【Java单元测试】如何进行单元测试、异常测试、参数化测试、超时测试、测试多线程
Junit单元测试的步骤
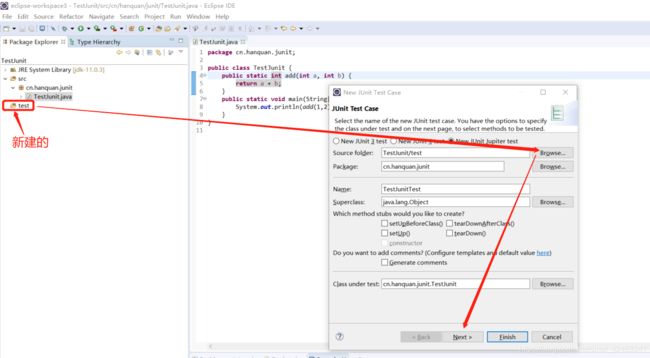
(1)新建一个单元测试
(2)选择位置
(3)选择需要测试的方法
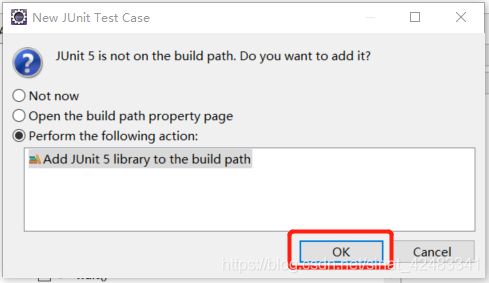
(4)是否将Junit 4添加到ClassPath中
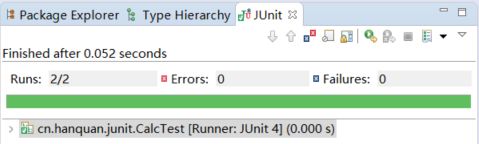
(5)自动生成的测试类
(6) 然后就可以编写单元测试了
单元测试的编写
(1)Assert断言
package cn.hanquan.junit;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class CalcTest {
@Test
void testAdd() {
assertEquals(3, new Calc().add(1, 2));
assertEquals(30, new Calc().add(10, 20));
assertEquals(159, new Calc().add(150, 9));
}
}
(2)Junit Fixture:Junit4 @Before、@After的使用
初始化测试资源称为Fixture
@Before:创建初始化对象,在执行所有每一个@Test之前都会执行一次。如is = new FileInputStream()
@After:销毁@Before创建的测试对象,在执行所有每一个@Test之后都会执行一次。如is.close()
@BeforeClass:在其中初始化非常耗时的对象,如:数据库的连接
@AfterClass:清理@BeforeClass创建的资源,比如:断开数据库连接
注意:在JUnit5中,@Before @After 注解不执行
官方文档:https://junit.org/junit5/docs/current/user-guide/#migrating-from-junit4-tips
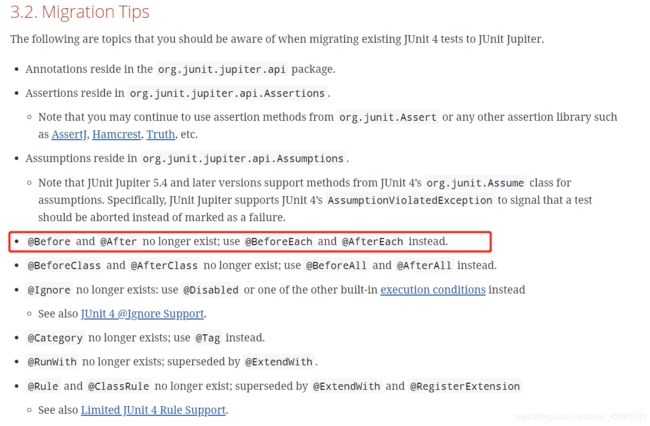
@Before 和@After 被 @BeforeEach 和@AfterEach给替代了。
还有一些其他的的注解也被替代了。
在JUnit5的环境下写了@Before @After , 讲道理 IDE应该提醒 该注解已经不存在, 然而Eclipse并没有这样的提示。
代码示例
被测试的类Calc.java
package cn.hanquan.junit;
public class Calc {
public Calc() {
}
public int add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + (a + b));
return a + b;
}
}
测试类CalcTest
package cn.hanquan.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CalcTest {
Calc c;
@Before
public void initialize() {
System.out.println(">>>>>>> initializing >>>>>>>");
c = new Calc();
}
@Test
public void testAdd1() {
assertEquals(3, c.add(1, 2));
assertEquals(30, c.add(10, 20));
assertEquals(159, c.add(150, 9));
}
@Test
public void testAdd2() {
assertEquals(4, c.add(2, 2));
assertEquals(36, c.add(13, 23));
assertEquals(1000, c.add(-3000, 4000));
}
@After
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("<<<<<<<<< cleaning <<<<<<<<<\n");
}
}
>>>>>>> initializing >>>>>>>
1+2=3
10+20=30
150+9=159
<<<<<<<<< cleaning <<<<<<<<<
>>>>>>> initializing >>>>>>>
2+2=4
13+23=36
-3000+4000=1000
<<<<<<<<< cleaning <<<<<<<<<
(3)测试抛出的异常是否符合预期
package cn.hanquan.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CalcTest {
Calc c;
@Before
public void initialize() {
System.out.println(">>>>>>> initializing >>>>>>>");
c = new Calc();
}
@Test // 测试输出是否符合预期
public void testAdd2() {
