MySQL基础
狂神说视频学习笔记
该笔记适合有一点基础的同学 来记录回顾
有一些特别基础的地方没有记录
零基础的还是到一些官方教程进行学习比较好
文章目录
- 1、初识MySQL
-
- 1.1、数据库分类
- 1.2、版本
- 1.3、安装
-
- 1.3.1、安装步骤
- 1.3.4、有关问题
- 1.4、基本命令操作
- 1.5、四大类语言
- 2、操作数据库
- 2.1、操作数据库
- 2.2、数据类型
- 2.3、每个数据库必要的列标签
- 2.4、创建数据库和表
- 2.5、数据库引擎
- 2.6、修改删除
- 3、MySQL数据管理
-
- 3.1、外键(了解即可)
- 3.2、DML语言(全部记住)
- 3.3、添加
- 3.4、修改
- 3.5、删除
- 4、DQL查询数据(最重点)
-
- 4.1、查询全部字段
- 4.2、去重 distinct
- 4.3、其他查询
- 4.4、模糊查询
- 4.5、联表join查询(重难点)
- 注意on和where的区别
- 总结:
- 4.6、自连接(了解)
- 4.7、分页和排序
- 4.8、子查询和嵌套查询
- 4.9、分组和过滤
- 4.10、select总结
- 5、MySQL函数
-
- 5.1、常用函数
- 5.2、聚合函数(常用)
- 6、事务
- 7、索引
-
- 7.1、索引的分类
- 8、权限管理和备份
-
- 8.1、权限
- 8.2、备份
- 9、规范数据库设计
-
- 9.1、为什么需要设计
- 9.2、三大范式
- 10、JDBC(重点)
-
- 10.1、数据库驱动
- 10.2、JDBC
- 10.3、第一个JDBC程序
-
- 10.3.1、JDBC中的对象
- 10.4、SQL注入
- 10.5、PreParedStatement对象
- 10.6、JDBC事务
- 10.7、数据库连接池
1、初识MySQL
1.1、数据库分类
关系型数据库:(SQL)
- MySQL、Oracle、Sql Server、DB2、SQLlite
- 通过表和表之间,行和列之间的关系进行数据的存储:学员信息表、考勤表、……
非关系型数据库:(NoSQL:Not Only SQL)
- Redis、MongoDB
- 非关系型数据库:对象存储,通过对象的自身的属性来决定
MySQL是最好的RDBMS(Relational Database Management System,关系数据库管理系统)应用软件之一。
1.2、版本
5.7或8.0
1.3、安装
尽量不使用exe,走注册表卸载复杂
建议使用压缩包安装
1.3.1、安装步骤
-
解压
-
移动到自己的目录
-
添加环境变量,path中添加bin目录
-
在根目录下新建配置文件 my.ini
-
[mysqld] basedir=D:\mysql-5.7.19\ datadir=D:\mysql-5.7.19\data\ # data会自动生成 port=3306 skip-grant-tables # 跳过密码验证 -
启动管理员模式的CMD,路径切换到 bin 目录,然后输入
mysqld -install -
输入
mysqld --initialize-insecure --user=mysql初始化数据文件(会建立data目录) -
启动mysql
net start mysql -
mysql -uroot -p进入管理页面 修改密码update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='root' and Host = 'localhost'; -
刷新权限
flush privileges; -
修改 my.ini 文件,删除最后一行,或者注释掉
-
重启mysql ,关闭
net stop mysql启动net start mysql -
mysql -uroot -p123456如果可以进入管理界面就安装好了
1.3.4、有关问题
- 缺少组件 .dll 等文件,搜索进行安装
- 命令输错了
- mysql命令需要分号
1.4、基本命令操作
所有语句用分号结尾
sql不区分大小写
show databases;查看所有数据库
use school;切换数据库
show tables;查看数据库中所有表
describe student;查看表所有信息
--单行注释
/*
多行注释
*/
1.5、四大类语言
DDL 定义(define)
DML 操作(Manage)
DQL 查询(Query)
DCL 控制(Control)
2、操作数据库
2.1、操作数据库
1、创建数据库
create database [if not exists] newdatabase;
2、删除数据库
drop database [if exists] newdatabase;
3、使用数据库
use newdatabase;
use `school`;
-- 如果数据库名是关键字需要加 ` ` 括起来
4、查看所有数据库
show databases;
2.2、数据类型
1、数值(数值设置的长度和零填充的长度有关,不会限制实际的数值大小)
| 名称 | 描述 | 位数 |
|---|---|---|
| tinyint | 十分小的数据 | 1个字节 |
| smallint | 较小的数据 | 2个字节 |
| mediumint | 中等大小的数据 | 3个字节 |
| int | 标准的数据(常用) | 4个字节 |
| bigint | 较大的数据 | 8个字节 |
| float | 浮点数 | 4个字节 |
| double | 浮点数(精度) | 8个字节 |
| decimal | 字符串形式的浮点数,金融计算使用 |
2、字符串
| 名称 | 描述 | 位数 |
|---|---|---|
| char | 字符串固定大小的 | 0~255 |
| varchar | 可变字符串(常用的变量) | 0~65535 |
| tinytext | 微型文本 | 0~255 |
| text | 文本(大文本) | 0~65535 |
3、时间日期
| 名称 | 格式 | 分解机覅 |
|---|---|---|
| date | YYYY-MM-DD | 日期格式 |
| time | HH:mm:ss | 时间格式 |
| datatime | YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss | 最常用的时间格式 |
| timestamp | 1234567891234 | 时间戳 |
| year | 2020 | 年份 |
4、null
没有值,未知
不要使用null进行运算,结果永远为null
2.3、每个数据库必要的列标签
- id 主键
- `version` 乐观锁
- is_delete 伪删除
- gmt_create 创建时间
- gmt_update 修改时间
2.4、创建数据库和表
注意:使用英文的符号
大小写不敏感
表名和字段尽量都使用 ` ` 括起来,以防冲突
字符串使用单引号或双引号,一般使用单引号
**所有语句后面加逗号 , 最后一个不用加 **
1、创建一个表 例如:
create table if not exists `student`(
`id` int(4) not null auto_increment comment '学号',
`name` varchar(30) not null default '匿名' comment '姓名',
