
}
// 打印文件信息
LOG << "视频文件包含流信息的数量:" << pAVFormatContext->nb_streams;
// 在Qt中av_dump_format不会进行命令行输出
// av_dump_format(pAVFormatContext, 1, fileName.toUtf8().data(), 0);
// 步骤三:提取流信息,提取视频信息
for(int index = 0; index < pAVFormatContext->nb_streams; index++)
{
pAVCodecContext = pAVFormatContext->streams[index]->codec;
switch (pAVCodecContext->codec_type)
{
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_UNKNOWN:
LOG << "流序号:" << index << "类型为:" << "AVMEDIA_TYPE_UNKNOWN";
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO:
LOG << "流序号:" << index << "类型为:" << "AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO";
videoIndex = index;
LOG;
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:
LOG << "流序号:" << index << "类型为:" << "AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO";
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA:
LOG << "流序号:" << index << "类型为:" << "AVMEDIA_TYPE_DATA";
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE:
LOG << "流序号:" << index << "类型为:" << "AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE";
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_ATTACHMENT:
LOG << "流序号:" << index << "类型为:" << "AVMEDIA_TYPE_ATTACHMENT";
break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_NB:
LOG << "流序号:" << index << "类型为:" << "AVMEDIA_TYPE_NB";
break;
default:
break;
}
// 已经找打视频品流
if(videoIndex != -1)
{
break;
}
}
if(videoIndex == -1 || !pAVCodecContext)
{
LOG << "Failed to find video stream";
goto END;
}
// 步骤四:对找到的视频流寻解码器
pAVCodec = avcodec_find_decoder(pAVCodecContext->codec_id);
if(!pAVCodec)
{
LOG << "Fialed to avcodec_find_decoder(pAVCodecContext->codec_id):"
<< pAVCodecContext->codec_id;
goto END;
}
// 步骤五:打开解码器
ret = avcodec_open2(pAVCodecContext, pAVCodec, NULL);
if(ret)
{
LOG << "Failed to avcodec_open2(pAVCodecContext, pAVCodec, pAVDictionary)";
goto END;
}
LOG << pAVCodecContext->width << "x" << pAVCodecContext->height;
// 步骤六:对拿到的原始数据格式进行缩放转换为指定的格式高宽大小
// Assertion desc failed at libswscale/swscale_internal.h:668
// 入坑:因为pix_fmt为空,需要对编码器上下文进一步探测
pSwsContext = sws_getContext(pAVCodecContext->width,
pAVCodecContext->height,
pAVCodecContext->pix_fmt,
pAVCodecContext->width,
pAVCodecContext->height,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
SWS_FAST_BILINEAR,
0,
0,
0);
numBytes = avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
pAVCodecContext->width,
pAVCodecContext->height);
outBuffer = (uchar *)av_malloc(numBytes);
// pAVFrame32的data指针指向了outBuffer
avpicture_fill((AVPicture *)pAVFrameRGB32,
outBuffer,
AV_PIX_FMT_RGBA,
pAVCodecContext->width,
pAVCodecContext->height);
// 此处无需分配
// av_read_frame时他会分配,av_new_packet多此一举,正好解释了一次new和多次free的问题
// av_new_packet(pAVPacket, pAVCodecContext->width * pAVCodecContext->height);
// 步骤七:读取一帧数据的数据包
while(av_read_frame(pAVFormatContext, pAVPacket) >= 0)
{
if(pAVPacket->stream_index == videoIndex)
{
// 步骤八:对读取的数据包进行解码
ret = avcodec_decode_video2(pAVCodecContext, pAVFrame, &gotPicture, pAVPacket);
if(ret < 0)
{
LOG << "Failed to avcodec_decode_video2(pAVFormatContext, pAVFrame, &gotPicture, pAVPacket)";
break;
}
// 等于0代表拿到了解码的帧数据
if(!gotPicture)
{
LOG << "no data";
break;
}else{
sws_scale(pSwsContext,
(const uint8_t * const *)pAVFrame->data,
pAVFrame->linesize,
0,
pAVCodecContext->height,
pAVFrameRGB32->data,
pAVFrameRGB32->linesize);
QImage imageTemp((uchar *)outBuffer,
pAVCodecContext->width,
pAVCodecContext->height,
QImage::Format_RGBA8888);
QImage image = imageTemp.copy();
LOG << image.save("1.jpg");
}
av_free_packet(pAVPacket);
}
QThread::msleep(100);
}
END:
LOG << "释放回收资源";
if(outBuffer)
{
av_free(outBuffer);
outBuffer = 0;
}
if(pSwsContext)
{
sws_freeContext(pSwsContext);
pSwsContext = 0;
LOG << "sws_freeContext(pSwsContext)";
}
if(pAVFrameRGB32)
{
av_frame_free(&pAVFrameRGB32);
pAVFrame = 0;
LOG << "av_frame_free(pAVFrameRGB888)";
}
if(pAVFrame)
{
av_frame_free(&pAVFrame);
pAVFrame = 0;
LOG << "av_frame_free(pAVFrame)";
}
if(pAVPacket)
{
av_free_packet(pAVPacket);
pAVPacket = 0;
LOG << "av_free_packet(pAVPacket)";
}
if(pAVCodecContext)
{
avcodec_close(pAVCodecContext);
pAVCodecContext = 0;
LOG << "avcodec_close(pAVCodecContext);";
}
if(pAVFormatContext)
{
avformat_free_context(pAVFormatContext);
pAVFormatContext = 0;
LOG << "avformat_free_context(pAVFormatContext)";
}
}
工程模板v1.1.0
对应工程模板v1.1.0
上一篇:《FFmpeg开发笔记(三):ffmpeg介绍、windows编译以及开发环境搭建》
下一篇:敬请期待
原博主博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936
原博主博客导航:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/article/details/102478062
本文章博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/article/details/108573195