CSS背景属性Background详解
【转】
本文详解了CSS的背景属性Background,包括CSS3中新增的背景属性。如果你是个CSS初学者,还可以查看之前介绍的CSS浮动属性和CSS透明属性详解。
CSS2 中有5个主要的背景(background)属性,它们是:
background-color: 指定填充背景的颜色。
background-image: 引用图片作为背景。
background-position: 指定元素背景图片的位置。
background-repeat: 决定是否重复背景图片。
background-attachment: 决定背景图是否随页面滚动。
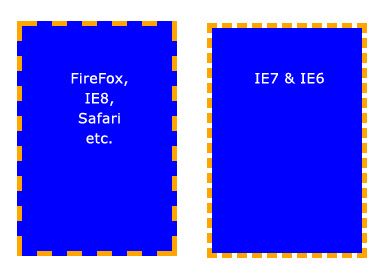
这些属性可以全部合并为一个缩写属性: background。需要注意的一个要点是背景占据元素的所有内容区域,包括 padding 和 border,但是不包括元素的 margin。它在 Firefox, Safari ,Opera 以及 IE8 中工作正常,但是 IE6 和 IE7 中,background 没把 border 计算在内。
背景色(background-color)
background-color 属性用纯色来填充背景。有许多方式指定这个颜色,以下方式都得到相同的结果。
background-color: blue;
background-color: rgb(0, 0, 255);
background-color: #0000ff;
background-color 也可被设置为透明(transparent),这会使得其下的元素可见。
背景图(background-image)
background-image 属性允许指定一个图片展示在背景中。可以和 background-color 连用,因此如果图片不重复地话,图片覆盖不到地地方都会被背景色填充。代码很简单,只需要记住,路径是相对于样式表的,因此以下的代码中,图片和样式表是在同一个目录中的。
background-image: url(image.jpg);
但是如果图片在一个名为 images 的子目录中,就应该是:
background-image: url(images/image.jpg);
背景平铺(background-repeat)
设置背景图片时,默认把图片在水平和垂直方向平铺以铺满整个元素。这也许是你需要的,但是有时会希望图片只出现一次,或者只在一个方向平铺。以下为可能的设置值和结果:
ackground-repeat: repeat; /* 默认值,在水平和垂直方向平铺 */ background-repeat: no-repeat; /* 不平铺。图片只展示一次。 */ background-repeat: repeat-x; /* 水平方向平铺(沿 x 轴) */ background-repeat: repeat-y; /* 垂直方向平铺(沿 y 轴) */ background-repeat: inherit; /* 继承父元素的 background-repeat 属性*/
背景定位(background-position)
background-position 属性用来控制背景图片在元素中的位置。技巧是,实际上指定的是图片左上角相对于元素左上角的位置。
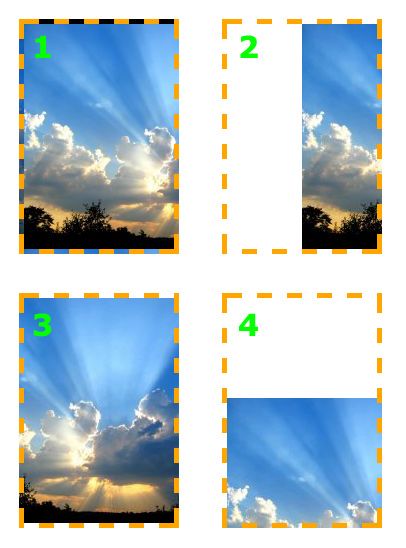
下面的例子中,设置了一个背景图片并且用 background-position 属性来控制它的位置,同时也设置了 background-repeat 为 no-repeat。计量单位是像素。第一个数字表示 x 轴(水平)位置,第二个是 y 轴(垂直) 位置。
/* 例 1: 默认值 */ background-position: 0 0; /* 元素的左上角 */ /* 例 2: 把图片向右移动 */ background-position: 75px 0; /* 例 3: 把图片向左移动 */ background-position: -75px 0; /* 例 4: 把图片向下移动 */ background-position: 0 100px;

background-position 属性可以用其它数值,关键词和百分比来指定,这比较有用,尤其是在元素尺寸不是用像素设置时。
x 轴上:
* left
* center
* right
y 轴上:
* top
* center
* bottom
顺序方面和使用像素值时的顺序几乎一样,首先是 x 轴,其次是 y 轴,像这样:
background-position: top right;
使用百分数时也类似。需要主要的是,使用百分数时,浏览器是以元素的百分比数值来设置图片的位置的。看例子就好理解了。假设设定如下:
background-position: 100% 50%;
使用百分数定位时,其实是将背景图片的百分比指定的位置和元素的百分比位置对齐。也就是说,百分数定位是改变了背景图和元素的对齐基 点。不再像使用像素和关键词定位时,使用背景图和元素的左上角为对齐基点。例如上例的 background-position: 100% 50%; 就是将背景图片的 100%(right) 50%(center) 这个点,和元素的 100%(right) 50%(center) 这个点对齐。