`pwd` varchar(20) not null default '123456' comment '密码',
`gender` varchar(2) not null default '女' comment '性别',
`birthday` datetime default null comment '出生日期',
`address` varchar(100) default null comment '家庭住址',
`email` varchar(50) default null comment '邮箱',
primary key (`id`)
)engine=innodb default charset = utf8;
格式:
create table [if not exists] `student`(
`字段名` 列属性 [属性] [索引] [注释],
`字段名` 列属性 [属性] [索引] [注释],
……
`字段名` 列属性 [属性] [索引] [注释]
)[表类型][字符集设置][注释];
2、技巧
show create database school; -- 查看创建数据库的语句
show create table student; -- 查看创建数据表的语句
desc student; -- 查看表的结构
2.5、数据库引擎
| MyISAM | InnoDB | |
|---|---|---|
| 事务支持 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 数据行锁定 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 外键 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 全文索引 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 表空间的大小 | 较小 | 较大,约为2倍 |
常规使用操作:
- MyISAM:节约空间,速度较快
- InnoDB:安全性高,事务的处理,多表多用户操作
在物理空间存在的区别:
- InnoDB在数据库表中只有一个*.frm 文件,以及上级目录下的 ibdata1 文件
- MyISAM 对应的文件: *.frm 表结构的定义文件, *.myd 数据文件, *.myi 索引文件
2.6、修改删除
1、修改表
-- 修改表名
alter table 表名 rename as 新表名;
alter table student rename as student1 ;
-- 添加字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名 列属性;
alter table student add age int(11) ;
-- 修改约束
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 [列属性];
alter table student modify age varchar(11) ;
-- 字段重命名
alter table 表名 change 旧名 新名 [列属性];
alter table student change age age1 int(1) ;
-- 删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
alter table student drop age ;
2、删除表
-- 删除表
drop table [if exists] 表名;
drop table if exists student;
3、MySQL数据管理
3.1、外键(了解即可)
3.2、DML语言(全部记住)
- insert
- update
- delet
3.3、添加
-- 语法
insert into 表名 [(`字段1`,`字段2`,`字段3`)] values('值1','值2','值3');
insert into `student` ( `id`, `name`, `age`) values (1001 , 'mars', 19);
-- 插入多条数据
insert into `student` ( `id`, `name`, `age`) values (1001 , 'mars', 19), (1002,'daming',20),(1003,'lilei',22);
-- 添加多行数据必须要对应
注意 ` ` 和 ’ ’ 的区别
3.4、修改
模板: update 表名 set 列标签=值1,列标签=值2 where 条件;
例子:update `student` set `name` = ‘mars’ , `gender` = ‘男’ where id = 1;
如果不加where 会对所有数据进行操作
条件:where子句 运算符
大于、小于、大等于、小等于、等于省略
| 操作符 | 含义 | 示例 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| <> 或 != | 不等于 | where `id` <> 8 | id不等于8 |
| between…and… | 在什么之间 | where `id` between 2 and 5 | [2,5] |
| and 或 && | 与 | where `id` > 8 and `age` between 10 and 18 | 同时满足 |
| or 或 || | 或 | where `id` > 8 and `age` between 10 or18 | 满足一个即可 |
| not 或 ! | 非 | where not `id` = 1 | id不等于· |
3.5、删除
-- 语法
delete from 表名 where 条件;
delete from `student` where 'id'=1;
-- 如果不加 where条件 会删除所有数据
-- 一般使用清空命令:
truncate 表名
(表的结构和索引等都不会变)
相同点:都能删除数据,都不会删除表机构
不同点:
- truncate 重新设置自增列 计数器会归零
- truncate 不会影响事务
delete删除后,重启数据库会有不同现象:
- InnoDB自增列会从1开始(存在内存中,断电即失)
- MyISAM继续从上一个自增量开始(存在文件中,不会丢失)
4、DQL查询数据(最重点)
建表插入数据,方便练习
create database if not exists `school`;
-- 创建一个school数据库
use `school`;
-- 创建学生表
drop table if exists `student`;
create table `student`(
`studentno` int(4) not null comment '学号',
`loginpwd` varchar(20) default null,
`studentname` varchar(20) default null comment '学生姓名',
`sex` tinyint(1) default null comment '性别,0或1',
`gradeid` int(11) default null comment '年级编号',
`phone` varchar(50) not null comment '联系电话,允许为空',
`address` varchar(255) not null comment '地址,允许为空',
