Linux工作队列
目录
1. 工作队列概览 1
1.1 重要数据结构说明 1
1.2 工作队列结构关系 3
2. 工作队列初始化 4
3. 工作队列接口 5
3.1 alloc_workqueue 5
3.2 queue_work 9
3.3 work的执行 10
4. 异常情况处理 11
4.1 worker_pool没有空闲的worker 11
4.2 创建worker超时 12
4.3 worker_pool中空闲worker太多 12
4.4 worker_pool卡住 13
1. 工作队列概览
1.1 重要数据结构说明
| struct workqueue_struct |
|
| struct list_head pwqs |
工作队列的所有pwq除了存在于数组numa_pwq_tbl[]中也会挂到这个链表上 |
| struct list_head list |
用于将工作队列挂到全局链表workqueues上 |
| struct worker *rescuer |
用于处理紧急情况的worker |
| struct workqueue_attrs *unbound_attrs |
工作队列属性,包含工作者线程优先级,允许的cpu位表 |
| char name[WQ_NAME_LEN] |
工作队列名 |
| struct pool_workqueue __percpu *cpu_pwqs |
如果是bund queue用于保存每cpu pwq |
| Struct pool_workqueue __rcu *numa_pwq_tbl[] |
用于保存Unbund queue的pwq |
| struct pool_workqueue |
|
| struct worker_pool *pool |
指向对应的worker_pool |
| struct workqueue_struct *wq |
指向所属的工作队列结构 |
| int nr_active |
活动的struct work_struct数 |
| int max_active |
当nr_active大于max_active之后再有添添加的work_struct将被添加到链表delayed_works中 |
| struct list_head pwqs_node |
用于挂到工作队列的wq-> pwqs |
| struct list_head delayed_works |
说明见max_active |
| struct worker_pool |
|
| int cpu |
worker_pool绑定到的cpu或者亲和性最高的cpu |
| int node |
所属的内存节点 |
| unsigned long watchdog_ts |
Jiffies, worker_pool被访问的时候更新 |
| struct list_head worklist |
用于链接添加到该worker_pool的work_struct |
| int nr_workers |
worker_pool中work_struct计数 |
| int nr_idle |
worker_pool中Idle worker的数量 |
| struct list_head idle_list |
Worker处于空闲的时候挂到idle_list上 |
| struct timer_list idle_timer |
Idle的worker太多而且这种状态持续一段指定的时候该timer将触发 |
| struct timer_list mayday_timer |
如果创建worker时间太长就,会触发rescuer |
| struct list_head workers |
worker_pool中的所有worker |
| struct hlist_node hash_node |
用于挂到哈希表unbound_pool_hash中 |
| struct worker |
|
| union { struct list_head entry; struct hlist_node hentry; }; |
空闲的时候用entry挂到worker_pool-> idle_list;忙碌的时候用hentry 挂到worker_pool->busy_hash中 |
| struct work_struct *current_work |
当前处理的work |
| work_func_t current_func |
当前处理的work function |
| struct pool_workqueue *current_pwq |
当前处理的work所属的pwq |
| struct list_head scheduled |
如果某个work设置了WORK_STRUCT_LINKED,会将该work和其依赖的work挂到scheduled一并处理 |
| struct task_struct *task |
工作者线程 |
| struct worker_pool *pool |
Worker所属的worker_pool |
| struct list_head node |
用于挂到worker_pool-> workers |
| struct work_struct |
|
| struct list_head entry |
用于挂到worker_pool-> worklist |
| work_func_t func |
Work的处理函数 |
1.2 工作队列结构关系
workqueue_struct:分为绑定到cpu的队列和共享队列,它管理着多个pwq:每个cpu(绑定)或者每个内
存节点(共享)对应一个pwq。
pool_workqueue:连接worker_pool和workqueue_struct,worker_pool是根据attrs到unbound_pool_hash
或者cpu_worker_pools中查找到的,worker_pool不是特定属于某个pwq的,一个attrs对应一个
worker_pool,系统中attr相同的所有pwq共享一个worker_pool。
worker_pool:管理着添加到pool中的work_struct,和worker,如果work_struct太多worker现有处理不过来就创建更多的worker来处理
worker:工作者线程,它的工作就是从worker_pool->worklist中取下work_struct来调用work_struct->func。
work_struct:就是用户使用的接口,实现work_struct->func添加到工作队列。