assertEquals(20, c.divide(100, 5));
}
@Test(expected = ArithmeticException.class) // 针对异常进行的测试
public void testAdd3() {
c.divide(8, 0);
}
@After
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("<<<<<<<<< cleaning <<<<<<<<<\n");
}
}
(4)参数化测试:一次运行多个测试
JUnit参数化测试的五个步骤:
(1)为准备使用参数化测试的测试类指定特殊的运行器 org.junit.runners.Parameterized
(2)为测试类声明几个变量,分别用于存放期望值和测试所用数据
(3)为测试类声明一个带有参数的公共构造函数,并在其中为第二个环节中声明的几个变量赋值
(4)为测试类声明一个使用注解 org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters 修饰的,返回值为 java.util.Collection 的公共静态方法,并在此方法中初始化所有需要测试的参数对
(5)编写测试方法,使用定义的变量作为参数进行测试。
示例代码
package cn.hanquan.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
/**
* 使用Junit进行参数化测试的步骤
*
* @author Buuug
*
*/
//(1)测试类指定特殊的运行器org.junit.runners.Parameterized
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class CalcTest {
Calc c;
@Before
public void bef() {
System.out.println("Before");
c = new Calc();
}
// (2)为测试类声明几个变量,分别用于存放期望值和测试所用数据。此处我只放了测试所有数据,没放期望值。
private int n1;
private int n2;
private int result;
// (3)为测试类声明一个带有参数的公共构造函数,并在其中为第二个环节中声明的几个变量赋值。
public CalcTest(int n1, int n2, int result) {
super();
this.n1 = n1;
this.n2 = n2;
this.result = result;
}
// (4)为测试类声明一个使用注解 org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters 修饰的,返回值为
// java.util.Collection 的公共静态方法,并在此方法中初始化所有需要测试的参数对。
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{
4, 2, 2 }, {
9, 3, 3 }, {
-100, 25, -4 }, {
88, 2, 44 }, {
25, 5, 5 },
{
72, 8, 9 }, {
42, 6, 7 }, {
1, 1, 1 }, {
1000000, 333333, 888888 }, {
56, 8, 7 }, {
55, 55, 1 },
{
12, 6, 2 }, {
21, 10, 2 }, {
70, 20, 3 }, {
45, 15, 3 }, {
46, 15, 3 }, {
47, 3, 15 }, {
2, 1, 2 } });
}
// (5)步骤五:编写测试方法,使用定义的变量作为参数进行测试。
@Test
public void testAdd() {
assertEquals(result, c.divide(n1, n2));
}
@After
public void aft() {
System.out.println("After\n");
}
}
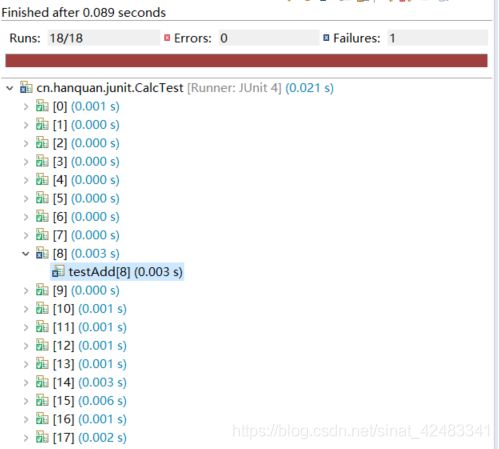
测试结果
(5)超时测试:设定运行时间限制,测试是否运行时间过长
在50行加一个@Test(timeout = 1)就行了。
一开始想通过Thread.sleep(1000);这种形式拖延时间,但是抛出了ThreadInterrupted异常,(没有具体去了解原因),然后我又在@Test的方法里加了一个Lambda表达式开启的多线程,结果开启之后,不管sleep多长也没有影响了,都可以在限定时间内结束,我寻思着是不是要join一下才可以。(后来加了Join,确实如此。)
我在被测试的类上面加了一些无用的循环拖延时间,然后把时间限定设置为1ms。看看效果吧:
示例代码1:没有使用多线程,只是加了没用的循环拖延时间
package cn.hanquan.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
/**
* 使用Junit进行参数化测试的步骤
*
* @author Buuug
*
*/