`borndate` datetime default null comment '出生时间',
`email` varchar (50) not null comment '邮箱账号允许为空',
`identitycard` varchar(18) default null comment '身份证号',
primary key (`studentno`),
unique key `identitycard`(`identitycard`),
key `email` (`email`)
)engine=myisam default charset=utf8;
-- 创建年级表
drop table if exists `grade`;
create table `grade`(
`gradeid` int(11) not null auto_increment comment '年级编号',
`gradename` varchar(50) not null comment '年级名称',
primary key (`gradeid`)
) engine=innodb auto_increment = 6 default charset = utf8;
-- 创建科目表
drop table if exists `subject`;
create table `subject`(
`subjectno`int(11) not null auto_increment comment '课程编号',
`subjectname` varchar(50) default null comment '课程名称',
`classhour` int(4) default null comment '学时',
`gradeid` int(4) default null comment '年级编号',
primary key (`subjectno`)
)engine = innodb auto_increment = 19 default charset = utf8;
-- 创建成绩表
drop table if exists `result`;
create table `result`(
`studentno` int(4) not null comment '学号',
`subjectno` int(4) not null comment '课程编号',
`examdate` datetime not null comment '考试日期',
`studentresult` int (4) not null comment '考试成绩',
key `subjectno` (`subjectno`)
)engine = innodb default charset = utf8;
-- 插入学生数据 其余自行添加 这里只添加了2行
insert into `student` (`studentno`,`loginpwd`,`studentname`,`sex`,`gradeid`,`phone`,`address`,`borndate`,`email`,`identitycard`)
values
(1000,'123456','张伟',0,2,'13800001234','北京朝阳','1980-1-1','[email protected]','123456198001011234'),
(1001,'123456','赵强',1,3,'13800002222','广东深圳','1990-1-1','[email protected]','123456199001011233');
-- 插入成绩数据 这里仅插入了一组,其余自行添加
insert into `result`(`studentno`,`subjectno`,`examdate`,`studentresult`)
values
(1000,1,'2013-11-11 16:00:00',85),
(1000,2,'2013-11-12 16:00:00',70),
(1000,3,'2013-11-11 09:00:00',68),
(1000,4,'2013-11-13 16:00:00',98),
(1000,5,'2013-11-14 16:00:00',58);
-- 插入年级数据
insert into `grade` (`gradeid`,`gradename`) values(1,'大一'),(2,'大二'),(3,'大三'),(4,'大四'),(5,'预科班');
-- 插入科目数据
insert into `subject`(`subjectno`,`subjectname`,`classhour`,`gradeid`)values
(1,'高等数学-1',110,1),
(2,'高等数学-2',110,2),
(3,'高等数学-3',100,3),
(4,'高等数学-4',130,4),
(5,'C语言-1',110,1),
(6,'C语言-2',110,2),
(7,'C语言-3',100,3),
(8,'C语言-4',130,4),
(9,'Java程序设计-1',110,1),
(10,'Java程序设计-2',110,2),
(11,'Java程序设计-3',100,3),
(12,'Java程序设计-4',130,4),
(13,'数据库结构-1',110,1),
(14,'数据库结构-2',110,2),
(15,'数据库结构-3',100,3),
(16,'数据库结构-4',130,4),
(17,'C#基础',130,1);
4.1、查询全部字段
-- 查询全部的学生 select 字段 from 表
select * from student;
-- 查询指定字段
select `sudentno`,`studentname` from student
-- 别名,给表和表头起一个名字
select `studentno` as 学号,`studentname` as 学生姓名 from student as s;
-- 函数 concat(a,b)
select concat('姓名:',studentname) as 新名字 from student;
语法: select 字段,…… from 表
4.2、去重 distinct
select distinct `studentno` from result;
去除重复的数据
4.3、其他查询
select version(); -- 查询系统版本 (函数)
select 100*3-1 as 计算结果; -- 用来计算(表达式)
select @@auto_increment_increment; -- 查询自增步长(变量)
select `studentno`,`studentresult`+1 as '提分后' from result -- 所有成绩+1
数据库中的表达式:文本值,列,null,函数,计算表达式,系统变量……
select 表达式 from 表
4.4、模糊查询
| 运算符 | 语法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| is null | a is null | 如果操作符为null,结果为真 |
| is not null | a is not null | 如果操作符不为null,结果为真 |
| like | a like b | 如果a匹配b,结果为真 |
| in | a in (a1,a2,a3…) | 假设a在(a1,a2,a3…)中,结果为真 |