2. 工作队列初始化
工作队列初始化流程如下:
![]()
开机的时候会对工作队列做一系列初始化,其流程如上图。逻辑很明了,下面看看主要代码实现:
int __init workqueue_init_early(void)
{
int std_nice[NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS] = { 0, HIGHPRI_NICE_LEVEL };
int i, cpu;
BUG_ON(!alloc_cpumask_var(&wq_unbound_cpumask, GFP_KERNEL));
cpumask_copy(wq_unbound_cpumask, cpu_possible_mask);
//为pool_workqueue创建缓存
pwq_cache = KMEM_CACHE(pool_workqueue, SLAB_PANIC);
/*下面是个双循环,每个cpu有两个worker_pool,分为高优先级和普通pool,这里的优先级最后会用于worker_pool中的worker线程优先级*/
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
struct worker_pool *pool;
i = 0;
for_each_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu) {
BUG_ON(init_worker_pool(pool));
pool->cpu = cpu;
cpumask_copy(pool->attrs->cpumask, cpumask_of(cpu));
pool->attrs->nice = std_nice[i++];
pool->node = cpu_to_node(cpu);
}
}
//创建非绑定工作队列和顺序工作队列属性
for (i = 0; i < NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS; i++) {
struct workqueue_attrs *attrs;
BUG_ON(!(attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(GFP_KERNEL)));
attrs->nice = std_nice[i];
unbound_std_wq_attrs[i] = attrs;
BUG_ON(!(attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(GFP_KERNEL)));
attrs->nice = std_nice[i];
attrs->no_numa = true;
ordered_wq_attrs[i] = attrs;
}
//创建系统工作中所需的工作队列
system_wq = alloc_workqueue("events", 0, 0);
system_highpri_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_highpri", WQ_HIGHPRI, 0);
system_long_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_long", 0, 0);
system_unbound_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_unbound", WQ_UNBOUND,
WQ_UNBOUND_MAX_ACTIVE);
system_freezable_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_freezable",
WQ_FREEZABLE, 0);
system_power_efficient_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_power_efficient",
WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT, 0);
system_freezable_power_efficient_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_freezable_power_efficient",
WQ_FREEZABLE | WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT,
0);
return 0;
}int __init workqueue_init(void)
{
struct workqueue_struct *wq;
struct worker_pool *pool;
int cpu, bkt;
……
//为per_cpu worker_pool分配worker
for_each_online_cpu(cpu) {
for_each_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu) {
pool->flags &= ~POOL_DISASSOCIATED;
BUG_ON(!create_worker(pool));
}
}
//为unbound_pool分配worker
hash_for_each(unbound_pool_hash, bkt, pool, hash_node)
BUG_ON(!create_worker(pool));
wq_online = true;
//初始化wq watchdog监控是否有work_pool卡住
wq_watchdog_init();
return 0;
}3. 工作队列接口
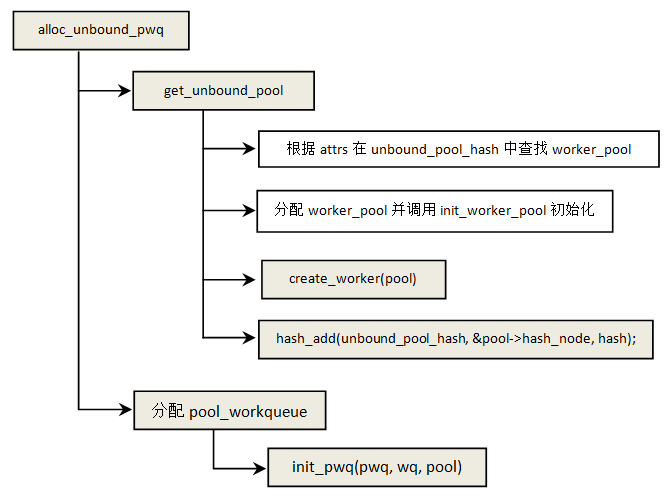
3.1 alloc_workqueue
alloc_workqueue是创建工作队列的接口,这是一个宏,实际工作由__alloc_workqueue_key完成
struct workqueue_struct *__alloc_workqueue_key(const char *fmt,
unsigned int flags,
int max_active,
struct lock_class_key *key,
const char *lock_name, ...)
