Android 时区设置以及设置系统属性的分析
在开发android系统设置的过程中会涉及许多内容。其中很简单的时区设定就包含很多内容。前面分析的设置时间自动同步的相关内容,下面接着分析一下系统中时区设定的相关内容。
以Android 5.1.1 LMY48M这个版本为例说明:
在时区设定里会调用到Settings\src\com\android\settings\ZonePicker.java这个文件其中:
@Override
public void onListItemClick(ListView listView, View v, int position, long id) {
// Ignore extra clicks
if (!isResumed()) return;
final Map map = (Map)listView.getItemAtPosition(position);
final String tzId = (String) map.get(KEY_ID);
// Update the system timezone value
final Activity activity = getActivity();
final AlarmManager alarm = (AlarmManager) activity.getSystemService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE);
alarm.setTimeZone(tzId);
final TimeZone tz = TimeZone.getTimeZone(tzId);
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.onZoneSelected(tz);
} else {
getActivity().onBackPressed();
}
}完成了时区的设定,这么看来完成这件事情的是AlarmManager这个类,为了知其然更要知其所以然我们继续跟进AlarmManager
/**
* Set the system default time zone.
* Requires the permission android.permission.SET_TIME_ZONE.
*
* @param timeZone in the format understood by {@link java.util.TimeZone}
*/
public void setTimeZone(String timeZone) {
try {
mService.setTimeZone(timeZone);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}可见AlarmManager也是调用AlarmManagerService.java这个来实现的,继续跟进,在这个服务中
public void setTimeZone(String tz) {
mContext.enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(
"android.permission.SET_TIME_ZONE",
"setTimeZone");
long oldId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(tz)) return;
TimeZone zone = TimeZone.getTimeZone(tz);
// Prevent reentrant calls from stepping on each other when writing
// the time zone property
boolean timeZoneWasChanged = false;
synchronized (this) {
String current = SystemProperties.get(TIMEZONE_PROPERTY);
if (current == null || !current.equals(zone.getID())) {
if (localLOGV) {
Slog.v(TAG, "timezone changed: " + current + ", new=" + zone.getID());
}
timeZoneWasChanged = true;
SystemProperties.set(TIMEZONE_PROPERTY, zone.getID());
}
// Update the kernel timezone information
// Kernel tracks time offsets as 'minutes west of GMT'
int gmtOffset = zone.getOffset(System.currentTimeMillis());
setKernelTimezone(mDescriptor, -(gmtOffset / 60000));
}
TimeZone.setDefault(null);
if (timeZoneWasChanged) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_TIMEZONE_CHANGED);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REPLACE_PENDING);
intent.putExtra("time-zone", zone.getID());
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(intent, UserHandle.ALL);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(oldId);
}
}其中 SystemProperties.set(TIMEZONE_PROPERTY, zone.getID());是实现问题的关键。我们继续查看SystemProperties.java这个文件,其中
private static native String native_get(String key);
private static native String native_get(String key, String def);
private static native int native_get_int(String key, int def);
private static native long native_get_long(String key, long def);
private static native boolean native_get_boolean(String key, boolean def);
private static native void native_set(String key, String def);
private static native void native_add_change_callback();
/**
* Set the value for the given key.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the key exceeds 32 characters
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value exceeds 92 characters
*/
public static void set(String key, String val) {
if (key.length() > PROP_NAME_MAX) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key.length > " + PROP_NAME_MAX);
}
if (val != null && val.length() > PROP_VALUE_MAX) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("val.length > " +
PROP_VALUE_MAX);
}
native_set(key, val);
}这就开始通过jni调到c 、cpp的代码了。在master/core/jni/android_os_SystemProperties.cpp中
static JNINativeMethod method_table[] = {
{ "native_get", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;",
(void*) SystemProperties_getS },
{ "native_get", "(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;",
(void*) SystemProperties_getSS },
{ "native_get_int", "(Ljava/lang/String;I)I",
(void*) SystemProperties_get_int },
{ "native_get_long", "(Ljava/lang/String;J)J",
(void*) SystemProperties_get_long },
{ "native_get_boolean", "(Ljava/lang/String;Z)Z",