-- like
-- " % " 代表0到任意个字符, " _ " 表示一个字符
-- 查询所有姓刘的同学
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student` where studentname like '刘%';
-- in中是具体的值,不能用 " % " 和 " _ "
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student` where `studentno` in (1001,1002,1003);
-- 查询地址为空的学生 null
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student` where address = '' or address is null;
-- 查询地址不为空的同学
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student` where address != '' or address is not null;
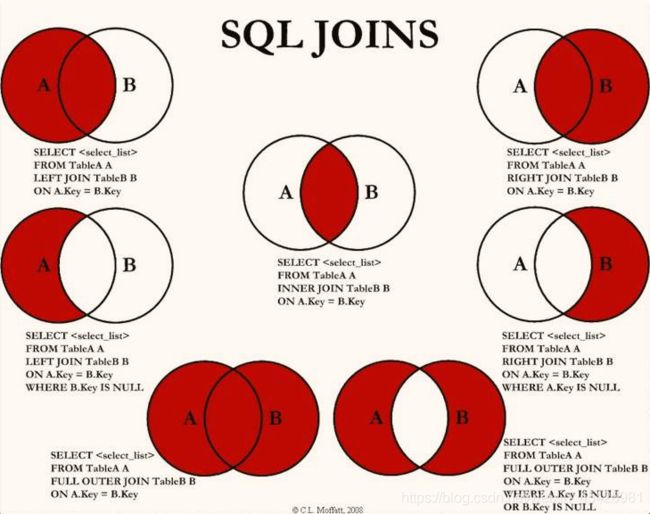
4.5、联表join查询(重难点)
-- 查询参加了考试的学生
-- Inner join
select s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult
from student as s
inner join result as r
where s.studentno = r.studentno;
-- as可省略 where也可以用on
-- right join
select s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult
from student s
right join result r
on s.studentno = r.studentno;
-- left join
select s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult
from student s
left join result r
on s.studentno = r.studentno;
个人理解:假设有两张表,分别是“1年级a班学生表” 取别名为 “a”,和“1年级成绩表” 取别名为“r”
情况1:查询 a班中参与考试的学生的成绩
根据上图中所示,“a班中参与考试的学生的成绩” 属于两个表中重叠的部分,所以要使用 inner join
我们要查询 “学号”、“姓名”、“科目”、“成绩”,其中“姓名”只在“a班学生表”中,“科目”和“成绩”只在“1年级成绩表”中,而“学号”在两个表中都有,所以我们要指定以哪个表为基准,但是因为查询的是重叠部分所以哪个表为基准都可以**(最好 所有字段 都 标明其所在的表)**
select s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult from student s, result r where s.studentno=r.studentno -- 这种方式只能查询重叠部分,而其他需求只能通过 join 来实现 select s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult from student as s inner join result as r where s.studentno = r.studentno;情况2:查询a班所有人的考试情况
根据上图中所示,“查询a班所有人的考试情况” 属于a表私有部分和ab重叠部分,所以使用left join
我们要查询 “学号”、“姓名”、“科目”、“成绩”,其中“姓名”只在“a班学生表”中,“科目”和“成绩”只在“1年级成绩表”中,而“学号”在两个表中都有,所以我们要指定以哪个表为基准,我们要“查询a班所有人的考试情况”,“a班学号”在“a班学生表”中是完整的,所以我们以“a班学生表”为基准进行查询
-- as可省略 select s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult from student s left join result r on s.studentno = r.studentno;情况3:查询a班未参加考试的人
根据上图中所示,“查询a班未参加考试的人” 属于a表私有部分,所以使用left join
我们要查询那些在“a班学生表”中存在,但是在“年级成绩表”中不存在的学生,所以我们只需要查询 “学号”、“姓名”即可,其中“姓名”只在“a班学生表”中,而“学号”在两个表中都有,所以我们要指定以哪个表为基准,我们要查询的属于a表私有部分,所以以“a班学生表”为基准进行查询
select s.studentno,studentname,subjectno,studentresult from student s left join result r on s.studentno = r.studentno where r.studentno is null;注意on和where的区别
join on 是连接查询 ,where是等值查询
在使用 inner join 的时候不存在问题
主要在查询左连接和右连接时候要特别注意
以左连接为例 left join:
有如下两个表:
tab1:
id size 1 10 2 20 3 30 tab2:
size name 10 AAA 20 BBB 20 CCC 如果查询
select * form tab1 left join tab2 on (tab1.size = tab2.size)因为 left join 的特殊性,不管on的条件是否为真都会先返回 left 表中的所有记录
而on的作用是对返回的结果进行合并将符合 ‘tab1.size = tab2.size’ 的放在一起
tab1.id tab1.size tab2.size tab2.name 1 10 10 AAA 2 20 20 BBB 2 20 20 CCC 3 30 (null) (null) 但是如果查询
select * form tab1 left join tab2 on (tab1.size = tab2.size) where tab2.name='AAA'上面的表格就会作为中间表,先生成中间表,然后在根据where条件进行过滤,结果为:
tab1.id tab1.size tab2.size tab2.name 1 10 10 AAA 如果使用on来进行查询
select * form tab1 left join tab2 on (tab1.size = tab2.size and tab2.name='AAA')结果为:
tab1.id tab1.size tab2.size tab2.name 1 10 10 AAA 2 20 (null) (null) 3 30 (null) (null) 先返回了左表的所有记录,然后on对结果进行合并
其实以上结果的关键原因就是 left join、right join、full join 的特殊性,不管 on 上的条件是否为真都会返回 left 或 right 表中的记录,full 则具有 left 和 right 的特性的并集。 而 inner jion 没这个特殊性,则条件放在 on 中和 where 中,返回的结果集是相同的。