{
size_t tbl_size = 0;
va_list args;
struct workqueue_struct *wq;
struct pool_workqueue *pwq;
if ((flags & WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT) && wq_power_efficient)
flags |= WQ_UNBOUND;
if (flags & WQ_UNBOUND)
tbl_size = nr_node_ids * sizeof(wq->numa_pwq_tbl[0]);
//如果是非绑定工作队列,就分配数组wq->numa_pwq_tbl[],用于每个内存节点的pool_workqueue
wq = kzalloc(sizeof(*wq) + tbl_size, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!wq)
return NULL;
if (flags & WQ_UNBOUND) {//分配unbound_attrs属性
wq->unbound_attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(GFP_KERNEL);
if (!wq->unbound_attrs)
goto err_free_wq;
}
va_start(args, lock_name);
//设置工作队列名
vsnprintf(wq->name, sizeof(wq->name), fmt, args);
va_end(args);
//最大active works
max_active = max_active ?: WQ_DFL_ACTIVE;
max_active = wq_clamp_max_active(max_active, flags, wq->name);
wq->flags = flags;
wq->saved_max_active = max_active;
......
//根据attrs找到对应的work_pool和分配pwq
if (alloc_and_link_pwqs(wq) < 0)
goto err_free_wq;
/*如果有标志WQ_MEM_RECLAIM就用于处理紧急情况的worker直接让wq管理。当工作队列中某个work_pool积压太多work等待处理就启用该worker*/
if (flags & WQ_MEM_RECLAIM) {
struct worker *rescuer;
//分配并初始化worker
rescuer = alloc_worker(NUMA_NO_NODE);
if (!rescuer)
goto err_destroy;
rescuer->rescue_wq = wq;
//创建worker线程用
rescuer->task = kthread_create(rescuer_thread, rescuer, "%s",
wq->name);
if (IS_ERR(rescuer->task)) {
kfree(rescuer);
goto err_destroy;
}
wq->rescuer = rescuer;
kthread_bind_mask(rescuer->task, cpu_possible_mask);
wake_up_process(rescuer->task);
}
mutex_lock(&wq_pool_mutex);
mutex_lock(&wq->mutex);
for_each_pwq(pwq, wq)
pwq_adjust_max_active(pwq);
mutex_unlock(&wq->mutex);
//将工作队列结构放到全局链表workqueues中去
list_add_tail_rcu(&wq->list, &workqueues);
mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_mutex);
return wq;
……
}
static int alloc_and_link_pwqs(struct workqueue_struct *wq)
{
bool highpri = wq->flags & WQ_HIGHPRI;
int cpu, ret;
/*如果是绑定到特定cpu的工作队列,就为其每个cpu分配一个pwq,并根据cpu和优先级找到每个pwq对应的worker_pool,然后将pwq添加到工作队列相关链表上*/
if (!(wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND)) {
wq->cpu_pwqs = alloc_percpu(struct pool_workqueue);//分配cpu_pwqs数组用于存储pwq
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
struct pool_workqueue *pwq =
per_cpu_ptr(wq->cpu_pwqs, cpu);
struct worker_pool *cpu_pools =
per_cpu(cpu_worker_pools, cpu);//根据cpu找到对应的worker_pool
//用wq和对应的worker_pool初始化pwq
init_pwq(pwq, wq, &cpu_pools[highpri]);
link_pwq(pwq); //把pwq添加到链表wq->pwqs
}
return 0;
} else if (wq->flags & __WQ_ORDERED) {
/*主要做了三件事:1)为每个内存节点创建pwq保存到wq->numa_pwq_tbl[];2)并根据attrs找到对应的worker_pool;3)将pwq添加到链表wq->pwqs*/
ret = apply_workqueue_attrs(wq, ordered_wq_attrs[highpri]);
return ret;
} else {
return apply_workqueue_attrs(wq, unbound_std_wq_attrs[highpri]);
}
}创建pool_workqueue
如果是非绑定的工作队列就通过函数alloc_unbound_pwq分配pwq,该函数主要做两件事:1)根据attrs找到对应的worker_pool,如果没有就创建一个;2)创建pool_workqueue,并将wq和worker_pool关联到pwq。
函数init_worker_pool用于初始化一个worker_pool:
static int init_worker_pool(struct worker_pool *pool)
{
spin_lock_init(&pool->lock);
pool->id = -1;
pool->cpu = -1;
pool->node = NUMA_NO_NODE;
pool->flags |= POOL_DISASSOCIATED;
pool->watchdog_ts = jiffies;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pool->worklist);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pool->idle_list);
hash_init(pool->busy_hash);
/* 如果有work进入idle会检查当前pool中空闲worker数,如果太多就触发idle_timer,在一定时间之后问题还没有缓解就尝试destroy一些空闲的worker*/
setup_deferrable_timer(&pool->idle_timer, idle_worker_timeout,
(unsigned long)pool);
/*果worker_pool中有太多的worke要处,就会不断尝试创建更多的worker,这个时候触发mayday_timer,如果一直没有创建到足够的worker,就会唤醒wq->rescuer->task*/
setup_timer(&pool->mayday_timer, pool_mayday_timeout,