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class CalcTest {
Calc c;
@Before
public void bef() {
System.out.println("Before");
c = new Calc();
}
private int n1;
private int n2;
private int result;
public CalcTest(int n1, int n2, int result) {
super();
this.n1 = n1;
this.n2 = n2;
this.result = result;
}
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{
4, 2, 2 }, {
9, 3, 3 }, {
-100, 25, -4 }, {
88, 2, 44 }, {
25, 5, 5 },
{
72, 8, 9 }, {
42, 6, 7 }, {
1, 1, 1 }, {
1000000, 333333, 888888 }, {
56, 8, 7 }, {
55, 55, 1 },
{
12, 6, 2 }, {
21, 10, 2 }, {
70, 20, 3 }, {
45, 15, 3 }, {
46, 15, 3 }, {
47, 3, 15 }, {
2, 1, 2 } });
}
@Test(timeout = 1) // 设置超时时间
public void testAdd() {
assertEquals(result, c.divide(n1, n2));
}
@After
public void aft() {
System.out.println("After\n");
}
}
测试结果
示例代码2:使用多线程sleep模拟运行耗时,记得join一下主线程,否则都来不及计算就完成了
CalcTest.java单元测试:时间限制为501ms。
package cn.hanquan.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
/**
* 使用Junit进行参数化测试的步骤
*
* @author Buuug
*
*/
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class CalcTest {
Calc c;
@Before
public void bef() {
System.out.println("Before");
c = new Calc();
}
private int n1;
private int n2;
private int result;
public CalcTest(int n1, int n2, int result) {
super();
this.n1 = n1;
this.n2 = n2;
this.result = result;
}
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{
4, 2, 2 }, {
9, 3, 3 }, {
-100, 25, -4 }, {
88, 2, 44 }, {
25, 5, 5 },
{
72, 8, 9 }, {
42, 6, 7 }, {
1, 1, 1 }, {
56, 8, 7 }, {
55, 55, 1 }, {
12, 6, 2 }, {
21, 10, 2 },
{
70, 20, 3 }, {
45, 15, 3 }, {
46, 15, 3 }, {
47, 3, 15 }, {
2, 1, 2 } });
}
@Test(timeout = 1000) // 设置超时时间
public void testAdd() {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
// ()表示的是函数的参数,这里无参
assertEquals(result, c.divide(n1, n2));
});
t.start();
try {
t.join();// join
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@After
public void aft() {
System.out.println("After\n");
}
}
- 被测试的类:
Calc,里面Thread.sleep(500);。由于时间限制为501ms,因此仅空余出1ms给它做计算。
package cn.hanquan.junit;
public class Calc {
public Calc() {
}
public int divide(int a, int b) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + (a / b));
return a / b;
}
}
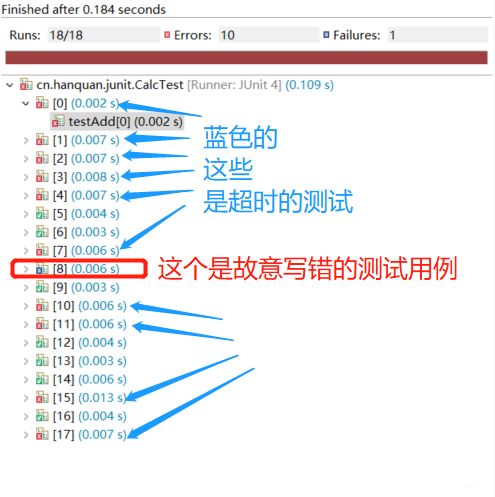
运行结果:部分未通过
那个抛出java.lang.InterruptedException异常的,是因为没有在限制时间内运行完毕,被打断了吧?(待解决,暂时没有深入研究)