情况4:查询成绩表的详细信息
成绩表中都是编号,需要从学生表中查询学号对应的姓名,以及科目表中学科编号对应的科目,这里成绩表是主体,所以左联右联都是以成绩表为主(阿里开发手册禁止超过3个表使用 join 联表查询)
select r.studentno 学号,stu.studentname 姓名,r.subjectno 学科编号,r.studentresult 成绩,sub.subjectname 科目 from student stu right join result r on r.studentno = stu.studentno left join `subject` sub on r.subjectno = sub.subjectno情况5:查询所有报名竞赛的学生名单
注:MySQL不支持 full join 所以图中最下面的两种情况需要使用别的办法实现
这里换两个表更好理解,“a班报名数学竞赛的学生” student1 取别名为s1,“a班报名英语竞赛的学生”student2 取别名为s2
根据上图中所示,“查询所有报名竞赛的学生名单” 属于s1和s2所有部分
对于full join 可以使用 union操作符:union 操作符用于合并两个或多个 SELECT 语句的结果集,每个select结果集必须有相同数量、类型和顺序的列
我们先查询 s1 表所有部分,在查询 s2 表所有部分,然后使用union联合起来就可以了
select s1.studentno,s1.studentname from student1 s1 left join student2 s2 on s1.studentno = s2.studentno union select s2.studentno,s2.studentname from student1 s1 right join student2 s2 on s1.studentno = s2.studentno情况6:查询只报名了一个竞赛的学生
这里查询的是 s1 表私有部分和 s2 表私有部分 同理,我们先查询 s1 表私有部分,在查询 s2 表私有部分,然后使用union联合起来就可以了
select s1.studentno,s1.studentname from student1 s1 left join student2 s2 on s1.studentno = s2.studentno where s2.studentno is null union select s2.studentno,s2.studentname from student1 s1 right join student2 s2 on s1.studentno = s2.studentno where s1.studentno is null总结:
1、要查询哪些数据 select …
2、从哪几个表中查询 from …
3、确定主体部分,左联还是右联 xxx join 表 on 条件
4、假设存在多张表,先查询两张表,然后一个一个加
4.6、自连接(了解)
核心:一张表拆为两张表
假设有如下课程信息表 course,课程有两种,“火焰”、“冰霜”、“奥术”可以直接学习,其他课程需要先学习对应的先修课程,如学习“火球术”需要先学习“火焰”
| 课程编号(subjectno) | 先修课程(presubjectno) | 课程名称(name) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 火焰 |
| 3 | 1 | 冰霜 |
| 4 | 1 | 奥术 |
| 5 | 2 | 火球术 |
| 6 | 2 | 烈焰冲击 |
| 7 | 3 | 寒冰箭 |
| 8 | 4 | 奥术飞弹 |
将这一个表看做两个表然后进行自连接查询
select f.name 课程,s.name 先修课程
from course f,course s
where f.presubjectno = s.subjectno;
结果
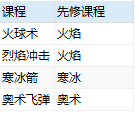
在代码中为 course起了两个不同的别名 f 和 s ,即看做是两个表。查询时通过where语句,要求 f 表中的先修课程号 presubjectno 与 s 表中的课程编号相同,而查询的结果就是 f 表中的 课程 name 和 s 表中的 课程 name,那么结果就是 f 表中一个课程name(“火球术”)的先修课程编号 presubjectno (2),及对应的 s 表中的课程编号 subjectno(2)的课程 name (“火焰”)。
像这样在一个表中表示多层关系,需要分层操作的时候 使用自连接是很方便的。
4.7、分页和排序
-- 排序:升序 asc ,降序 desc
select 字段1,字段2
from 表
where 条件
order by 字段 desc;
升序:asc 降序:desc
-- 分页:limit
select 字段1,字段2
from 表
where 条件
order by 字段 desc
limit 起始行, 每页显示的条数;
-- 例子:
-- 查询第1条到第10条的数据
select * from student limit 0,10;
-- 查询第11条到第20条的数据
select * from student limit 10,10;
分页: limit (page-1)*pageSize , pageSize
page:页码,pageSize:每页显示的条数
4.8、子查询和嵌套查询
select * from student where studentid = (
select studentid from result where mathscore = 100
);
-- 查询数学考了100分的学生信息
-- 也可以使用联表查询
select * from student inner join result
on student.studentid = result.studentid
where result.mathscore = 100;
-- 还可在联表查询的 where中嵌套 子查询
-- 以上两个例子中,where 后的判断条件都是确定的值,如果是一个范围,则使用where in 查询
select * from student where studentid in (
select studentid from result where mathscore < 60
)
-- 查询成绩不及格的学生信息
4.9、分组和过滤
这里最好先看一下MySQL的函数
mysql 结果集的列(即select后的字段)必须是列标签或列函数
select subjectname ,AVG(studentresult),MAX(studentresult),MIN(studentresult)
from result
INNER JOIN `subject`
on result.subjectno = subject.subjectno
GROUP BY subjectname
-- 查询成绩单中每个学科的平均分、最高分、最低分
-- 这里通过group by 按照学科将成绩单进行了分组,相同的学科为一个组
-- 查询语句则对每个小组取平均、最高、最低分
-- 注意,这里是对小组进行了计算,而不是整体的,如果不加 group by 那么就是对整体进行计算
-- 如果想对分组后的数据进行筛选,那么使用 having