(unsigned long)pool);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pool->workers);//用于链接worker
ida_init(&pool->worker_ida);
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&pool->hash_node);//用于将worker_pool添加到哈希表unbound_pool_hash
pool->refcnt = 1;
pool->attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(GFP_KERNEL);// worker_pool的属性,工作队列就是根据属性找到对应的worker_pool的
if (!pool->attrs)
return -ENOMEM;
return 0;
}pwq关联到其所属的wq和选定的worker_pool
static void init_pwq(struct pool_workqueue *pwq, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct worker_pool *pool)
{
memset(pwq, 0, sizeof(*pwq));
pwq->pool = pool;
pwq->wq = wq;
pwq->flush_color = -1;
pwq->refcnt = 1;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pwq->delayed_works);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pwq->pwqs_node);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pwq->mayday_node);
INIT_WORK(&pwq->unbound_release_work, pwq_unbound_release_workfn);
}create_worker
static struct worker *create_worker(struct worker_pool *pool)
{
struct worker *worker = NULL;
int id = -1;
char id_buf[16];
……
//分配一个worker并初始化其相关链表
worker = alloc_worker(pool->node);
if (!worker)
goto fail;
worker->pool = pool; //关联到所属的worker_pool
worker->id = id;
//获取worker线程名
if (pool->cpu >= 0)
snprintf(id_buf, sizeof(id_buf), "%d:%d%s", pool->cpu, id,
pool->attrs->nice < 0 ? "H" : "");
else
snprintf(id_buf, sizeof(id_buf), "u%d:%d", pool->id, id);
//创建worker线程,用于一一处理worker_pool-> worklist上的work_struct
worker->task = kthread_create_on_node(worker_thread, worker, pool->node,
"kworker/%s", id_buf);
//设置worker->task优先级
set_user_nice(worker->task, pool->attrs->nice);
kthread_bind_mask(worker->task, pool->attrs->cpumask);
//将worker链接到pool->workers上
worker_attach_to_pool(worker, pool);
spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock);
worker->pool->nr_workers++; //增加pool上的worker计数
worker_enter_idle(worker);
wake_up_process(worker->task);
spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock);
return worker;
fail:
……
return NULL;
}3.2 queue_work
static void __queue_work(int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct work_struct *work)
{
struct pool_workqueue *pwq;
struct worker_pool *last_pool;
struct list_head *worklist;
unsigned int work_flags;
unsigned int req_cpu = cpu;
//1)根据work找到在工作队列中找到合适的pwq
retry:
if (req_cpu == WORK_CPU_UNBOUND)
cpu = wq_select_unbound_cpu(raw_smp_processor_id());
if (!(wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND))
pwq = per_cpu_ptr(wq->cpu_pwqs, cpu);
else
pwq = unbound_pwq_by_node(wq, cpu_to_node(cpu));
……
pwq->nr_in_flight[pwq->work_color]++;
work_flags = work_color_to_flags(pwq->work_color);
//2)找到将要添加到的链表
if (likely(pwq->nr_active < pwq->max_active)) {
trace_workqueue_activate_work(work);
pwq->nr_active++;
worklist = &pwq->pool->worklist;
if (list_empty(worklist))
pwq->pool->watchdog_ts = jiffies;
} else {//如果活跃的work太多就添加到pwq->delayed_works中
work_flags |= WORK_STRUCT_DELAYED;
worklist = &pwq->delayed_works;
}
//3)将work插入到链表中并唤醒工作者线程
insert_work(pwq, work, worklist, work_flags);
spin_unlock(&pwq->pool->lock);
}static void insert_work(struct pool_workqueue *pwq, struct work_struct *work,
struct list_head *head, unsigned int extra_flags)
{
struct worker_pool *pool = pwq->pool;
set_work_pwq(work, pwq, extra_flags);
list_add_tail(&work->entry, head);
get_pwq(pwq);
if (__need_more_worker(pool))
wake_up_worker(pool); //唤醒工作者线程
}3.3 work的执行
static int worker_thread(void *__worker)
{
struct worker *worker = __worker;
struct worker_pool *pool = worker->pool;
worker->task->flags |= PF_WQ_WORKER;
woke_up:
spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock);
......