(void*) SystemProperties_get_boolean },
{ "native_set", "(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)V",
(void*) SystemProperties_set },
};
static void SystemProperties_set(JNIEnv *env, jobject clazz,
jstring keyJ, jstring valJ)
{
int err;
const char* key;
const char* val;
if (keyJ == NULL) {
jniThrowNullPointerException(env, "key must not be null.");
return ;
}
key = env->GetStringUTFChars(keyJ, NULL);
if (valJ == NULL) {
val = ""; /* NULL pointer not allowed here */
} else {
val = env->GetStringUTFChars(valJ, NULL);
}
err = property_set(key, val);
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(keyJ, key);
if (valJ != NULL) {
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(valJ, val);
}
if (err < 0) {
jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/RuntimeException",
"failed to set system property");
}
}其中 err = property_set(key, val);这行代码是真正实现该功能的。进去继续查看。这代码声明在#include “cutils/properties.h”这个文件中。在说下面的代码逻辑之前先再说一点关于宏的一些概念。众所周知c语言中不存在重载的概念,更不能在同一个文件中同时定义同名的函数,为了实现这个功能源码中通过 宏来指定不同条件下的编译选择。所以在 properties.c的代码中存在多份property_set。控制具体编译那个的宏是在/build/core/combo/include/arch 下面的某个AndroidConfig.h文件其中就有HAVE_LIBC_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES的定义,但是其中注意这个和在编译系统时候选择的编译版本有关系,如果是darwin-x86或者windows下面的文件就没有这个定义。其实现就是另外一套逻辑了。就我手机里的系统当时的编译选项而说的话是包含这个定义的。所以
#ifdef HAVE_LIBC_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES
#define _REALLY_INCLUDE_SYS__SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_H_
#include 其中在libc/bionic/system_properties.cpp
int __system_property_set(const char *key, const char *value)
{
if (key == 0) return -1;
if (value == 0) value = "";
if (strlen(key) >= PROP_NAME_MAX) return -1;
if (strlen(value) >= PROP_VALUE_MAX) return -1;
prop_msg msg;
memset(&msg, 0, sizeof msg);
msg.cmd = PROP_MSG_SETPROP;
strlcpy(msg.name, key, sizeof msg.name);
strlcpy(msg.value, value, sizeof msg.value);
const int err = send_prop_msg(&msg);
if (err < 0) {
return err;
}
return 0;
}
static int send_prop_msg(const prop_msg *msg)
{
const int fd = socket(AF_LOCAL, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0);
if (fd == -1) {
return -1;
}
const size_t namelen = strlen(property_service_socket);
sockaddr_un addr;
memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr));
strlcpy(addr.sun_path, property_service_socket, sizeof(addr.sun_path));
addr.sun_family = AF_LOCAL;
socklen_t alen = namelen + offsetof(sockaddr_un, sun_path) + 1;
if (TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(connect(fd, reinterpret_cast(&addr), alen)) < 0) {
close(fd);
return -1;
}
const int num_bytes = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(send(fd, msg, sizeof(prop_msg), 0));
int result = -1;
if (num_bytes == sizeof(prop_msg)) {
// We successfully wrote to the property server but now we
// wait for the property server to finish its work. It
// acknowledges its completion by closing the socket so we
// poll here (on nothing), waiting for the socket to close.
// If you 'adb shell setprop foo bar' you'll see the POLLHUP
// once the socket closes. Out of paranoia we cap our poll
// at 250 ms.
pollfd pollfds[1];
pollfds[0].fd = fd;
pollfds[0].events = 0;
const int poll_result = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(poll(pollfds, 1, 250 /* ms */));
if (poll_result == 1 && (pollfds[0].revents & POLLHUP) != 0) {
result = 0;
} else {
// Ignore the timeout and treat it like a success anyway.
// The init process is single-threaded and its property
// service is sometimes slow to respond (perhaps it's off
// starting a child process or something) and thus this
// times out and the caller thinks it failed, even though
// it's still getting around to it. So we fake it here,
// mostly for ctl.* properties, but we do try and wait 250
// ms so callers who do read-after-write can reliably see
// what they've written. Most of the time.
// TODO: fix the system properties design.
result = 0;
}
}
close(fd);
return result;
} 其中send_prop_msg是发消息给property_service.c,这个文件是整个过程的终结点。在这个类中会将数据写入/data/property这个目录下有 persist.sys.timezone 这个文件中
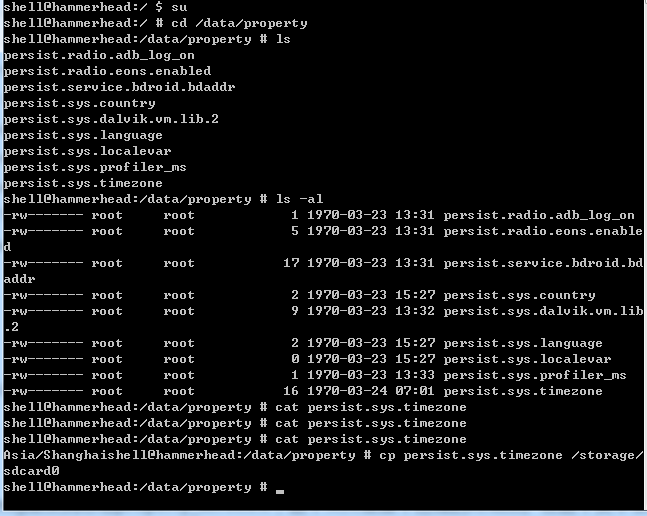
ok整个过程分析完了,至于为什么用socket通信到property_service,请看老罗的:
http://blog.csdn.net/Luoshengyang/article/details/38102011