select subjectname ,AVG(studentresult),MAX(studentresult),MIN(studentresult)
from result
INNER JOIN `subject`
on result.subjectno = subject.subjectno
GROUP BY subjectname
having AVG(studentresult) > 60
-- 查询成绩单中平均分在60分以上的所有学科的平均分、最高分、最低分
-- where在group by 之前执行,所以不能使用where进行条件判断
-- having让我们可以筛选分组后的数据
4.10、select总结
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT | DISTINCTROW ]
{
* | table.*|[table.field1[as alias1][,table.field2[as alias2]][,...]]}
FROM table_name [as table_alias]
[left | right | inner join table_name2] -- 联合查询
[where ...] -- 指定结果满足的条件
[group by ...] -- 指定结果按照哪几个字段分组
[having ...] -- 过滤分组的记录必须满足的次要条件
[order by ...] -- 指定查询记录按一个或多个条件排序
[limit {
[offset,]row_count | row_countOFFSET offset}]; -- 指定查询的记录从哪条到哪条
伪代码:
select 去重 要查询的字段 from 表 (字段和表都可以取别名)
[left|right|inner join 要连接的表 on 等值判断]
where 具体的值或子查询语句
group by 通过那个字段分组
having 过滤分组后的信息
order by 通过那个字段排序 升序还是降序
limit startindex,pagesize
5、MySQL函数
官网MySQL函数
5.1、常用函数
-- 数学运算
select abs(-8); -- 绝对值 8
select ceiling(9.4); -- 向上取整 10
select floor(9.4); -- 向下取整 9
select rand(); -- 返回一个 0~1 之间的随机数
select sign(); -- 判断一个数的符号 负数返回 -1,正数返回 1,0返回0
-- 字符串函数
select char_length('这是几个字'); -- 返回字符串长度 5
select concat('这','是','几','个','字'); -- 拼接字符串
select insert('这是几个字',1,2,'随便说'); -- 替换字符串 "随便说几个字"
select lower('MArs'); -- 转小写
select upper('MArs'); -- 转大写
select instr('Mars','a'); -- 查询某个字符第一次出现的索引 2
select replace('这是几个字','这是','随便说'); -- 替换出现的指定的字符串 “随便说几个字”
select substr('这是几个字',2,2); -- 从2开始截取2个字符串 "是几"
select recerse('这是几个字'); -- 反转字符串
-- 时间和日期函数(记住)
select current_date(); select current -- 获取当前日期
select now(); -- 获取当前日期和时间
select localtime(); -- 获取本地时间
select sysdate(); -- 获取系统时间
select year(now()); -- 年
select month(now()); -- 月
select day(now()); -- 日
select hour(now()); -- 时
select minute(now()); -- 分
select second(now()); -- 秒
select system_user(); select user(); -- 获取当前登录用户名
select version(); -- 获取当前版本
5.2、聚合函数(常用)
-- 查询表有多少行
select count(studentname) from student; -- count(指定列) 会忽略所有的null 值
select count(*) from student; -- count(*) 不会忽略null值
select count(1) from student; -- count(1) 不会忽略null值
-- 执行效率:
-- 表的列名为主键,count(列名)会比count(1)快,列名不为主键,count(1)更快
-- 表有多个列,且没有主键,则count(1)比count(*)快
-- 如果表只有一个字段,count(*)最快
-- 常用计算
select sum('studentresult') from result; -- 分数总和
select avg('studentresult') from result; -- 平均分
select max('studentresult') from result; -- 最高分
select min('studentresult') from result; -- 最低分
6、事务
要么都成功,要么都失败
将一组sql放在一个批次中去执行~
事务原则:ACID原则 原子性,一致性,隔离性,持久性 (脏读、不可重复读、幻读……)
原子性(Atomicity)、一致性(Consistency)、隔离性(Isolation)、持久性(Durability)
原子性(Atomicity)
原子性是指事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都发生,要么都不发生。
一致性(Consistency)
事务前后数据的完整性必须保持一致
隔离性(Isolation)
事务的隔离性是多个用户并发访问数据库时,数据库为每一个用户开启的事务,不能被其他事务的操作数据所干扰,多个并发事务之间要相互隔离
持久性(Durability)
持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据的改变就是永久性的,接下来即使数据库发生故障也不应该对其有任何影响
隔离导致的问题
脏读:
指一个事务读取了另一个事务未提交的数据。
不可重复读:
在一个事务内读取表中的某一行,多次读取结果不同。
虚读(幻读):
指在一个事务内读取到了别的事务插入的数据,导致前后读取不一致。
(一般是行影响,多了一行)
-- mysql是默认开启了事务的自动提交的
set autocommit = 0; -- 关闭
set autocommit = 1; -- 开启
-- ================手动处理事务的流程===================
set autocommit = 0; -- 关闭自动提交
-- 手动开启事务
start transaction; -- 标记一个事务的开始,从这个之后的sql 都在同一个事务
xxx;
xxx;
commit; -- 提价:持久化(成功!)
rollback; -- 回滚:回到原来的样子(失败!)