//将worker从worker_pool 的idle_list中取下来并将统计计数nr_idle减一
worker_leave_idle(worker);
recheck:
if (!need_more_worker(pool))
goto sleep;
//如果没有空闲worker了就尝试创建更多的worker
if (unlikely(!may_start_working(pool)) && manage_workers(worker))
goto recheck;
do {
struct work_struct *work =
list_first_entry(&pool->worklist,
struct work_struct, entry);
pool->watchdog_ts = jiffies;
/*如果work有设置WORK_STRUCT_LINKED,表示该work有依赖的work,(依赖的work用entry链接在一起),如果有依赖就将依赖的work都添加到worker->scheduled上一并处理*/
if (likely(!(*work_data_bits(work) & WORK_STRUCT_LINKED))) {
//将work_struct从worker_pool->worklist中取下来调用work_struct->func。
process_one_work(worker, work);
if (unlikely(!list_empty(&worker->scheduled)))
process_scheduled_works(worker);
} else {
//将依赖的work都添加到worker->scheduled上
move_linked_works(work, &worker->scheduled, NULL);
process_scheduled_works(worker);
}
} while (keep_working(pool));
worker_set_flags(worker, WORKER_PREP);
sleep:
worker_enter_idle(worker); //将worker重新添加到worker_pool 的idle_list中
__set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock);
schedule();
goto woke_up;
}
static void process_one_work(struct worker *worker, struct work_struct *work)
__releases(&pool->lock)
__acquires(&pool->lock)
{
struct pool_workqueue *pwq = get_work_pwq(work);
struct worker_pool *pool = worker->pool;
bool cpu_intensive = pwq->wq->flags & WQ_CPU_INTENSIVE;
int work_color;
struct worker *collision;
......
collision = find_worker_executing_work(pool, work);
if (unlikely(collision)) {
move_linked_works(work, &collision->scheduled, NULL);
return;
}
debug_work_deactivate(work);
hash_add(pool->busy_hash, &worker->hentry, (unsigned long)work);
worker->current_work = work;
worker->current_func = work->func;
worker->current_pwq = pwq;
work_color = get_work_color(work);
list_del_init(&work->entry);
if (need_more_worker(pool))
wake_up_worker(pool);
set_work_pool_and_clear_pending(work, pool->id);
......
worker->current_func(work); //函数最终要的工作就在这里
hash_del(&worker->hentry);
......