background-attachment
决定用户滚动页面时图片的状态。三个可用属性为 scroll(滚动),fixed(固定) 和 inherit(继承)。inherit 单纯地指定元素继承他的父元素的 background-attachment 属性。
为了正确地理解 background-attachment,首先需要明白页面(page)和视口(view port)是如何协作地。视口(view port)是浏览器显示网页的部分(就是去掉工具栏的浏览器)。视口(view port)的位置固定,不变动。
当向下滚动网页时,视口(view port)是不动的,而页面的内容向上滚动。看起来貌似视口(view port)向页面下方滚动了。如果设置 background-attachment:scroll,就设置了当元素滚动时,元素背景也必需随着滚动。简而言之,背景是紧贴元素的。这是 background-attachment 默认值。
用一个例子来更清楚地描述下:
background-image: url(test-image.jpg);
background-position: 0 0;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: scroll;

但是当设置 background-attachment 为 fixed 时,当页面向下滚动时,背景要待在它原来的位置(相对于浏览器来说)。也就是不随元素滚动。用另一个例子描述下:
background-image: url(test-image.jpg);
background-position: 0 100%;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
背景的简写属性可以把背景的各个属性合为一行,而不用每次都单独把他们写出来。格式如下:background: 《color》 《image》 《position》 《attachment》 《repeat》例如,下面的声明
background-color: transparent;
background-image: url(image.jpg);
background-position: 50% 0 ;
background-attachment: scroll;
background-repeat: repeat-y;
可以合为单独一行:
background: transparent url(image.jpg) 50% 0 scroll repeat-y;
而且不需要指定每一个值。如果省略值地话,就使用属性地默认值。例如,上面那行和下面这个效果一样:
background: url(image.jpg) 50% 0 repeat-y;
背景的一般用法
除了可以用来使元素更加优雅这类显然的用法之外,背景也可以用于其它的目的。
仿栏
当使用 css 的 float 属性来定位布局元素时,要确保两栏或多栏有相同的长度是比较困难的。如果长度不同,其中一栏的背景会比另外的短,这会破坏整个设计。
仿栏是个非常简单的背景技巧,这个技巧最早发表在A List Apart 。思路很简单:不再给每列单独设置背景,而是给各列的父元素设置一个背景图。所有栏的设计都包含在这张图片之中。
文本替换
在网页上,对于字体的选择是相当有限的。可以使用 sIFR 之类的工具来定制字体,但是这需要用户启用 JavaScript 。一个适用于任意浏览器的简单方法是,用想用的字体来做一张文本图片,并用这张图片作为背景。这样,文本依然出现在文档标记中以供搜索引擎检索和屏幕浏览 器识别,但是在浏览器中就会显示首选的字体。
例如,HTML 标记可能是这样的:
《h3》Blogroll《/h3》
假如有一个 200 乘 75 的图片,上面有更好看的字体,就可以用如下方式来替换文本:
h3.blogroll { width: 200px; height: 75px; /* So that the element will show the whole image. */ background:url(blogroll-text.jpg) 0 0 no-repeat; /* Sets the background image */ text-indent: -9999px; /* Hides the regular text by moving it 9999 pixels to the left */ }
简单的圆点
无需列表中的圆点看起来很难看。不用再处理所有不同的 list-style 属性,只需要简单地把他们隐藏并用背景图代替就可以了。因为图片可以随意选择,这些圆点就可以看起来更漂亮。
下面,我们把一个无需列表改造成有圆滑圆点的:
ul { list-style: none; /* Removes default bullets. */ } ul li { padding-left: 40px; /* Indents list items, leaving room for background image on the left. */ background: url(bulletpoint.jpg) 0 0 no-repeat; }
CSS3 中的背景
CSS3 中的背景有较多改进。最显著的是多背景图片的选项,同时也增加了4个新属性。
多背景
CSS3 中,可以对一个元素应用一个或多个图片作为背景。代码和 css2 中的一样,只需要用逗号来区别各个图片。第一个声明的图片定位在元素顶部,其它的图片按序在其下排列,例如:
background-image: url(top-image.jpg), url(middle-image.jpg), url(bottom-image.jpg);
新属性:背景修剪(background-clip)
这又把我们带回了文章开始讨论的那个关于边框内图片显示的话题。它被描述为“背景描绘区”。
background-clip 属性用来增强背景显示位置的控制能力。可能的值为:
* background-clip: border-box;
背景显示在边框内。
* background-clip: padding-box;
背景显示在内补白(padding)内,而不是边框内。
* background-clip: content-box;
只在内容内显示背景,而不是内补白(padding)和边框内。
* background-clip: no-clip;
默认值,和 border-box 一样。
新属性:背景原点(background-origin)
这个属性和 background-position 结合起来使用。可以从边框,内补白或者内容盒子开始计算 background-position (类似于 background-clip)。
* background-origin: border-box;
以边框为原点开始计算 background-position.
* background-origin: padding-box;
以内补白为原点开始计算 background-position
* background-origin: content-box;
以内容盒子为原点开始计算 background-position
对于 background-clip 和 background-origin 不同的一个解释参看 CSS3.info
新属性: 背景尺寸(background-size)
background-size 用来调整背景图的大小。有好几个可能值:
* background-size: contain;
缩小图片来适应元素的尺寸(保持像素的长宽比)
* background-size: cover;
扩展图片来填满元素(保持像素的长宽比)
* background-size: 100px 100px;
调整图片到指定大小
* background-size: 50% 100%;
调整图片到指定大小。百分比是相对于包含元素的尺寸的。
可以看一下 CSS3规则 网站上的几个例子。
新属性:(background-break)
CSS3 中,元素可以被分成几个独立的盒子(例如 使内联元素 span 跨越多行)。background-break 属性用来控制背景怎样在这些不同的盒子中显示。
可能值为:
* Background-break: continuous;
默认值。忽略盒之间的距离(也就是像元素没有分成多个盒子,依然是一个整体一样)
* Background-break: bounding-box;
把盒之间的距离计算在内
* Background-break: each-box;
为每个盒子单独重绘背景
背景色(background-color)的改进
background-color 在 css3 中有了稍许改进。除了设置背景颜色之外,如果元素底层的背景图不可用,还可以设置一个“回退色”。
通过在回退色之前增加一个斜杠(/)来实现,例如:
background-color: green / blue;
此例中,背景色应该是绿色(green)。然而,如果底层背景图不能使用的话,背景色就是蓝色而不是绿色。如果在斜杠前不指定颜色,默认为透明(transparent)。
背景平铺(background-repeat)的改进
CSS2中当图片平铺时,会被元素在末端截断。CSS3 引入了两个属性来修正这个问题:
* space: 应用同等数量的空白到图片之间,直到填满整个元素
* round: 缩小图片直到正好平铺满元素
关于 background-repeat: space; 的一个例子,可以在 CSS3 规则网站看到。
背景附着(background-attachment)的改进
background-attachment 属性增加了一个新值:local。这是用来配合可以滚动的元素的(设置为 overflow: scroll; 的元素)。当 background-attachment 设置为滚动(scroll)时,背景图不会随元素内容的滚动而滚动。
设置为 background-attachment :local; 时,背景图会随内容的滚动而滚动。