set autocommit = 1; -- 开启自动提交
-- =================手动处理事务的流程===================
-- 了解
savepoint; -- 记录一个保存点
rollback to savepoint; -- 回滚到保存点
release savepoint; -- 撤销保存点
7、索引
MySQL官方对索引的定义为:索引(index)是帮助MySQL搞笑获取数据的数据结构。
7.1、索引的分类
- 主键索引(primary key)
- 唯一的标志,主键不可重复,只能有一个列作为主键,不能为空
- 唯一索引(unique key)
- 可以为空,索引列不能重复
- 常规索引(key/index)
- 全文索引(fulltext)
-- 插入100万数据
delimiter $$ -- 写函数之前的标志
create function mock_data() -- 创建一个函数
returns int -- 返回值类型是int
begin -- 函数开始
declare num int default 1000000; -- 定义一个int类型的变量
declare i int default 0; -- 定义一个int类型的
while i < num do -- while循环
insert into app_user(`name`,`email`,`phone`,`gender`,`password`,`age`)
values(
concat('用户',i),'[email protected]',
concat('18',floor(rand()*899999999+100000000)),
floor(rand()*10+1)&1,uuid(),floor(rand()*100+1));
set i = i+1;
end while; -- 结束while循环
RETURN i;
end; -- 函数结束
MySQL索引背后的数据结构及算法原理
8、权限管理和备份
8.1、权限
-- 创建用户 create user 用户名 identified by '密码'
create user mars identified by '123456';
-- 修改密码(当前用户)
set password = password('123456');
-- 修改密码(指定用户)
set password for mars = password('123456');
-- 重命名 rename user 原名字 to 新名字
rename user mars to newmars;
-- 用户授权 grant 权限 on 库.表 to 用户
grant all privileges on *.* to mars;
-- 查看权限 show grants for 用户
show grants for mars;
-- 撤销权限 revoke 权限 on 库.表 from 用户
revoke all privileges on *.* from mars;
-- 删除用户
drop user mars
8.2、备份
- 直接拷贝物理文件(data文件夹)
- 在可视化工具中备份
- 命令行 在cmd中 mysqldump
# mysqldump -h主机 -u用户名 -p密码 数据库 [表1 表2] >磁盘/文件名
mysqldump -hlocalhost -uroot -proot school student >d:/a.sql
# 导入1
# source -h主机 -u用户名 -p密码 数据库 [表1 表2] <磁盘/文件名
# 导入2,[选择想要导入的数据库]后进行导入
mysql -uroot -proot;
use school;
source d:/a.sql;
9、规范数据库设计
9.1、为什么需要设计
糟糕的数据库设计:
- 数据冗余,浪费空间
- 数据库插入和删都会麻烦、异常(避免使用物理外键)
- 程序的性能差
良好的数据库设计:
- 节省内存空间
- 保证数据库的完整性
- 方便开发系统
软件开发关于数据库的设计:
- 分析需求:分析业务和需要处理的数据库需求
- 概要设计:设计关系图E-R图
设计数据库的步骤:(个人博客)
- 收集信息,分析需求
- 用户表(用户登录注销,用户的个人信息,写博客,创建分类)
- 分类表(文章分离,谁创建的)
- 文章表(文章的信息)
- 评论表
- 友链表(友情链接信息)
- 自定义表(系统信息,某个关键的字,或者一些主字段)key:value
- 标志实体(把需求落地到字段)
- 标志实体之间的关系
9.2、三大范式
第一范式(1NF):要求数据库表的每一列都是不可分割的原子数据项。
第二范式(2NF):在1NF基础上,非码属性必须完全依赖于候选码(在1NF基础上消除非主属性对主吗的部分函数依赖)
确保数据库表中的每一列都和主键相关,而不能只与主键的某一部分相关(主要针对联合主键而言)
即满足第一范式前提下,每张表只描述一件事情。
例如:订单编号、产品编号、产品单价、产品数量、订单金额、订单时间
应该拆开两个表:订单编号、产品编号、产品单价 和 订单编号、订单金额、订单时间
第三范式(3NF):在2NF基础上,任何非主属性不依赖于其他非主属性(在2NF基础上消除传递依赖)
第三范式需要确保数据表汇中的每一列都和主键直接相关,而不能间接相关。
例如:学号、姓名、性别、家庭人口、班主任姓名、班主任性别、班主任年龄
班主任姓名、班主任性别、班主任年龄都 直接依赖于 班主任姓名而不是主键“学号”,应该拆开就符合3NF了
规范性和性能的问题
如果遵循规范性,那么性能就慢了,阿里规约 “关联查询的表不得超过三张表”
- 考虑商业化的需求和模板(成本、用户体验)数据库的性能更加重要
- 在规范性能的问题的时候,需要适当考虑规范性
- 故意给表增加一些冗余字段。(从多表查询变为单表查询)
- 故意增加一些计算列(从大数据量降低为小数据量的查询或索引)
10、JDBC(重点)
10.1、数据库驱动
10.2、JDBC
sun公司为开发人员对数据库的统一操作提供的一个java操作数据库的规范,俗称JDBC
对于开发人员,只需掌握JDBC接口的操作即可
包:java.sql javax.sql mysql-connector-java
10.3、第一个JDBC程序
url 参数
URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jnshu?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC";
useUnicode:支持中文编码
character:设置中文字符集为utf8
useSSlSSl:使用安全连接
serverTimezone:设置时区
public class OnlyJDBC {
/**创建建立连接需要的信息*/
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jnshu?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC";
private static final String USER = "root";
private static final String PASSWORD = "root";
private static final String DRIVER = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
public static void main(String[] args) {
//连接对象
Connection conn = null;
//执行sql的对象
Statement stmt = null;
//接收sql执行结果的对象
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//此处通过反射 加载了驱动类,该类被加载后,就完成了向驱动管理器的注册。
Class.forName(DRIVER);
//驱动管理器通过相应的信息返回一个Connection对象
System.out.println("与数据库建立连接......");
conn= DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER,PASSWORD);
//获取连接后得到一个Statement对象该对象用来将sql发送到数据库执行
System.out.println("创建 statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from stu where id <=10";
//ResultSet对象是sql语句执行的结果集
System.out.println("接收结果集并输出......");
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//判断是否有下一行来进行处理
while (rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
System.out.println("id:" + id + '\t' + "name:" + name);
}
} catch (SQLException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭流
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
10.3.1、JDBC中的对象
注册驱动:DriverManager
原本的写法:
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
但是在 “com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver” 该类中只有一个静态方法
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
所以直接使用反射 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); 让该类进行加载,静态方法执行,就完成了注册。
URL
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jnshu?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC";
// 协议 ://主机地址:端口号/数据库名?参数1&参数2&参数3
// mysql -- 3306
// oracle -- 1521
// jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:sid
Connection 代表数据库
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER,PASSWORD);
//connection 代表数据库
connection.setAutoCommit(); // 数据库设置自动提交
connection.commit(); // 事务提交
connection.rollback(); // 事务回滚
Statement 执行SQL的对象 PreparedStatement 执行SQl的对象
statement.extcuteQuery(); // 执行查询sql 返回ResultSet
statement.executeUpdate(); // 执行操作sql 更新、插入、删除都用这个,返回受影响的行数
statement.execute(); // 执行任何sql
ResultSet 查询的结果集:封装了所有的查询结果
获得指定的数据类型
resultSet.getObject(); //在不知道列数据的情况下使用
// 知道列的类型就使用指定的类型
resultSet.getString();
resultSet.getInt();
...