pwq_dec_nr_in_flight(pwq, work_color);
}4. 异常情况处理
4.1 worker_pool没有空闲的worker
如果worker_pool中没有空闲的worker就调用函数manage_workers尝试创建一个worker。函数manage_workers调用maybe_create_worker完成实际的工作:
static void maybe_create_worker(struct worker_pool *pool)
{
restart:
spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock);
//启动mayday_timer,如果创建worker时间太长就唤醒紧急worker(rescuer)处理work_struct
mod_timer(&pool->mayday_timer, jiffies + MAYDAY_INITIAL_TIMEOUT);
while (true) {
if (create_worker(pool) || !need_to_create_worker(pool))
break;
schedule_timeout_interruptible(CREATE_COOLDOWN);
if (!need_to_create_worker(pool))
break;
}
del_timer_sync(&pool->mayday_timer);
spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock);
/* need_to_create_worker 需要三个条件同时成立:1)pool->worklist有待处理的work_struct;2)没有正在运行的worker(pool->nr_running为0);3)没有空闲的worker(pool->nr_idle为0)*/
if (need_to_create_worker(pool))
goto restart;
}4.2 创建worker超时
如果创建worker超时就唤醒wq->rescuer->task处理pool->worklist上的work
static void pool_mayday_timeout(unsigned long __pool)
{
struct worker_pool *pool = (void *)__pool;
struct work_struct *work;
spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock);
spin_lock(&wq_mayday_lock); /* for wq->maydays */
if (need_to_create_worker(pool)) {
list_for_each_entry(work, &pool->worklist, entry)
send_mayday(work);
}
spin_unlock(&wq_mayday_lock);
spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock);
mod_timer(&pool->mayday_timer, jiffies + MAYDAY_INTERVAL);
}
static void send_mayday(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct pool_workqueue *pwq = get_work_pwq(work);
struct workqueue_struct *wq = pwq->wq;
lockdep_assert_held(&wq_mayday_lock);
if (!wq->rescuer)
return;
if (list_empty(&pwq->mayday_node)) {
get_pwq(pwq);
list_add_tail(&pwq->mayday_node, &wq->maydays);
wake_up_process(wq->rescuer->task);
}
}4.3 worker_pool中空闲worker太多
如果worker进入idle就检查worker_pool中当前idle worker的数量,如果大于busy worker的1/4就启动idle_timer,在IDLE_WORKER_TIMEOUT时间之后如果idle worker仍然没有减少就destroy部分worker。
static void worker_enter_idle(struct worker *worker)
{
struct worker_pool *pool = worker->pool;
……
worker->flags |= WORKER_IDLE;
pool->nr_idle++;
worker->last_active = jiffies;
list_add(&worker->entry, &pool->idle_list);
if (too_many_workers(pool) && !timer_pending(&pool->idle_timer))
mod_timer(&pool->idle_timer, jiffies + IDLE_WORKER_TIMEOUT);
}static void idle_worker_timeout(unsigned long __pool)
{
struct worker_pool *pool = (void *)__pool;
spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock);
while (too_many_workers(pool)) {
struct worker *worker;
unsigned long expires;
worker = list_entry(pool->idle_list.prev, struct worker, entry);
expires = worker->last_active + IDLE_WORKER_TIMEOUT;
if (time_before(jiffies, expires)) {
mod_timer(&pool->idle_timer, expires);
break;
}
destroy_worker(worker);
}
spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock);
}4.4 worker_pool卡住
工作队列初始化的时候会初始化一个wq_watchdog_timer,用于检测worker_pool,如果哪个worker_pool卡住机会打印出警告信息:
static void wq_watchdog_init(void)
{
wq_watchdog_set_thresh(wq_watchdog_thresh);
}static void wq_watchdog_set_thresh(unsigned long thresh)
{
wq_watchdog_thresh = 0;
del_timer_sync(&wq_watchdog_timer);
if (thresh) {
wq_watchdog_thresh = thresh;
wq_watchdog_reset_touched();
mod_timer(&wq_watchdog_timer, jiffies + thresh * HZ);
}
}wq_watchdog 超时函数:wq_watchdog_timer_fn
static void wq_watchdog_timer_fn(unsigned long data)
{
unsigned long thresh = READ_ONCE(wq_watchdog_thresh) * HZ;
bool lockup_detected = false;
struct worker_pool *pool;
int pi;
if (!thresh)
return;
rcu_read_lock();
for_each_pool(pool, pi) { //遍历系统中的所有worker_pool
unsigned long pool_ts, touched, ts;
if (list_empty(&pool->worklist))
continue;
pool_ts = READ_ONCE(pool->watchdog_ts);
touched = READ_ONCE(wq_watchdog_touched);
if (time_after(pool_ts, touched))
ts = pool_ts;
else
ts = touched;
if (pool->cpu >= 0) {
unsigned long cpu_touched =
READ_ONCE(per_cpu(wq_watchdog_touched_cpu,
pool->cpu));
if (time_after(cpu_touched, ts))
ts = cpu_touched;
}
if (time_after(jiffies, ts + thresh)) { //如果哪个worker_pool卡住30s就打印出该worker_pool的信息
lockup_detected = true;
pr_emerg("BUG: workqueue lockup - pool");
pr_cont_pool_info(pool);
pr_cont(" stuck for %us!\n",
jiffies_to_msecs(jiffies - pool_ts) / 1000);
}
}
rcu_read_unlock();
if (lockup_detected)
show_workqueue_state();
wq_watchdog_reset_touched();
mod_timer(&wq_watchdog_timer, jiffies + thresh);
}