大数据Spark面试,distinct去重原理,是如何实现的
最近,有位朋友问我,distinct去重原理是怎么实现的?
“在面试时,面试官问他了解distinct算子吗?”
“了解啊,Spark的rdd,一种transFormation去重的算子,主要用来去重的”。
“哟,看来你经常使用distinct算子,对distinct算子很熟悉啊”。
“好说,好说”。
“那你能说说distinct是如何实现去重的吗?”
我朋友支支吾吾半天:“就是这样、那样去重的啊”。
“这样、那样是怎么去重的呢”
“具体有点忘记了(其实是根本就不知道)”。
那么distinct,底层到底是如何实现去重功能的呢?这个是面试spark部分时,经常被问到的问题。
先来看一段代码,我们测试一下distinct去重的作用:
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object SparkDistinct {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("SparkDistinct")
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)
//定义一个数组
val array: Array[Int] = Array(1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4)
//把数组转为RDD算子,后面的数字2代表分区,也可以指定3,4....个分区,也可以不指定。
val line: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(array,2)
line.distinct().foreach(x => println(x))
//输出的结果已经去重:1,2,3,4
}
}
通过上面的代码可以看出,使用distinct以后,会对重复的元素进行去重。我们来看下源码
/**
* Return a new RDD containing the distinct elements in this RDD.
*/
def distinct(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T] = withScope {
map(x => (x, null)).reduceByKey((x, y) => x, numPartitions).map(_._1)
}
/**
* Return a new RDD containing the distinct elements in this RDD.
*/
def distinct(): RDD[T] = withScope {
distinct(partitions.length)
}
上面是distinct的源码,有带参和无参两种。当我们调用无参的distinct时,底层调用的是如下源码:
def distinct(): RDD[T] = withScope {
distinct(partitions.length)
}
而无参distinct()中又调用了带参数的distinct(partitions.length)。
其中,partitions.length代表是分区数,而这个分区则是我们在使用 sc.parallelize(array,2) 时指定的2个分区。
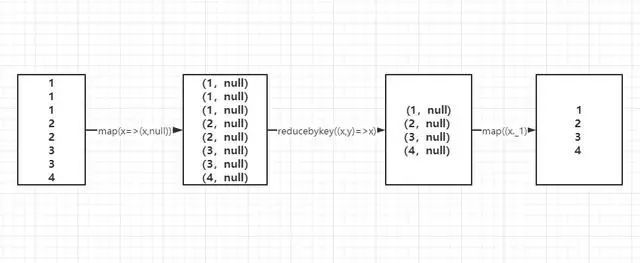
带参数的distinct其内部就很容易理解了,这就是一个wordcount统计单词的方法,区别是:后者通过元组获取了第一个单词元素。
map(x => (x, null)).reduceByKey((x, y) => x, numPartitions).map(_._1)
其中,numPartitions就是分区数。
我们也可以写成这样:
map(x => (x, null)).reduceByKey((x, y) => x).map(_._1)
也可以这样写:
line.map(x =>(x,1)).reduceByKey(_+_).map(_._1)通过上面的流程图很清晰的看出来,distinct的原理流程。
使用map算子把元素转为一个带有null的元组;使用reducebykey对具有相同key的元素进行统计;之后再使用map算子,取得元组中的单词元素,实现去重的效果。