遍历,指针
resultSet.beforeFirst(); // 移动到最前面
resultSet.afterLast(); // 移动到最后面
resultSet.next(); // 移动到下一个数据
resultSet.previous(); // 移动到前一行
resultSet.absolute(int row); // 移动到指定行
释放内存:耗资源,用完关掉
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connectin.close();
10.4、SQL注入
10.5、PreParedStatement对象
PreparedStatement 可以防止SQL注入,效率更高
防止sql的本质:参数会直接当做字符串,并且符号直接转义
区别:
// 编写sql 使用 ? 占位符代替参数
String sql = "insert into users(id,`name`,`password`,`email`,`birthday`) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
// 获取对象的方式也不同
PreparedStatement ps = connection.preparedStatement(sql); // 预编译SQL,先写sql,然后不执行
// 手动给参数赋值 参数下标从1开始
ps.setInt(1,4); // 给第一个参数“id”,赋值 4
ps.setString(2,"mars"); // name mars
ps.setString(3,"123456"); // password 123456
ps.setString(4,"[email protected]"); // email [email protected]
ps.setDate(5,new java.sql.Date(new java.util.Date).getTime()); // birthday
// 注意: sql.Date 数据库用的 util.Date java用的
//执行
int i = ps.executeUpdate(); // 查询同样是返回ResultSet对象
// 释放
10.6、JDBC事务
// 1、关闭自动提交,开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
// 2、编写需要操作的sql组
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
...
// 3、提价事务
connection.commit();
// 如果失败在catch中rollback (默认执行失败就会回滚,显式定义更好)
connection.rollback();
// 释放资源
10.7、数据库连接池
数据库连接 – 执行完毕 – 释放
连接 – 释放 十分浪费资源
DataSource:
数据池都是实现了该接口
该接口封装了连接数据库的相关信息等
可以看做数据源
常用参数:
最小连接数 和 常用连接数 一般相同
最大连接数
等待超时
开源数据源实现(DBCP、C3P0、Druid(阿里))
DBCP:
jar包:commons-dbcp-1.4、commons-pool-1.6
配置文件
# 连接设置 这里的名字 DBCP定义好的
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSl=true
username=root
password=root
# 初始化连接
initialSize=10
# 最大连接数量
maxActive=50
# 最大空闲连接
mzxIdle=20
# 最小空闲连接
minIdle=5
# 超时等待 时间以毫秒为单位 (多余空闲的连接超时后才会释放)
maxWait=60000
# 指定由连接池所创建的连接的自动提交(auto-commit)状态。
defaultAutoCommit=true
# driver default 指定由连接池所创建的连接的只读(read-only)状态
# 如果没有设置该值,则“setReadOnly”方法将不被调用。(某些驱动并不支持只读模式,如:Informix)
defaultReadOnly=
# driver default 指定由连接池锁创建的连接的事务级别(TransactionIsolation)
# 可用值为下列之一:NONE,READ_UNCOMMITTED,READ_COMMITTED,REPEATABLE_READ,SERIALIZABLE
defaultTransactionIsolation=READ_UNCOMMITTED
通过io流获取到该配置文件的 InputStream对象 is
然后使用 Properties对象读取 is
使用 BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); 读取之后就可以获取到数据源对象 datasource
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = null;
Connection connection = null;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("dbcp.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(fis);
//获取数据源对象
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
//获取连接
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
// 进行后续曹组
.........
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//释放连接
}
}
C3P0
配置文件
<c3p0-config>
<default-config>
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driverproperty>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSl=trueproperty>
<property name="user">rootproperty>
<property name="password">rootproperty>
<property name="acquireIncrement">5property>
<property name="initialPoolSize">10property>
<property name="mixPoolSize">5property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">20property>
default-config>
<default-config name="MySQL">
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driverproperty>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSl=trueproperty>
<property name="user">rootproperty>
<property name="password">rootproperty>
<property name="acquireIncrement">5property>
<property name="initialPoolSize">10property>
<property name="mixPoolSize">5property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">20property>
default-config>
c3p0-config>
获取数据源
datasource = new ComboPooledDataSource(“MySQL”);
然后进行接下来的操作
还可以直接通过代码进行配置,不通过配置文件
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = null;
// 以下在try catch中
dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass(xxx);
dataSource.setUser(xxx);
......